Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hashimoto, Kei*; Shiwaku, Toru*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Yokoyama, Hideaki*; Mayumi, Koichi*; Ito, Kozo*
Science Advances (Internet), 9(47), p.eadi8505_1 - eadi8505_8, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:45.8(Multidisciplinary Sciences)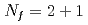 lattice QCD with chiral fermions
lattice QCD with chiral fermionsAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Kanamori, Issaku*; Kaneko, Takashi*; Nakamura, Yoshifumi*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 396, p.332_1 - 332_7, 2022/07
The axial U(1) anomaly in high-temperature QCD plays an important role to understand the phase diagram of QCD. The previous works by JLQCD Collaboration studied high-temperature QCD using 2-flavor dynamical chiral fermions such as the domain-wall fermion and reweighted overlap fermion. We extend our simulations to QCD with 2+1-flavor dynamical quarks, where the masses of the up, down, and strange quarks are near the physical point, and the temperatures are close to or higher than the pseudocritical temperature. In this talk, we will present the results for the Dirac spectrum, topological susceptibility, axial U(1) susceptibility, and hadronic collelators.
Aoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 396, p.050_1 - 050_9, 2022/07
In the early days of QCD, the axial  anomaly was considered as a trigger for the breaking of the
anomaly was considered as a trigger for the breaking of the 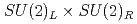 symmetry through topological excitations of gluon fields. However, it has been a challenge for lattice QCD to quantify the effect. In this work, we simulate QCD at high temperatures with chiral fermions. The exact chiral symmetry enables us to separate the contribution from the axial
symmetry through topological excitations of gluon fields. However, it has been a challenge for lattice QCD to quantify the effect. In this work, we simulate QCD at high temperatures with chiral fermions. The exact chiral symmetry enables us to separate the contribution from the axial  breaking from others among the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that the chiral susceptibility, which is conventionally used as a probe for
breaking from others among the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that the chiral susceptibility, which is conventionally used as a probe for 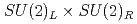 breaking, is actually dominated by the axial
breaking, is actually dominated by the axial  breaking at temperatures
breaking at temperatures 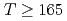 MeV.
MeV.
Murase, Kiyoka*; Kataoka, Ryuho*; Nishiyama, Takanori*; Nishimura, Koji*; Hashimoto, Taishi*; Tanaka, Yoshimasa*; Kadokura, Akira*; Tomikawa, Yoshihiro*; Tsutsumi, Masaki*; Ogawa, Yasunobu*; et al.
Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate (Internet), 12, p.18_1 - 18_16, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:20.65(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We identified two energetic electron precipitation (EEP) events during the growth phase of moderate substorms and estimated the mesospheric ionization rate for an EEP event for which the most comprehensive dataset from ground-based and space-born instruments was available. The mesospheric ionization signature reached below 70 km altitude and continued for ~15 min until the substorm onset, as observed by the PANSY radar and imaging riometer at Syowa Station in the Antarctic region. We also used energetic electron flux observed by the Arase and POES 15 satellites as the input for the air-shower simulation code PHITS to quantitatively estimate the mesospheric ionization rate. Combining the cutting-edge observations and simulations, we shed new light on the space weather impact of the EEP events during geomagnetically quiet times, which is important to understand the possible link between the space environment and climate.
 anomaly in the chiral susceptibility of QCD at high temperature
anomaly in the chiral susceptibility of QCD at high temperatureAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2022(2), p.023B05_1 - 023B05_12, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:82.94(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The chiral susceptibility, or the first derivative of the chiral condensate with respect to the quark mass, is often used as a probe for the QCD phase transition since the chiral condensate is an order parameter of 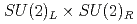 symmetry breaking. However, the chiral condensate also breaks the axial
symmetry breaking. However, the chiral condensate also breaks the axial  symmetry, which is usually not studied as it is already broken by the anomaly and apparently has little impact on the transition. We investigate the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels in order to quantify how much the axial
symmetry, which is usually not studied as it is already broken by the anomaly and apparently has little impact on the transition. We investigate the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels in order to quantify how much the axial  breaking contributes to the chiral phase transition. Employing a chirally symmetric lattice Dirac operator and its eigenmode decomposition, we separate the axial
breaking contributes to the chiral phase transition. Employing a chirally symmetric lattice Dirac operator and its eigenmode decomposition, we separate the axial  breaking effects from others. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that both of the connected and disconnected chiral susceptibilities are dominated by axial
breaking effects from others. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that both of the connected and disconnected chiral susceptibilities are dominated by axial  breaking at temperatures
breaking at temperatures 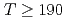 MeV after the quadratically divergent constant is subtracted.
MeV after the quadratically divergent constant is subtracted.
Hashimoto, Shoji*; Tanaka, Taku*; Komatsu, Masabumi*; Gonze, M.-A.*; Sakashita, Wataru*; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Nishina, Kazuya*; Ota, Masakazu; Ohashi, Shinta*; Calmon, P.*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 238-239, p.106721_1 - 106721_10, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:62.58(Environmental Sciences)This study was aimed at analysing performance of models for radiocesium migration mainly in evergreen coniferous forest in Fukushima, by inter-comparison between models of several research teams. The exercise included two scenarios of countermeasures against the contamination, namely removal of soil surface litter and forest renewal, and a specific konara oak forest scenario in addition to the evergreen forest scenario. All the models reproduced trend of time evolution of radiocesium inventories and concentrations in each of the components in forest such as leaf and organic soil layer. However, the variations between models enlarged in long-term predictions over 50 years after the fallout, meaning continuous field monitoring and model verification/validation is necessary.
 anomaly at high temperature with lattice chiral fermions
anomaly at high temperature with lattice chiral fermionsAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Cossu, G.*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Kaneko, Takashi*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 103(7), p.074506_1 - 074506_18, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:73.22(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We investigate the axial  anomaly of two-flavor QCD at temperatures 190-330 MeV. In order to preserve precise chiral symmetry on the lattice, we employ the M
anomaly of two-flavor QCD at temperatures 190-330 MeV. In order to preserve precise chiral symmetry on the lattice, we employ the M bius domain-wall fermion action as well as overlap fermion action implemented with a stochastic reweighting technique. Compared to our previous studies, we reduce the lattice spacing to 0.07 fm, simulate larger multiple volumes to estimate finite size effect, and take more than four quark mass points, including one below physical point to investigate the chiral limit. We measure the topological susceptibility, axial
bius domain-wall fermion action as well as overlap fermion action implemented with a stochastic reweighting technique. Compared to our previous studies, we reduce the lattice spacing to 0.07 fm, simulate larger multiple volumes to estimate finite size effect, and take more than four quark mass points, including one below physical point to investigate the chiral limit. We measure the topological susceptibility, axial  susceptibility, and examine the degeneracy of
susceptibility, and examine the degeneracy of  partners in meson/baryon correlators. All the data above the critical temperature indicate that the axial
partners in meson/baryon correlators. All the data above the critical temperature indicate that the axial  violation is consistent with zero within statistical errors. The quark mass dependence suggests disappearance of the
violation is consistent with zero within statistical errors. The quark mass dependence suggests disappearance of the  anomaly at a rate comparable to that of the
anomaly at a rate comparable to that of the 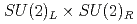 symmetry breaking.
symmetry breaking.
Nakashima, Nobuaki*; Yatsuhashi, Tomoyuki*; Sakota, Kenji*; Iwakura, Izumi*; Hashimoto, Sena*; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Matsuda, Shohei
Chemical Physics Letters, 752, p.137570_1 - 137570_5, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.85(Chemistry, Physical)Photo-redox reactions between Eu and Eu
and Eu ions are induced by laser irradiation in alcoholic solution. Efficiency, wavelength dependence, and laser-power dependence are investigated with three different lasers. Nano second laser pulses at a wavelength of 308 nm is found to cause one-photon redox reactions with a quantum yield around 0.5. Nano second laser pulses at a wavelength of 394 nm induces two-photon reduction of Eu
ions are induced by laser irradiation in alcoholic solution. Efficiency, wavelength dependence, and laser-power dependence are investigated with three different lasers. Nano second laser pulses at a wavelength of 308 nm is found to cause one-photon redox reactions with a quantum yield around 0.5. Nano second laser pulses at a wavelength of 394 nm induces two-photon reduction of Eu to form Eu
to form Eu . When the pulse energy is 5 mJ, the quantum yield is measured to be 0.015. Although the quantum yield is one order of magnitude lower than that of the one photon reduction, reduction phenomena can be easily observed under the moderate laser field strength. Because of the two-photon nature, there should be a room to improve the efficiency by increasing the laser field strength.
. When the pulse energy is 5 mJ, the quantum yield is measured to be 0.015. Although the quantum yield is one order of magnitude lower than that of the one photon reduction, reduction phenomena can be easily observed under the moderate laser field strength. Because of the two-photon nature, there should be a room to improve the efficiency by increasing the laser field strength.
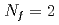 lattice QCD
lattice QCDSuzuki, Kei; Aoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Cossu, G.*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Rohrhofer, C.*
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 363, p.178_1 - 178_7, 2020/08
We investigate the high-temperature phase of QCD using lattice QCD simulations with 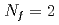 dynamical M
dynamical M bius domain-wall fermions. On generated configurations, we study the axial
bius domain-wall fermions. On generated configurations, we study the axial  symmetry, overlap-Dirac spectra, screening masses from mesonic correlators, and topological susceptibility. We find that some of the observables are quite sensitive to lattice artifacts due to a small violation of the chiral symmetry. For those observables, we reweight the M
symmetry, overlap-Dirac spectra, screening masses from mesonic correlators, and topological susceptibility. We find that some of the observables are quite sensitive to lattice artifacts due to a small violation of the chiral symmetry. For those observables, we reweight the M bius domain-wall fermion determinant by that of the overlap fermion. We also check the volume dependence of observables. Our data near the chiral limit indicates a strong suppression of the axial
bius domain-wall fermion determinant by that of the overlap fermion. We also check the volume dependence of observables. Our data near the chiral limit indicates a strong suppression of the axial  anomaly at temperatures
anomaly at temperatures  220 MeV.
220 MeV.
Rohrhofer, C.*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Cossu, G.*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Gattringer, C.*; Glozman, L. Ya.*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Lang, C. B.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 363, p.227_1 - 227_7, 2020/08
Properties of QCD matter change significantly around the chiral crossover temperature, and the effects on 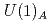 and topological susceptibilities, as well as the meson spectrum have been studied with much care. Baryons and the effect of parity doubling in this temperature range have been analyzed previously by various other groups employing different setups. Here we construct suitable operators to investigate chiral and axial
and topological susceptibilities, as well as the meson spectrum have been studied with much care. Baryons and the effect of parity doubling in this temperature range have been analyzed previously by various other groups employing different setups. Here we construct suitable operators to investigate chiral and axial 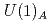 symmetries in the baryon spectrum. Measurements for different volumes and quark-masses are done with two flavors of chirally symmetric domain-wall fermions at temperatures above the critical one. The possibility of emergent
symmetries in the baryon spectrum. Measurements for different volumes and quark-masses are done with two flavors of chirally symmetric domain-wall fermions at temperatures above the critical one. The possibility of emergent 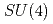 and
and 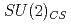 symmetries is discussed.
symmetries is discussed.
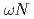 scattering length from
scattering length from  photoproduction on the proton near the reaction threshold
photoproduction on the proton near the reaction thresholdIshikawa, Takatsugu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fukasawa, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Ryo*; He, Q.*; Honda, Yuki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kaida, Shun*; Kasagi, Jirota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(5), p.052201_1 - 052201_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:44.35(Physics, Nuclear)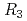 Ir
Ir Sn
Sn (
( : La and Ce) investigated using neutron and X-ray diffraction
: La and Ce) investigated using neutron and X-ray diffractionNakazato, Seiya*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Hashimoto, Daisuke*; Shiozawa, Mami*; Kuwahara, Keitaro*; Nakao, Hironori*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Ohara, Takashi; Nakao, Akiko*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 30, p.011128_1 - 011128_6, 2020/03
Manabe, Seiya*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Liao, W.*; Hashimoto, Masanori*; Nakano, Keita*; Sato, Hikaru*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Abe, Shinichiro; Hamada, Koji*; Tampo, Motonobu*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 65(8), p.1742 - 1749, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:62.29(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Recently, the malfunction of microelectronics caused by secondary cosmic-ray muon is concerned as semiconductor devices become sensitive to radiation. In this study, we have performed muon irradiation testing for 65-nm ultra-thin body and thin buried oxide (UTBB-SOI) SRAMs in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), in order to investigate dependencies of single event upset (SEU) cross section on incident muon momentum and supply voltage. It was found that the SEU cross section by negative muon are approximately two to four times larger than those by positive muon in the momentum range from 35 MeV/c to 39 MeV/c. The supply voltage dependence of muon-induced SEU cross section was measured with the momentum of 38 MeV/c. SEU cross sections decrease with increasing supply voltage, but the decreasing of SEU cross section by negative muon is gentler than that by positive muon. Experimental data of positive and negative muon irradiation with the momentum of 38 MeV/c were analyzed by PHITS. It was clarified that the negative muon capture causes the difference between the SEU cross section by negative muon and that by positive muon.
Liao, W.*; Hashimoto, Masanori*; Manabe, Seiya*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Abe, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita*; Sato, Hikaru*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Hamada, Koji*; Tampo, Motonobu*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 65(8), p.1734 - 1741, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:81.29(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Soft error induced by secondary cosmic-ray muon is concerned since susceptibility of semiconductor device to soft error increases with the scaling of technology. In this study, we have performed irradiation tests of muons on 65-nm bulk CMOS SRAM in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) and measured soft error rate (SER) to investigate mechanism of muon-induced soft errors. It was found that SER by negative muon increases above 0.5 V supply voltage, although SER by positive muon increases monotonically as the supply voltage lowers. SER by negative muon also increases with forward body bias. In addition, negative muon causes large multiple cell upset (MCU) of more than 20 bits and the ratio of MCU events to all the events is 66% at 1.2V supply voltage. These tendencies indicate that parasitic bipolar action (PBA) is highly possible to contribute to SER by negative muon. Experimental data are analyzed by PHITS. It was found that negative muon can deposit larger charge than positive muon, and such events that can deposit large charge may trigger PBA.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Okumura, Keisuke; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.06008_1 - 06008_6, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:95.14(Nuclear Science & Technology)Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, has been developed under the collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. It can deal with the transport of nearly all particles up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ion) using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. More than 2,500 researchers and technicians have used the code for a variety of applications such as accelerator design, radiation shielding and protection, medical physics, and space and geosciences. This paper briefly summarizes physics models and functions newly implemented in PHITS between versions 2.52 and 2.82.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwase, Hiroshi*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.63 - 69, 2016/09
A general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through the collaboration of several institutes. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. PHITS users apply the code to various research and development fields such as nuclear technology, accelerator design, medical physics, and cosmic-ray research. This presentation briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some new models such as muon-induced nuclear reaction model and a  de-excitation model EBITEM. We will also present the radiation damage cross sections for materials, PKA spectra and kerma factors calculated by PHITS under the IAEA-CRP activity titled "Primary radiation damage cross section."
de-excitation model EBITEM. We will also present the radiation damage cross sections for materials, PKA spectra and kerma factors calculated by PHITS under the IAEA-CRP activity titled "Primary radiation damage cross section."
 Cs + ICs' (Contract research)
Cs + ICs' (Contract research)Kobayashi, Takanori; Hashimoto, Masashi; Yokoyama, Keiichi
JAEA-Research 2015-014, 7 Pages, 2015/12
To discuss the exchange reaction of Cs isotope by CsI + Cs' Cs + ICs', the structure and chemical properties of Cs
Cs + ICs', the structure and chemical properties of Cs I intermediate and potential energy surface are calculated using M06/def2-TZVPPD density functional calculation. The calculation shows that the reaction to the intermediate has no barrier and the two Cs-I bonds of Cs
I intermediate and potential energy surface are calculated using M06/def2-TZVPPD density functional calculation. The calculation shows that the reaction to the intermediate has no barrier and the two Cs-I bonds of Cs I are chemically equivalent. Thus, the collision of CsI + Cs' results in Cs exchange with the high probability.
I are chemically equivalent. Thus, the collision of CsI + Cs' results in Cs exchange with the high probability.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Furuta, Takuya; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 82, p.110 - 115, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:94.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)The general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through a collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency is responsible for managing the entire project. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. This paper briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some important functions useful for particular purposes, such as an event generator mode and beam transport functions.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Furuta, Takuya; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2014-002, p.69 - 74, 2015/02
A general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through the collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. All components of PHITS such as its source, executable and data-library files are assembled in one package and then distributed to many countries. More than 1,000 researchers apply the code to various research and development fields such as nuclear technology, accelerator design, medical physics, and cosmic-ray research. This presentation briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some important functions for specific applications, such as an event generator mode and a radiation damage calculation function.
 Lu for radioimmunotherapy
Lu for radioimmunotherapyWatanabe, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Watanabe, Shigeki; Iida, Yasuhiko*; Hanaoka, Hirofumi*; Endo, Keigo*; Ishioka, Noriko
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(1), p.935 - 940, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:67.09(Chemistry, Analytical)