Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Cs discharge from a forested catchment
Cs discharge from a forested catchmentSakuma, Kazuyuki; Hayashi, Seiji*; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Malins, A.; Funaki, Hironori; Tsuji, Hideki*; Kobayashi, Takamaru*; Kitamura, Akihiro; Iijima, Kazuki
Water Resources Research, 58(8), p.e2021WR031181_1 - e2021WR031181_16, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.29(Environmental Sciences) Cs activity concentration in the aquatic insect
Cs activity concentration in the aquatic insect  (Tricoptera: Stenopsychidae) in the Ota River, Fukushima, Japan
(Tricoptera: Stenopsychidae) in the Ota River, Fukushima, JapanIshii, Yumiko*; Miura, Hikaru*; Jo, J.*; Tsuji, Hideki*; Saito, Rie; Koarai, Kazuma; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Urushidate, Tadayuki*; Nishikiori, Tatsuhiro*; Wada, Toshihiro*; et al.
PLOS ONE (Internet), 17(5), p.e0268629_1 - e0268629_17, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:39.89(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We investigated the variability in  Cs activity concentration in individual aquatic insects in detritivorous caddisfly (
Cs activity concentration in individual aquatic insects in detritivorous caddisfly ( ) and carnivorous dobsonfly (
) and carnivorous dobsonfly ( ) larvae from the Ota River, Fukushima. Caddisfly larvae showed sporadically higher radioactivity, whereas no such outliers were observed in dobsonfly larvae. Autoradiography and scanning electron microscopy analyses confirmed that these caddisfly larvae samples contained radiocesium-bearing microparticles (CsMPs), which are insoluble Cs-bearing silicate glass particles. CsMPs were also found in potential food sources of caddisfly larvae, such as periphyton and drifting particulate organic matter, indicating that larvae may ingest CsMPs along with food particles of similar size. Although CsMPs distribution and uptake by organisms in freshwater ecosystems is relatively unknown, our study demonstrates that CsMPs can be taken up by aquatic insects.
) larvae from the Ota River, Fukushima. Caddisfly larvae showed sporadically higher radioactivity, whereas no such outliers were observed in dobsonfly larvae. Autoradiography and scanning electron microscopy analyses confirmed that these caddisfly larvae samples contained radiocesium-bearing microparticles (CsMPs), which are insoluble Cs-bearing silicate glass particles. CsMPs were also found in potential food sources of caddisfly larvae, such as periphyton and drifting particulate organic matter, indicating that larvae may ingest CsMPs along with food particles of similar size. Although CsMPs distribution and uptake by organisms in freshwater ecosystems is relatively unknown, our study demonstrates that CsMPs can be taken up by aquatic insects.
Funaki, Hironori; Tsuji, Hideki*; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Hayashi, Seiji*
Science of the Total Environment, 812, p.152534_1 - 152534_10, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:70.76(Environmental Sciences)Reservoir sediments generally act as a sink for radionuclides derived from nuclear accidents, but under anaerobic conditions, several radionuclides remobilise in bioavailable form from sediment to water columns, which may contribute to a long-term contamination in aquatic products. This study systematically investigated the  Cs activities between sediment and pore water, which is a direct evidence of the remobilisation of bioavailable
Cs activities between sediment and pore water, which is a direct evidence of the remobilisation of bioavailable  Cs from sediments, in two highly contaminated reservoirs affected by the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Our results strongly indicate a competitive ion exchange process between
Cs from sediments, in two highly contaminated reservoirs affected by the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Our results strongly indicate a competitive ion exchange process between  Cs and NH
Cs and NH via a highly selective interaction with the frayed edges sites of phyllosilicate minerals to be the major reason for the variability of the Kd values between sediment and pore water, even in the Fukushima case.
via a highly selective interaction with the frayed edges sites of phyllosilicate minerals to be the major reason for the variability of the Kd values between sediment and pore water, even in the Fukushima case.
Hashimoto, Shoji*; Tanaka, Taku*; Komatsu, Masabumi*; Gonze, M.-A.*; Sakashita, Wataru*; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Nishina, Kazuya*; Ota, Masakazu; Ohashi, Shinta*; Calmon, P.*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 238-239, p.106721_1 - 106721_10, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:55.86(Environmental Sciences)This study was aimed at analysing performance of models for radiocesium migration mainly in evergreen coniferous forest in Fukushima, by inter-comparison between models of several research teams. The exercise included two scenarios of countermeasures against the contamination, namely removal of soil surface litter and forest renewal, and a specific konara oak forest scenario in addition to the evergreen forest scenario. All the models reproduced trend of time evolution of radiocesium inventories and concentrations in each of the components in forest such as leaf and organic soil layer. However, the variations between models enlarged in long-term predictions over 50 years after the fallout, meaning continuous field monitoring and model verification/validation is necessary.
Ozaki, Hirokazu*; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Asaoka, Yoshihiro*; Hayashi, Seiji*
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193(6), p.369_1 - 369_9, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:31.11(Environmental Sciences) Cs in water and phyto- and zooplankton in a reservoir affected by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant Accident
Cs in water and phyto- and zooplankton in a reservoir affected by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant AccidentTsuji, Hideki*; Nakagawa, Megumi*; Iijima, Kazuki; Funaki, Hironori; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Hayashi, Seiji*
Global Environmental Research (Internet), 24(2), p.115 - 127, 2021/06
Lake water, phytoplankton and zooplankton were sampled by a total of 12 quarterly surveys from August 2014 to May 2017 at a dam lake in the Fukushima nuclear disaster area, and variations of dissolved form of  Cs and planktonic
Cs and planktonic  Cs were observed. Seasonal variations in dissolved
Cs were observed. Seasonal variations in dissolved  Cs concentration with high in summer and low in winter were observed in the upstream, midstream and downstream areas of the lake, but no seasonal or site specific differences in planktonic
Cs concentration with high in summer and low in winter were observed in the upstream, midstream and downstream areas of the lake, but no seasonal or site specific differences in planktonic  Cs concentrations and dominant species were found. The amount of planktonic form of
Cs concentrations and dominant species were found. The amount of planktonic form of  Cs in the water was less than 1.4% of the total
Cs in the water was less than 1.4% of the total  Cs in the lake water, therefore the effect of plankton on the dynamics of
Cs in the lake water, therefore the effect of plankton on the dynamics of  Cs in the lake was minimal.
Cs in the lake was minimal.
Iijima, Kazuki; Hayashi, Seiji*; Tamaoki, Masanori*
Global Environmental Research (Internet), 24(2), p.85 - 93, 2021/06
Environmental radioactive contamination by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident has clearly been declining during the passage of almost 10 years from the accident. However, the prolongation of radioactive contamination in natural ecosystems probably derived from forested area without decontamination is pointed out by many studies, so more detailed examination will be needed for environmental dynamics of bioavailable radiocesium and its transfer to ecosystems. Also for influence of radiation to organisms, effects of evacuation on wild organisms are more pronounced than direct effect from radiation, especially in Fukushima evacuation area.
Takechi, Seiichi*; Tsuji, Hideki*; Koshikawa, Masami*; Ito, Shoko*; Funaki, Hironori; Hayashi, Seiji*
Rikusuigaku Zasshi, 82(1), p.1 - 16, 2021/02
Since the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in 2011, soil minerals and organic matter including radiocesium have been deposited in the dam lakes near the nuclear power plant. There is concern that radiocesium will gradually leach from the lake bottom into the lake water, resulting in prolonged radioactive contamination of the freshwater ecosystems especially in downstream of the dams. In this study, we collected undisturbed sediment core samples at the center of the Yokokawa Dam lake in Fukushima Prefecture and suspended sediment in the inflowing river of the dam for 4 years and evaluated the amount of bioavailable form of radiocesium (exchanged, oxidized, and organic forms) in these samples by sequential extraction tests using the BCR method focusing on the temporal change.
 Cs concentrations in east Japanese rivers
Cs concentrations in east Japanese riversTsuji, Hideki*; Ishii, Yumiko*; Shin, M.*; Taniguchi, Keisuke*; Arai, Hirotsugu*; Kurihara, Momo*; Yasutaka, Tetsuo*; Kuramoto, Takayuki*; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Lee, S*; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 697, p.134093_1 - 134093_11, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:56.54(Environmental Sciences)To investigate the main factors that control the dissolved radiocesium concentration in river water in the area affected by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, the correlations between the dissolved  Cs concentrations at 66 sites normalized to the average
Cs concentrations at 66 sites normalized to the average  Cs inventories for the watersheds with the land use, soil components, topography, and water quality factors were assessed. We found that the topographic wetness index is significantly and positively correlated with the normalized dissolved
Cs inventories for the watersheds with the land use, soil components, topography, and water quality factors were assessed. We found that the topographic wetness index is significantly and positively correlated with the normalized dissolved  Cs concentration. Similar positive correlations have been found for European rivers because wetland areas with boggy organic soils that weakly retain
Cs concentration. Similar positive correlations have been found for European rivers because wetland areas with boggy organic soils that weakly retain  Cs are mainly found on plains. However, for small Japanese river watersheds, the building area ratio in the watershed strongly affected the dissolved
Cs are mainly found on plains. However, for small Japanese river watersheds, the building area ratio in the watershed strongly affected the dissolved  Cs concentration.
Cs concentration.
Kurihara, Momo*; Yasutaka, Tetsuo*; Aono, Tatsuo*; Ashikawa, Nobuo*; Ebina, Hiroyuki*; Iijima, Takeshi*; Ishimaru, Kei*; Kanai, Ramon*; Karube, Jinichi*; Konnai, Yae*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 322(2), p.477 - 485, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.76(Chemistry, Analytical)We assessed the repeatability and reproducibility of methods for determining low dissolved radiocesium concentrations in freshwater in Fukushima. Twenty-one laboratories pre-concentrated three of 10 L samples by five different pre-concentration methods (prussian-blue-impregnated filter cartridges, coprecipitation with ammonium phosphomolybdate, evaporation, solid-phase extraction disks, and ion-exchange resin columns), and activity of radiocesium was measured. The z-scores for all of the  Cs results were within
Cs results were within  2, indicating that the methods were accurate. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) indicating the variability in the results from different laboratories were larger than the RSDs indicating the variability in the results from each separate laboratory.
2, indicating that the methods were accurate. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) indicating the variability in the results from different laboratories were larger than the RSDs indicating the variability in the results from each separate laboratory.
 for modelling dissolved
for modelling dissolved  Cs concentrations in Fukushima river water; Case study of the upstream Ota River
Cs concentrations in Fukushima river water; Case study of the upstream Ota RiverSakuma, Kazuyuki; Tsuji, Hideki*; Hayashi, Seiji*; Funaki, Hironori; Malins, A.; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Kitamura, Akihiro; Iijima, Kazuki; Hosomi, Masaaki*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 184-185, p.53 - 62, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.11(Environmental Sciences)A study is presented on the applicability of the distribution coefficient ( ) absorption/desorption model to simulate dissolved
) absorption/desorption model to simulate dissolved  Cs concentrations in Fukushima river water. The simulation results were in good agreement with the observations on water and suspended sediment fluxes, and on particulate bound
Cs concentrations in Fukushima river water. The simulation results were in good agreement with the observations on water and suspended sediment fluxes, and on particulate bound  Cs concentrations under both ambient and high flow conditions. By contrast the measured concentrations of dissolved
Cs concentrations under both ambient and high flow conditions. By contrast the measured concentrations of dissolved  Cs in the river water were much harder to reproduce with the simulations. By tuning the
Cs in the river water were much harder to reproduce with the simulations. By tuning the  values for large particles, it was possible to reproduce the mean dissolved
values for large particles, it was possible to reproduce the mean dissolved  Cs concentrations during base flow periods (observation: 0.32 Bq/L, simulation: 0.36 Bq/L). However neither the seasonal variability in the base flow dissolved
Cs concentrations during base flow periods (observation: 0.32 Bq/L, simulation: 0.36 Bq/L). However neither the seasonal variability in the base flow dissolved  Cs concentrations (0.14-0.53 Bq/L), nor the peaks in concentration that occurred during storms (0.18-0.88 Bq/L, mean: 0.55 Bq/L), could be reproduced with realistic simulation parameters.
Cs concentrations (0.14-0.53 Bq/L), nor the peaks in concentration that occurred during storms (0.18-0.88 Bq/L, mean: 0.55 Bq/L), could be reproduced with realistic simulation parameters.
Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Niizato, Tadafumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Dohi, Terumi; Nakama, Shigeo; Funaki, Hironori; Misono, Toshiharu; Oyama, Takuya; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Hayashi, Seiji*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2017-018, 86 Pages, 2017/10
Since the accidents at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant following the Tohoku Region Pacific Coast Earthquake on March 11th, 2011, Fukushima Environmental Safety Center has carried out research on natural mobilization of radionuclide (especially radiocesium) and future forecast from forest to water system and surrounding residential areas. The report summarizes the latest results that have been accumulated from each study field, of our agency together with the other related research organizations. The contents of the report is to be used as evidence-based information for the QA-styled pages in the website of JAEA Sector of Fukushima Research and Development at the time of next renewal.
 emission reduction of active carbon recycling energy system for ironmaking by modeling with Aspen Plus
emission reduction of active carbon recycling energy system for ironmaking by modeling with Aspen PlusSuzuki, Katsuki*; Hayashi, Kentaro*; Kurihara, Kohei*; Nakagaki, Takao*; Kasahara, Seiji
ISIJ International, 55(2), p.340 - 347, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:71.64(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Use of the Active Carbon Recycling Energy System in ironmaking (iACRES) has been proposed for reducing CO emissions. To evaluate the performance of iACRES quantitatively, a process flow diagram of a blast furnace model with iACRES was developed using Aspen Plus, a chemical process simulator. CO
emissions. To evaluate the performance of iACRES quantitatively, a process flow diagram of a blast furnace model with iACRES was developed using Aspen Plus, a chemical process simulator. CO emission reduction and exergy analysis were performed by using mass and energy balance obtained from simulation results. The following CO
emission reduction and exergy analysis were performed by using mass and energy balance obtained from simulation results. The following CO reduction methods were evaluated as iACRES: solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOEC) with CO
reduction methods were evaluated as iACRES: solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOEC) with CO capture and separation (CCS), SOEC without CCS, and a reverse water-gas shift reactor powered by a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor. iACRES enabled CO
capture and separation (CCS), SOEC without CCS, and a reverse water-gas shift reactor powered by a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor. iACRES enabled CO emission reduction by 3-11% by recycling CO and H
emission reduction by 3-11% by recycling CO and H , whereas effective exergy ratio decreased by 1-7%.
, whereas effective exergy ratio decreased by 1-7%.
Hayashi, Kentaro*; Kasahara, Seiji; Kurihara, Kohei*; Nakagaki, Takao*; Yan, X.; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Ogawa, Masuro
ISIJ International, 55(2), p.348 - 358, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:42.45(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Reducing coking coal consumption and CO emissions by application of iACRES (ironmaking system based on active carbon recycling energy system) was investigated using process flow modeling to show effectiveness of HTGRs (high temperature gas-cooled reactors) adoption to iACRES. Two systems were evaluated: a SOEC (solid oxide electrolysis cell) system using CO
emissions by application of iACRES (ironmaking system based on active carbon recycling energy system) was investigated using process flow modeling to show effectiveness of HTGRs (high temperature gas-cooled reactors) adoption to iACRES. Two systems were evaluated: a SOEC (solid oxide electrolysis cell) system using CO electrolysis and a RWGS (reverse water-gas shift reaction) system using RWGS reaction with H
electrolysis and a RWGS (reverse water-gas shift reaction) system using RWGS reaction with H produced by IS (iodine-sulfur) process. Both the effects on saving of the coking coal and reduction of CO
produced by IS (iodine-sulfur) process. Both the effects on saving of the coking coal and reduction of CO emissions were greater in the RWGS system. It was the reason of the result that excess H
emissions were greater in the RWGS system. It was the reason of the result that excess H which was not consumed in the RWGS reaction was used as reducing agent in the BF as well as CO. Heat balance in the HTGR, SOEC and RWGS modules were evaluated to clarify process components to be improved. Optimization of the SOEC temperature was desired to reduce Joule heat input for high efficiency operation of the SOEC system. Higher H
which was not consumed in the RWGS reaction was used as reducing agent in the BF as well as CO. Heat balance in the HTGR, SOEC and RWGS modules were evaluated to clarify process components to be improved. Optimization of the SOEC temperature was desired to reduce Joule heat input for high efficiency operation of the SOEC system. Higher H production thermal efficiency in the IS process for the RWGS system is effective for more efficient HTGR heat utilization. The SOEC system was able to utilize HTGR heat to reduce CO
production thermal efficiency in the IS process for the RWGS system is effective for more efficient HTGR heat utilization. The SOEC system was able to utilize HTGR heat to reduce CO emissions more efficiently by comparing CO
emissions more efficiently by comparing CO emissions reduction per unit heat of HTGR.
emissions reduction per unit heat of HTGR.
Hayashi, Kentaro*; Suzuki, Katsuki*; Kurihara, Kohei*; Nakagaki, Takao*; Kasahara, Seiji
Tanso Junkan Seitetsu Kenkyukai Saika Hokokusho; Tanso Junkan Seitetsu No Tenkai, p.27 - 41, 2015/02
Applying Active Carbon Recycling Energy System to ironmaking (iACRES) process is a promising technology to reduce coal usage and CO emissions. To evaluate performance of iACRES quantitatively, a process flow diagram of the blast furnace model with iACRES was developed using Aspen Plus. CO
emissions. To evaluate performance of iACRES quantitatively, a process flow diagram of the blast furnace model with iACRES was developed using Aspen Plus. CO emission reduction and exergy analysis was predicted by using mass and energy balance obtained from the simulation results. The followings were investigated as iACRES: solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOEC) with CO
emission reduction and exergy analysis was predicted by using mass and energy balance obtained from the simulation results. The followings were investigated as iACRES: solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOEC) with CO capture and separation (CCS), SOEC without CCS, and a reverse water-gas shift reactor as the a CO
capture and separation (CCS), SOEC without CCS, and a reverse water-gas shift reactor as the a CO reduction reactor powered by a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor. iACRES could provide CO
reduction reactor powered by a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor. iACRES could provide CO emission reductions of 3-11% by recycling CO and H
emission reductions of 3-11% by recycling CO and H , whereas the effective exergy ratio decreased by 1-7%.
, whereas the effective exergy ratio decreased by 1-7%.
Hayashi, Kentaro*; Kasahara, Seiji; Kurihara, Kohei*; Nakagaki, Takao*; Yan, X.; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Ogawa, Masuro
Tanso Junkan Seitetsu Kenkyukai Saika Hokokusho; Tanso Junkan Seitetsu No Tenkai, p.42 - 62, 2015/02
Reducing coking coal consumption and CO emissions by application of HTGRs (high temperature gas-cooled reactors) to iACRES (ironmaking system based on active carbon recycling energy system) was investigated using process flow modeling. Two systems were evaluated: a SOEC (solid oxide electrolysis cell) system using CO
emissions by application of HTGRs (high temperature gas-cooled reactors) to iACRES (ironmaking system based on active carbon recycling energy system) was investigated using process flow modeling. Two systems were evaluated: a SOEC (solid oxide electrolysis cell) system using CO electrolysis and a RWGS (reverse water-gas shift reaction) system using RWGS reaction with H
electrolysis and a RWGS (reverse water-gas shift reaction) system using RWGS reaction with H produced by IS (iodine-sulfur) process. Coking coal consumption was reduced from a conventional BF (blast furnace) steelmaking system by 4.3% in the SOEC system and 10.3% in the RWGS system. CO
produced by IS (iodine-sulfur) process. Coking coal consumption was reduced from a conventional BF (blast furnace) steelmaking system by 4.3% in the SOEC system and 10.3% in the RWGS system. CO emissions were decreased by 3.4% in the SOEC system and 8.2% in the RWGS system. Remaining H
emissions were decreased by 3.4% in the SOEC system and 8.2% in the RWGS system. Remaining H from the RWGS reactor was used as reducing agent in the BF in the RWGS system. This was the reason of the larger reduction of coking coal consumption and CO
from the RWGS reactor was used as reducing agent in the BF in the RWGS system. This was the reason of the larger reduction of coking coal consumption and CO emissions. Electricity generation for SOEC occupied most of HTGR heat usage in the SOEC system. H
emissions. Electricity generation for SOEC occupied most of HTGR heat usage in the SOEC system. H production in the IS process used most of the HTGR heat in the RWGS system. Optimization of the SOEC temperature for the SOEC system and higher H
production in the IS process used most of the HTGR heat in the RWGS system. Optimization of the SOEC temperature for the SOEC system and higher H production thermal efficiency in the IS process for the RWGS system will be useful for more efficient heat utilization. One typical-sized BF required 0.5 HTGRs and 2 HTGRs for in the SOEC system and RWGS system, respectively. CO
production thermal efficiency in the IS process for the RWGS system will be useful for more efficient heat utilization. One typical-sized BF required 0.5 HTGRs and 2 HTGRs for in the SOEC system and RWGS system, respectively. CO emissions reduction per unit heat input was larger in the SOEC system. Recycling H
emissions reduction per unit heat input was larger in the SOEC system. Recycling H to the RWGS will be useful for smaller emissions per unit heat in the RWGS system.
to the RWGS will be useful for smaller emissions per unit heat in the RWGS system.
 Cs discharge rates after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident from two distinct watershed simulation models
Cs discharge rates after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident from two distinct watershed simulation modelsKitamura, Akihiro; Imaizumi, Yoshitaka*; Yamaguchi, Masaaki; Yui, Mikazu; Suzuki, Noriyuki*; Hayashi, Seiji*
Kankyo Hoshano Josen Gakkai-Shi, 2(3), p.185 - 192, 2014/09
Annual discharge rates of radioactive cesium through selected rivers due to the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident were simulated by two different watershed models. One is the Soil and Cesium Transport, SACT, model which was developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency and the other one is the Grid-Catchment Integrated Modeling System, G-CIEMS, which was developed by National Institute of Environmental Studies. We choose the Abukuma, the Ukedo, and the Niida rivers for the present study. Comparative results showed that while components and assumptions adopted in two models differ, both methods predicted the same order of magnitude estimates.
Kim, J.*; Sinha, J.*; Mitani, Seiji*; Hayashi, Masamitsu*; Takahashi, Saburo*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Yamanouchi, Michihiko*; Ohno, Hideo*
Physical Review B, 89(17), p.174424_1 - 174424_8, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:95 Percentile:93.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have studied the underlayer thickness and temperature dependencies of the current-induced effective field in CoFeB/MgO heterostructures with Ta-based underlayers. The underlayer thickness at which the effective field saturates is found to be different between the two orthogonal components of the effective field; i.e., the dampinglike term tends to saturate at a smaller underlayer thickness than the fieldlike term. For large underlayer thickness films in which the effective field saturates, we find that the measurement temperature significantly influences the size of the effective field. A striking difference is found in the temperature dependence of the two components: the dampinglike term decreases whereas the fieldlike term increases with increasing temperature. Using a simple spin diffusion-spin transfer model, we find that all of these results can be accounted for provided the real and imaginary parts of an effective spin mixing conductance are negative. These results imply that either spin transport in this system is different from conventional metallic interfaces or effects other than spin diffusion into the magnetic layer need to be taken into account in order to model the system accurately.
 Sn superconducting wires
Sn superconducting wiresMiyatake, Takayuki*; Murakami, Yukinobu*; Kurahashi, Hidefumi*; Hayashi, Seiji*; Zaitsu, Kyoji*; Seeber, B.*; Mondonico, G.*; Nabara, Yoshihiro
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 22(3), p.4805005_1 - 4805005_5, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:40.25(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)In order to develop bronze processed Nb Sn strands for ITER TF and CS coils, the influences of various parameters of Nb
Sn strands for ITER TF and CS coils, the influences of various parameters of Nb Sn strands such as filament diameter, barrier materials, barrier thickness, heat treatment pattern and Ti addition on critical current (
Sn strands such as filament diameter, barrier materials, barrier thickness, heat treatment pattern and Ti addition on critical current (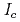 ) vs. axial strain
) vs. axial strain 
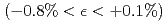 characteristics were investigated. The change of theses parameters brought significant changes to superconducting properties involving
characteristics were investigated. The change of theses parameters brought significant changes to superconducting properties involving 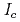 and n-value at zero applied strain. In spite of different strand parameters, the strain dependency of normalized
and n-value at zero applied strain. In spite of different strand parameters, the strain dependency of normalized 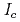 was almost the same, except for Ti-addition affecting the critical field
was almost the same, except for Ti-addition affecting the critical field 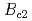 . Based on the results, bronze processed Nb
. Based on the results, bronze processed Nb Sn strands with non-Cu critical current density more than 1,100 A/mm
Sn strands with non-Cu critical current density more than 1,100 A/mm at 12T, 4.2K have been successfully developed for the CS coil.
at 12T, 4.2K have been successfully developed for the CS coil.
Hayashi, Naoki; Kawase, Masato; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Hiroki, Seiji; Saeki, Riuji; Takahashi, Hiroki; Teruyama, Yuzo*; Toyokawa, Ryoji*; Arakawa, Dai*; Hiramatsu, Shigenori*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 677, p.94 - 106, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:68.81(Instruments & Instrumentation)A beam position monitor (BPM) system at J-PARC RCS is described. The J-PARC RCS is a rapid-cycling proton synchrotron and its designed beam power is 1 MW. A diameter of the BPM detector is larger than 250 mm, however the system has to measure the beam position very accurately. The system should work not only for the high intensity but also for lower intensity. There are 54 BPM around the ring and most of them are placed inside steering magnets because of quite limited space. The BPM detector is an electro static type and it has four electrodes, and a pair of electrode gives a good linear response with diagonal cut shape to detect the charge center precisely. The signal processing unit, which is equipped with 14-bit 40 MSPS ADC and 600 MHz DSP, has been developed. They are controlled via shared memory space and EPICS. It is capable to record full 25 Hz pulse data for averaged mode and it could also store whole waveform data for further analysis, like turn-by-turn position calculation.