Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
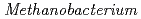 strain induces severe corrosion by retrieving electrons from Fe
strain induces severe corrosion by retrieving electrons from Fe under a freshwater environment
under a freshwater environmentHirano, Shinichi*; Ihara, Sota*; Wakai, Satoshi*; Dotsuta, Yuma; Otani, Kyohei; Kitagaki, Toru; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Okamoto, Akihiro*
Microorganisms (Internet), 10(2), p.270_1 - 270_12, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:81.48(Microbiology)To understand the role of methanogens in corrosion under anoxic conditions in freshwater, we investigated the corrosion activities of methanogens in samples collected from groundwater and rivers. We enriched microorganisms that can grow with CO /NaHCO
/NaHCO and Fe
and Fe as the sole carbon source and electron donor, respectively, in ground fresh water. Electrochemical analysis revealed that
as the sole carbon source and electron donor, respectively, in ground fresh water. Electrochemical analysis revealed that 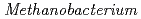 strain can uptake electrons from the cathode at lower than -0.61 V vs SHE and has a redox-active component with electrochemical potential different from those of other previously reported methanogens with extracellular electron transfer ability. This study indicated the corrosion risk by methanogens capable of taking up electrons from Fe
strain can uptake electrons from the cathode at lower than -0.61 V vs SHE and has a redox-active component with electrochemical potential different from those of other previously reported methanogens with extracellular electron transfer ability. This study indicated the corrosion risk by methanogens capable of taking up electrons from Fe in anoxic freshwater environments and the necessity of understanding the corrosion mechanism to contribute to risk diagnosis.
in anoxic freshwater environments and the necessity of understanding the corrosion mechanism to contribute to risk diagnosis.
Abe, Toru*; Hirano, Fumio; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 27(1), p.3 - 11, 2020/06
Degradation of TRU waste in a geological disposal facility may cause the formation of a nitrate plume. A Nitrate Evolution model due to mineral reactions, microbial activity, and metal corrosiON (NEON) has therefore been developed to evaluate the safety case for geological disposal of TRU waste. Small scale laboratory experiments can be reproduced satisfactorily, however, it is necessary to demonstrate the applicability of the NEON model on scales relevant to the geological disposal of TRU waste. In the current study, an industrial analogue of a nitrate plume from the pollution of groundwater from nitrate fertilizers used on Ikuchi Island, Japan was selected to test the applicability of the NEON model. Concentration profiles of nitrate ions in the groundwater were successfully reproduced over the hundreds of meters scale demonstrating the applicability of the NEON model in evaluating the chemical behavior of a nitrate plume derived from the geological disposal of TRU waste.
Saito, Yoshimoto*; Hirano, Shinichi*; Nagaoka, Toru*; Amano, Yuki
Ecological Genetics and Genomics, 12, p.100042_1 - 100042_9, 2019/10
Culture-independent molecular techniques enable us to analyze microflora in various environments. Many uncultured prokaryotes have been detected by the molecular methods from extreme environments, including anaerobic, no light, high-pressure, and high temperature. Recently, microbial eukaryotes were also detected in deep-sea environments, suggesting that microbial eukaryotes can adapt to a wider range of environments than previously thought. Here, we performed a culture-independent analysis of eukaryotes from approximately -250 m depth in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory at Horonobe, Japan. Our results indicate that fungi are the dominant eukaryotic flora in deep sedimentary rocks of Horonobe. We detected a wide range of species, including Zygomycete, Basidiomycete, and Ascomycete fungi from the rocks. This study is the first report of eukaryotic diversity in deep subsurface sedimentary rocks.
Hirano, Shinichi*; Nagaoka, Toru*; Ise, Kotaro; Amano, Yuki; Matsumoto, Norio*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 64(12), p.535 - 539, 2015/12
To obtain the knowledge about the corrosion ability and its mechanism as a target the soil environment microorganisms, lake mud was cultured with metallic iron. As a result, corrosion of carbon steel was observed with sulfate reduction and methane producing activity in brackish medium with lactate as substrate. Inhibition test of SRB and MPA suggested that SRB plays a major role for this corrosion, and MPA enhanced corrosion activity by the coexistence of SRB.
Tomita, Takuro*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Hasegawa, Noboru; Minami, Yasuo*; Takei, Ryota*; Baba, Motoyoshi*; Eyama, Tsuyoshi*; Takayoshi, Shodai*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Morita, Toshimasa; et al.
Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering, 9(2), p.137 - 142, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:27.94(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Femtosecond laser ablation processes on platinum, gold, and tungsten were observed by the single shot pump and probe reflective imaging using a soft X-ray laser probe. To avoid the timing error due to the jitter, we adopted a posteriori correction technique by simultaneous measurement of timing between the pump and probe pulses for every single shot, using a soft X-ray streak camera. A clear difference was found in the temporal behavior of the dynamical response of the soft X-ray reflectivity depending on the irradiated laser fluence in these three materials. On the other hand, the narrow dark rings were found in Pt and W, while an additional bright ring was found outside the dark disk in Au. Our result gives the experimental data comparable with various numerical simulations.
Hikima, Ryoichi*; Hirano, Toru*; Yamashita, Masayuki*; Ishiyama, Koji*; Tanno, Takeo*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sato, Toshinori
JAEA-Research 2013-040, 51 Pages, 2014/03
For the research and development about high-level radioactive waste disposal, it is important to evaluate the mechanical stability of the excavation and the long-term behavior of in situ rock. However, from the limited information such as the bowling core before the excavation, it is difficult to evaluate the mechanical properties of in situ rock containing cracks. For this reason, evaluation of rock properties based on Specific Energy using mechanical data from an excavation machine is carried out. This report describes the results of the joint research carried out in FY 2010 to FY 2012.
Hikima, Ryoichi*; Hirano, Toru*; Yamashita, Masayuki*; Ishiyama, Koji*; Sato, Toshinori; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Tanno, Takeo
Heisei-25 Nendo (2013 Nen) Shigen, Sozai Gakkai Shuki Taikai Koenshu, p.247 - 248, 2013/08
no abstracts in English
Soma, Nobukazu*; Oikawa, Yasuki*; Hirano, Toru*; Matsui, Hiroya; Asanuma, Hiroshi*
Butsuri Tansa, 66(2), p.69 - 83, 2013/04
We have studied a reflection imaging technique in which passive seismic signals from other construction activity such as drilling noise are used as a wave source in order to develop a low-cost measurement method inside underground gallery. In this paper, we show an application to data sets from Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The drilling was conducted with a main purpose of extraction rock core samples for rock mechanics research. The three-dimensional reflection imaging results and comparison with well observation are shown in this paper.
Kamei, Gento; Honda, Akira; Oda, Chie; Hirano, Fumio; Ichige, Satoru; Kurimoto, Yoshitaka; Hoshino, Seiichi; Akagi, Yosuke; Sato, Nobuyuki; Takahashi, Kuniaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2012-010, 80 Pages, 2012/06
Based on Japanese governmental policy and general scheme, research and development of geological disposal technology for TRU waste has been proceeding to improve reliability of the safety assessment of the co-locational disposal of TRU waste and of HLW, to expand the basement of generic safety assessment, and to develop the alternative technology to cope with the broad geologic environment of Japan. Japan Atomic Energy Agency is dealing with the assignments in the governmental generic scheme. We report here the progress of the studies at the end of H22 (2010) Japanese fiscal year and their products during the last 5 years. These include (1) evaluation of long-term mechanical stability in the near-field including development of a creep mode of rock and analyses of mechanical behavior of TRU waste repository, (2) performance assessment of the disposal system including cementitious material alteration, bentonite and hostrock alteration with alkaline solution and nitrate effect, and (3) alternative technology development including decomposition of nitrate.
Hirano, Toru*; Seno, Yasuhiro*; Hikima, Ryoichi; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2011-019, 51 Pages, 2011/09
In order to establish the scientific and technical basis for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is proceeding with the geoscientific research in the research galleries excavated at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU). One of the scientific and technical objective of this project is to understand the change of geological environment due to excavation of research galleries. The investigation described herein is the measurement of the rock strain / displacement while pre-excavation grouting or excavating of the shaft around the GL.-200m level research gallery.
Hikima, Ryoichi; Sato, Toshinori; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Tanno, Takeo; Hirano, Toru*; Yamashita, Masayuki*; Ishiyama, Koji*
Heisei-23 Nendo (2011 Nen) Shigen, Sozai Gakkai Shuki Taikai Koenshu, p.265 - 266, 2011/09
no abstracts in English
Tanno, Takeo; Hirano, Toru*; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2011-013, 59 Pages, 2011/06
This report presents the following FY2009 activities undertaken to achieve the above goals. (1) Suitability of Laboratory Tests of Physical and Mechanical Properties on Waste Rock from Excavation of the Shaft, (2) Suitability of the Phase I Rock Mechanical Environment Model, (3) Preliminary Deformation Analysis of Rock Mass around the Underground Facilities, (4) Phenomenological Study on Crystalline Rock for Evaluating Long-term Behavior, (5) Theoretical Study on Crystalline Rock for Evaluating of Long-term Behavior, (6) Fundamental Study on Evaluation Methods of Excavation Distributed Zones. As the result of above 6 activities, suitability of laboratory test and Phase I Rock mechanical Environment Model are confirmed and also methods for EDZ estimation were specified by estimation of in situ stress with core and SWD (Seismic While Drilling).
Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Choi, J. H.*; Tanno, Takeo; Hirano, Toru*; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2011-007, 91 Pages, 2011/06
We first surveyed the classical theories of fracture mechanics, and discussed the subcritical crack growth (SCG), which is observed under less load than the fracture toughness Kc. This SCG is a result of coupled mechanical and chemical effect. The SCG for granite was treated on this basis. We performed pressure dissolution experiments using specimens of single crystal quartz, since the dissolution reaction is engaged with a deformation and failure process of polycrystalline rock. The series of experiments were managed by a flow-through type changing temperature, pH and applied stress. Si concentrations we here measured. We first surveyed the theories of pressure solution. Then we proposed a theory of saluting velocity of quart which accounts for the effects of temperature, chemical (pH), solid pressure and pore pressure.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Hayano, Akira; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Oyama, Takuya; Mizuno, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-007, 145 Pages, 2011/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). Geoscientific research and the MIU Project are planned in three overlapping phases; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase 1), Construction Phase (Phase 2) and Operation Phase (Phase 3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document introduces the results of the research and development in fiscal year 2009, as a part of the Construction Phase based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation at the MIU Construction Site and the Shobasama Site, (2) Construction at the MIU Construction Site, (3) Research Collaboration, etc. The goals of the Phase 2 are to develop and revise the models of the geological environment using the investigation results obtained during excavation and determine and assess changes in the geological environment in response to excavation, to evaluate the effectiveness of engineering techniques used for construction, maintenance and management of underground facilities, to establish detailed investigation plans of Phase 3.
Oikawa, Yasuki*; Soma, Nobukazu*; Tosha, Toshiyuki*; Matsui, Hiroya; Hirano, Toru*; Tanno, Takeo; Hikima, Ryoichi
JAEA-Research 2010-048, 45 Pages, 2011/02
In excavating a gallery or a shaft in deep underground, an excavation disturbed zone (EDZ) develops around the opening with new cracks due to both stress redistribution and excavation induced damage. The investigation and the evaluation of an EDZ are needed because the changes in rock properties and the EDZ development influence performance assessment of geological disposal and design of the underground structures. However, the in situ investigation of an EDZ is time consuming and costly because investigations are large-scale and required specialized equipment. We conducted a fundamental study for the development of an EDZ investigation method that is easy and inexpensive using the information obtained from only drilling. This report describes the results of the joint research carried out in fiscal year 2008 and fiscal year 2009. In Chapter 1, we provide the overview and the background of this study. In Chapter 2, we discuss the estimation of stress state around the research gallery at a depth of 200m in Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) by Acoustic Emission / Deformation Rate Analysis (AE/DRA) method using rock cores obtained from the drilling. In Chapter 3, results of the evaluation of geological structure around the research gallery at a depth of 200m in MIU based on Seismic While Drilling (SWD) method using the vibrations caused by the drilling are described.
Horiuchi, Yasuharu; Hirano, Toru*; Ikeda, Koki; Matsui, Hiroya
Dai-40-Kai Gamban Rikigaku Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.242 - 247, 2011/01
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) installed the intelligent type strain meters, at G.L-500m depth in pilot boreholes drilled from the 200m level in the ventilation and main shafts of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU). Strain variations due to several events including the excavation itself were monitored and analyzed. Monitoring results indicate that the intelligent type strain meter is able to measure very small fluctuations and detect rock deformation from blasting with 300m vertical separation from the measurement section. The strain meter can detect conditions in the rock mass such as differences in deformability.
Matsui, Hiroya; Tanno, Takeo; Hirano, Toru*; Goke, Mitsuo*; Kumasaka, Hiroo*; Tada, Hiroyuki*; Ishii, Takashi*
JAEA-Research 2010-043, 87 Pages, 2010/12
The results are as follows (1) For the ventilation shaft at GL-350m, the crack tensor deformation analysis based on FY2004 work's results showed the calculated displacement was smaller than the measured displacement. A geometrical parameters of fractures in FY2004 work's result was different from one based on geological observation in the shaft. Therefore, the crack tensor of FY2004 work's results seems to be underestimated. (2) Large discontinuities with NE strike and high dipping observed in a shaft were major reason for the difference of crack tensors determined by borehole investigation from surface and geological observations in a shaft. Therefore, the crack tensor for pilot borehole investigation in a shaft was calculated as well and compared with each results. It was found that the fabric tensor is similar with it of geological observation and the vale was medium. (3) The crack tensor around GL-500m was estimated by relation of statistical quantities for fractures between GL-300m and GL-500m. Consequently, the deformation analysis based on the estimated crack tensor showed an increase in convergence and stress in the support system compared to FY2004 work's results.
Okubo, Seisuke*; Hikima, Ryoichi; Hirano, Toru*; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2010-031, 45 Pages, 2010/10
Rock shows time-dependent behavior such as creep/relaxation. With respect to high-level radioactive waste disposal, knowledge of the long-term mechanical stability of shafts and galleries excavated in rock are required, not only during construction and operation but also over a period of thousands of years after closure. Therefore, it is very important to understand the time-dependent behavior of rock for evaluating long-term mechanical stability. The purpose of this study is determining the mechanisms of time-dependent behavior of rock by the precise test, observation and measurement, to develop methods for evaluating long-term mechanical stability. In previous work, testing techniques have been established and basic evaluation methods were developed. Recently, some parameters needed for simulation of time-dependent behavior were determined at the Mizunami underground research facilities. However, we did not have enough data to check on the reliability of the evaluation method for these parameters. This report describes the results of the activities in fiscal year 2009. In Chapter 1, we provide an overview and the background to this study. In Chapter 2, the results of the long-term creep test on Tage tuff, started in fiscal year, 1997 are described. In Chapter 3, methods for obtaining parameters of the constitutive equation for rock are reviewed and summarized. The time dependent behavior of Toki granite and Inada granite (40-80  C) are also summarized based on data obtained prior to the previous fiscal year. In Chapter 4, the FEM analysis implemented with a generalized variable-compliance-type constitutive equation carried out to clarify the long-term behavior of Toki granite is described. Finally, based on the numerical analysis, an in situ testing method is proposed.
C) are also summarized based on data obtained prior to the previous fiscal year. In Chapter 4, the FEM analysis implemented with a generalized variable-compliance-type constitutive equation carried out to clarify the long-term behavior of Toki granite is described. Finally, based on the numerical analysis, an in situ testing method is proposed.
Takeuchi, Shinji; Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Hayano, Akira; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Oyama, Takuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2010-029, 28 Pages, 2010/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). Geoscientific research and the MIU project is planned in three overlapping phases; Surface-based investigation phase (Phase1), Construction phase (Phase2) and Operation phase (Phase3). The project is currently under the construction phase, and the operation phase starts in 2010. This document introduces the research and development activities planned for 2010 fiscal year plan based on the MIU master plan updated in 2010, (1) Investigation plan, (2) Construction plan, (3) Research collaboration plan, etc.
Horiuchi, Yasuharu; Hirano, Toru; Ikeda, Koki; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Technology 2010-017, 122 Pages, 2010/07
Knowledge of strain variations at an excavation face is important for the prediction of rock bursts and for the application of the appropriate supplementary construction methods for excavation of shafts to great depths. JAEA installed the intelligent type strain meters, at G.L-500m depth in pilot boreholes drilled from the 200m level in the ventilation and main shafts of the Mizunami URL. Strain variations due to several events including the excavation itself were monitored and analyzed. Because of the breakdown of the monitoring system, the data is very short term. Nevertheless, it was possible to do some analysis for the study and important understanding derived from the analysis. Monitoring results indicate that the intelligent type strain meter is able to measure very small fluctuations and detect rock deformation from blasting with 300m vertical separation from the measurement section. The strain meter can detect conditions in the rock mass such as differences in deformability.