Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sakon, Atsushi*; Nakajima, Kunihiro*; Takahashi, Kazuki*; Hohara, Shinya*; Sano, Tadafumi*; Fukaya, Yuji; Hashimoto, Kengo*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 247, p.09009_1 - 09009_8, 2021/02
In graphite-reflected thermal reactors, even a detector placed far from fuel region may detect a certain degree of the correlation amplitude. This is because mean free path of neutrons in graphite is longer than that in water or polyethylene. The objective of this study is experimentally to confirm a high flexibility of neutron detector placement in graphite reflector for reactor noise analysis. The present reactor noise analysis was carried out in a graphite-moderated and -reflected thermal core in Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). BF proportional neutron counters (1" dia.) were placed in graphite reflector region, where the counters were separated by about 35cm and 30cm -thick graphite from the core, respectively. At a critical state and subcritical states, time-sequence signal data from these counters were acquired and analyzed by a fast Fourier transform (FFT) analyzer, to obtain power spectral density in frequency domain. The auto-power spectral density obtained from the counters far from the core contained a significant degree of correlated component. A least-squares fit of a familiar formula to the auto-power spectral density data was made to determine the prompt-neutron decay constant. The decay constant was 63.3
proportional neutron counters (1" dia.) were placed in graphite reflector region, where the counters were separated by about 35cm and 30cm -thick graphite from the core, respectively. At a critical state and subcritical states, time-sequence signal data from these counters were acquired and analyzed by a fast Fourier transform (FFT) analyzer, to obtain power spectral density in frequency domain. The auto-power spectral density obtained from the counters far from the core contained a significant degree of correlated component. A least-squares fit of a familiar formula to the auto-power spectral density data was made to determine the prompt-neutron decay constant. The decay constant was 63.3 14.5 [1/s] in critical state. The decay constant determined from the cross-power spectral density and coherence function data between the two counters also had a consistent value. It is confirmed that reactor noise analysis is possible using a detector placed at about 35cm far from the core, as we expected.
14.5 [1/s] in critical state. The decay constant determined from the cross-power spectral density and coherence function data between the two counters also had a consistent value. It is confirmed that reactor noise analysis is possible using a detector placed at about 35cm far from the core, as we expected.
Yonomoto, Taisuke; Mineo, Hideaki; Murayama, Yoji; Hohara, Shinya*; Nakajima, Ken*; Nakatsuka, Toru; Uesaka, Mitsuru*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 63(1), p.73 - 77, 2021/01
, 63(1), p.73 - 77, 2021/01
no abstracts in English
Uozumi, Yusuke*; Sawada, Yusuke*; Mzhavia, A.*; Nogamine, Sho*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Kin, Tadahiro; Hohara, Shinya*; Wakabayashi, Genichiro*; Nakano, Masahiro*
Physical Review C, 84(6), p.064617_1 - 064617_11, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:72.25(Physics, Nuclear)Deuteron production from intermediate-energy proton-nucleus interactions was investigated through experiments and model calculations, mainly to develop a theoretical model by elucidating the mechanism of cluster production. Spectral double-differential cross sections were measured for inclusive ( ,
, 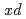 ) reactions on five targets in the periodic table, namely
) reactions on five targets in the periodic table, namely  C,
C,  Al,
Al, 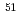 V,
V,  Nb, and
Nb, and  Au, at beam energies of 300 and 392 MeV. The cross sections were determined in almost the entire outgoing energy range from the highest down to 30 MeV and at laboratory angles from 20
Au, at beam energies of 300 and 392 MeV. The cross sections were determined in almost the entire outgoing energy range from the highest down to 30 MeV and at laboratory angles from 20 to 104
to 104 . To interpret the measured spectra, we proposed a new model that includes the nucleon correlations of the initial- and final-state interactions to describe cluster knockout and pickup within the intranuclear cascade model. The results of the model calculations showed reasonable agreements with those of the experiments. Moreover, the model indicated reasonable predictive power for the (
. To interpret the measured spectra, we proposed a new model that includes the nucleon correlations of the initial- and final-state interactions to describe cluster knockout and pickup within the intranuclear cascade model. The results of the model calculations showed reasonable agreements with those of the experiments. Moreover, the model indicated reasonable predictive power for the ( ,
,  He
He ), (
), ( ,
, 
 ), and (
), and ( ,
, 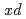 ) reactions measured elsewhere.
) reactions measured elsewhere.
 Se as a probe of neutron capture for the s-process branch-point nucleus
Se as a probe of neutron capture for the s-process branch-point nucleus 
Makinaga, Ayano*; Hohara, Shinya*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Goko, Shinji*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Goriely, S.*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Harano, Hideki*; et al.
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 28, p.239_1 - 239_4, 2010/12
no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Imamura, Minoru*; Koba, Yusuke*; Fukui, Yoshinori*; Wakabayashi, Genichiro*; Uozumi, Yusuke*; Kin, Tadahiro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hohara, Shinya*; Nakano, Masahiro*
Physical Review C, 82(3), p.034604_1 - 034604_8, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:63.2(Physics, Nuclear)We investigate proton-production double-differential cross sections (DDXs) for 300- and 392-MeV proton-induced reactions on O, V, Tb, Ta, Au, Pb, and Bi. Emitted proton energies are measured with stacked scintillator spectrometers by the 
 -
- technique. Experimental results are compared with the intranuclear cascade (INC) and quantum molecular dynamics models. Although both models can reproduce spectral DDXs, there is a difference at the most forward and backward angles. The cause of these differences is discussed in terms of the refraction caused by the nuclear potential. Angular distributions of the present data are well accounted for by the Kalbach systematics plus INC one-step calculations. The quasi-free-scattering contribution increases with decreasing target mass and increasing emission energy.
technique. Experimental results are compared with the intranuclear cascade (INC) and quantum molecular dynamics models. Although both models can reproduce spectral DDXs, there is a difference at the most forward and backward angles. The cause of these differences is discussed in terms of the refraction caused by the nuclear potential. Angular distributions of the present data are well accounted for by the Kalbach systematics plus INC one-step calculations. The quasi-free-scattering contribution increases with decreasing target mass and increasing emission energy.
 Se; Implications for the s-process branching at
Se; Implications for the s-process branching at  Se
SeMakinaga, Ayano*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Goriely, S.*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Goko, Shinji*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Harano, Hideki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 79(2), p.025801_1 - 025801_8, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:79.65(Physics, Nuclear)Photoneutron cross sections were measured for  Se immediately above the neutron separation energy with quasimonochromatic
Se immediately above the neutron separation energy with quasimonochromatic  -ray beams to experimentally constrain the E1
-ray beams to experimentally constrain the E1  strength function for
strength function for  Se. Two sets of the
Se. Two sets of the  strength function and the level density that equally meet the experimental constraint predict largely different neutron capture cross sections for
strength function and the level density that equally meet the experimental constraint predict largely different neutron capture cross sections for  Se. Based on the Maxwell-averaged cross sections of the latest compilation complemented with the predicted cross sections for
Se. Based on the Maxwell-averaged cross sections of the latest compilation complemented with the predicted cross sections for  Se, we calculated
Se, we calculated  N values of the main s-process component using a phenomenological model and deduced empirical abundances of the weak s-process component.
N values of the main s-process component using a phenomenological model and deduced empirical abundances of the weak s-process component.
 Se; Implications for the s-process thermometer
Se; Implications for the s-process thermometerMakinaga, Ayano*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Goriely, S.*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Harano, Hideki*; Harada, Hideo; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 805(1-4), p.564 - 566, 2008/06
Photoneutron cross sections were measured for  Se near the neutron threshold energy with quasi-monochromatic
Se near the neutron threshold energy with quasi-monochromatic  rays. Using the
rays. Using the  Se(
Se( ,
, ) cross section as experimental constraints on the E1
) cross section as experimental constraints on the E1  strength function, we estimate the neutron capture rates for
strength function, we estimate the neutron capture rates for  Se. The solar abundance ratio of s-only nuclides
Se. The solar abundance ratio of s-only nuclides  Kr and
Kr and 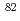 Kr are analyzed in terms of the s-process branching at
Kr are analyzed in terms of the s-process branching at  Se within the local approximation. The corresponding temperature and neutron density regimes are discussed in the light of the s-process scenario in massive stars.
Se within the local approximation. The corresponding temperature and neutron density regimes are discussed in the light of the s-process scenario in massive stars.
 Sm(
Sm( ,n) cross section with laser-Compton scattering
,n) cross section with laser-Compton scattering  rays and the photon difference method
rays and the photon difference methodHara, Kaoru; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Goko, Shinji*; Hohara, Shinya*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Makinaga, Ayano*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Kawakatsu*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 44(7), p.938 - 945, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:91.43(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 Sm
SmHara, Kaoru; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Goko, Shinji*; Hohara, Shinya*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Makinaga, Ayano*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Kawakatsu*; et al.
EUR-22794-EN, p.65 - 68, 2007/00
Neutron capture cross sections of the unstable nuclei  Sm (t
Sm (t =90yr) are the fundamental data for the nuclear transmutation, since the
=90yr) are the fundamental data for the nuclear transmutation, since the  Sm is one of radioactive fission products in the nuclear waste. On the other hand, the branching point nucleus
Sm is one of radioactive fission products in the nuclear waste. On the other hand, the branching point nucleus  Sm is important for characterizing the slow neutron capture process (s-process) nucleosynthesis in the AGB stars. The cross sections of the inverse
Sm is important for characterizing the slow neutron capture process (s-process) nucleosynthesis in the AGB stars. The cross sections of the inverse  Sm(
Sm( ,n)
,n) Sm reaction were measured with the laser-Compton scattering (LCS)
Sm reaction were measured with the laser-Compton scattering (LCS)  rays at 8.3-12.4 MeV. Quasi-monochromatic beams of LCS photons irradiated an enriched
rays at 8.3-12.4 MeV. Quasi-monochromatic beams of LCS photons irradiated an enriched  Sm
Sm O
O sample. The emitted neutrons were detected with a 4
sample. The emitted neutrons were detected with a 4 neutron detector consisting of 20
neutron detector consisting of 20  He proportional counters embedded in a polyethylene moderator. The
He proportional counters embedded in a polyethylene moderator. The  Au(
Au( ,n) reaction cross sections were also measured as a standard. In the data analysis, the (
,n) reaction cross sections were also measured as a standard. In the data analysis, the ( ,n) cross sections are deduced with two methods. The present data for
,n) cross sections are deduced with two methods. The present data for  Sm and
Sm and  Au are compared with the previous data compiled in the IAEA document and the calculation with a nuclear reaction code TALYS. The neutron capture cross sections for
Au are compared with the previous data compiled in the IAEA document and the calculation with a nuclear reaction code TALYS. The neutron capture cross sections for  Sm in the keV-MeV energy range are evaluated with the present photonuclear data for
Sm in the keV-MeV energy range are evaluated with the present photonuclear data for  Sm as constraint in the statistical model calculations.
Sm as constraint in the statistical model calculations.
 Zr using laser inverse Compton
Zr using laser inverse Compton 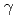 rays
raysHohara, Shinya*; Goko, Shinji*; Makinaga, Ayano*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Hara, Kaoru; Kitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2006-009, p.66 - 69, 2006/11
no abstracts in English
 Sm(
Sm( ,n) reaction cross section with laser-Compton scattering
,n) reaction cross section with laser-Compton scattering  rays
raysHara, Kaoru; Kitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Goko, Shinji*; Hohara, Shinya*; Makinaga, Ayano*; Yamagata, Tamio*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
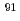 Zr(
Zr( ,n)
,n) Zr cross section
Zr cross sectionHohara, Shinya*; Goko, Shinji*; Makinaga, Ayano*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Hara, Kaoru; Kitatani, Fumito; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Harano, Hideki*; Harada, Hideo; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Sm(
Sm( ,n) reaction and s-process
,n) reaction and s-processHara, Kaoru; Kitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Goko, Shinji*; Hohara, Shinya*; Makinaga, Ayano*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Se
SeMakinaga, Ayano*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Goko, Shinji*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Hara, Kaoru; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Harano, Hideki*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hara, Kaoru; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Goko, Shinji*; Hohara, Shinya*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Makinaga, Ayano*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
no journal, ,
Neutron capture cross sections of the unstable nuclei  Cl (t
Cl (t =3.0
=3.0 10
10 yr) and
yr) and  Sm (t
Sm (t =90 yr) are the fundamental data for the nuclear transmutation. The cross sections of the inverse
=90 yr) are the fundamental data for the nuclear transmutation. The cross sections of the inverse  Cl(
Cl( ,n)
,n) Cl and
Cl and 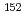 Sm(
Sm( ,n)
,n) Sm reaction were measured with the laser-Compton scattering (LCS)
Sm reaction were measured with the laser-Compton scattering (LCS)  rays at 10.4-12.0 MeV and 8.3-12.4 MeV, respectively. Quasi-monochromatic beams of LCS photons irradiated a natural NaCl sample and an enriched
rays at 10.4-12.0 MeV and 8.3-12.4 MeV, respectively. Quasi-monochromatic beams of LCS photons irradiated a natural NaCl sample and an enriched  Sm
Sm O
O sample. The emitted neutrons were detected with a 4
sample. The emitted neutrons were detected with a 4 neutron detector. The energy distribution of LCS
neutron detector. The energy distribution of LCS  beam was measured with a 120
beam was measured with a 120  Ge detector or the high-resolution high-energy photon spectrometer (HHS). The present data for
Ge detector or the high-resolution high-energy photon spectrometer (HHS). The present data for  Cl,
Cl,  Sm, and
Sm, and  Au are compared with the previous data compiled in the IAEA document and the calculation with a nuclear reaction code TALYS.
Au are compared with the previous data compiled in the IAEA document and the calculation with a nuclear reaction code TALYS.
Takahashi, Kazuki*; Nakajima, Kunihiro*; Sakon, Atsushi*; Hohara, Shinya*; Hashimoto, Kengo*; Fukaya, Yuji; Sano, Tadafumi*
no journal, ,
A Mock-up core for HTTR was configured on the B rack of the Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA), and control rod and center core drop experiments were conducted to obtain time-series data. As a result of performing inverse kinetics analysis on the acquired time-series data, position dependency of each detector was confirmed. Furthermore, in the case with large reactivity worth, such as C1 and the central core, significant differences were found between the analysis results of the integration method and the least squares inverse kinetics method.
 analysis for HTTR simulated core in KUCA
analysis for HTTR simulated core in KUCANakajima, Kunihiro*; Sakon, Atsushi*; Takahashi, Kazuki*; Hohara, Shinya*; Hashimoto, Kengo*; Fukaya, Yuji; Sano, Tadafumi*
no journal, ,
Time series data of neutron detector was obtained under Am-Be steady neutron source driven condition and neutron source from fuel in the graphite core system configured on B rack of the Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA), and the reactor noise analysis with Rossi- method was performed. As a result, neutron correlation component could not be observed under Am-Be neutron source driven condition, but a significant correlation component was observed under fuel neutron source driven condition, and prompt neutron decay constant could be determined.
method was performed. As a result, neutron correlation component could not be observed under Am-Be neutron source driven condition, but a significant correlation component was observed under fuel neutron source driven condition, and prompt neutron decay constant could be determined.
Sakon, Atsushi*; Nakajima, Kunihiro*; Takahashi, Kazuki*; Hohara, Shinya*; Sano, Tadafumi*; Fukaya, Yuji; Hashimoto, Kengo*
no journal, ,
Subcriticality measurement experiment by reactor noise analysis was performed in mock-up core for HTTR configured on B rack of the Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). The experiments were carried out in low power critical state and in the subcritical state driven by Am-Be neutron source, and the measurements were performed with several neutron detectors at different positions. We analyzed neutron detector time series data acquired by experiment by power spectrum method, and tried to estimate the prompt neutron decay constant of the system.