Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwasaki, Riyo*; Hama, Katsuhiro; Morikawa, Keita*; Hosoya, Shinichi*
JAEA-Technology 2016-037, 62 Pages, 2017/02
Mass transport study is mainly performed as part of Phase III in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory Project. In Phase III, the goal of mass transport study is to obtain a better understanding of mass transport phenomena in the geological environment as well as to develop technologies for measurement of the mass transport parameters, model construction, numerical analysis and validation of those technologies. This study was planned to understand the influence of the geological characteristics of fracture on the mass transport parameters.
Hosoya, Shinichi*; Yamashita, Tadashi*; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Onoe, Hironori; Ishibashi, Masayuki
JAEA-Technology 2015-027, 128 Pages, 2016/01
The study for development of drift backfilling technologies is one of the critical issues in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project, and its purposes are to develop closure methodology and technology, and long-term monitoring technology, and to evaluate resilience of geological environment. To achieve the purposes, previous information from the case example of underground facility constructed in crystalline rock in Europe has been collected. In particular, the boundary conditions for the closure, geological characteristics, technical specifications, and method of monitoring have been focused. The information on the international project regarding drift closure test and development of monitoring technologies has also been collected. In addition, interviews were conducted to specialists who have experiences involving planning, construction management, monitoring, and safety assessment for the closure. Based on the collected information, concept and point of attention, which are regarding drift closure testing, and planning, execution management and monitoring on the closure of MIU, have been specified.
Yamashita, Riyo; Hama, Katsuhiro; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Morikawa, Keita*; Hosoya, Shinichi*; Nakamura, Toshiaki*; Tanaka, Yumiko*
JAEA-Technology 2014-029, 118 Pages, 2014/09
This study is to gain a better understanding of mass transfer phenomena in the geological environment as well as to develop technologies for: measurement of the solute transport parameters, model construction, numerical analysis and validation of all those technologies based on the existing information. As part of solute transport study, laboratory experiments were planned to understand the influence of the geological characteristics of fracture on the solute transport parameters, also understand the differences in test results by the different sizes of the samples used for an experiment, and moreover to validate the parameters obtained by numerical analysis.
Ishibashi, Masayuki; Onoe, Hironori; Sawada, Atsushi; Atsumi, Hiroyuki*; Masumoto, Kazuhiko*; Hosoya, Shinichi*
Dai-42-Kai Gamban Rikigaku Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.101 - 106, 2014/01
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is proceeding with the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory Project in order to establish comprehensive techniques for the investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment in fractured crystalline rock for geological disposal of high level radioactive wastes. We have carried out discrete fracture network modeling, groundwater flow and particle tracking simulation in order to understand the important factors for the solute transport characterizations. In this paper, a method of discrete fracture network modeling based on in-situ data at underground gallery and the influences of different data interpretation are described.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Morikawa, Keita; Tachi, Yukio; Kuno, Yoshio*; Hosoya, Shinichi*; Shimoda, Satoko*; Kato, Hiroyasu*; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Ikuse, Hiroyuki*; Kubota, Masako*
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-013, 96 Pages, 2012/07
For the purpose to understand the relationship between characteristic of mass transport and characteristic of fracture, the following experiments were carried out using core sample, which was sampled from the -300 m Stage. This paper compiled the results of these experiment. (1) Diffusion experiments of Cs, Sr, I and uranin in granite samples (2) Sorption experiments of Cs and Sr on crushed granite (3) Measurement of pore physicality by Mercury Intrusion and water saturation
Nanjo, Isao; Amano, Yuki; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Kunimaru, Takanori; Murakami, Hiroaki; Hosoya, Shinichi*; Morikawa, Keita
JAEA-Research 2011-048, 162 Pages, 2012/03
The observation technique of hydrochemical condition in low permeable sedimentary rock around the facility is one of R&D subjects. We report, (1) development of hydrochemical monitoring system to observe water pressure, pH, electric conductivity, dissolved oxygen, redox potential and temperature, (2) hydrochemical observation results around URL under construction. The applicability of the hydrochemical monitoring system is evaluated for low permeable sedimentary rock bearing abundant dissolved gases. The hydrochemical observation during facility construction demonstrates that pH and redox potential of groundwater almost did not changed even at hydraulic disturbed zone (water pressure decreased zone).
Iwatsuki, Teruki; Morikawa, Keita*; Hosoya, Shinichi*; Yoshikawa, Hideki
Chikasui Gakkai-Shi, 51(3), p.205 - 214, 2009/08
Physicochemical parameters of deep groundwater at the depth of 500 m were measured at ground surface and the in-situ sampling depth of borehole to understand the redox condition and dominant redox process. The results show that the redox potential at the depth was approximately -100 mV and was controlled by the reaction of chemical pairs of (Fe
 , SO
, SO
 )/(FeS
)/(FeS ) or (SO
) or (SO
 , FeCO
, FeCO )/(FeS). The pH value at ground surface changed approximately 0.4 from that at the in-situ depth by degassing of dissolved carbon dioxide. The time to reach the stable ORP value in monitoring depends on the shape and surface area of Pt electrode. The columnar-shape Pt electrode is more sensitive for deep groundwater rather than a dot-shape Pt electrode. It is important to correct the pH measured at ground surface for the analysis of in-situ redox reaction process.
)/(FeS). The pH value at ground surface changed approximately 0.4 from that at the in-situ depth by degassing of dissolved carbon dioxide. The time to reach the stable ORP value in monitoring depends on the shape and surface area of Pt electrode. The columnar-shape Pt electrode is more sensitive for deep groundwater rather than a dot-shape Pt electrode. It is important to correct the pH measured at ground surface for the analysis of in-situ redox reaction process.
Hosoya, Shinichi*; Kunimaru, Takanori; Shibano, Kazunori
JAEA-Research 2008-088, 78 Pages, 2009/01
Spectral analyses of the groundwater pressure data which has been monitored in the boreholes; HDB-3, 6, 7 and 8, were carried out to estimate formation properties and remove the components of response to atmospheric pressure fluctuation and earth tide from time series. The results revealed that groundwater pressure at the all intervals responds to atmospheric pressure but does not respond to earth tide at all above the resolution of measurements. Specific storage, vertical hydraulic conductivity and shear modulus were estimated from the response to atmospheric loading and compared with the data obtained in the laboratory experiments.
Hosoya, Shinichi*
JNC TJ7440 2005-066, 80 Pages, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Hosoya, Shinichi*; Ishii, Eiichi; Hishiya, Tomoyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nanjo, Isao; Mizuno, Takashi; Murakami, Hiroaki; Amano, Yuki; Hosoya, Shinichi*; Wakahama, Hiroshi*; Yamashita, Riyo*
no journal, ,
This study aimed to develop a hydrochemical monitoring system for in-situ groundwater. JAEA has developed the hydrochemical monitoring system which is available at underground facility focused on low-permeable sedimentary rocks. After performance test, it can be demonstrated that the monitoring system is workable completely at 350m depth research gallery.
Hosoya, Shinichi*; Suzuki, Kazushige*; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sawada, Atsushi; Atsumi, Hiroyuki*; Iwano, Keita*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takata, Shinichi; Suzuki, Junichi*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Iwase, Hiroki*; Shinohara, Takenao; Oku, Takayuki; Nakatani, Takeshi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Ito, Takayoshi*; Tominaga, Taiki*; et al.
no journal, ,
The small and wide angle neutron scattering instrument, 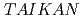 , was installed at the
, was installed at the 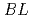 15 in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility,
15 in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility, 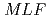 , of
, of 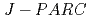 .
.  is designed for efficient measurement in wide-q range by using of the wide wavelength and the four detector banks which cover small-, middle-, high-, and backward-angle. At the present stage, 1,216
is designed for efficient measurement in wide-q range by using of the wide wavelength and the four detector banks which cover small-, middle-, high-, and backward-angle. At the present stage, 1,216  s are mounted on
s are mounted on  , where the number is about 50% of the installable total
, where the number is about 50% of the installable total  s number. On beam commissioning started in January 2012, and user program began in March 2012. The software of data reduction has newly developed and some sample environment devices such as a sample changer, tension tester, and refrigerator have been improved. In this presentation, we present the current status of
s number. On beam commissioning started in January 2012, and user program began in March 2012. The software of data reduction has newly developed and some sample environment devices such as a sample changer, tension tester, and refrigerator have been improved. In this presentation, we present the current status of  about the new software, sample environment devices, and the results on some samples to show the instrument performance of
about the new software, sample environment devices, and the results on some samples to show the instrument performance of  .
.
Morikawa, Keita*; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Hosoya, Shinichi*
no journal, ,
Measurement of redox potential in deep groundwater was conducted at ground surface and in-situ monitoring part of borehole to refine the properties of ORP electrode. The results show that the time to reach the stable value of redox potential depends on shape of Pt electrode.
Nanjo, Isao; Kunimaru, Takanori; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Hosoya, Shinichi*; Morikawa, Keita*
no journal, ,
The instrument for groundwater monitoring technique, which can continuously monitor the pore water pressure and physico-chemical parameters has developed, to monitor the hydrological and geochemical disturbances caused by underground facility construction. The pore water pressure was observed almost the same value after the circulation for the measurement of physico-chemical parameters. It was able to be confirmed that the continuous measurement for physico-chemical parameters doesn't influence the observation of pore water pressure.
Morikawa, Keita; Kunimaru, Takanori; Yuguchi, Takashi; Hosoya, Shinichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hosoya, Shinichi*; Seno, Shoji*; Nakajima, Makoto*; Atsumi, Hiroyuki*; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Morikawa, Keita; Onoe, Hironori; Kunimaru, Takanori
no journal, ,
Discrete Fracture Network (DFN) model provides the basis of groundwater flow analysis and solute transport analysis for crystalline rock. Due to its complexity, it is difficult to estimate how the input parameters influence the result of the analysis. In this study, using the data obtained in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project conducted by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), we examined how the modeling methodology influenced the result of groundwater flow analysis and solute transport analysis.
Hosoya, Shinichi*; Suzuki, Kazushige*; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Atsumi, Hiroyuki*; Masumoto, Kazuhiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Atsumi, Hiroyuki*; Nakajima, Makoto*; Iwano, Keita*; Masumoto, Kazuhiko*; Seno, Shoji*; Kawabata, Junichi*; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Hosoya, Shinichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Riyo; Hama, Katsuhiro; Morikawa, Keita*; Hosoya, Shinichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takeuchi, Shinji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Shiozaki, Isao*; Hosoya, Shinichi*; Osada, Masahiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English