Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Motooka, Takafumi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Corrosion Science and Technology, 20(3), p.105 - 111, 2021/06
We constructed three dimensional computational model using cellular automata method to simulate the intergranular corrosion propagation of stainless steel. In the model, the computational system was constructed by three types of cells: grain (bulk), grain boundary (GB), and solution cell. Our simulations revealed that the surface roughness calculated by the model adopted distributed dissolution rates of GBs was greater than that adopted constant dissolution rates of GBs. The cross-sectional images obtained by our simulation were comparable with that obtained by corrosion tests. These results indicate that the surface roughness during corrosion relates the distribution of corrosion rate.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Motooka, Takafumi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Proceedings of 19th International Corrosion Congress (19th ICC) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2014/11
We constructed three dimensional computational model using cellular automata method to simulate the intergranular corrosion propagation of stainless steel. By the simulation using the model, we verified the relationship between surface roughness during corrosion and dispersion of dissolution rate of grain boundaries (GB). The relationship was investigated by the simulation applying constant dissolution rate for GB cells and distributed dissolution rate of GB cells. Our simulations revealed that the surface roughness calculated by the model adopted distributed dissolution rates of GBs was greater than that adopted constant dissolution rates of GBs. The cross-sectional images obtained by our simulation were comparable with that obtained by corrosion tests. These results indicate that the surface roughness during corrosion relates the distribution of corrosion rate.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Motooka, Takafumi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo, 63(7), p.431 - 437, 2014/07
In order to obtain the relation between an intergranular corrosion behavior and an impurities for stainless steel, cellular automata modeling and simulation of intergranular corrosion was carried out. From intergranular corrosion simulation considering non-uniform phosphorus component distribution on grain boundary, it suggested that complicated intergranular corrosion shape as in experimental data was caused by the large precipitation of phosphorus compounds in part of grain boundary.
Shimo, Michito*; Yamamoto, Hajime*; Jo, Mayumi*; Yamagami, Masahito*; Fumimura, Kenichi*; Kumamoto, So*; Igarashi, Takafumi*
JNC TJ7440 2005-083, 991 Pages, 2003/01
None
Ijiri, Yuji*; Hattori, Hiromichi*; Suzuki, Shunichi*; Oishi, Masaya*; Kubota, Shigeru*; Adachi, Tetsuya*; Yamamoto, Takuya*; Igarashi, Takafumi*; Sugihara, Yutaka*
JNC TJ8400 2001-009, 41 Pages, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Anezaki, Susumu*; Sugihara, Yutaka*; Igarashi, Takafumi*; Yamamoto, Takuya*; Adachi, Tetsuya*; Suzuki, Shunichi*; Oishi, Masaya*
JNC TJ1410 2000-001, 123 Pages, 2000/03
Anezaki, Susumu*; Sugihara, Yutaka*; Igarashi, Takafumi*; Kubota, Shigeru*; Adachi, Tetsuya*
JNC TJ1410 98-001, 74 Pages, 1998/10
As a technical problem to be solved in the underground research of sedimentary rock formation, the specification for access drift from the surface to the experimental area in the underground was studied. Considering ground condition, safety for construction and experiment execution, maintenance of experimental environment, construction period and cost, the feasibility of access drift was carried out.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Komatsu, Atsushi; Motooka, Takafumi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Igarashi, Takahiro; Motooka, Takafumi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Nojima, Yasuo*; Fujine, Sachio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Komatsu, Atsushi; Motooka, Takafumi; Igarashi, Takahiro; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
no journal, ,
The effect of phosphorous on intergranular corrosion of 310 stainless steel at transpassive potential was investigated. High purity 310 stainless steel containing 270 ppm phosphorous with different heat treatments was polarized at transpassive potential. Intergranular corrosion depth was measured by SEM observation, and grain boundaries were observed using 3D atom probe. Intergranular corrosion became severe in heat treated sample to enhance phosphate precipitation. 3D atom probe measurement revealed that grain boundary of high dissolution rate had phosphorous and chromium concentration layer of less than 10 nm thick. On the other hand, grain boundary of low dissolution rate had no concentration layer of phosphorous. From these results, it is suggested that intergranular corrosion of 310 stainless steel at transpassive potential is related to phosphorous and chromium concentration layer.
Yamamoto, Masahiro; Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Motooka, Takafumi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
no journal, ,
Intergranular corrosion occurred in stainless steels in nitric acid solution at a spent fuel reprocessing plant. Several reports introduced that intergranular corrosion affected by the impurity elements. We analyzed the initial stages of intergranular corrosion microscopically and attempted to simulate them numerically. The specially prepared 25Cr-20Ni stainless steel which was include only phosphorus for an impurity element was used for analyzing the initial stage of intergranular corrosion. Phosphorus segregated into grain boundary using various thermal treatments. The results indicated that the initial stage of intergranular corrosion was characterized by the ratio of corrosion rates between grain boundary and matrix. The ratio increased with higher phosphorus segregation by thermal treatment. These values were used for numerical simulation of intergranular corrosion. The cross sectional images calculated by the simulation were very good agreement to the actual observations.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Motooka, Takafumi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
no journal, ,
We simulated intergranular corrosion considering various fluctuations of corrosion rates (CR) for grain boundaries (GB): exponential, normal and uniform distributions. The relationship among the roughness of corroded surface, maximum intergranular corrosion depth, and fluctuations of CRs of GBs was evaluated. The cross-sectional images by simulation with the case of exponential distribution was relatively resemble to cross-sectional images obtained by corrosion tests in terms of roughness of corrosion surface. The simulation using normal and uniform distributions of CR of GB indicated that maximum corrosion depth became deeper with increasing deviation range of fluctuations. These results suggested that the roughness of corroded surface was controlled by fluctuation of CRs of GBs.
 Co
Co Ca
Ca Ru
Ru O
O
Horie, Akihiro*; Yasui, Yukio*; Igarashi, Taichi*; Yatagai, Ryo*; Yamamoto, Takafumi*; Terasaki, Ichiro*; Matsukawa, Takeshi*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Ishigaki, Toru*; Igawa, Naoki
no journal, ,
The magnetic and crystal structures, and magnetic properties of Ba Co
Co Ca
Ca Ru
Ru O
O have been studied by using the neutron powder diffraction and the magnetization analysis. With increasing
have been studied by using the neutron powder diffraction and the magnetization analysis. With increasing 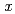 , an antiferromagnetic transition temperature
, an antiferromagnetic transition temperature 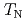 decreases such as
decreases such as 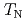 = 88 K (
= 88 K (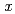 =0.1), 82 K (
=0.1), 82 K (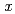 =0.2), and 76 K (
=0.2), and 76 K (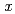 =0.3), respectively. We have observed magnetic reflections, which can not be explained by the collinear structure. Though the lattice volume increases, we have found that a Ru-Ru bond length decreases with increasing
=0.3), respectively. We have observed magnetic reflections, which can not be explained by the collinear structure. Though the lattice volume increases, we have found that a Ru-Ru bond length decreases with increasing 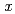 . It is considered to be related with the Ru-Ru dimerization. By the combined studies of the magnetic properties and neutron diffraction analysis, we will discuss the change of Ru
. It is considered to be related with the Ru-Ru dimerization. By the combined studies of the magnetic properties and neutron diffraction analysis, we will discuss the change of Ru -spins with varying
-spins with varying 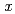 .
.
 Co
Co Ca
Ca Ru
Ru O
O
Horie, Akihiro*; Yasui, Yukio*; Igarashi, Taichi*; Yamamoto, Takafumi*; Misaswa, Kazuki*; Terasaki, Ichiro*; Matsukawa, Takeshi*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Ishigaki, Toru*; Igawa, Naoki
no journal, ,
The crystal and magnetic structures of Ba Co
Co Ca
Ca Ru
Ru O
O has been studied by using the neutron powder diffraction. We also carried out the measurements of magnetic properties of this sample.
has been studied by using the neutron powder diffraction. We also carried out the measurements of magnetic properties of this sample. 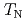 is decreased with increasing the fraction of Ca ion, and we found that
is decreased with increasing the fraction of Ca ion, and we found that 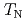 is 76 K at the fraction of Ca = 0.3. although the lattice constants of the sample are increased by the substituting Ca for Co ion, a Ru-Ru bond length decreases with increasing fraction of Ca ion. In this presentation, the details of the magnetic properties and magnetic structure of this material will be discussed.
is 76 K at the fraction of Ca = 0.3. although the lattice constants of the sample are increased by the substituting Ca for Co ion, a Ru-Ru bond length decreases with increasing fraction of Ca ion. In this presentation, the details of the magnetic properties and magnetic structure of this material will be discussed.
Hayashi, Takeru*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; Hatori, Kimihito*; Awano, Takaaki*; Igarashi, Takahiro; Koshina, Takafumi*
no journal, ,
In order to establish deterioration diagnosis technology for surface coating materials, we examined the measurement method and analysis method. The local thermal diffusivity could be measured by the laser spot periodic heating radiation thermometry method. In addition, it was also measured the thermal diffusivity by the xenon flash method to compare that by the laser spot periodic heating radiation thermometry method. A two-layer analytical formula was constructed for the coating sample, because there is a possibility that single-layer analysis may not give accurate results. As a result of measurement at room temperature, the thermal diffusivity decreased remarkably in the thickness direction measurement when the coating surface was placed on the detection surface side. On the other hand, the thermal diffusivity kept remained when the coating surface was placed on the heating surface side.