Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshimura, Kazuo; Doda, Norihiro; Igawa, Kenichi*; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Tanaka, Masaaki; Nemoto, Toshiyuki*
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/03
To investigate possibility of the insertion of the reactivity by the deflection of the upper core support plate, structural mechanics analyses of the domain consisting of the fuel assemblies and core support plates and evaluation of the reactivity due to the inclination of the fuel assemblies in EBR-II were carried out. As a result, it was indicated that the upper core support plate deflected downward larger at the low flowrate condition than that at the high flowrate condition and positive reactivity was inserted due to the inclination of the fuel assemblies at the low flowrate condition.
Yoshimura, Kazuo; Doda, Norihiro; Nakamine, Yoshiaki*; Fujisaki, Tatsuya*; Igawa, Kenichi*; Iida, Masaki*; Tanaka, Masaaki
Dai-27-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/09
In Japan Atomic Energy Agency, a virtual plant model of the sodium-cooled fast reactor plant composed in a computer is being developed to reduce the development cost, by replacing the experiments to the numerical simulations with coupled analyses of the physical phenomena accounting for the interaction between components under various plant conditions. Through the numerical analysis of the ULOHS test in the U.S. experimental fast reactor named EBR-II, applicability of the virtual plant model was confirmed in comparison with the measured data including the core inlet temperature and the reactor power.
Doda, Norihiro; Igawa, Kenichi*; Iwasaki, Takashi*; Murakami, Satoshi*; Tanaka, Masaaki
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 410, p.112377_1 - 112377_15, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)To enhance the safety of sodium-cooled fast reactors, the decay heat in the core must be removed by natural circulation even if the AC power supply to the forced circulation equipment is lost. Under natural circulation conditions, sodium flow is driven by buoyancy, and flow velocity and temperature distribution influence each other. Thus, it is difficult to evaluate the core hot spot temperature by deterministically considering the uncertainties affecting flow and heat. In this study, a statistical evaluation method is developed for the core hot spot temperature by using Monte Carlo sampling methods. The applicability of the core hotspot evaluation method was confirmed in three representative events during natural circulation decay heat removal operations in loop-type sodium-cooled fast reactors.
Yoshimura, Kazuo; Doda, Norihiro; Fujisaki, Tatsuya*; Igawa, Kenichi*; Tanaka, Masaaki; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
The benchmark analyses for the unprotected loss of heat sink (ULOHS) tests in the pool-type experimental SFR in the United States, EBR-II (BOP-301 and BOP-302R) have been conducted in order to validate the evaluation method of the reactivity feedback equipped in the plant dynamics analysis code named Super-COPD. In this study, 1D-CFD coupled analyses adding the core bowing reactivity model were conducted. Through the analysis, the applicability of the modified reactivity model was confirmed for the BOP-301 test. For the BOP-302R test, consideration of the core restraint system in the core and modeling the control rod driveline expansion reactivity was indicated.
Yoshimura, Kazuo; Doda, Norihiro; Igawa, Kenichi*; Tanaka, Masaaki; Yamano, Hidemasa
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 9(2), p.021601_1 - 021601_9, 2023/04
Feedback reactivity automatically caused by radial expansion of the core is known as one of the inherent safety features in a sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR). In order to validate the evaluation models of the reactivity feedback equipped in the in-house plant dynamics analysis code named Super-COPD, the benchmark analyses for the unprotected loss of heat sink (ULOHS) tests of BOP-302R and BOP-301 in an experimental SFR, EBR-II were conducted and the applicability of the evaluation method for the reactivity feedback was indicated during the ULOHS even, by comparing the numerical results and the experimental data.
Yoshimura, Kazuo; Doda, Norihiro; Fujisaki, Tatsuya*; Igawa, Kenichi*; Tanaka, Masaaki; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 29th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 29) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/08
To confirm the applicability of the reactivity model, the authors have been conducting the benchmark exercises of the unprotected loss of heat sink event tests in a pool-type experimental fast reactor EBR-II. In the blind phase in the benchmark analyses using the plant dynamics analysis (1D) code in which the cold pool was modeled by means of the perfect mixing volume, it was found the increase of the core inlet temperature was evaluated lower than that of the measured data and the feedback reactivity was underestimated, because the thermal stratification in the cold pool was ignored. Then, the detailed model of the cold pool for the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) code was introduced and the 1D-CFD codes coupling method was applied to the benchmark analyses. It was confirmed that both the thermal stratification in the cold pool and the increase of the core inlet temperature were successfully reproduced.
Doda, Norihiro; Nakamine, Yoshiaki*; Igawa, Kenichi*; Iwasaki, Takashi*; Murakami, Satoshi*; Tanaka, Masaaki
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 27, 6 Pages, 2022/06
As a part of the development of the "Advanced Reactor Knowledge- and AI-aided Design Integration Approach through the whole plant lifecycle (ARKADIA)" to automatically optimize the life cycle of innovative nuclear reactors including fast reactors, ARKADIA-design is being developed to support the optimization of fast reactor design in the conceptual stage. ARKADIA-Design consists of three systems (Virtual plant Life System (VLS), Evaluation assistance and Application System (EAS), and Knowledge Management System (KMS)). A design optimization framework controls the cooperation between the three systems through the interfaces in each system. This paper reports on the development status of the "VLS interface," which has a control function of coupling analysis codes in VLS.
Yoshimura, Kazuo; Doda, Norihiro; Tanaka, Masaaki; Yamano, Hidemasa; Igawa, Kenichi*
Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 28) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2021/08
The numerical results of the benchmark analyses for the unprotected loss of heat sink (ULOHS) tests in the pool-type experimental SFR in the United States, EBR-II (BOP-302R and BOP-301) are discussed in order to validate the evaluation method of the reactivity feedback equipped in the in-house plant dynamics analysis code named Super-COPD. By comparing the numerical results and the experimental data, the profiles of the increase of the core inlet temperature and the decrease of the reactor power calculated by Super-COPD were comparable with those of the experimental data and the applicability of the evaluation method for the reactivity feedback was indicated during the ULOHS event.
 C
CKikuchi, Kenji; Kamata, Kinya*; Ono, Mikinori*; Kitano, Teruaki*; Hayashi, Kenichi*; Oigawa, Hiroyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 377(1), p.232 - 242, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:72.65(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Corrosion behavior of F82H and JPCA was studied in the circulating LBE loop. Those are candidate materials of Japanese ADS beam windows. Maximum temperatures were kept to 450 and 500  C with 100
C with 100  C constant temperature difference. Main flow velocity was 0.4 to 0.6 m/s in every case. Oxygen concentration was controlled to 2
C constant temperature difference. Main flow velocity was 0.4 to 0.6 m/s in every case. Oxygen concentration was controlled to 2 4
4 10
10 mass% although there was an exception. Testing time durations were 500 to 3000 hrs. Round bar type specimens were put in the circular tube of the loop. Electron beam welded joint in the middle part of specimens were also studied. Optical micrograph, electron micrograph, X-ray element analyses and X-ray diffraction were investigated. Consequently for a long-term behavior a linear law is recommended to predict corrosion in the ADS beam design.
mass% although there was an exception. Testing time durations were 500 to 3000 hrs. Round bar type specimens were put in the circular tube of the loop. Electron beam welded joint in the middle part of specimens were also studied. Optical micrograph, electron micrograph, X-ray element analyses and X-ray diffraction were investigated. Consequently for a long-term behavior a linear law is recommended to predict corrosion in the ADS beam design.
Hayashi, Kenichi*; Ono, Mikinori*; Kikuchi, Kenji; Tokunaga, Noriya*; Kitano, Teruaki*; Oigawa, Hiroyuki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 7(1), p.44 - 57, 2008/03
Accelerator driven nuclear transmutation system aims at transmuting minor actinides and long-lived fission products to stable or short-lived nuclei. A design study of proton beam window, which is an interface component between accelerator and nuclear reactor. Thermal-hydraulic experiment of the beam window was done. Two experiments were conducted: one was particle image velocimetry measurement around the beam window in flowing water and the other was temperature measurement at the beam window under flowing lead bismuth. Numerical simulation was also done to validate the beam window model for design work. Results show that heat transfer characteristics of the beam widow averaged in space and with time under flowing lead bismuth was formulized by the experimental equation. Numerical simulation model can estimate the mean heat transfer coefficient. However, a local heat transfer coefficient was not stable: it fluctuates with time and even in space, especially around stagnation point.
Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Igawa, Naoki; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Shimura, Kenichiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 242(1-2), p.469 - 472, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.12(Instruments & Instrumentation)SiC/SiC composites are one of the candidate materials for first wall in a fusion reactor because of their high strength at high temperature and low residual radioactivity after irradiation. In the fusion reactor, these materials are required to have high thermal diffusivity for heat exchange and reducing the thermal shock. Under fusion conditions, helium (He) and hydrogen (H) are produced in SiC. In this study, the effect of He ions implantation on the thermal diffusivities of SiC and SiC/SiC composite were investigated. In the results, the thermal diffusivities of SiC and SiC/SiC composites decreased after He ions implantation. However, the thermal diffusivities of SiC and SiC/SiC composites hardly reduced in the operation temperature of fusion reactor. The thermal diffusivities of He implanted specimens were partly recovered by annealing. The defect concentration induced by He implantation, X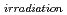 , in SiC/SiC composites was estimated. The X
, in SiC/SiC composites was estimated. The X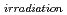 rapidly decreased around 500
rapidly decreased around 500  C. The reason is that the He release from SiC starts at 500
C. The reason is that the He release from SiC starts at 500  C.
C.
Hayafune, Hiroki; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Soman, Yoshindo; Konomura, Mamoru; Mizuno, Tomoyasu; Igawa, Kenichi*
JNC TN9400 2004-054, 339 Pages, 2004/08
Concepts of the reactor, SG and main coolant pump have been studied considering maintainability and aseismic capability, which is a medium size pool type lead-bismuth cooled reactor. The results are following.(1) Reconsideration of reactor design concepts concerning maintainability. In pursuit of good reactor maintainability, the structural concepts of SG, UIS and core support structures have been changed to be drawn up above the upper area of the reactor system. After a few decade of interval, lead-bismuth inventory in the reactor vessel shall be fully drained for easy ISI operation of in-vessel main components such as core support structures. From the viewpoint of the reactor aseismic capability, the axial length of reactor vessel was reduced and the reactor vessel support location was changed from the top hanging to the circumference of the vessel.(2) SG concept selection in conjunction with a compact reactor vessel.The concept of SG consisting of a once through type with helical coil tube is selected. 6 units of a small scale SG are arranged on a reactor roof deck along the peripheral direction, in addition to 3 units of a centrifugal mechanical pump.(3) Aseismic structural integrity of the reactor components. Aseismic structural integrity of the reactor vessel, core support structures, UIS, FHM, SG and the main pumps has been vigorously examined respectively. These components besides FHM could keep the aseismic structural integrity for strong S2 earthquake under the design condition FHM could also keep the integrity for S1 earthquake.(4) Safety evaluation. Thermal translents following loss of flow type accident due to plant total blackout and typical manual reactor trip incident, have been evaluated to assure the plant safety design, by analyzing thermal hydraulic behavior of transients concerning core flow rate and temperatures of the plant cooling system. *Loss of flow accident due to plant total blackout. The reactor coolant pumps shall be tripped and the
Imo, Kazumichi; Onuki, Koji; Kikuchi, H.; Morishita, Masaki; Igawa, Kenichi*; Nishibayashi, Yohei; Ikeda, Makinori
JNC TN2400 2003-004, 78 Pages, 2004/03
About the secondary system floor liner of Monju, the mechanical soundness of a floor liner to the thermal load conditions by combustion of leak sodium was evaluated by large displacement inelastic analysis and the partial structure model test.In large displacement inelastic analysis, it was confirmed that heat strain of a floor liner was less than the standard value of the strain for no through-wall crack. In addition, the influence evaluation by a temperature increasing rate, liner board thickness, and the existence of corrosion thinning was performed. The result, the influence on the maximum strain was small in any parameter.In the partial structure model test, even when a strain more excessive than the standard value of strain was given, it was confirmed no through-wall crack in a liner plate.In addition, this report improves the evaluation conditions of the conventional research report [1], and resummarizes them to detailed design evaluation.
; Igawa, Kenichi*
JNC TN9400 2002-019, 81 Pages, 2002/05
The cost minimization of commercialized FBR plant systems requires the integration of an intermediate-heat-exchanger (IHX) and a primary sodium mechanical pump into one component. The pump is installed in the center of the integrated component and heat transfer tubes surround the pump. Primary sodium flows down inside the heat transfer tubes and secondary sodium flows up outside the tubes in a zigzag. Therefore, the pump rotation and sodium flow induce the vibration of heat transfer tubes and it leads the tubes to fretting wearing against support plates. Then the tube wearing must be evaluated to confirm its integrity during the plant life span (60 years). However, the knowledge of the pump rotation influence on tube wearing is not sufficiently acquired because the integrated component is a new concept in JNC. To evaluate the tube fretting wearing ratio due to the pump rotation, a new calculation model of FINAS was composed. In the first place, the beam vibration analysis model of a pump shaft, shells, tube bundle etc. of the integrated component reveals its properties such as frequency, amplitude and vibration mode. In the second place, based on the above mentioned vibration analysis, the frequency and amplitude of abrasion between the tubes and support plates can be obtained by a contact analysis model of FINAS. Eventuany, this calculation shows that the tube wearing will not affect the tube integrity during the plant life time. However further evaluation by more detailed analysis and abrasion tests are needed to obtain more accurate results.
*; ; ; ; Fukami, Akihiro*; *; Igawa, Kenichi*
PNC TN9410 91-175, 52 Pages, 1991/05
An acoustic detection method is one of the FBR reactor core malfunction detection methods, and is regarded as being promising. In this study, the preliminary experiment of boiling detection by acoustic method was conducted at JOYO to measure the acoustic signal level and to investigate the applicability of the acoustic method. The experiment was performed on June 13 and 14, 1990 during the 8th periodic inspection of JOYO. The results obtained though the experiment are as follows: (1)Sodium bubbling (boiling) induced by the electric heater was detected as the fluctuation of temperature single of the thermocouple attached to surface of the electric heater. (2)Bubbling single of the acoustic detector could not be identified cleary because of the high background noise caused by the primary main pump vibration, sodium flow in the reacter vessel and the electric supply in the containment vessel. (3)The correlation between the signal of the acoustic detector or the fluctuation of temperature signal of the thermocouple and the flow rate of the primary loops was not ascertained. It became clear through this study that the validity of the reactor core malfunction detction by acoustic method depend on the peculiar noise level in the reactor vessel, and the reduction of noise is the subject for a future study.
*; *; Fukami, Akihiro*; *; Igawa, Kenichi*
PNC TN9440 89-006, 49 Pages, 1989/09
In Experimental Fast Reactor "JOYO", "Development of operation Support System" is continued as the enhancement, of opration support by using computer, in order to improve the availability and reliability of "JOYO" and future fast reactors. Plant State Prediction is one of these systems, and its function is to predict important parameters with respect to the security of safety and to figure them as valid data on CRT. This report deals with the examinations to put this function into JOYDAS (JOYO Data Acqisition System). Main results are as follows. (1) Objective phenomena and signals were selected from Emergency Procedure-Operation (EPO) and so on. (2)From these signls, sodium level in R/V and decay heat were selected and these prediction models were produced. (3)AS for sodium level in R/V, its prediction model was compared with the data at Primary Main Pump Trip (1987-9-7) and this reasonability was confirmed.
Nishihara, Kenji; Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Nakayama, Shinichi; Fujiwara, Takeshi; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Kano, Shigeru; Sasage, Kenichi; Yamashita, Teruo; Ono, Kiyoshi; Shiotani, Hiroki
no journal, ,
The reduction of the storage facility and repository were evaluated for the cases with or without partitioning of Sr-Cs and transmutation of MA in the advanced FBR fuel cycle with the cost estimation for the storage facilities, transporting and repository. As the result, the transmutation of minor actinides is inevitable for the small repository because the heat generation by  Am is considerable in FBR. The introduction of partitioning, transmutation and long-term storage enable the very compact layout in the repository like TRU wastes such as hulls and end-pieces of the fuel assembly. The cost for the storage and disposal in this case is much smaller than that in other cases, which mitigates the cost increase by the separation process and transmutor.
Am is considerable in FBR. The introduction of partitioning, transmutation and long-term storage enable the very compact layout in the repository like TRU wastes such as hulls and end-pieces of the fuel assembly. The cost for the storage and disposal in this case is much smaller than that in other cases, which mitigates the cost increase by the separation process and transmutor.
Takeda, Nobukazu; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Ueno, Kenichi; Maruyama, Takahito; Noguchi, Yuto; Kakudate, Satoshi
no journal, ,
In the vacuum vessel of the ITER, dose rate is very high (250 Gy/h) even during the plasma shutdown. Therefore, in-vessel components such as blanket and divertor must be maintained by remote handling. Procurement of the remote handling system of the blanket is allocated to Japan and the JAEA is performing the final design of it toward handover to the ITER Organization scheduled in 2020. This report shows progress of the final design activity. In the final design, the major part of the systems are more detailed and the tools for welding and cutting of blanket pipes are newly designed. In the same time, feasibility of operation scenario is confirmed by system analyses such as the reliability, availability, maintainability and inspectability analysis and structural analysis. By these activities, it is confirmed that the main components whose manufacturing contract will be awarded in this year can be fabricated without any concern and will be handed over to the ITER Organization in 2020 as planned.
Tanigawa, Hisashi; Ueno, Kenichi; Inoue, Ryuichi; Takeda, Nobukazu; Kakudate, Satoshi
no journal, ,
The shield blanket in ITER has an active cooling structure necessitating hydraulic connections to the cooling water manifold. To maintain or replace the blanket, welding the hydraulic connection by remote handling is necessary. Access for the welding is limited in a small hole in the first wall because of spatial constraints related to neutron and heat fluxes. A bore welding tool is required. Laser and TIG welding tools have been developed, and the welding conditions have been optimized for all position welding to horizontally located pipes. Additionally capability of re-welding between as-cut and new pipes has been confirmed. Based on the results, applicability of laser and TIG welding are comparatively assessed.
Ueno, Kenichi; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Noguchi, Yuto; Inoue, Ryuichi; Anzai, Katsunori; Kazawa, Minoru; Takeda, Nobukazu; Kakudate, Satoshi
no journal, ,
At the ITER blanket, there are cooling pipes for cooling. They will be cut and welded by dedicated tools. For the cooling pipe cutting, remaining the dust and swarf at the cooling pipe are prohibited and suitable cutting surface for rewelding are required. To implement these requirement, swage cutter cutting system were made as a mockup and tested for simulated cooling pipes. There were no cutting dust and suitable cutting surface by the swage cutter cutting system. For the blanket cooling pipe welding, relaxation for the positioning of welding groove, improvement for optical system durability of LASER welding are required. The mockup of LASER welding tool head were made and tested for simulated cooling pipes. As the result of welding condition improvement, relaxed welding condition with low sputter generation were taken. For the cooling pipe welding groove alignment, alignment tool was made and tested for correction of simulated cooling pipe misalignment. For less than 1.5mm of linear misalignment and 0.5 degree angular misalignment, required alignment accuracy were confirmed. Positioning accuracy and stability improvement at the tool operation were issued for the ITER blanket cooling pipe tool heads development.