Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
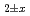 mixed oxides
mixed oxidesVauchy, R.; Matsumoto, Taku; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154786_1 - 154786_13, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.31(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Takeda, Tetsuaki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Aihara, Jun; Aoki, Takeshi; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ho, H. Q.; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Imai, Yoshiyuki; et al.
High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.5, 464 Pages, 2021/02
As a general overview of the research and development of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) in JAEA, this book describes the achievements by the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) on the designs, key component technologies such as fuel, reactor internals, high temperature components, etc., and operational experience such as rise-to-power tests, high temperature operation at 950 C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Ioka, Ikuo; Kuriki, Yoshiro*; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kawai, Daisuke*; Yokota, Hiroki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Kubo, Shinji
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2020/08
A thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur processes (IS process) is one of candidates for the large-scale production of hydrogen using heat from solar power. Severe corrosive environment which is thermal decomposition of sulfuric acid exists in the IS process. A hybrid material with the corrosion-resistance and the ductility was made by a plasma spraying and laser treatment. The specimen had excellent corrosion resistance in the condition of 95 mass% boiling sulfuric acid. This was attributed to the formation of SiO on the surface. The container using the hybrid material was experimentally made. The pre-oxidized container using hybrid technique was prepared for the corrosion test in boiling sulfuric acid to evaluate the corrosion characteristics of the container. There was no detaching of the surface with the weld part and the R processing. We proposed the calculation method of corrosion rate from the ions dissolved in the sulfuric acid solution after the corrosion test.
on the surface. The container using the hybrid material was experimentally made. The pre-oxidized container using hybrid technique was prepared for the corrosion test in boiling sulfuric acid to evaluate the corrosion characteristics of the container. There was no detaching of the surface with the weld part and the R processing. We proposed the calculation method of corrosion rate from the ions dissolved in the sulfuric acid solution after the corrosion test.
Ioka, Ikuo; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kuriki, Yoshiro*; Kawai, Daisuke*; Yokota, Hiroki*; Kubo, Shinji; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Sakaba, Nariaki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00377_1 - 19-00377_11, 2020/06
A thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur processes (IS process) is one of candidates for the large-scale production of hydrogen with high cost performance. Severe corrosive environment which is thermal decomposition of sulfuric acid exists in the IS process. A hybrid material with the corrosion-resistance and the ductility was made by a plasma spraying and laser treatment. The specimen had excellent corrosion resistance in the condition of 95 mass% boiling sulfuric acid. This was attributed to the formation of SiO on the surface. To confirm the production characteristics of a container using the hybrid material, the container which has a welded part, a chamfer, a curved surface was experimentally made. There was no detachment in the plasma spraying and laser treated layer of the container after the laser treatment. It was confirmed that the construction of the container with high corrosion resistance in sulfuric acid was possible in the hybrid technique.
on the surface. To confirm the production characteristics of a container using the hybrid material, the container which has a welded part, a chamfer, a curved surface was experimentally made. There was no detachment in the plasma spraying and laser treated layer of the container after the laser treatment. It was confirmed that the construction of the container with high corrosion resistance in sulfuric acid was possible in the hybrid technique.
Myagmarjav, O.; Iwatsuki, Jin; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Ioka, Ikuo; Kubo, Shinji; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Sawada, Shinichi*; et al.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(35), p.19141 - 19152, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:48.9(Chemistry, Physical)Noguchi, Hiroki; Kubo, Shinji; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kasahara, Seiji; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Terada, Atsuhiko; Takegami, Hiroaki; Kamiji, Yu; Onuki, Kaoru; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 271, p.201 - 205, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:53.13(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting research and development on a thermochemical iodine-sulfur (IS) process. An examination is planned to verify the integrity of the components in the sulfuric acid decomposition section. A bayonet-type sulfuric acid decomposer made of SiC ceramics, a key component in the section, was test-fabricated. In parallel, a direct-contact heat exchanger (DCHX) is contemplated for use in the sulfuric acid decomposition section to simplify the process. Although the concept is very attractive, little is known about the heat and mass transfer behavior in the DCHX. Therefore, a test apparatus was constructed to measure the gas-phase mass transfer coefficients required for the optimal design of the DCHX. These coefficients of water were acquired and compared with an empirical correlation. The experimental data were in good agreement with those obtained from empirical correlation, and thus, the apparatus was confirmed to be reasonable.
Kubo, Shinji; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Iwatsuki, Jin; Onuki, Kaoru; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
JAEA-Technology 2012-043, 41 Pages, 2013/02
Providing safety measures for workers and external environments are indispensable in R&D activities of the iodine sulfur water-splitting hydrogen production process, since this process uses toxic chemicals as sulfur dioxide, sulfuric acid, iodine and hydriodic acid. One of the R&D subjects is proof of manufacturability of chemical reactors made of practical structural materials and confirmation of the reactors' sound performance in the harsh process conditions. In order to examine the task, test apparatuses of the process are being constructed; the apparatus for a Bunsen reactor has been built and assembled. Capacities of vessels of the apparatus are about 50-150 liter; normal operating pressure will be 0.5 MPa [abs], and that of temperature will be 90 degrees centigrade. Safety measures for the test apparatus, operations, and in abnormal situations were considered prior to the start of the operation. This report summarizes the results of the considerations.
Noguchi, Hiroki; Kubo, Shinji; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kasahara, Seiji; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Terada, Atsuhiko; Takegami, Hiroaki; Kamiji, Yu; Onuki, Kaoru; et al.
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting research and development on a thermochemical iodine-sulfur (IS) process. An examination is planned to verify the integrity of the components in the sulfuric acid decomposition section. A bayonet-type sulfuric acid decomposer made of SiC ceramics, a key component in the section, was test-fabricated. In parallel, a direct-contact heat exchanger (DCHX) is contemplated for use in the sulfuric acid decomposition section to simplify the process. Although the concept is very attractive, little is known about the heat and mass transfer behavior in the DCHX. Therefore, a test apparatus was constructed to measure the gas-phase mass transfer coefficients required for the optimal design of the DCHX. These coefficients of water were acquired and compared with an empirical correlation. The experimental data were in good agreement with those obtained from empirical correlation, and thus, the apparatus was confirmed to be reasonable.
Terada, Atsuhiko; Noguchi, Hiroki; Takegami, Hiroaki; Kamiji, Yu; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2012/10
We have proposed a hydrogen supply-chain system, which is a supply system of hydrogen produced by HTGR-IS hydrogen production system. The organic chemical hydride method is one of the candidate techniques in the system for hydrogen storage/transportation. In this study, properties of organic hydrides and conventional hydrogen supply system were surveyed to make use of the conceptual design of the hydrogen supply system using an organic hydrides method with VHTR-IS hydrogen production process. It was also clarified the problems of hydrogen supply system, such as energy efficiency and system optimization.
Ogawa, Masuro; Kasahara, Seiji; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki
"Gurin Enerugi Seitetsu Kenkyukai" Seika Hokokusho, p.4 - 44, 2012/03
Green hydrogen production by using nuclear energy for hydrogen steelmaking is one of the candidates of CO emission reduction. Very high temperature reactor (VHTR) is the most appropriate reactor type among generation IV nuclear reactors. In Japan, a large-scale national R&D project for nuclear steelmaking had been carried out during 1973-1980. The process was: reforming of bottom residue of oil distillation using nuclear heat to produce reducing gas: direct reduction of ore to produce iron by the reforming gas. R&D of 6 themes had been conducted: total systems, high temperature heat exchangers, very high temperature resistant alloy, high temperature thermal insulation materials, reforming gas generators, and shaft furnaces to produce direct reduced iron. A new type nuclear steelmaking is proposed now by the requirement of technology and a new problem of CO
emission reduction. Very high temperature reactor (VHTR) is the most appropriate reactor type among generation IV nuclear reactors. In Japan, a large-scale national R&D project for nuclear steelmaking had been carried out during 1973-1980. The process was: reforming of bottom residue of oil distillation using nuclear heat to produce reducing gas: direct reduction of ore to produce iron by the reforming gas. R&D of 6 themes had been conducted: total systems, high temperature heat exchangers, very high temperature resistant alloy, high temperature thermal insulation materials, reforming gas generators, and shaft furnaces to produce direct reduced iron. A new type nuclear steelmaking is proposed now by the requirement of technology and a new problem of CO reduction. The largest change is the shift of reducing gas to hydrogen. R&D of VHTR continues since the national project and thermochemical water splitting IS (iodine-sulfur) process has been studied for hydrogen production in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Conceptual design of a hydrogen steelmaking process applying VHTR-IS process and direct reduction steelmaking with hydrogen had been carried out in Green Energy Steelmaking Research Group in Iron and Steel Institute of Japan during 2008-2012.
reduction. The largest change is the shift of reducing gas to hydrogen. R&D of VHTR continues since the national project and thermochemical water splitting IS (iodine-sulfur) process has been studied for hydrogen production in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Conceptual design of a hydrogen steelmaking process applying VHTR-IS process and direct reduction steelmaking with hydrogen had been carried out in Green Energy Steelmaking Research Group in Iron and Steel Institute of Japan during 2008-2012.
Terada, Atsuhiko; Noguchi, Hiroki; Takegami, Hiroaki; Kamiji, Yu; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
JAEA-Research 2011-041, 62 Pages, 2012/02
We have proposed a hydrogen supply-chain system, which is a storage/supply system of large amount of hydrogen produced by HTGR-IS hydrogen production system. The organic chemical hydride method is one of the candidate techniques in the system for hydrogen storage and transportation. In this study, properties of organic hydrides and conventional hydrogen storage/supply system were examined to help the conceptual design of the hydrogen supply system using an organic hydrides method with VHTR-IS hydrogen production process (hydrogen production: 85,400 Nm /h). Conceptual specifications of the main apparatus were designed for the hydrogen supply system with hydrogenation and dehydrogenation process. It was also clarified the problems of hydrogen supply system, such as efficiency of energy and system optimization.
/h). Conceptual specifications of the main apparatus were designed for the hydrogen supply system with hydrogenation and dehydrogenation process. It was also clarified the problems of hydrogen supply system, such as efficiency of energy and system optimization.

 , H
, H D
D , H
, H D
D
 , and H
, and H D
D
 in solid parahydrogen
in solid parahydrogenKumagai, Jun*; Inagaki, Hiroki*; Kariya, Susumu*; Ushida, Takahiro*; Shimizu, Yuta*; Kumada, Takayuki
Journal of Chemical Physics, 127(2), p.024505_1 - 024505_13, 2007/07
We carried out an electron spin resonance (ESR) study on hydrogen ion radicals produced by radiolysis of solid parahydrogen. We newly observed totally more than fifty resolved lines in irradiated solid parahydrogens. We assigned these lines to be isotope substituents of H
 -core H
-core H
 ions such as H
ions such as H D
D , H
, H D
D
 , and H
, and H D
D
 throughout comparison of their ESR parameters with theoretical results. These results show conclusive evidence that H
throughout comparison of their ESR parameters with theoretical results. These results show conclusive evidence that H
 -core H
-core H
 ions are produced and stably trapped in irradiated solid hydrogens. We also observed a lowering symmetry on electron wave function in H
ions are produced and stably trapped in irradiated solid hydrogens. We also observed a lowering symmetry on electron wave function in H D
D and H
and H D
D
 , and isotope-substitution reactions such as H
, and isotope-substitution reactions such as H
 +D
+D
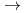 H
H D
D
 +H
+H and H
and H
 +HD
+HD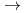 H
H D
D +H
+H .
.
Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Terada, Atsuhiko; Takegami, Hiroaki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwatsuki, Jin; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kubo, Shinji; Kasahara, Seiji; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Takegami, Hiroaki; Onuki, Kaoru; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting R&D on IS process for the future hydrogen energy system. The basic technique for the closed-cycle hydrogen production has been developed and a membrane process is under study for the efficient hydrogen production. Presently, main efforts are devoted to examine the integrity of components made of industrial materials screened by corrosion tests in the IS process environments. So far, fabrication of HI decomposer as key component of the HI decomposition section was completed. Test-fabricated HI decomposer has a performance to produce hydrogen for 150 NL/h, and maximum pressure is 0.95 MPa, maximum temperature is 500 C. The components are consisted of triple structure, pressure vessel, outer tube, and inner tube. In order to secure corrosion-resistance, alloy C-276 as corrosion-resistant material was used for component.
C. The components are consisted of triple structure, pressure vessel, outer tube, and inner tube. In order to secure corrosion-resistance, alloy C-276 as corrosion-resistant material was used for component.
Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Kubo, Shinji; Iwatsuki, Jin; Takegami, Hiroaki; Kasahara, Seiji; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki
no journal, ,
IS process can be considered as one of the promising heat utilization systems of HTGR, because it can produce hydrogen by the thermal water decomposition at around 900 C using chemical reactions with iodine (I) and sulfur (S). In 1994, JAEA successfully achieved the continuous hydrogen production of 30 liters per hour for one week by connection of three chemical reactions, that is, Bunsen, sulfuric acid decomposition and hydrogen iodide decomposition reactions, using glass components. Currently, research and development of corrosion resistant technology is underway, especially focusing on integrity of components made of industrial materials such as metals and ceramics. The test on Bunsen reaction components was successfully finished by confirmation structural integrity and ones on sulfuric acid and hydrogen iodide decomposition reactions are ongoing. This presentation describes the present status of research and development of IS process in JAEA.
C using chemical reactions with iodine (I) and sulfur (S). In 1994, JAEA successfully achieved the continuous hydrogen production of 30 liters per hour for one week by connection of three chemical reactions, that is, Bunsen, sulfuric acid decomposition and hydrogen iodide decomposition reactions, using glass components. Currently, research and development of corrosion resistant technology is underway, especially focusing on integrity of components made of industrial materials such as metals and ceramics. The test on Bunsen reaction components was successfully finished by confirmation structural integrity and ones on sulfuric acid and hydrogen iodide decomposition reactions are ongoing. This presentation describes the present status of research and development of IS process in JAEA.
Matsumoto, Taku; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
The diffusion couples of (U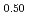 Pu
Pu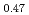 Am
Am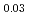 )O
)O and UO
and UO were annealed at 1873K in an atmosphere of
were annealed at 1873K in an atmosphere of  G
G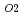 that correspond to O/M = 2.00 or 1.96, and the concentration profile of each actinide elements around the interface was measured with EPMA. It was clearly found that the diffusion coefficient at O/M = 2.00 was about two orders of magnitude greater than that at O/M = 1.96. In addition, it was observed that grain boundary diffusion is so large compared to bulk one for O/M = 2.00. On the other hand, for O/M = 1.96, grain boundary and bulk diffusions of these actinides were not clearly observed.
that correspond to O/M = 2.00 or 1.96, and the concentration profile of each actinide elements around the interface was measured with EPMA. It was clearly found that the diffusion coefficient at O/M = 2.00 was about two orders of magnitude greater than that at O/M = 1.96. In addition, it was observed that grain boundary diffusion is so large compared to bulk one for O/M = 2.00. On the other hand, for O/M = 1.96, grain boundary and bulk diffusions of these actinides were not clearly observed.
Matsumoto, Taku; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
O/M ratio dependence of inter-diffusion coefficient of U and Pu at 1873 K was evaluated from MOX and UO diffusion couple. The diffusion coefficient at O/M = 2.00 was about two orders of magnitude greater than that at O/M = 1.96. In addition, it was observed that grain boundary diffusion is so large compared to bulk one for O/M = 2.00. On the other hand, GB and bulk diffusions were not clearly observed for O/M = 1.96.
diffusion couple. The diffusion coefficient at O/M = 2.00 was about two orders of magnitude greater than that at O/M = 1.96. In addition, it was observed that grain boundary diffusion is so large compared to bulk one for O/M = 2.00. On the other hand, GB and bulk diffusions were not clearly observed for O/M = 1.96.
Myagmarjav, O.; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Kubo, Shinji; Ioka, Ikuo; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Iwatsuki, Jin; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Sakaba, Nariaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sakaba, Nariaki; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Myagmarjav, O.; Noguchi, Hiroki; Iwatsuki, Jin; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Kamiji, Yu; Ioka, Ikuo; Kubo, Shinji
no journal, ,
The research and development program of the IS process using the membrane technology and solar heat is now on progress aiming at improvement of the hydrogen production efficiency up to 40%. In the H SO
SO decomposition reaction process, oxygen production process, the decomposition rate of sulphur trioxide (SO
decomposition reaction process, oxygen production process, the decomposition rate of sulphur trioxide (SO ) is expected more than 80% at the reaction temperature of 800 - 900
) is expected more than 80% at the reaction temperature of 800 - 900 C. On the other hand, the decomposition rate of SO
C. On the other hand, the decomposition rate of SO decreases to around 30% in the reaction temperature of 600
decreases to around 30% in the reaction temperature of 600 C which temperature will be provided by solar heat, ceramic oxygen permselective membrane and catalyst have been developing to promote SO
C which temperature will be provided by solar heat, ceramic oxygen permselective membrane and catalyst have been developing to promote SO decomposition in the reaction temperature of 600
decomposition in the reaction temperature of 600 C. In addition, the ceramic hydrogen permselective membrane and catalyst to promote HI decomposition for hydrogen production, the cation-exchange membrane and catalyst to reduce amount of iodine in the HI circulation process. Also, the corrosion-resistance material to use metal components in the H
C. In addition, the ceramic hydrogen permselective membrane and catalyst to promote HI decomposition for hydrogen production, the cation-exchange membrane and catalyst to reduce amount of iodine in the HI circulation process. Also, the corrosion-resistance material to use metal components in the H SO
SO decomposition process is underway. This work was supported by Council for Science, Technology and Innovation (CSTI), Cross-ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program (SIP), energy carrier (Funding agency: JST).
decomposition process is underway. This work was supported by Council for Science, Technology and Innovation (CSTI), Cross-ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program (SIP), energy carrier (Funding agency: JST).
Myagmarjav, O.; Iwatsuki, Jin; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Ioka, Ikuo; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Tsuru, Toshinori*; Machida, Masato*; et al.
no journal, ,
 production technology on thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur process
production technology on thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur processTakegami, Hiroaki; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Iwatsuki, Jin; Myagmarjav, O.; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Kubo, Shinji
no journal, ,
A thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur process offers the potential for the mass production of hydrogen at high levels of efficiency. This chemical process uses high-temperature heat sources such as the high-temperature gas-cooled reactors, solar heat, and waste heat. Raw materials of H O splits into H
O splits into H and O
and O with combining three chemical reactions using sulfur and iodine compounds. Currently important R&D tasks are to verify integrity of components made of practical-structural materials and stability of hydrogen production operation in the harsh working conditions, and to develop methods for high thermal efficiency. A test facility of hydrogen production was constructed applying corrosion-resistant components developed using industrial materials. The entire process connecting the three process chemical sections was operated in hydrogen production for 31 hours at rate of 20 L / h. Through the operations, technical issues were obtained that prevention of clogging and leakage are important for next longer operation. For improvement of thermal efficiency, membrane technologies have been devised for HI decomposition section, H
with combining three chemical reactions using sulfur and iodine compounds. Currently important R&D tasks are to verify integrity of components made of practical-structural materials and stability of hydrogen production operation in the harsh working conditions, and to develop methods for high thermal efficiency. A test facility of hydrogen production was constructed applying corrosion-resistant components developed using industrial materials. The entire process connecting the three process chemical sections was operated in hydrogen production for 31 hours at rate of 20 L / h. Through the operations, technical issues were obtained that prevention of clogging and leakage are important for next longer operation. For improvement of thermal efficiency, membrane technologies have been devised for HI decomposition section, H SO
SO decomposition section, and Bunsen reaction section. Permselective membranes (H
decomposition section, and Bunsen reaction section. Permselective membranes (H , O
, O ) and a cation exchange membrane were developed to adopt to membrane reactors which work to increase chemical equilibrium and to reduce processing energy of chemical reactions.
) and a cation exchange membrane were developed to adopt to membrane reactors which work to increase chemical equilibrium and to reduce processing energy of chemical reactions.