Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
中堂 博之; 横井 直人*; 松尾 衛; 針井 一哉*; 鈴木 淳*; 今井 正樹; 佐藤 正寛*; 前川 禎通*; 齊藤 英治*
Physical Review Letters, 134(13), p.130603_1 - 130603_5, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A spin 1/2 is the simplest system that has been believed to support a single two-level quantum system, represented by a single resonance. We experimentally demonstrate that a spin-1/2 nucleus of  F in C
F in C F
F exhibits an extra resonance corresponding to the emergence of the states, by mechanically rotating a sample and a coil in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements. On the basis of the Floquet formalism, we identify the emergence of the extra two-level state due to the temporal periodicity generated by the mechanical rotation (mechanical spin multiplexing) and derive an operator algebra analogous to the planar rotor algebra in an effective description of the system. The observed multiplexing allows a single spin 1/2 to carry more than two states and potentially enabling the processing of multiple quantum bits on a single spin.
exhibits an extra resonance corresponding to the emergence of the states, by mechanically rotating a sample and a coil in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements. On the basis of the Floquet formalism, we identify the emergence of the extra two-level state due to the temporal periodicity generated by the mechanical rotation (mechanical spin multiplexing) and derive an operator algebra analogous to the planar rotor algebra in an effective description of the system. The observed multiplexing allows a single spin 1/2 to carry more than two states and potentially enabling the processing of multiple quantum bits on a single spin.
 GeTe
GeTe homojunctions
homojunctions小幡 玲二*; 齊藤 英治; 吉川 貴史; 他13名*
Advanced Materials, 37(8), p.2411459_1 - 2411459_11, 2025/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:84.76(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Twistronics, a novel engineering approach involving the alignment of van der Waals (vdW) integrated two-dimensional materials at specific angles, has recently attracted significant attention. Novel nontrivial phenomena have been demonstrated in twisted vdW junctions (the so-called magic angle), such as unconventional superconductivity, topological phases, and magnetism. However, there have been only few reports on integrated vdW layers with large twist angles 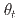 , such as twisted interfacial Josephson junctions using high-temperature superconductors. Herein, vdW homojunctions of the thin-magnetic flakes, Fe
, such as twisted interfacial Josephson junctions using high-temperature superconductors. Herein, vdW homojunctions of the thin-magnetic flakes, Fe GeTe
GeTe (FGT), with large
(FGT), with large 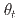 ranging from 0 to 90 deg, without inserting any tunnel barriers are assembled. Nevertheless, these vdW homojunctions exhibit tunnel-magnetoresistance (TMR) like behavior (pseudo-TMR (PTMR) effect) with the ratios highly sensitive to the
ranging from 0 to 90 deg, without inserting any tunnel barriers are assembled. Nevertheless, these vdW homojunctions exhibit tunnel-magnetoresistance (TMR) like behavior (pseudo-TMR (PTMR) effect) with the ratios highly sensitive to the 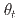 values, revealing that the vdW gap at the junction interface between the twisted FGT layers behaves like a tunnel barrier and the
values, revealing that the vdW gap at the junction interface between the twisted FGT layers behaves like a tunnel barrier and the 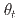 serves a control parameter for PTMR by drastically varying magnitudes of the lattice-mismatch and the subsequent appearance of antiferromagnetic (AFM) spin alignment. First-principles calculations considering vacuum gaps indicate strong dependence of TMR on the
serves a control parameter for PTMR by drastically varying magnitudes of the lattice-mismatch and the subsequent appearance of antiferromagnetic (AFM) spin alignment. First-principles calculations considering vacuum gaps indicate strong dependence of TMR on the 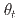 driven by the sixfold screw rotational symmetry of bulk FGT. The present homojunctions hold promise as a platform for novel AFM spin-dependent phenomena and spintronic applications.
driven by the sixfold screw rotational symmetry of bulk FGT. The present homojunctions hold promise as a platform for novel AFM spin-dependent phenomena and spintronic applications.
北條 智彦*; 小山 元道*; 熊井 麦弥*; Zhou, Y.*; 柴山 由樹; 城 鮎美*; 菖蒲 敬久; 齋藤 寛之*; 味戸 沙耶*; 秋山 英二*
ISIJ International, 65(2), p.284 - 296, 2025/02
被引用回数:0Stress and plastic strain distributions and those partitioning behaviors of ferrite and retained austenite were investigated in the medium manganese (Mn) and the transformation-induced plasticity-aided bainitic ferrite (TBF) steels, and the martensitic transformation behaviors of retained austenite during Luders elongation and work hardening were analyzed using synchrotron X-ray diffraction at SPring-8. The stress and plastic strain of retained austenite and volume fraction of retained austenite were remarkably changed during Luders deformation in the medium Mn steel, implying that the medium Mn steel possessed inhomogeneous deformation at the parallel part of the tensile specimen. On the other hand, the distributions of the stress, plastic strain and volume fraction of retained austenite were homogeneous and the homogeneous deformation occurred at the parallel part of the tensile specimen at the plastic deformation regime with work hardening in the medium Mn and TBF steels. The martensitic transformation of retained austenite at uders deformation in the medium Mn steel was possessed owing to the application of high stress and preferential deformation at retained austenite, resulting in a significant increase in the plastic deformation and reduction of stress in the retained austenite. The martensitic transformation of retained austenite at the plastic deformation regime with work hardening was induced by the high dislocation density and newly applied plastic deformation in retained austenite in the medium Mn steel whereas the TBF steel possessed gradual transformation of retained austenite which is applied high tensile stress and moderate plastic deformation.

小杉 美央子*; 吉川 貴史; 齊藤 英治; 他10名*
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 16(46), p.64190 - 64196, 2024/11
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:30.18(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Atom-vacancy-defects present in various materials yield numerous interesting physical phenomena, even obstructing high performance in some cases. On the other hand, their valuable applications to novel devices, such as nitrogen vacancy centers in diamond for quantum bits, have gathered significant attention. In particular, these tendencies become more substantial in two-dimensional (2D) (atomically) thin van der Waals layers. However, correlations with various kinds of atom defects are still under exploration. Herein, we find the stochastic behaviors of large hysteresis loops with strong photoresponse in the static electrical properties in few-atom layer semiconductors, molybdenum disulfide (MoS ). The temperature dependence and transmission electron microscopy reveal that they arise from pairs of two neighboring in-plane S-vacancy defects, which predominantly present only around the interface at the MoS
). The temperature dependence and transmission electron microscopy reveal that they arise from pairs of two neighboring in-plane S-vacancy defects, which predominantly present only around the interface at the MoS flake/substrate, with activation energies similar to 0.35 eV. The low-frequency (
flake/substrate, with activation energies similar to 0.35 eV. The low-frequency ( ) (LF) noise measurements clarify a high f shift in the two 1/
) (LF) noise measurements clarify a high f shift in the two 1/ 2-dependent regimes, implying stochastic behaviors of electric charges through the S-vacancy pairs with high-speed charge(spin) transitions across low kinetic energy barriers between narrow discrete states. The shallow energy sates are formed from the highly uniform S-vacancy pairs interacting with Mo atoms, which act like quantum dots. The observed stochastic operation holds promise for various application, particularly for probabilistic neuromorphic computation in artificial intelligence.
2-dependent regimes, implying stochastic behaviors of electric charges through the S-vacancy pairs with high-speed charge(spin) transitions across low kinetic energy barriers between narrow discrete states. The shallow energy sates are formed from the highly uniform S-vacancy pairs interacting with Mo atoms, which act like quantum dots. The observed stochastic operation holds promise for various application, particularly for probabilistic neuromorphic computation in artificial intelligence.
 GeTe
GeTe nanomeshes
nanomeshes小幡 玲二*; 吉川 貴史*; 齊藤 英治; 他7名*
Nanotechnology, 35(47), p.475601_1 - 475601_9, 2024/11
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:35.22(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The growth of two-dimensional van der Waals magnetic materials presents attractive opportunities for exploring new physical phenomena and valuable applications. Among these materials, Fe GeTe
GeTe (FGT) exhibits a variety of remarkable properties and has garnered significant attention. Herein, we have for the first time created a nanomesh structure-a honeycomb-like array of hexagonal nanopores-with the zigzag pore-edge atomic structure on thin FGT flakes with and without oxidation of the pore edges. It is revealed that the magnitude of ferromagnetism (FM) significantly increases in both samples compared with bulk flakes without nanomeshes. Critical temperature annealing results in the formation of zigzag pore edges and interpore zigzag-edge nanoribbons. We unveil that the non-oxide (O) termination of the Fe dangling bonds on these zigzag edges enhances FM behavior, while O-termination suppresses this FM by introducing antiferromagnetic behavior through edge O-Fe coupling. FGT nanomeshes hold promise for the creation of strong FM and their effective application in magnetic and spintronic systems.
(FGT) exhibits a variety of remarkable properties and has garnered significant attention. Herein, we have for the first time created a nanomesh structure-a honeycomb-like array of hexagonal nanopores-with the zigzag pore-edge atomic structure on thin FGT flakes with and without oxidation of the pore edges. It is revealed that the magnitude of ferromagnetism (FM) significantly increases in both samples compared with bulk flakes without nanomeshes. Critical temperature annealing results in the formation of zigzag pore edges and interpore zigzag-edge nanoribbons. We unveil that the non-oxide (O) termination of the Fe dangling bonds on these zigzag edges enhances FM behavior, while O-termination suppresses this FM by introducing antiferromagnetic behavior through edge O-Fe coupling. FGT nanomeshes hold promise for the creation of strong FM and their effective application in magnetic and spintronic systems.
 Fe
Fe O
O /Pt bilayer disk
/Pt bilayer diskEmdi, G.*; 日置 友智*; 巻内 崇彦*; 齊藤 英治
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 22(3), p.L031002_1 - L031002_6, 2024/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)Sigmoidal curve behavior of 0 and n state probability in a magnon parametron, using yttrium iron garnet (Y Fe
Fe O
O ) thin disk, is systematically investigated. We demonstrate that the probability distribution can be tuned by bias and pump microwave power. Our numerical calculation that considers increasing damping due to four-magnon scattering processes reproduces the results well.
) thin disk, is systematically investigated. We demonstrate that the probability distribution can be tuned by bias and pump microwave power. Our numerical calculation that considers increasing damping due to four-magnon scattering processes reproduces the results well.
星 幸治郎*; 日置 友智*; 齊藤 英治
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 21(6), p.064057_1 - 064057_6, 2024/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)Spin-motive force induced by standing spin waves under nonlinear magnon scattering in a permalloy strip is investigated numerically. When the power of an applied microwave field is increased above a threshold under ferromagnetic resonance, spin waves with finite wave numbers are excited via fourmagnon scattering, leading to standing spin waves in real space. We calculate the Spin-motive force induced by the spin waves with finite wave numbers in a permalloy strip and estimate the electric voltage due to the Spin-motive force. We demonstrate the increase of electric voltage as a result of steep magnetization modulation of the nonlinearly excited spin waves and the nonlinear spin waves produced.
 substrate
substrate小幡 玲二*; 齊藤 英治; 吉川 貴史; 他7名*
Advanced Materials, 36(19), p.2311339_1 - 2311339_8, 2024/05
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)SrTiO (STO) substrate, a perovskite oxide material known for its high dielectric constant (epsilon), facilitates the observation of various (high-temperature) quantum phenomena. A quantum Hall topological insulating (QHTI) state, comprising two copies of QH states with antiparallel two ferromagnetic edge-spin overlap protected by the U(1) axial rotation symmetry of spin polarization, has recently been achieved in low magnetic field (B) even as high as approximate to 100 K in a monolayer graphene/thin hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) spacer placed on an STO substrate, thanks to the high epsilon of STO. Despite the use of the heavy STO substrate, however, proximity-induced quantum spin Hall (QSH) states in 2D TI phases, featuring a topologically protected helical edge spin phase within time-reversal-symmetry, is not confirmed. Here, with the use of a monolayer hBN spacer, it is revealed the coexistence of QSH (at B = 0T) and QHTI (at B not equal 0) states in the same single graphene sample placed on an STO, with a crossover regime between the two at low B. It is also classified that the different symmetries of the two nontrivial helical edge spin phases in the two states lead to different interaction with electron-puddle quantum dots, caused by a local surface pocket of the STO, in the crossover regime, resulting in a spin dephasing only for the QHTI state. The results obtained using STO substrates open the doors to investigations of novel QH spin states with different symmetries and their correlations with quantum phenomena. This exploration holds value for potential applications in spintronic devices.
(STO) substrate, a perovskite oxide material known for its high dielectric constant (epsilon), facilitates the observation of various (high-temperature) quantum phenomena. A quantum Hall topological insulating (QHTI) state, comprising two copies of QH states with antiparallel two ferromagnetic edge-spin overlap protected by the U(1) axial rotation symmetry of spin polarization, has recently been achieved in low magnetic field (B) even as high as approximate to 100 K in a monolayer graphene/thin hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) spacer placed on an STO substrate, thanks to the high epsilon of STO. Despite the use of the heavy STO substrate, however, proximity-induced quantum spin Hall (QSH) states in 2D TI phases, featuring a topologically protected helical edge spin phase within time-reversal-symmetry, is not confirmed. Here, with the use of a monolayer hBN spacer, it is revealed the coexistence of QSH (at B = 0T) and QHTI (at B not equal 0) states in the same single graphene sample placed on an STO, with a crossover regime between the two at low B. It is also classified that the different symmetries of the two nontrivial helical edge spin phases in the two states lead to different interaction with electron-puddle quantum dots, caused by a local surface pocket of the STO, in the crossover regime, resulting in a spin dephasing only for the QHTI state. The results obtained using STO substrates open the doors to investigations of novel QH spin states with different symmetries and their correlations with quantum phenomena. This exploration holds value for potential applications in spintronic devices.
巻内 崇彦*; 日置 友智*; 清水 祐樹*; 星 幸治郎*; Elyasi, M.*; 山本 慧; 横井 直人*; Serga, A. A.*; Hillebrands, B.*; Bauer, G. E. W.*; et al.
Nature Materials, 23(5), p.627 - 632, 2024/05
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:93.86(Chemistry, Physical)When excited, a magnetization in a magnet precesses around the field in an anticlockwise manner on a time scale governed by viscous magnetization damping, after which any information carried by the initial actuation seems to be lost. The damping appears to be a fundamental bottleneck for the use of magnets in information processing. Nevertheless, here we demonstrate recall of the magnetization-precession phase after times that far exceed the damping time scale by two orders of magnitude using dedicated two-colour microwave pump-and-probe experiments for a Y Fe
Fe O
O microstructured film. Time- resolved magnetization state tomography confirms the magnetic persistent coherence (MPC) by revealing a double-exponential decay of the magnetization correlation. We attribute MPC to a feedback effect, viz. coherent coupling of the uniform precession with long-lived excitations at the minima of the spin-wave dispersion relation. Our finding liberates magnetic systems from the strong damping in nanostructures tyranny that limits their use in coherent information storage and processing.
microstructured film. Time- resolved magnetization state tomography confirms the magnetic persistent coherence (MPC) by revealing a double-exponential decay of the magnetization correlation. We attribute MPC to a feedback effect, viz. coherent coupling of the uniform precession with long-lived excitations at the minima of the spin-wave dispersion relation. Our finding liberates magnetic systems from the strong damping in nanostructures tyranny that limits their use in coherent information storage and processing.
Elyasi, M.*; 山本 慧; 日置 友智*; 巻内 崇彦*; 清水 祐樹*; 齊藤 英治*; Bauer, G. E. W.*
Physical Review B, 109(18), p.L180402_1 - L180402_7, 2024/05
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:35.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Magnets are interesting materials for classical and quantum information technologies. However, the short decoherence and dephasing times that determine the scale and speed of information networks severely limit the appeal of employing the ferromagnetic resonance. Here we show that the lifetime and coherence of the uniform Kittel mode can be enhanced by three-magnon interaction-induced mixing with the long-lived magnons at the minima of the dispersion relation. Analytical and numerical calculations based on this model explain recent experimental results and predict experimental signatures of quantum coherence.
丸山 遥香*; 齊藤 英治; 他2名*
AIP Advances (Internet), 14(3), p.035217_1 - 035217_8, 2024/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)We developed a radio frequency discharge apparatus for He gas to investigate the spin states of metastable helium (He ) interacting with solid-state surfaces. Our apparatus consisted of a stainless steel vacuum chamber, in which a coil produced He
) interacting with solid-state surfaces. Our apparatus consisted of a stainless steel vacuum chamber, in which a coil produced He by discharging introduced He gas. The spin states of the He
by discharging introduced He gas. The spin states of the He were detected using optical pumping and probing techniques. The chamber was designed to accommodate various solid-state samples. We measured the He
were detected using optical pumping and probing techniques. The chamber was designed to accommodate various solid-state samples. We measured the He polarization produced at a dielectric prism surface by total internal reflection of the circularly polarized pumping light. Our apparatus can be used to investigate possible spin transfer from various solid surfaces to He
polarization produced at a dielectric prism surface by total internal reflection of the circularly polarized pumping light. Our apparatus can be used to investigate possible spin transfer from various solid surfaces to He atoms.
atoms.
 Fe
Fe O
O
川本 陽*; 吉川 貴史; 齊藤 英治; 他9名*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(13), p.132406_1 - 132406_7, 2024/03
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:78.60(Physics, Applied)Magnon spin currents in the ferrimagnetic garnet Tb Fe
Fe O
O with 4
with 4 electrons were examined through the spin-Seebeck effect and neutron scattering measurements. The compound shows a magnetic compensation, where the spin-Seebeck signal reverses above and below
electrons were examined through the spin-Seebeck effect and neutron scattering measurements. The compound shows a magnetic compensation, where the spin-Seebeck signal reverses above and below 
 = 249.5(4) K. Unpolarized neutron scattering unveils two major magnon branches with finite energy gaps, which are well explained in the framework of spin-wave theory. Their temperature dependencies and the direction of the precession motion of magnetic moments, i.e., magnon polarization, defined using polarized neutrons, explain the reversal at
= 249.5(4) K. Unpolarized neutron scattering unveils two major magnon branches with finite energy gaps, which are well explained in the framework of spin-wave theory. Their temperature dependencies and the direction of the precession motion of magnetic moments, i.e., magnon polarization, defined using polarized neutrons, explain the reversal at 
 and decay of the spin-Seebeck signals at low temperatures. We illustrate an example that momentum- and energy-resolved microscopic information is a prerequisite to understand the magnon spin current.
and decay of the spin-Seebeck signals at low temperatures. We illustrate an example that momentum- and energy-resolved microscopic information is a prerequisite to understand the magnon spin current.
 Fe
Fe O
O /Pt bilayer disk
/Pt bilayer diskEmdi, G.*; 日置 友智*; 星 幸治郎*; 齊藤 英治
Physical Review B, 108(14), p.L140410_1 - L140410_6, 2023/10
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:25.54(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report a systematic quantitative evaluation of parametric amplification gain of magnetization dynamics in an yttrium iron garnet (Y Fe
Fe O
O ) thin disk via ac spin pumping and the inverse spin Hall effect. We demonstrate its signature phase dependence where amplification and attenuation occur every i phase shift of the input signal. The results also show the pump-power dependence of the gain that is explained well by our theoretical model. Finally, the optimal conditions for amplification are investigated by measuring the magnetic field dependence, where we find the highest gain of 11.4 dB.
) thin disk via ac spin pumping and the inverse spin Hall effect. We demonstrate its signature phase dependence where amplification and attenuation occur every i phase shift of the input signal. The results also show the pump-power dependence of the gain that is explained well by our theoretical model. Finally, the optimal conditions for amplification are investigated by measuring the magnetic field dependence, where we find the highest gain of 11.4 dB.
 layers on SrTiO
layers on SrTiO substrates
substrates小杉 美央子*; 齊藤 英治; 吉川 貴史*; 他11名*
APL Materials (Internet), 11(8), p.081106_1 - 081106_6, 2023/08
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:12.23(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Strontium titanate [SrTiO (STO)], a perovskite oxide with an extremely high gate-tunable dielectric constant (
(STO)], a perovskite oxide with an extremely high gate-tunable dielectric constant ( ) due to quantum paraelectric phases, is attracting considerable attention for yielding various physical phenomena when two-dimensional (2D) layers are integrated. Superconductivity is such a typical phenomenon. However, the influence of the STO substrates on enhancing transition temperatures (
) due to quantum paraelectric phases, is attracting considerable attention for yielding various physical phenomena when two-dimensional (2D) layers are integrated. Superconductivity is such a typical phenomenon. However, the influence of the STO substrates on enhancing transition temperatures (
 ) for (atomically) thin 2D flakes attached to them has been rarely investigated. Here, we report gate-tunable and gradual four-terminal resistance drops with critical onset
) for (atomically) thin 2D flakes attached to them has been rarely investigated. Here, we report gate-tunable and gradual four-terminal resistance drops with critical onset  (
(
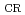 ) and scanning tunneling spectroscopy (STS) spectra in devices comprising thin TaS
) and scanning tunneling spectroscopy (STS) spectra in devices comprising thin TaS flakes attached on monolayer hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) spacer/STO substrates. Observation of STS spectra confirms the presence of local superconducting gaps. (similar to 1.5 meV) with transition
flakes attached on monolayer hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) spacer/STO substrates. Observation of STS spectra confirms the presence of local superconducting gaps. (similar to 1.5 meV) with transition  (
(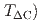 three-times higher than previous reports of
three-times higher than previous reports of 
 under absent pressure and strong position dependence of
under absent pressure and strong position dependence of 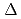 . Depending on
. Depending on  on back gate voltages (
on back gate voltages (
 ) and magnetic fields, there is a strong correlation between
) and magnetic fields, there is a strong correlation between 
 and the onset
and the onset 
 of superconductivity, implying an enhancement of approximately five times compared with the previous highest-onset
of superconductivity, implying an enhancement of approximately five times compared with the previous highest-onset 
 values without pressure as the applied
values without pressure as the applied 
 increases. The high onset
increases. The high onset 
 and. are discussed based on screening of the long-range Coulomb interaction (CI) due to the high-
and. are discussed based on screening of the long-range Coulomb interaction (CI) due to the high- of SrTiO
of SrTiO , while the short-ranged CI remains strong in the 2D limit, causing the superconductivity. Using a monolayer hBN/SrTiO
, while the short-ranged CI remains strong in the 2D limit, causing the superconductivity. Using a monolayer hBN/SrTiO substrate with
substrate with 
 opens doors to
opens doors to 
 enhancement in thin superconducting layers integrated on it and wide application due to the solid-state high-
enhancement in thin superconducting layers integrated on it and wide application due to the solid-state high- substrates.
substrates.
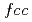 -base GdO
-base GdO precipitations in a Mg-Zn-Gd alloy
precipitations in a Mg-Zn-Gd alloy伊東 祐斗*; 江草 大佑*; 山口 正剛; 阿部 英司*
Materials Transactions, 64(8), p.2022 - 2025, 2023/08
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:11.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)走査型透過電子顕微鏡によるその場観察で、Mg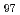 Zn
Zn Gd
Gd (at.%)合金を623Kで加熱すると、面心立方(
(at.%)合金を623Kで加熱すると、面心立方(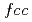 )系のGdナノ粒子がダイナミックに析出することを発見した。5.32
)系のGdナノ粒子がダイナミックに析出することを発見した。5.32 という観察された格子定数は、密度汎関数理論(DFT)計算による純粋な
という観察された格子定数は、密度汎関数理論(DFT)計算による純粋な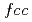 -Gdの5.06
-Gdの5.06 よりも大きいため、酸素原子が四面体の格子間サイトに部分的に挿入されているためである可能性が高いことがわかった。体系的なDFT計算により、四面体あるいは八面体の格子間サイトを占有することで、広い不定比性範囲を持つ
よりも大きいため、酸素原子が四面体の格子間サイトに部分的に挿入されているためである可能性が高いことがわかった。体系的なDFT計算により、四面体あるいは八面体の格子間サイトを占有することで、広い不定比性範囲を持つ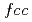 -Gd系酸化物相が出現する可能性があり、GdO
-Gd系酸化物相が出現する可能性があり、GdO として表現できることが分かった。
として表現できることが分かった。
堀部 聡平*; 清水 祐樹*; 星 幸治郎*; 巻内 崇彦*; 日置 友智*; 齊藤 英治
Applied Physics Express, 16(7), p.073001_1 - 073001_4, 2023/07
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:12.23(Physics, Applied)Parametric oscillation occurs when the resonance frequency of an oscillator is periodically modulated. Owing to time-reversal symmetry breaking in magnets, nonreciprocal magnons can be parametrically excited when spatial-inversion symmetry breaking is provided. This means that magnons with opposite propagation directions have different amplitudes. Here we demonstrate switching on and off the magnon parametric oscillation by reversing the external field direction applied to a Y Fe
Fe O
O micro-structured film. The result originates from the nonreciprocity of surface mode magnons, leading to field-direction dependence of the magnon accumulation under nonuniform microwave pumping. Our numericalcalculation well reproduces the experimental result.
micro-structured film. The result originates from the nonreciprocity of surface mode magnons, leading to field-direction dependence of the magnon accumulation under nonuniform microwave pumping. Our numericalcalculation well reproduces the experimental result.
埋田 真樹; 中堂 博之; 今井 正樹; 佐藤 奈々; 齊藤 英治
Review of Scientific Instruments, 94(6), p.063906_1 - 063906_8, 2023/06
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:27.04(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have developed experimental equipment for observing the Barnett effect, in which mechanical rotation magnetizes an object, at low temperatures. A sample in a rotor is rotated bidirectionally using a temperature-controlled high-pressure gas. The stray field generated from the sample due to the Barnett effect was detected using a fluxgate magnetic sensor with a sensitivity on the order of several picoteslas, even at low temperatures. By replacing the rotor with a solenoid coil, the magnetic susceptibility of the sample was estimated from the stray field to be of the same order of magnitude as that due to the Barnett effect. The Barnett field was estimated using the dipole model. To assess the performance of the setup at low temperatures, measurements were performed on commercial magnetite (Fe O
O ) nanogranules. We confirmed the accordance of the
) nanogranules. We confirmed the accordance of the 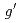 factor between the experimental results using the present setup and those of our previous study performed at room temperature.
factor between the experimental results using the present setup and those of our previous study performed at room temperature.
Meer, H.*; Wust, S.*; Schmitt, C.*; Herrgen, P.*; Fuhrmann, F.*; Hirtle, S.*; Bednarz, B.*; Rajan, A.*; Ramos, R.*; Ni o, M. A.*; et al.
o, M. A.*; et al.
Advanced Functional Materials, 33(21), p.2213536_1 - 2213536_6, 2023/05
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:62.75(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The antiferromagnetic order in heterostructures of NiO/Pt thin films can be modified by optical pulses. After the irradiation with laser light, the optically induced creation of antiferromagnetic domains can be observed by imaging the created domain structure utilizing the X-ray magnetic linear dichroism effect. The effect of different laser polarizations on the domain formation can be studied and used to identify a polarization-independent creation of 180 domain walls and domains with 180
domain walls and domains with 180 different N
different N el vector orientation. By varying the irradiation parameters, the switching mechanism can be determined to be thermally induced. This study demonstrates experimentally the possibility to optically create antiferromagnetic domains, an important step towards future functionalization of all optical switching mechanisms in antiferromagnets.
el vector orientation. By varying the irradiation parameters, the switching mechanism can be determined to be thermally induced. This study demonstrates experimentally the possibility to optically create antiferromagnetic domains, an important step towards future functionalization of all optical switching mechanisms in antiferromagnets.
Zhou, Z.*; Frost, W.*; Lloyd, D. C.*; 関 剛斎*; 窪田 崇秀*; Ramos, R.*; 齊藤 英治; 高梨 弘毅; 廣畑 貴文*
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 571, p.170575_1 - 170575_5, 2023/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:10.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Recent development in neuromorphic computation allows us to achieve low power and highly efficient calculations better than the conventional von Neumann computation. In order to achieve realistic synaptic operation, potentiation to add weighting to strengthen a selected artificial synapse. Such functionality can be achieved by reducing the electrical resistance of the artificial synapse. Recently, a ferromagnetic Heusler alloy used in a magnetoresistive junction has been demonstrated to crystallise via the layer-by-layer mode by introducing an electrical current pulse. In this study, we have extended the current-induced crystallisation to a junction with epitaxially-grown Heusler alloy after post-annealing for crystallisation. By combining this potentiation functionality with the neuromorphic operation, realistic synaptic computation can be developed.
安立 裕人*; 池田 直*; 齊藤 英治
Physical Review B, 107(15), p.155142_1 - 155142_10, 2023/04
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:56.18(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In comparison to transport of spin polarization in ferromagnets, transport of electric polarization in ferroelectrics remains less explored. Taking an excitonic insulator model of electronic ferroelectricity as a prototypical example, we theoretically investigate the low-energy dynamics and transport of electric polarization by microscopically constructing the Ginzburg-Landau action. We show that, because of the scalar nature of the excitonic order parameter, only the longitudinal fluctuations are relevant to the transport of electric polarization. We also formulate the electric-polarization diffusion equation, in which the electric-polarization current is defined purely electronically without recourse to the lattice degrees of freedom.