Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
益木 悠馬*; 勝田 長貴*; 内藤 さゆり*; 村上 拓馬*; 梅村 綾子*; 藤田 奈津子; 松原 章浩*; 南 雅代*; 丹羽 正和; 吉田 英一*; et al.
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 485, p.136843_1 - 136843_10, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Engineering, Environmental)滋賀県東部の姉川上流域には、伊吹山の斜面崩壊でせき止められて生じた2つの湖成層の河岸段丘が分布する。このうち、下位の湖成層は、植物遺体のC-14年代測定から完新世中期に形成されたことが明らかとなった。また、湖成層の岩相は、mmスケールの縞状構造に富む層が10cmオーダーでシルト質粘土層と互層し、化学分析からヒ素が大陸地殻の約30倍の濃度(77 g/g)で濃集する。さらに、蛍光X線やX線吸収分光などを用いた微小領域測定から、縞状構造は1年に1枚の縞を刻む年層であること、ヒ素は春季と秋季の循環期に堆積したこと、ヒ素は硫化物として存在し非晶質有機物と共存することなどが示された。これらの結果から、年縞のヒ素濃集は、季節変動に伴う有機物の供給と、続成過程における有機物分解によるレドックス変動によって生じたことが明らかとなった。
g/g)で濃集する。さらに、蛍光X線やX線吸収分光などを用いた微小領域測定から、縞状構造は1年に1枚の縞を刻む年層であること、ヒ素は春季と秋季の循環期に堆積したこと、ヒ素は硫化物として存在し非晶質有機物と共存することなどが示された。これらの結果から、年縞のヒ素濃集は、季節変動に伴う有機物の供給と、続成過程における有機物分解によるレドックス変動によって生じたことが明らかとなった。
勝田 長貴*; 梅村 綾子*; 内藤 さゆり*; 益木 悠馬*; 板山 由依*; 丹羽 正和; 城野 信一*; 吉田 英一*; 川上 紳一*
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 210, p.106817_1 - 106817_11, 2023/12
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:19.24(Spectroscopy)湖成堆積物から過去の気候変動を読み取る上で、蛍光X線分析による化学組成マッピングは非常に有効な分析手法の一つとなっている。ただしその際、粒子径や鉱物組成がX線強度に及ぼす影響、すなわち「不均一効果」の評価が課題となっていた。本研究では、組成既知のいくつかの2種混合粉末試料、およびバイカル湖の湖成堆積物を対象とした走査型X線顕微鏡による分析を行い、X線強度や粒子径などとの関係を検証した。その結果、粒子径が小さい場合において、不均一効果の影響が大きくなることが分かった。
 -edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samples
-edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samplesLi, W.*; 山田 真也*; 橋本 直; 奥村 拓馬*; 早川 亮大*; 新田 清文*; 関澤 央輝*; 菅 大暉*; 宇留賀 朋哉*; 一戸 悠人*; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1240, p.340755_1 - 340755_9, 2023/02
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:65.24(Chemistry, Analytical)希土類元素は放射性元素であるアクチノイドのアナログ元素としてしばしば利用される。セリウム(Ce)は希土類元素の中でも+3価と+4価の両方をとり得る特別な元素である。環境試料中のCeの+3価と+4価の比を調べる手段としてX線吸収端近傍構造(XANES)が有力であったが、チタン濃度が高いと蛍光X線の干渉のために測定ができないという問題があった。本研究では、L 吸収端だけでなくL
吸収端だけでなくL 吸収端を調べ、さらに新しい検出器であるtransition-edge sensor (TES)を利用することでこれまでは測定が難しかった試料も測定可能にした。この結果は様々な環境試料に応用可能である。
吸収端を調べ、さらに新しい検出器であるtransition-edge sensor (TES)を利用することでこれまでは測定が難しかった試料も測定可能にした。この結果は様々な環境試料に応用可能である。
勝田 長貴*; 高野 雅夫*; 佐野 直美; 谷 幸則*; 落合 伸也*; 内藤 さゆり*; 村上 拓馬*; 丹羽 正和; 川上 紳一*
Sedimentology, 66(6), p.2490 - 2510, 2019/10
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:51.05(Geology)海や湖の堆積物の連続的な化学組成変化は、古環境の変化を推定する上で重要な情報となる。しかし、このような含水堆積物の化学組成をX線蛍光分析で測定する際は、吸着水がX線強度に及ぼす影響の評価が問題となる。本研究では、X線吸収・放出理論に基づきX線強度を補正する手法を検討し、含水堆積物に対して、 -XRF走査型顕微鏡により化学組成の定量データを連続的に取得することを可能にした。
-XRF走査型顕微鏡により化学組成の定量データを連続的に取得することを可能にした。
勝田 長貴*; 池田 久士*; 柴田 健二*; 國分 陽子; 村上 拓馬*; 谷 幸則*; 高野 雅夫*; 中村 俊夫*; 田中 敦*; 内藤 さゆり*; et al.
Global and Planetary Change, 164, p.11 - 26, 2018/05
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:40.44(Geography, Physical)バイカル湖ブグルジェイカサドルの堆積物中の化学組成を高分解能に分析することにより過去3.3万年以上の内陸シベリアの古環境及び古気候変動を復元した。完新世の気候は、6500年前に温暖、乾燥に変化し、氷期から間氷期の気候システムに遷移したことを示唆する。最終氷期においては、プリモールスキー山脈に起因する砕屑性炭酸塩の堆積がハインリッヒイベント(H3とH1)に伴って生じた。また、ハマル-ダバン山脈の氷河融解水がセレンガ川を通じて供給された。アレレード・ヤンガードリアス時に発生した無酸素底層水は、セレンガ川からの流水の減少とプリモールスキー山脈から供給された有機物の微生物分解で生じたものと考えられる。完新世初期の降水の減少は、8200年前の寒冷イベントに対応する。
中村 進一*; 鈴井 伸郎; 長坂 俊紀*; 小松 史弥*; 石岡 典子; 伊藤 小百合*; 河地 有木; 頼 泰樹*; 服部 浩之*; 茅野 充男*; et al.
Journal of Experimental Botany, 64(4), p.1073 - 1081, 2013/02
被引用回数:58 パーセンタイル:85.58(Plant Sciences)This study investigated the effects of the reduced form of glutathione (GSH) applied to specific organs (source leaves, sink leaves, and roots) on cadmium (Cd) distribution and behaviour in the roots of oilseed rape plants (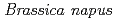 ) cultured hydroponically. The translocation ratio of Cd from roots to shoots was significantly lower in plants that had root treatment of GSH than in control plants. GSH applied to roots reduced the Cd concentration in the symplast sap of root cells and inhibited root-to-shoot Cd translocation via xylem vessels significantly. GSH applied to roots also activated Cd efflux from root cells to the hydroponic solution. Inhibition of root-to-shoot translocation of Cd was visualized, and the activation of Cd efflux from root cells was also shown by using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). This study investigated a similar inhibitory effect on root-to-shoot translocation of Cd by the oxidized form of glutathione, GSSG. Inhibition of Cd accumulation by GSH was abolished by a low-temperature treatment. Root cells of plants exposed to GSH in the root zone had less Cd available for xylem loading by actively excluding Cd from the roots. Consequently, root-to-shoot translocation of Cd was suppressed and Cd accumulation in the shoot decreased.
) cultured hydroponically. The translocation ratio of Cd from roots to shoots was significantly lower in plants that had root treatment of GSH than in control plants. GSH applied to roots reduced the Cd concentration in the symplast sap of root cells and inhibited root-to-shoot Cd translocation via xylem vessels significantly. GSH applied to roots also activated Cd efflux from root cells to the hydroponic solution. Inhibition of root-to-shoot translocation of Cd was visualized, and the activation of Cd efflux from root cells was also shown by using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). This study investigated a similar inhibitory effect on root-to-shoot translocation of Cd by the oxidized form of glutathione, GSSG. Inhibition of Cd accumulation by GSH was abolished by a low-temperature treatment. Root cells of plants exposed to GSH in the root zone had less Cd available for xylem loading by actively excluding Cd from the roots. Consequently, root-to-shoot translocation of Cd was suppressed and Cd accumulation in the shoot decreased.
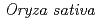 ) using positron-emitting
) using positron-emitting  Cd tracer
Cd tracer石川 覚*; 鈴井 伸郎; 伊藤 小百合*; 石井 里美; 井倉 将人*; 安部 匡*; 倉俣 正人*; 河地 有木; 藤巻 秀
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 91, 2013/01
We have visualized and quantitatively analysed the real-time Cd dynamics from roots to grains in typical rice cultivars that differed in grain Cd concentrations. We used positron-emitting  Cd tracer and an innovative imaging technique, PETIS. A new method for direct and real-time visualization of the Cd uptake by the roots in the culture was first realized in this work. Imaging and quantitative analyses revealed the different patterns in time-varying curves of Cd amounts in the roots of rice cultivars tested. Three low-Cd accumulating cultivars showed rapid saturation curves, whereas three high-Cd accumulating cultivars were characterized by curves with a peak within 30 min after
Cd tracer and an innovative imaging technique, PETIS. A new method for direct and real-time visualization of the Cd uptake by the roots in the culture was first realized in this work. Imaging and quantitative analyses revealed the different patterns in time-varying curves of Cd amounts in the roots of rice cultivars tested. Three low-Cd accumulating cultivars showed rapid saturation curves, whereas three high-Cd accumulating cultivars were characterized by curves with a peak within 30 min after  Cd supplementation, and a subsequent steep decrease resulting in maintenance of lower Cd concentrations in their roots. This difference in Cd dynamics may be attributable to OsHMA3 transporter protein, which was recently shown to be involved in Cd storage in root vacuoles and not functional in the high-Cd accumulating cultivars. Moreover, the PETIS analyses revealed that the high-Cd accumulating cultivars were characterized by rapid and abundant Cd transfer to the shoots from the roots, a faster transport velocity of Cd to the panicles, and Cd accumulation at high levels in their panicles, passing through the nodal portions of the stems where the highest Cd intensities were observed.
Cd supplementation, and a subsequent steep decrease resulting in maintenance of lower Cd concentrations in their roots. This difference in Cd dynamics may be attributable to OsHMA3 transporter protein, which was recently shown to be involved in Cd storage in root vacuoles and not functional in the high-Cd accumulating cultivars. Moreover, the PETIS analyses revealed that the high-Cd accumulating cultivars were characterized by rapid and abundant Cd transfer to the shoots from the roots, a faster transport velocity of Cd to the panicles, and Cd accumulation at high levels in their panicles, passing through the nodal portions of the stems where the highest Cd intensities were observed.
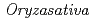 ) using positron-emitting
) using positron-emitting  Cd tracer
Cd tracer石川 覚*; 鈴井 伸郎; 伊藤 小百合*; 石井 里美; 井倉 将人*; 安部 匡*; 倉俣 正人*; 河地 有木; 藤巻 秀
BMC Plant Biology, 11, p.172_1 - 172_12, 2011/11
被引用回数:76 パーセンタイル:88.40(Plant Sciences)In this study, we have visualized and quantitatively analysed the real-time Cd dynamics from roots to grains in typical rice cultivars that differed in grain Cd concentrations. We used positron-emitting  Cd tracer and an innovative imaging technique, the positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). In particular, a new method for direct and real-time visualization of the Cd uptake by the roots in the culture was first realized in this work. Imaging and quantitative analyses revealed the different patterns in time-varying curves of Cd amounts in the roots of rice cultivars tested. Three low-Cd accumulating cultivars (japonica type) showed rapid saturation curves, whereas three high-Cd accumulating cultivars (indica type) were characterized by curves with a peak within 30 min after
Cd tracer and an innovative imaging technique, the positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). In particular, a new method for direct and real-time visualization of the Cd uptake by the roots in the culture was first realized in this work. Imaging and quantitative analyses revealed the different patterns in time-varying curves of Cd amounts in the roots of rice cultivars tested. Three low-Cd accumulating cultivars (japonica type) showed rapid saturation curves, whereas three high-Cd accumulating cultivars (indica type) were characterized by curves with a peak within 30 min after  Cd supplementation, and a subsequent steep decrease resulting in maintenance of lower Cd concentrations in their roots. Moreover, the PETIS analyses revealed that the high-Cd accumulating cultivars were characterized by rapid and abundant Cd transfer to the shoots from the roots, a faster transport velocity of Cd to the panicles, and Cd accumulation at high levels in their panicles, passing through the nodal portions of the stems where the highest Cd intensities were observed.
Cd supplementation, and a subsequent steep decrease resulting in maintenance of lower Cd concentrations in their roots. Moreover, the PETIS analyses revealed that the high-Cd accumulating cultivars were characterized by rapid and abundant Cd transfer to the shoots from the roots, a faster transport velocity of Cd to the panicles, and Cd accumulation at high levels in their panicles, passing through the nodal portions of the stems where the highest Cd intensities were observed.
 C translocation using positron-emitting tracer imaging system
C translocation using positron-emitting tracer imaging system河地 有木; 鈴井 伸郎; 石井 里美; 伊藤 小百合; 石岡 典子; 山崎 治明; 岩崎 郁*; 小川 健一*; 藤巻 秀
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 648(Suppl.1), p.S317 - S320, 2011/08
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:78.40(Instruments & Instrumentation)Elucidation of carbon kinetics in a plant is important from viewpoint of environmental reduction in the amounts of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO ) and from an agricultural viewpoint in terms of the growth and development of the plant body. In articular photosynthetic CO
) and from an agricultural viewpoint in terms of the growth and development of the plant body. In articular photosynthetic CO fixation and photoassimilate translocation are important topics for understanding the mechanisms underlying carbon kinetics. In this study, we have developed a method to investigate the carbon kinetics by using one of the most powerful radionuclide-based imaging techniques for plant study, that is, the positron emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). Carbon-11-labeled carbon dioxide (
fixation and photoassimilate translocation are important topics for understanding the mechanisms underlying carbon kinetics. In this study, we have developed a method to investigate the carbon kinetics by using one of the most powerful radionuclide-based imaging techniques for plant study, that is, the positron emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). Carbon-11-labeled carbon dioxide ( CO
CO ) and PETIS enable video imaging of tracer dynamics of carbon fixation, photosynthesis, and translocation. Because of a large field of view (FOV) provided by the PETIS and the sufficiently small size of soybeans (
) and PETIS enable video imaging of tracer dynamics of carbon fixation, photosynthesis, and translocation. Because of a large field of view (FOV) provided by the PETIS and the sufficiently small size of soybeans (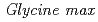 cultive Jack) that fit in the FOV, dynamic quantitative PETIS data of gradual changing in
cultive Jack) that fit in the FOV, dynamic quantitative PETIS data of gradual changing in  C activity and
C activity and  C distribution throughout the entire intact plant body after pulse-chase
C distribution throughout the entire intact plant body after pulse-chase  CO
CO treatment is acquired. This indicates the successful imaging of CO
treatment is acquired. This indicates the successful imaging of CO photoassimilate translocation from the time of infusion into leafs to that of distribution of the whole plant body; further, carbon kinetics is analyzable to understand plant physiology and nutrition.
photoassimilate translocation from the time of infusion into leafs to that of distribution of the whole plant body; further, carbon kinetics is analyzable to understand plant physiology and nutrition.
 CO
CO )
)河地 有木; 鈴井 伸郎; 石井 里美; 伊藤 小百合; 石岡 典子; 山崎 治明; 岩崎 郁*; 小川 健一*; 藤巻 秀
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 101, 2011/01
Elucidation of carbon kinetics in a plant is important from viewpoint of environmental reduction in the amounts of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO ) and from an agricultural viewpoint in terms of the growth and development of the plant body. In particular photosynthetic CO
) and from an agricultural viewpoint in terms of the growth and development of the plant body. In particular photosynthetic CO fixation and photoassimilate translocation are important topics for understanding the mechanisms underlying carbon kinetics. In this study, we have developed a method to investigate the carbon kinetics by using one of the most powerful radionuclide-based imaging techniques for plant study, that is, the Positron Emitting Tracer Imaging System (PETIS) and carbon-11-labeled carbon dioxide (
fixation and photoassimilate translocation are important topics for understanding the mechanisms underlying carbon kinetics. In this study, we have developed a method to investigate the carbon kinetics by using one of the most powerful radionuclide-based imaging techniques for plant study, that is, the Positron Emitting Tracer Imaging System (PETIS) and carbon-11-labeled carbon dioxide ( CO
CO ).
).
石川 覚*; 鈴井 伸郎; 伊藤 小百合*; 石井 里美; 山崎 治明*; 河地 有木; 石岡 典子; 藤巻 秀
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 102, 2011/01
In this study, we evaluated the activities on Cd translocation of a few candidate varieties and analyzed the biological mechanisms using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). Three common rice cultivars, Nipponbare, Koshihikari and Sasanishiki and three candidate varieties were subjected. We equally fed the hydroponic culture solution including  Cd to the six test plants and obtained the serial images of the Cd distribution in the aerial parts for 36 h using PETIS. As a result, It was found that the three candidate plants accumulated Cd in their aerial parts approximately two times as common cultivars. It was also found that almost all Cd in the culture solution was absorbed by all the tested plants. Therefore, this result indicates that the difference was due to greater activities of the candidates in the process to export Cd from the root tissue to the aerial parts, but not in the process of absorption from the culture.
Cd to the six test plants and obtained the serial images of the Cd distribution in the aerial parts for 36 h using PETIS. As a result, It was found that the three candidate plants accumulated Cd in their aerial parts approximately two times as common cultivars. It was also found that almost all Cd in the culture solution was absorbed by all the tested plants. Therefore, this result indicates that the difference was due to greater activities of the candidates in the process to export Cd from the root tissue to the aerial parts, but not in the process of absorption from the culture.
 Cd accumulation in oilseed rape plants treated with glutathione
Cd accumulation in oilseed rape plants treated with glutathione中村 進一*; 鈴井 伸郎; 伊藤 小百合*; 河地 有木; 石岡 典子; 頼 泰樹*; 服部 浩之*; 茅野 充男*; 藤巻 秀
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 104, 2011/01
Glutathione (GSH) is involved in many aspects of metabolism. In our previous work, GSH concentration in the phloem sap collected from oilseed rape plants increased by Cd treatment. These results suggested that GSH might be playing important roles in controlling Cd long-distance transport and accumulation in plants. In this work, we investigated effects of GSH to Cd long-distance transport and accumulation by using positron emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). After setting two week old oilseed rape plants in the chamber, PETIS experiments were started by adding purified  Cd in the nutrient solutions which were including GSH. As a result, we succeeded to obtain images of
Cd in the nutrient solutions which were including GSH. As a result, we succeeded to obtain images of  Cd accumulation in these plants.
Cd accumulation in these plants.  Cd signals were observed in the shoot and root of oilseed rape plants. In the shoot, Cd accumulation was inhibited by GSH treatment. However, we could not see any difference in the Cd accumulation in the root of oilseed rape plants. Further research enables us to understand effects of GSH on Cd long-distance transport and accumulation.
Cd signals were observed in the shoot and root of oilseed rape plants. In the shoot, Cd accumulation was inhibited by GSH treatment. However, we could not see any difference in the Cd accumulation in the root of oilseed rape plants. Further research enables us to understand effects of GSH on Cd long-distance transport and accumulation.
伊藤 小百合; 藤巻 秀; 加藤 太一*; 大竹 憲邦*; 末吉 邦*; 大山 卓爾*
Nitrogen assimilation in plants, p.205 - 214, 2010/07
Leguminous plants can form root nodules as symbiotic organs with soil bacterium rhizobia. The rhizobia fix atmospheric nitrogen in nodules, and the host plants can use this fixed nitrogen in exchange for providing photosynthate as an energy source. The nodule formation is regulated systemically in the host plants to prevent excess nodulation. This process is referred to as autoregulation of nodulation (AON), which includes communication between shoot and root. Hypernodulation mutants, a part of the AON is impaired, can form large number of nodules than the wild type. Using the hypernodulation mutants is thought to be an effective approach to clarify the mechanism of the AON. Recently, we found that the AON is related to the control system of leaf cell proliferation by analysis of the growth of the mutants. In this report, the AON mechanism is reviewed especially in relations to physiological features of the hypernodulation mutants.
 CO
CO と植物用ポジトロンイメージング装置を用いたダイズ植物の根粒に対する光合成産物移行のリアルタイム解析
と植物用ポジトロンイメージング装置を用いたダイズ植物の根粒に対する光合成産物移行のリアルタイム解析伊藤 小百合; 鈴井 伸郎; 河地 有木; 石井 里美; 石岡 典子; 藤巻 秀
Radioisotopes, 59(3), p.145 - 154, 2010/03
ダイズ植物の根粒に対する光合成産物移行について、ポジトロンイメージング装置とポジトロン放出核種 Cで標識した二酸化炭素トレーサを用いて解析した。特に、多数の小さな根粒を着生する根粒超着生変異系統NOD1-3を用いて親系統との比較を行った。変異系統,親系統いずれも、地下部へ移行した
Cで標識した二酸化炭素トレーサを用いて解析した。特に、多数の小さな根粒を着生する根粒超着生変異系統NOD1-3を用いて親系統との比較を行った。変異系統,親系統いずれも、地下部へ移行した C-光合成産物のほとんどは、根の基部に密集する根粒に蓄積しており、基部の根粒には遠位の根粒と比較して、根粒1個あたりでも根粒体積あたりでも光合成産物の移行量が大きいことが示された。基部と遠位、それぞれの部位において、根粒体積あたりの光合成産物の移行量について変異系統と親系統を比較すると、両者に違いがないことが明らかになった。一般的に変異系統では親系統よりも一個体あたりの窒素固定能が劣るが、これは従来考えられてきたように単に根粒数の増加により根粒全体の光合成産物の消費量が増加するためというより、光合成産物の分配の乏しい遠位への着生割合が増加することが原因であることが示唆された。本研究では、ダイズを用いた個々の根粒への光合成産物の移行について、非侵襲的放射線イメージング技術により解析することに初めて成功した。
C-光合成産物のほとんどは、根の基部に密集する根粒に蓄積しており、基部の根粒には遠位の根粒と比較して、根粒1個あたりでも根粒体積あたりでも光合成産物の移行量が大きいことが示された。基部と遠位、それぞれの部位において、根粒体積あたりの光合成産物の移行量について変異系統と親系統を比較すると、両者に違いがないことが明らかになった。一般的に変異系統では親系統よりも一個体あたりの窒素固定能が劣るが、これは従来考えられてきたように単に根粒数の増加により根粒全体の光合成産物の消費量が増加するためというより、光合成産物の分配の乏しい遠位への着生割合が増加することが原因であることが示唆された。本研究では、ダイズを用いた個々の根粒への光合成産物の移行について、非侵襲的放射線イメージング技術により解析することに初めて成功した。
藤巻 秀; 鈴井 伸郎; 石岡 典子; 河地 有木; 伊藤 小百合; 茅野 充男*; 中村 進一*
Plant Physiology, 152(4), p.1796 - 1806, 2010/02
被引用回数:217 パーセンタイル:98.09(Plant Sciences)We characterized the absorption and translocation of cadmium (Cd) in rice using serial images observed with a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). We fed a positron-emitting  Cd tracer to the hydroponic culture. The absorption rates by the root were proportional to Cd concentrations in the culture within the tested range below 100 nM. It was estimated that the radial transport from the culture to the xylem in the root tissue was completed in less than 10 min. Cd moved up through the shoot with velocities of a few centimeters per hour, which was obviously slower than the bulk flow in the xylem. Cd reached the panicles 7 h after feeding and accumulated there constantly. The nodes exhibited the most intensive Cd accumulation in the shoot and Cd transport from the basal nodes to crown root was observed. We concluded that the nodes are the central organ where xylem-to-phloem transfer occurs and play a pivotal role in the half-day travel of Cd from the soil to the grains.
Cd tracer to the hydroponic culture. The absorption rates by the root were proportional to Cd concentrations in the culture within the tested range below 100 nM. It was estimated that the radial transport from the culture to the xylem in the root tissue was completed in less than 10 min. Cd moved up through the shoot with velocities of a few centimeters per hour, which was obviously slower than the bulk flow in the xylem. Cd reached the panicles 7 h after feeding and accumulated there constantly. The nodes exhibited the most intensive Cd accumulation in the shoot and Cd transport from the basal nodes to crown root was observed. We concluded that the nodes are the central organ where xylem-to-phloem transfer occurs and play a pivotal role in the half-day travel of Cd from the soil to the grains.
 Cd translocation in Tobacco plants
Cd translocation in Tobacco plants中村 進一*; 鈴井 伸郎; 石岡 典子; 河地 有木; 伊藤 小百合; 服部 浩之*; 茅野 充男*; 藤巻 秀
JAEA-Review 2009-041, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2008, P. 103, 2009/12
Tabacco plant is one of model plants which enable us to manipulate its gene expression, it is expected to create crop plants with low Cd content in the future. In this study, we visualized Cd dynamics in tobacco plant. Tobacco plants ( ) were grown hydroponically in a growth chamber where the growth conditions of plants were controlled completely for two weeks after sowing. After setting plants in the chamber, PETIS experiments were started by adding purified
) were grown hydroponically in a growth chamber where the growth conditions of plants were controlled completely for two weeks after sowing. After setting plants in the chamber, PETIS experiments were started by adding purified  Cd in nutrient solutions. Time-series images of the
Cd in nutrient solutions. Time-series images of the  Cd distribution were obtained with the PETIS apparatus. Each image was obtained every four minute for 36 hours. We succeeded to obtain fine serial images of Cd transport and accumulation in tobacco plants. Strong
Cd distribution were obtained with the PETIS apparatus. Each image was obtained every four minute for 36 hours. We succeeded to obtain fine serial images of Cd transport and accumulation in tobacco plants. Strong  Cd signals were observed in the roots of tobacco plants. We also could see strong signals of
Cd signals were observed in the roots of tobacco plants. We also could see strong signals of  Cd in the stems. In leaves,
Cd in the stems. In leaves,  Cd signals were distributed thoroughly. The pattern of Cd signal distribution in the tobacco plants was similar to that in oilseed plants). These results demonstrated that dicotyledonous plants had the similar pattern of Cd distribution when plants were treated at low concentration of Cd.
Cd signals were distributed thoroughly. The pattern of Cd signal distribution in the tobacco plants was similar to that in oilseed plants). These results demonstrated that dicotyledonous plants had the similar pattern of Cd distribution when plants were treated at low concentration of Cd.
鈴井 伸郎; 中村 進一*; 伊藤 小百合; 河地 有木; 石岡 典子; 藤巻 秀
JAEA-Review 2009-041, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2008, P. 102, 2009/12
We have developed a monitoring system of  Cd radioactivity in tracer solution using Positron Multi-Probe System (PMPS) that enables the noninvasive measurement of the amounts of
Cd radioactivity in tracer solution using Positron Multi-Probe System (PMPS) that enables the noninvasive measurement of the amounts of  Cd uptake by an intact plant. Two-week old oilseed rape plant (
Cd uptake by an intact plant. Two-week old oilseed rape plant ( L.) was placed into a plastic cylindrical container containing 30 ml of 0.5 mM CaCl
L.) was placed into a plastic cylindrical container containing 30 ml of 0.5 mM CaCl solution with approximately 10 MBq of
solution with approximately 10 MBq of  Cd. The cylindrical container was divided by nylon mesh into two compartments, the root of the plant was immersed in the upper compartment, and a pair of PMPS detectors was placed outside the bottom compartment. As a result, we successfully obtained the continuous data of the amount of a radioactive tracer taken up by the intact plant for 36 hours.
Cd. The cylindrical container was divided by nylon mesh into two compartments, the root of the plant was immersed in the upper compartment, and a pair of PMPS detectors was placed outside the bottom compartment. As a result, we successfully obtained the continuous data of the amount of a radioactive tracer taken up by the intact plant for 36 hours.
菊地 郁*; 河地 有木; 石井 里美; 鈴井 伸郎; 伊藤 小百合; 石岡 典子; 本多 一郎*; 藤巻 秀
JAEA-Review 2009-041, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2008, P. 105, 2009/12
In the eggplant cultivation, defoliation is normally used to prevent the disease and insect as well as raise the efficiency of light interception for efficient fruit production. However the general guideline for defoliation is not established yet because fundamental knowledge about effects of defoliation on the nutritional balance in individuals has hardly been obtained. For these reason, it is important to clarify the accumulation mechanism of the photoassimilates which is translocated from each leaf to the fruit in eggplant. Previously, we succeeded to observe translocation of  C-labeled photoassimilates from a leaf into a fruit and established a method for the quantitative analysis of photoassimilates using the positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). PETIS can noninvasively visualize the movement of
C-labeled photoassimilates from a leaf into a fruit and established a method for the quantitative analysis of photoassimilates using the positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). PETIS can noninvasively visualize the movement of  C-labeled photoassimilates in plants and repetitive analyses using one plant are possible due to the short half-life (20 min) of
C-labeled photoassimilates in plants and repetitive analyses using one plant are possible due to the short half-life (20 min) of  C. In this study, we analyzed translocation of photoassimilates from each of major leaves to a fruit, and estimated the contribution of the respective leaves to accumulation of photoassimilates in the fruit using
C. In this study, we analyzed translocation of photoassimilates from each of major leaves to a fruit, and estimated the contribution of the respective leaves to accumulation of photoassimilates in the fruit using  CO
CO and PETIS.
and PETIS.
 N-labeled nitrogen gas tracer and the imaging of nitrogen fixation in soybean nodules
N-labeled nitrogen gas tracer and the imaging of nitrogen fixation in soybean nodules石井 里美; 鈴井 伸郎; 伊藤 小百合; 石岡 典子; 河地 有木; 松橋 信平; 大竹 憲邦*; 大山 卓爾*; 藤巻 秀
JAEA-Review 2009-041, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2008, P. 106, 2009/12
The nodule is a symbiotic organ of leguminous plants with rhizobium. Soybean plants utilize nitrogen (N) fixed by nodules from atmospheric N . Until now,
. Until now,  N, a stable isotope, has long been used for studies of N
N, a stable isotope, has long been used for studies of N fixation. However, because this method is invasive, it has been difficult to analyze an instant response to an environmental (ex. temperature, light) changes. The purpose of our study is to image the N
fixation. However, because this method is invasive, it has been difficult to analyze an instant response to an environmental (ex. temperature, light) changes. The purpose of our study is to image the N fixation and analyze the kinetics quantitatively and noninvasively by using nitrogen gas labeled with
fixation and analyze the kinetics quantitatively and noninvasively by using nitrogen gas labeled with  N (half life: 10 min), a positron emitting isotope, and PETIS (positron-emitting tracer imaging system). Previously, we succeeded in producing
N (half life: 10 min), a positron emitting isotope, and PETIS (positron-emitting tracer imaging system). Previously, we succeeded in producing  N-labeled nitrogen gas However, it was required to purify the gas because it was likely to contain physiologically active
N-labeled nitrogen gas However, it was required to purify the gas because it was likely to contain physiologically active  N-labeled impurities. In this paper, we report development of a new method of production of pure
N-labeled impurities. In this paper, we report development of a new method of production of pure  N
N and the imaging of nitrogen fixation.
and the imaging of nitrogen fixation.
 Cd
Cd伊藤 小百合; 鈴井 伸郎; 河地 有木; 石岡 典子; 藤巻 秀
JAEA-Review 2009-041, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2008, P. 104, 2009/12
Recently, Cd accumulation in soybean seed is considered one of the acute agricultural problems in Japan. However, characteristics of Cd transport and accumulation in soybean plants are unclear so far. In this study, the mechanism of Cd transport in young soybean plants was characterized using tracer of a positron-emitting  Cd (half-life: 6.5 hours) and the positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). Soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr. cv. Williams) seeds were grown hydroponically for 3 weeks after sowing. The test plants were placed between a set of the PETIS detector heads in another growth chamber.
Cd (half-life: 6.5 hours) and the positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). Soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr. cv. Williams) seeds were grown hydroponically for 3 weeks after sowing. The test plants were placed between a set of the PETIS detector heads in another growth chamber.  Cd and was added to the hydroponic solution with non-radioactive Cd. The imaging with PETIS was performed for 36 hours. In the field of view of PETIS,
Cd and was added to the hydroponic solution with non-radioactive Cd. The imaging with PETIS was performed for 36 hours. In the field of view of PETIS,  Cd was observed very weakly. Cd appeared in the shoot base at about 10 hours after Cd feeding, which timing was 10 times later compared with the results of rice. Cd was not reached the leaves within 36 hours. These results may indicate that Cd transport might be particularly slow in soybean plants.
Cd was observed very weakly. Cd appeared in the shoot base at about 10 hours after Cd feeding, which timing was 10 times later compared with the results of rice. Cd was not reached the leaves within 36 hours. These results may indicate that Cd transport might be particularly slow in soybean plants.