Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kadono, Ryosuke*; Ito, Takashi
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(6), p.064601_1 - 064601_11, 2025/06
 Co
Co )Sn studied by
)Sn studied by  SR
SRCai, Y.*; Yoon, S.*; Sheng, Q.*; Zhao, G.*; Seewald, E. F.*; Ghosh, S.*; Ingham, J.*; Pasupathy, A. N.*; Queiroz, R.*; Lei, H.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(21), p.214412_1 - 214412_17, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0 SR
SRIto, Takashi; Kadono, Ryosuke*
Kotai Butsuri, 60(4), p.197 - 206, 2025/04
We extended the dynamical Kubo-Toyabe model to resolve inconsistencies in a conventional protocol for  SR-based analysis of ion dynamics in solids. Our new model not only provides a means for quantitative analysis based on the immobile-muon assumption, but also offers a method to evaluate the validity of this assumption.
SR-based analysis of ion dynamics in solids. Our new model not only provides a means for quantitative analysis based on the immobile-muon assumption, but also offers a method to evaluate the validity of this assumption.
 Sb
Sb with a honeycomb network
with a honeycomb networkAdachi, Tadashi*; Ogawa, Taiki*; Komiyama, Yota*; Sumura, Takuya*; Saito-Tsuboi, Yuki*; Takeuchi, Takaaki*; Mano, Kohei*; Manabe, Kaoru*; Kawabata, Koki*; Imazu, Tsuyoshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(10), p.L100508_1 - L100508_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) GeTe
GeTe homojunctions
homojunctionsObata, Reiji*; Saito, Eiji; Kikkawa, Takashi; 13 of others*
Advanced Materials, 37(8), p.2411459_1 - 2411459_11, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:84.76(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Yano, Yasuhide; Miyazawa, Takeshi; Tanno, Takashi; Akasaka, Naoaki; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Kaito, Takeji; Otsuka, Satoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 8 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The effects of strain rate on tensile properties of irradiated modified 316 stainless steel (PNC316) claddings were investigated. PNC316 claddings were irradiated at the experimental fast reactor Joyo using CRT402 control rod assembly at 400 C up to 25 dpa. Post-irradiation ring tensile tests were carried out at strain rates of 3.3
C up to 25 dpa. Post-irradiation ring tensile tests were carried out at strain rates of 3.3 10
10 , 3.3
, 3.3 10
10 and 3.3
and 3.3 10
10 s
s at a test temperature of 350
at a test temperature of 350 C. The results showed no obvious dependence of all strain rates on tensile properties, although a slight decrease in total elongation was observed at the slowest strain rate of 3.3
C. The results showed no obvious dependence of all strain rates on tensile properties, although a slight decrease in total elongation was observed at the slowest strain rate of 3.3 10
10 s
s . In addition, only a part of fracture surface at the slowest strain rate showed intergranular type region in the inner surface area, although the grain boundary separation occurred on inner surfaces near the fracture region at all strain rates. It is suggested that presence of a high content of helium near the inner surfaces would be related to the fracture behavior.
. In addition, only a part of fracture surface at the slowest strain rate showed intergranular type region in the inner surface area, although the grain boundary separation occurred on inner surfaces near the fracture region at all strain rates. It is suggested that presence of a high content of helium near the inner surfaces would be related to the fracture behavior.
Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Pant, A. D.*; Sunagawa, Hikaru*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Fujihara, Masayoshi; Tampo, Motonobu*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.31_1 - 31_6, 2024/12
 Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M
Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer and
ssbauer and  SR studies of Sm
SR studies of Sm Ru
Ru Ge
Ge
Tsutsui, Satoshi; Ito, Takashi; Nakamura, Jin*; Yoshida, Mio*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Koda, Akihiro*; Higashinaka, Ryuji*; Aoki, Dai*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.55_1 - 55_9, 2024/12
 )
) (SrAl
(SrAl Ta
Ta O
O )
) with
with 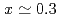
Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Koda, Akihiro*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Shimomura, Koichiro*
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.25_1 - 25_7, 2024/12
 Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M
Sm synchrotron-radiation-based M ssbauer spectroscopy of Sm-based heavy fermion compounds
ssbauer spectroscopy of Sm-based heavy fermion compoundsTsutsui, Satoshi; Higashinaka, Ryuji*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Nakamura, Jin*; Ito, Takashi; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Aoki, Yuji*; Sato, Hideyuki*
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.9_1 - 9_10, 2024/12
Wakui, Takashi; Saito, Shigeru; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Jikken Rikigaku, 24(4), p.212 - 218, 2024/12
Irradiation damage is one of the main factors determining the lifetime of the mercury target vessel for spallation neutron source in J-PARC. To understand material degradation of the used vessels, it is planned to conduct an evaluation using inverse analyses with indentation tests on the structural materials of the used vessels and numerical experiments. This evaluation technique was applied to two kinds of ion-irradiated materials with different displacement damage doses, in which the irradiation condition was simulated. It could be confirmed that the ultimate strength increased, and the total elongation decreased with increasing irradiation. These trends are like the material degradation behaviors which have been reported by using small specimen's tensile tests.
Wakui, Takashi; Saito, Shigeru; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Materials, 17(23), p.5925_1 - 5925_14, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)The ductile properties of irradiated materials are one of the important indicators related to their structural integrity. Indentation tests are used for evaluating the ductile properties easily and rapidly. Constants in the material constitutive equation were identified via inverse analysis using the Kalman filter, such that the numerical experimental results reproduced the indentation test results. Numerical tensile experiments were conducted using stress-strain curves with the identified constants to obtain nominal stress-strain curves. Furthermore, two methods were proposed for evaluating the total elongation. Evaluated minimum total elongation was 10 %. The evaluation results of ion-irradiated materials were similar to the tensile test results of irradiated materials.
 SR study on the noncentrosymmetric superconductor NbGe
SR study on the noncentrosymmetric superconductor NbGe
Jiao, J. C.*; Chen, K. W.*; Hillier, A. D.*; Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Li, Z.*; Lv, B.*; Xu, Z.-A.*; Shu, L.*
Physical Review B, 110(21), p.214516_1 - 214516_9, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Kosugi, Mioko*; Kikkawa, Takashi; Saito, Eiji; 10 of others*
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 16(46), p.64190 - 64196, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.18(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) GeTe
GeTe nanomeshes
nanomeshesObata, Reiji*; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Saito, Eiji; 7 of others*
Nanotechnology, 35(47), p.475601_1 - 475601_9, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:35.22(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Miyazawa, Takeshi; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Yano, Yasuhide; Tanno, Takashi; Otsuka, Satoshi; Onizawa, Takashi; Ando, Masanori; Kaito, Takeji
JAEA-Technology 2024-009, 140 Pages, 2024/10
For the purpose of enhancing the reliability of fast reactor fuel designing using modified type 316 steel, the out-of-pile and in-pile mechanical data of modified type 316 steel cladding tubes and wrapper tubes were statistically analyzed with the knowledge on material science and engineering; the high-temperature strength equations of modified type 316 steel, which can be applied to high-dose neutron irradiation environment, were derived. The out-of-pile high-temperature tensile and creep data of modified type 316 steel cladding tubes and wrapper tubes were derived up to 900 C, which is higher than the upper limit temperature of anticipated transient event of fast reactor. Using the extended database, the best-fit equation and the lower limit equation were derived for out-of-pile 0.2% proof strength, ultimate tensile strength and creep rupture strength while the best-fit equation and the upper and lower limit equations for creep strain. Furthermore, the degradation factors for tensile and creep strength, which will be produced by in-reactor environment (i.e., neutron irradiation in liquid sodium), were evaluated using the existing neutron irradiation data of modified type 316 steel, which were derived using the experimental fast reactor Joyo, the French proto-type fast reactor Phenix, the American experimental fast reactor FFTF. The derived equations were validated by the comparison with the experimental data.
C, which is higher than the upper limit temperature of anticipated transient event of fast reactor. Using the extended database, the best-fit equation and the lower limit equation were derived for out-of-pile 0.2% proof strength, ultimate tensile strength and creep rupture strength while the best-fit equation and the upper and lower limit equations for creep strain. Furthermore, the degradation factors for tensile and creep strength, which will be produced by in-reactor environment (i.e., neutron irradiation in liquid sodium), were evaluated using the existing neutron irradiation data of modified type 316 steel, which were derived using the experimental fast reactor Joyo, the French proto-type fast reactor Phenix, the American experimental fast reactor FFTF. The derived equations were validated by the comparison with the experimental data.
Toyama, Takeshi*; Tanno, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide; Inoue, Koji*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Otsuka, Satoshi; Miyazawa, Takeshi; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; Nakashima, Hideharu*; Onuma, Masato*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 599, p.155252_1 - 155252_14, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the stability of oxide nano particles in oxide dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel, which is a promising candidate material for next-generation reactors, under neutron irradiation at high temperature to high doses. MA957, a 14Cr-ODS steel, was irradiated with Joyo in Japan Atomic Energy Agency under irradiation conditions of 130 dpa at 502 C, 154 dpa at 589
C, 154 dpa at 589 C, and 158 dpa at 709
C, and 158 dpa at 709 C. Three-dimensional atom probe (3D-AP) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) observation were performed to characterize the oxide particles in the ODS steels. A high number density of Y-Ti-O particle was observed in the unirradiated and irradiated samples. Almost no change in the morphology of the oxide particles, i.e. average diameter, number density, and chemical composition, has been observed in the samples irradiated to 130 dpa at 502
C. Three-dimensional atom probe (3D-AP) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) observation were performed to characterize the oxide particles in the ODS steels. A high number density of Y-Ti-O particle was observed in the unirradiated and irradiated samples. Almost no change in the morphology of the oxide particles, i.e. average diameter, number density, and chemical composition, has been observed in the samples irradiated to 130 dpa at 502 C and to 154 dpa at 589
C and to 154 dpa at 589 C. A slight decrease in number density was observed in the sample irradiated to 158 dpa at 709
C. A slight decrease in number density was observed in the sample irradiated to 158 dpa at 709 CC. The hardness of any of the irradiated samples was almost unchanged from that of the unirradiated sample. It was revealed that the oxide particles existed stable, and the strength of the material was sufficiently maintained even after being neutron irradiated to high dose of
CC. The hardness of any of the irradiated samples was almost unchanged from that of the unirradiated sample. It was revealed that the oxide particles existed stable, and the strength of the material was sufficiently maintained even after being neutron irradiated to high dose of  160 dpa at high temperature up to 700
160 dpa at high temperature up to 700 C. A part of this study includes the results of MEXT Innovative Nuclear Research and Development Program Grant Number JPMXD0219214482.
C. A part of this study includes the results of MEXT Innovative Nuclear Research and Development Program Grant Number JPMXD0219214482.
Otsuka, Satoshi; Tanno, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide; Kaito, Takeji
Materials and Processes for Nuclear Energy Today and in the Future, p.279 - 297, 2024/10
The oxide dispersion strengthening is an effective technique for improving the mechanical strength of the steel. The dispersed oxides prevent the gliding motion of dislocations, thus remarkably enhancing the resistance to high-temperature deformation and rupture of steels. Extensive efforts have been made to develop ODS steels in the fields of nuclear and fusion engineering. Research has been done to improve their performance and meet the requirements such as irradiation resistance, high-temperature strength, and corrosion resistance. Based on recent research, the high-density dispersion of nanosized oxides could improve the irradiation resistance of the steels in addition to high-temperature strength because the interface between oxide and matrix could act as sink sites for point defects. This section overviews the ODS steel development for nuclear application.
Kawabata, Kuniaki; Imabuchi, Takashi; Shirasaki, Norihito*; Suzuki, Soichiro; Ito, Rintaro; Aoki, Yuto; Omori, Takazumi
ROBOMECH Journal (Internet), 11, p.11_1 - 11_11, 2024/09
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Kubo, Kenya*; Inagaki, Makoto*; Yoshida, Go*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Tampo, Motonobu*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Strasser, P.*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 333(7), p.3445 - 3450, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Chemistry, Analytical)