Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwase, Akihiro*; Fukuda, Kengo*; Saito, Yuichi*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Amekura, Hiroshi*; Matsui, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Applied Physics, 132(16), p.163902_1 - 163902_10, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)Amorphous SiO samples were implanted with 380 keV Fe ions at room temperature. After implantation, some of the samples were irradiated with 16 MeV Au ions. magnetic properties were investigated using a SQUID magnetometer, and the morphology of the Fe-implanted SiO
samples were implanted with 380 keV Fe ions at room temperature. After implantation, some of the samples were irradiated with 16 MeV Au ions. magnetic properties were investigated using a SQUID magnetometer, and the morphology of the Fe-implanted SiO samples was examined using transmission electron microscopy and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (EXAFS and XANES), which showed that the size of Fe nanoparticles was increasing The size of Fe nanoparticles increased with increasing Fe implantation amount; some of the Fe nanoparticles consisted of Fe oxides, and the valence and structure of Fe atoms became closer to that of metallic
samples was examined using transmission electron microscopy and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (EXAFS and XANES), which showed that the size of Fe nanoparticles was increasing The size of Fe nanoparticles increased with increasing Fe implantation amount; some of the Fe nanoparticles consisted of Fe oxides, and the valence and structure of Fe atoms became closer to that of metallic  -Fe with increasing Fe injection amount. The magnetization-field curve of the sample implanted with a small amount of Fe was reproduced by Langevin's equation, suggesting that the Fe nanoparticles behave in a superparamagnetic manner. In addition, when a large amount of Fe was implanted, the magnetization-magnetic field curve shows a ferromagnetic state. These magnetic property results are consistent with the X-ray absorption results. Subsequent 16 MeV Au irradiation crushed the Fe nanoparticles, resulting in a decrease in magnetization.
-Fe with increasing Fe injection amount. The magnetization-field curve of the sample implanted with a small amount of Fe was reproduced by Langevin's equation, suggesting that the Fe nanoparticles behave in a superparamagnetic manner. In addition, when a large amount of Fe was implanted, the magnetization-magnetic field curve shows a ferromagnetic state. These magnetic property results are consistent with the X-ray absorption results. Subsequent 16 MeV Au irradiation crushed the Fe nanoparticles, resulting in a decrease in magnetization.
Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Umetsu, Rie*; Kuroda, Fumiaki*; Miyawaki, Jun*; Kashiuchi, Toshiyuki*; Nishimoto, Kohei*; Nagai, Kodai*; Sekiyama, Akira*; Irizawa, Akinori*; Takeda, Yukiharu; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.18654_1 - 18654_9, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Sakakibara, Hiroshi; Aoki, Nobuhiro; Muto, Masahiro; Otabe, Jun; Takahashi, Kenji*; Fujita, Naoyuki*; Hiyama, Kazuhiko*; Suzuki, Hirokazu*; Kamogawa, Toshiyuki*; Yokosuka, Toru*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2020-020, 73 Pages, 2021/03
The decommissioning is currently in progress at the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju. Fuel assemblies will be taken out of its core for the first step of the great task. Fuel assemblies stand on their own spike plugged into a socket on the core support plate and support with adjacent assemblies through their housing pads each other, resulting in steady core structure. For this reason, some substitutive assemblies are necessary for the purpose of discharging the fuel assemblies of the core. Monju side commissioned, therefore, Plutonium Fuel Development Center to manufacture the substitutive assemblies and the Center accepted it. This report gives descriptions of design, manufacture, and shipment in regard to the substitutive assemblies.
 -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:96.69(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,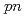 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Shumpei*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.78_1 - 78_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:55.71(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Searching for effective pathways for the production of proton- and neutron-rich isotopes through an optimal combination of reaction mechanism and energy is one of the main driving forces behind experimental and theoretical nuclear reaction studies as well as for practical applications in nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste. We report on a study on incomplete fusion induced by deuteron, which contains one proton and one neutron with a weak binding energy and is easily broken up. This reaction study was achieved by measuring directly the cross sections for both proton and deuteron for  Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Ashida, Takashi; Nakamura, Toshiyuki*; Ito, Hideaki
JAEA-Technology 2017-024, 198 Pages, 2017/11
In the experimental fast reactor Joyo, the disconnecting of an irradiation test subassembly MARICO-2 (Material Testing Irradiation Rig with Temperature Control) from its holding mechanism was conducted in May 2007. After the operation, the rotating plug was rotated despite the fact that the test subassembly was not disconnected completely. Consequently, top of wrapper tube of the MARICO-2 subassembly was bent onto the in-vessel storage rack. Since the overhanging part of the subassembly was in the height in which contacts with the upper core structure, it had damaged the bottom surface of the upper core structure. As the result, it was necessary to replace the damaged upper core structure and to retrieve the bent MARICO-2 subassembly for Joyo restart. Retrieval devices for MARICO-2 subassembly consist of a gripper mechanism to lift subassembly together with transfer pot, a guide tube built-in a pantograph mechanism to adjust lifting axis and safety mechanisms to prevent or mitigate falling of MARICO-2 subassembly, a retrieval cask and so on. Design of the retrieval devices have been verified in ex-vessel partial or full-scale mock-up tests and in-vessel function tests. In 2014, MARICO-2 subassembly was successfully retrieved from the reactor vessel by applying these retrieval devices. Then, retrieved subassembly was transported to a hot-cell facility for post-irradiation examinations. Devices have demonstrated expected performance under the actual environmental conditions of a sodium cooled fast reactor. This is a synthetic report about the retrieval work of the deformed and irradiated test subassembly in Joyo. This report includes the detail design and fabrication of the special retrieval device, results of tests for confirmation including the mock-up tests in manufacturer's factory, and results of MARICO-2 retrieval work from the reactor vessel.
 Cr
CrShizuma, Toshiyuki*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Daito, Izuru*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Miyamoto, Shuji*; Minato, Futoshi
Physical Review C, 96(4), p.044316_1 - 044316_10, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:59.02(Physics, Nuclear)The low-lying dipole strength in  Cr was measured in nuclear resonance fluorescence experiments using a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The parities of the excited dipole states were determined by the intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered
Cr was measured in nuclear resonance fluorescence experiments using a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The parities of the excited dipole states were determined by the intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered  -rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The summed magnetic dipole (M1) strength was determined as
-rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The summed magnetic dipole (M1) strength was determined as 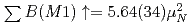 at excitation energies between 7.5 and 12.1 MeV; the summed electric dipole (E1) strength was obtained as
at excitation energies between 7.5 and 12.1 MeV; the summed electric dipole (E1) strength was obtained as 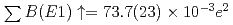 fm
fm . The observed M1 and E1 strengths were compared via random phase approximation calculations using the Skyrme interaction. The effects of 2 particle-2 hole configuration mixing and tensor force on dipole strength distributions were investigated.
. The observed M1 and E1 strengths were compared via random phase approximation calculations using the Skyrme interaction. The effects of 2 particle-2 hole configuration mixing and tensor force on dipole strength distributions were investigated.
 =28 and
=28 and  =50; Spectroscopy of
=50; Spectroscopy of 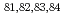 Zn
ZnShand, C. M.*; Podoly k, Zs.*; G
k, Zs.*; G rska, M.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; Otsuka, T.*; Sieja, K.*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Tsunoda, T.*; et al.
rska, M.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; Otsuka, T.*; Sieja, K.*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Tsunoda, T.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 773, p.492 - 497, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:87.8(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Sato, Toshinori; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Ishii, Eiichi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Hayano, Akira; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Fujita, Tomoo*; Tanai, Kenji; Nakayama, Masashi; Takeda, Masaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2016-025, 313 Pages, 2017/03
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary formations at Horonobe, northern Hokkaido. This report summarizes the results of the Phase II investigations carried out from April 2005 to June 2014 to a depth of 350m. Integration of work from different disciplines into a "geosynthesis" ensures that the Phase II goals have been successfully achieved and identifies key issues that need to made to be addressed in the Phase II investigations Efforts are made to summarize as many lessons learnt from the Phase II investigations and other technical achievements as possible to form a "knowledge base" that will reinforce the technical basis for both implementation and the formulation of safety regulations.
Ashida, Takashi; Ito, Hideaki; Miyamoto, Kazuyuki*; Nakamura, Toshiyuki; Koga, Kazuhiro*; Ohara, Norikazu*; Ino, Hiroichi*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 15(4), p.210 - 222, 2016/12
In the experimental fast reactor Joyo, it was confirmed that the top of the irradiation test sub-assembly of material testing rig named "MARICO-2" had been broken and bent onto the in-vessel storage rack as an obstacle and had damaged the upper core structure (UCS). As the result, for Joyo restart, it was necessary to replace the damaged UCS and to retrieve the bent sub-assembly. This paper describes in-vessel repair techniques performed in the retrieval work of the obstacle inside of the reactor vessel. The devices which were prepared for this work demonstrated expected performance under the environmental conditions of an SFR such as high temperature and radiation dose, and the work was completed in 2014. The successful operation of this retrieval work of the damaged component inside of a reactor vessel will contribute to the development of in-service inspections and repair technics in an SFR.
Naito, Fujio*; Anami, Shozo*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Uota, Masahiko*; Ouchi, Toshikatsu*; Onishi, Takahiro*; Oba, Toshiyuki*; Obina, Takashi*; Kawamura, Masato*; Kumada, Hiroaki*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1244 - 1246, 2016/11
The proton linac installed in the Ibaraki Neutron Medical Research Center is used for production of the intense neutron flux for the Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT). The linac consists of the 3-MeV RFQ and the 8-MeV DTL. Design average beam current is 10mA. Target is made of Beryllium. First neutron production from the Beryllium target was observed at the end of 2015 with the low intensity beam as a demonstration. After the observation of neutron production, a lot of improvement s was carried out in order to increase the proton beam intensity for the real beam commissioning. The beam commissioning has been started on May 2016. The status of the commissioning is summarized in this report.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Onoe, Hironori; Sato, Toshinori; Fujita, Tomoo; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Takeda, Masaki; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2016-014, 274 Pages, 2016/08
We synthesized the research results from the Mizunami/Horonobe Underground Research Laboratories (URLs) and geo-stability projects in the second midterm research phase. This report can be used as a technical basis for the Nuclear Waste Management Organization of Japan/Regulator at each decision point from siting to beginning of disposal (Principal Investigation to Detailed Investigation Phase).
Obana, Tetsuhiro*; Murakami, Haruyuki; Takahata, Kazuya*; Hamaguchi, Shinji*; Chikaraishi, Hirotaka*; Mito, Toshiyuki*; Imagawa, Shinsaku*; Kizu, Kaname; Natsume, Kyohei; Yoshida, Kiyoshi
Physica C, 518, p.96 - 100, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:31.9(Physics, Applied)Hama, Katsuhiro; Mizuno, Takashi; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Sato, Toshinori; Fujita, Tomoo; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Yokota, Hideharu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2015-007, 269 Pages, 2015/08
We have synthesised the research results from Mizunami/Horonobe URLs and geo-stability projects in the second mid-term research phase. It could be used as technical bases for NUMO/Regulator in each decision point from sitting to beginning of disposal (Principal Investigation to Detailed Investigation Phase). High quality construction techniques and field investigation methods have been developed and implemented and these will be directly applicable to the National Disposal Program (along with general assessments of hazardous natural events and processes). It will be crucial to acquire technical knowledge on decisions of partial backfilling and final closure by actual field experiments in Mizunami/Horonobe URLs as main themes for the next phases.
Koga, Kazuhiro*; Ohara, Norikazu*; Ino, Hiroichi*; Kondo, Katsumi*; Ito, Hideaki; Ashida, Takashi; Nakamura, Toshiyuki
FAPIG, (190), p.3 - 8, 2015/07
no abstracts in English
Murakami, Haruyuki; Kizu, Kaname; Ichige, Toshikatsu; Furukawa, Masato; Natsume, Kyohei; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kamiya, Koji; Koide, Yoshihiko; Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Obana, Tetsuhiro*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 25(3), p.4201305_1 - 4201305_5, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:34.11(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)JT-60U magnet system will be upgraded to the superconducting coils in the JT-60SA programme of the Broader Approach activities. Terminal joint of Central Solenoid (CS) is wrap type Nb Sn-NbTi joint used for connecting CS (Nb
Sn-NbTi joint used for connecting CS (Nb Sn) and current feeder (NbTi). The terminal joints are placed at the top and the bottom of the CS systems. CS modules located at middle position of CS system need the lead extension from the modules to the terminal joint. The joint resistance measurement of terminal joint was performed in the test facility of National Institute for Fusion Science. The joint resistance was evaluated by the operating current and the voltage between both ends of the terminal joint part. Test results met the requirement of JT-60SA magnet system. The structural analysis of the lead extension and its support structure was conducted to confirm the support design. In this paper, the results of resistance test of joint and the structural analysis results of lead extension are reported.
Sn) and current feeder (NbTi). The terminal joints are placed at the top and the bottom of the CS systems. CS modules located at middle position of CS system need the lead extension from the modules to the terminal joint. The joint resistance measurement of terminal joint was performed in the test facility of National Institute for Fusion Science. The joint resistance was evaluated by the operating current and the voltage between both ends of the terminal joint part. Test results met the requirement of JT-60SA magnet system. The structural analysis of the lead extension and its support structure was conducted to confirm the support design. In this paper, the results of resistance test of joint and the structural analysis results of lead extension are reported.
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Takaki, Motonobu*; Miya, Hiroyuki*; Ota, Shinsuke*; Michimasa, Shinichiro*; Shimoura, Susumu*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 6, p.030005_1 - 030005_4, 2015/06
 ,
,  ') reaction of
') reaction of  U on the target thickness
U on the target thicknessNegm, H.*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Daito, Izuru*; Hayakawa, Takehito; Zen, H.*; Kii, Toshiteru*; Masuda, Kai*; Hori, Toshitada*; Hajima, Ryoichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(6), p.811 - 820, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.95(Nuclear Science & Technology)The dependence of the nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) yield on the target thickness was studied. To this end, an NRF experiment was performed on  U using a laser Compton back-scattering (LCS)
U using a laser Compton back-scattering (LCS)  -ray beam at the High Intensity
-ray beam at the High Intensity  -ray Source facility at Duke University.
-ray Source facility at Duke University.
Yamamoto, Seiichi*; Toshito, Toshiyuki*; Komori, Masataka*; Morishita, Yuki*; Okumura, Satoshi*; Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka; Saito, Yuichi; Kawachi, Naoki; Fujimaki, Shu
Annals of Nuclear Medicine, 29(3), p.268 - 275, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:67.44(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging) -ray irradiation facilities
-ray irradiation facilitiesAgematsu, Takashi; Hanaya, Hiroaki; Yamagata, Ryohei; Seito, Hajime; Nagao, Yuto; Kaneko, Hirohisa; Yamaguchi, Toshiyuki*; Kawashima, Ikuo*; Yagi, Norihiko*; Takagi, Masahide*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 183, 2015/03
The electron accelerator and the three  -ray irradiation facilities were operated for various research subjects according to the operation plan in FY 2013. The number of research subjects at the electron accelerator and at the
-ray irradiation facilities were operated for various research subjects according to the operation plan in FY 2013. The number of research subjects at the electron accelerator and at the  -ray irradiation facilities kept constant from FY 2012. Among these research subjects, 47 and 91 ones respectively performed at the electron accelerator and the
-ray irradiation facilities kept constant from FY 2012. Among these research subjects, 47 and 91 ones respectively performed at the electron accelerator and the  -ray irradiation facilities were relevant to recovery from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster.
-ray irradiation facilities were relevant to recovery from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster.