Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 elik, Y.*; Stankovskiy, A.*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Van den Eynde, G.*
elik, Y.*; Stankovskiy, A.*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Van den Eynde, G.*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 212, p.111048_1 - 111048_12, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:57.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Yonehara, Katsuya*; Pellemoine, F.*; Liu, Z.*; Lynch, K.*; Yoshida, Makoto*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Yoshiie, Toshimasa*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165543_1 - 165543_8, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The number of displacements per atom is widely used as an indicator of irradiation damage to materials in proton accelerator facilities. Experiments have been carried out on protons below 3 GeV to verify the dpa of metallic materials. However, the dpa for high-energy protons above 3 GeV has not been measured. In order to validate the displacement cross sections of metals in the high-energy region, the electrical resistivity changes of aluminium, copper and tungsten wires at a temperature of 8 K were measured using protons with energy of 120 GeV. The results show that the conventional irradiation damage model of PHITS overestimates the experimental data. On the other hand, the calculation results using the athermal recombination correction model were in agreement with the experimental data.
Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Furuta, Takuya; Iwamoto, Yosuke
JAEA-Conf 2024-002, 216 Pages, 2024/11
The 2023 Symposium on Nuclear Data was held at Tokai Industry and Information Plaza "iVil" on November 15-17, 2023. The symposium was organized by the Nuclear Data Division of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ) in cooperation with Radiation Engineering Division of AESJ, North Kanto Branch of AESJ, Investigation Committee on Nuclear Data in AESJ, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, and High Energy Accelerator Research Organization. In the symposium, tutorials "Overview of the nuclear data processing code, FRENDY version 2" was proposed and held. Two sessions of lectures and discussions were held: "Recent Topics on Nuclear Data and Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS)". In addition, recent research progress on experiments, nuclear theory, evaluation, benchmark, and applications were presented in the poster session. The total number of participants was 108 participants. Each oral and poster presentation was followed by an active question and answer session. This report consists of a total of 36 papers including 17 oral and 19 poster presentations.
Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Hirata, Yuho; Matsuya, Yusuke; Kai, Takeshi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Norihiro; et al.
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 10, p.13_1 - 13_8, 2024/11
The latest updates on PHITS, a versatile radiation transport code, focusing specifically on track-structure models are presented. Track structure calculations are methods used to simulate the movement of charged particles while explicitly considering each atomic reaction. Initially developed for radiation biology, these calculation methods aimed to analyze the radiation-induced damage to DNA and chromosomes. Several track-structure calculation models, including PHITS-ETS, PHITS-ETS for Si, PHITS-KURBUC, ETSART, and ITSART, have been developed and implemented to PHITS. These models allow users to study the behavior of various particles at the nano-scale across a wide range of materials. Furthermore, potential applications of track-structure calculations have also been proposed so far. This collection of track-structure calculation models, which encompasses diverse conditions, opens up new avenues for research in the field of radiation effects.
 I and
I and  I using the NaI(Tl) spectrometer of the ANNRI beamline at J-PARC
I using the NaI(Tl) spectrometer of the ANNRI beamline at J-PARCRovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Toh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*
European Physical Journal A, 60(5), p.120_1 - 120_14, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 549, p.165255_1 - 165255_4, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:58.81(Instruments & Instrumentation)Atomic defect is one of the critical factors that determines the irradiation effects in materials. The atoms are recoiled by the impulse of incoming radiation, which changes the mechanical, electrical and chemical properties of the target materials. Methods to calculate atomic displacement based on nuclear reaction cross sections and Rutherford scattering cross sections were proposed but they were dedicated to calculation of the defect density in macroscopic scale whereas some phenomena are attributed to the topological arrangements of defects in microscopic scale. Application of a track-structure calculation model, ITSART implemented to a general-purpose radiation transport code PHITS for calculation of the topological arrangement of radiation-induced defects is proposed in this study. To verify the defect production calculated by ITSART, DPA (Displacement Per Atom) cross section in Cu was calculated and compared with literature data. The agreement indicates the accuracy of ITSART for calculating atomic displacement. By using the same methodology to a smaller volume, the defects in SiO exposed to 600 MeV proton beam was calculated. PHITS users can make use of the outputs by forwarding them to other tools, such as molecular dynamics codes, to analyse the further evolution of the defects.
exposed to 600 MeV proton beam was calculated. PHITS users can make use of the outputs by forwarding them to other tools, such as molecular dynamics codes, to analyse the further evolution of the defects.
 Ta
TaEndo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Toh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 198(4), p.786 - 803, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:25.62(Nuclear Science & Technology) I and
I and  I using ANNRI at MLF/J-PARC
I using ANNRI at MLF/J-PARCRovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Toh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*
JAEA-Conf 2023-001, p.74 - 79, 2024/02
 particle impinging on Al at 230 MeV/u
particle impinging on Al at 230 MeV/uFuruta, Toshimasa*; Uozumi, Yusuke*; Yamaguchi, Yuji; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Koba, Yusuke*; Velicheva, E.*; Kalinnikov, V.*; Tsamalaidze, Z.*; Evtoukhovitch, P.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(2), p.230 - 236, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Charged particle production from  particle fragmentation reactions was investigated experimentally by measurement of 230-MeV/u
particle fragmentation reactions was investigated experimentally by measurement of 230-MeV/u  particles bombarding an aluminum target. Double differential cross sections were measured for each ejectile of p, d, t,
particles bombarding an aluminum target. Double differential cross sections were measured for each ejectile of p, d, t,  He, and
He, and  He at laboratory angles between 15 and 60 deg. The results of analyzed data found the following common characteristics: (1) spectra of proton- and neutron-emission are similar in high energy region at forward angle, (2) triton-to-
He at laboratory angles between 15 and 60 deg. The results of analyzed data found the following common characteristics: (1) spectra of proton- and neutron-emission are similar in high energy region at forward angle, (2) triton-to- He ratio of
He ratio of  -breakup yield is 1:2, which is similar to lower incident energy experiment, and (3) the shape of broad peak formed by
-breakup yield is 1:2, which is similar to lower incident energy experiment, and (3) the shape of broad peak formed by  He and
He and  particles could be explained by the process with collision between induced
particles could be explained by the process with collision between induced  particle and target nucleus.
particle and target nucleus.
Iwamoto, Yosuke
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (137), p.54 - 61, 2024/02
The joint meeting of the Nuclear Data Workshop and the PHITS Workshop for the year 2023 was held at the Tokai-mura Industry and Information Plaza, on November 15 17, 2023. The Nuclear Data Workshop was originally organized by the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute and the Sigma Research Committee in 1978. This year, the Nuclear Science and Engineering Center is the main organizer and the author is the chairperson of the committee. The PHITS Workshop is a gathering of PHITS users and developers, where presentations are made on PHITS applications in the fields of radiation shielding, medicine, space, etc. This joint workshop was planned to provide a good opportunity to obtain new research perspectives through mutual research exchange. The meeting consisted of 14 presentations on nuclear data, 12 presentations on PHITS, and 25 poster presentations. In this report, we mainly introduce the lectures at the nuclear data workshop.
17, 2023. The Nuclear Data Workshop was originally organized by the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute and the Sigma Research Committee in 1978. This year, the Nuclear Science and Engineering Center is the main organizer and the author is the chairperson of the committee. The PHITS Workshop is a gathering of PHITS users and developers, where presentations are made on PHITS applications in the fields of radiation shielding, medicine, space, etc. This joint workshop was planned to provide a good opportunity to obtain new research perspectives through mutual research exchange. The meeting consisted of 14 presentations on nuclear data, 12 presentations on PHITS, and 25 poster presentations. In this report, we mainly introduce the lectures at the nuclear data workshop.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuya, Yusuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hirata, Yuho; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(1), p.127 - 135, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:129 Percentile:99.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) is a general-purpose Monte Carlo radiation transport code that can simulate the behavior of most particle species with energies up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ions). Its new version, PHITS3.31, was recently developed and released to the public. In the new version, the compatibility with high-energy nuclear data libraries and the algorithm of the track-structure modes have been improved. In this paper, we summarize the upgraded features of PHITS3.31 with respect to the physics models, utility functions, and application software introduced since the release of PHITS3.02 in 2017.
 Pb and
Pb and  Bi in proton-induced reactions near 100 MeV
Bi in proton-induced reactions near 100 MeVIwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Sugihara, Kenta*;  elik, Y.*; et al.
elik, Y.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 544, p.165107_1 - 165107_15, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:73.39(Instruments & Instrumentation)The lack of double-differential cross-section (DDX) data for neutron production below the incident proton energy of 200 MeV hinders the validation of spallation models in technical applications, such as research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs). The present study aims to obtain experimental DDX data for ADS spallation target materials in this energy region and identify issues related to the spallation models by comparing them with the analytical predictions. The DDXs for the (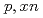 ) reactions of
) reactions of  Pb and
Pb and  Bi in the 100-MeV region were measured over an angular range of 30
Bi in the 100-MeV region were measured over an angular range of 30 to 150
to 150 using the time-of-flight method. The measurements were conducted at Kyoto University utilizing the FFAG accelerator. The DDXs obtained were compared with calculation results from Monte Carlo-based spallation models and the evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5. Comparison between the measured DDX and analytical values based on the spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library indicated that, in general, the CEM03.03 model demonstrated the closest match to the experimental values. Additionally, the comparison highlighted several issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the reproducibility of the proton-induced neutron-production DDX in the 100 MeV region by these spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library.
using the time-of-flight method. The measurements were conducted at Kyoto University utilizing the FFAG accelerator. The DDXs obtained were compared with calculation results from Monte Carlo-based spallation models and the evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5. Comparison between the measured DDX and analytical values based on the spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library indicated that, in general, the CEM03.03 model demonstrated the closest match to the experimental values. Additionally, the comparison highlighted several issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the reproducibility of the proton-induced neutron-production DDX in the 100 MeV region by these spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library.
Iwamoto, Yosuke
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (136), p.7 - 13, 2023/10
The number of displacements per atom (dpa) derived from the NRT model is used as an index of irradiation damage in structural materials of nuclear facilities. On the other hand, in 2018, Nordlund reported the results of a non-thermal recombination correction (arc) of defects derived by molecular dynamics calculations. In order to enable irradiation damage estimation (NRT-dpa and arc-dpa) of materials, we have developed a method to evaluate the irradiation damage of materials over a wide energy range using the PHITS and the nuclear data library. In order to validate the calculation method, a cryogenic irradiation apparatus was developed, and measurements of the displacement damage cross sections related to dpa for proton irradiation were performed. This report presents a presentation report at the joint session of the Nuclear Data Division and the Materials Division of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan.
Kodeli, I. A.*; Fleming, M.*; Cabellos, O.*; Leal, L.*; Celik, Y.*; Ding, Y.*; Jansky, B.*; Neudecker, D.*; Novak, E.*; Simakov, S.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.15002_1 - 15002_8, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:86.54(Nuclear Science & Technology)Working Party on International Nuclear Data Evaluation Co-operation Subgroup 47 (WPEC SG47) entitled "Use of Shielding Integral Benchmark Archive and Database for Nuclear Data Validation" was started in June 2019 with the objectives to promote more systematic and wider use of shielding benchmark experiments in nuclear data and transport code validation and development, to provide feedback on the Shielding Integral Benchmark Archive and Database (SINBAD). Complementing the database with new features was discussed, for example providing the nuclear data sensitivity profiles more systematically would facilitate and better guide the use of data, and the information on the geometry, (radiation source) and materials is expected to allow an easier and less error prone computational model preparation for different transport codes. Examples of the use and some views on future development of the SINBAD benchmark database will be presented in the paper.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01023_1 - 01023_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)For accurate prediction of neutronic characteristics for accelerator-driven systems (ADS) and a source term of spallation neutrons for reactor physics experiments for the ADS at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA), we have launched an experimental program to measure nuclear data on ADS using the Fixed Field Alternating Gradient (FFAG) accelerator at Kyoto University. As part of this program, the proton-induced double-differential thick-target neutron-yields (TTNYs) and cross-sections (DDXs) for iron, lead, and bismuth have been measured with the time-of-flight (TOF) method. For each measurement, the target was installed in a vacuum chamber on the beamline and bombarded with 107-MeV proton beams accelerated from the FFAG accelerator. Neutrons produced from the targets were detected with stacked, small-sized neutron detectors for several angles from the incident beam direction. The TOF spectra were obtained from the detected signals and the FFAG kicker magnet's logic signals, where gamma-ray events were eliminated by pulse shape discrimination. Finally, the TTNYs and DDXs were obtained from the TOF spectra by relativistic kinematics. The measured TTNYs and DDXs were compared with calculations by the Monte Carlo transport code PHITS with its default physics model of INCL version 4.6 combined with GEM and those with the JENDL-4.0/HE nuclear data library.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita*; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.05001_1 - 05001_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:70.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)In high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as Accelerator Driven System (ADS) and the spallation neutron source, it is crucial to evaluate the damage of beam-interception materials and accelerator components, such as a magnet coil. The displacement per atom (dpa) is used as a damage index, which is derived by integrating the particle flux and the displacement cross section based on the NRT model. Although the dpa is employed as the standard, the experimental data of displacement cross section are scarce for a proton in the energy region above 20 MeV. To obtain the data for superconducting materials for high-intensity accelerators and magnets, the displacement cross section of Nb for proton irradiation with a kinetic energy range between 0.4 and 3 GeV was measured. For sustaining damage in the sample, the Nb sample was cooled at a cryogenic temperature ( 8 K), where the recombination of Frenkel pairs due to thermal motion was well suppressed with maintaining the normal conductivity to maintain Matthiessen's rule. The displacement cross section of Nb was calculated using the PHITS code, and was compared with the present experimental results. It was found that the widely utilized NRT model overestimates the cross section by a factor of 2, as suggested by the previous works. It was also found that the calculation with a recently proposed athermal recombination corrected (arc) model based on Molecular Dynamics (MD) shows good agreement with the present data.
8 K), where the recombination of Frenkel pairs due to thermal motion was well suppressed with maintaining the normal conductivity to maintain Matthiessen's rule. The displacement cross section of Nb was calculated using the PHITS code, and was compared with the present experimental results. It was found that the widely utilized NRT model overestimates the cross section by a factor of 2, as suggested by the previous works. It was also found that the calculation with a recently proposed athermal recombination corrected (arc) model based on Molecular Dynamics (MD) shows good agreement with the present data.
Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Sadamatsu, Hiroki*; Araki, Shohei; Nakano, Keita; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Satoh, Daiki; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01041_1 - 01041_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Intensive fast neutron sources using deuteron accelerators have been proposed for the study of medical RI production, radiation damage for fusion reactor materials, nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste, and so on. Neutron production data from various materials bombarded by deuterons are required for the design of such neutron sources. In the present work, we have conducted a systematic measurement of double-differential neutron production cross sections (DDXs) for a wide atomic number range of targets (Li, Be, C, Al, Cu, Nb, In, Ta, and Au) at an incident energy of 200 MeV in the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP), Osaka University. A deuteron beam accelerated to 200 MeV was transported to the neutron experimental hall and focused on a thin target foil. Emitted neutrons from the target were detected by two different-size EJ301 liquid organic scintillators located at two distances of 7 m and 20 m, respectively. The neutron DDXs were measured at six angles from 0 to 25
to 25 ). The neutron energy was determined by a conventional time-of-flight (TOF) method. The measured DDXs were compared with theoretical model calculations by the DEUteron-induced Reaction Analysis Code System (DEURACS) and PHITS. The result indicated that the DEURACS calculation provides better agreement with the measured DDXs than the PHITS calculation.
). The neutron energy was determined by a conventional time-of-flight (TOF) method. The measured DDXs were compared with theoretical model calculations by the DEUteron-induced Reaction Analysis Code System (DEURACS) and PHITS. The result indicated that the DEURACS calculation provides better agreement with the measured DDXs than the PHITS calculation.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.435 - 449, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:53.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)Double-differential thick target neutron yields (TTNYs) for Fe, Pb, and Bi targets induced by 107-MeV protons were measured using the fixed-field alternating gradient accelerator at Kyoto University for research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs) and fundamental ADS reactor physics research at the Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). Note that TTNYs were obtained with the time-of-flight method using a neutron detector system comprising eight neutron detectors; each detector has a small NE213 liquid organic scintillator and photomultiplier tube. The TTNYs obtained were compared with calculation results using Monte Carlo-based spallation models (i.e., INCL4.6/GEM, Bertini/GEM, JQMD/GEM, and JQMD/SMM/GEM) and the evaluated high-energy nuclear data library, i.e., JENDL-4.0/HE, implemented in the particle and heavy iontransport code system (PHITS). All models, including JENDL-4.0/HE, failed to predict high-energy peaks at a detector angle of 5 . Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of
. Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of  20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Tsuda, Shuichi; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko
Frontiers in Energy Research (Internet), 11, p.1085264_1 - 1085264_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Energy & Fuels)This review describes experimental data useful for validation of radiation shielding design in advanced reactor systems such as nuclear fusion and accelerator-driven subcritical systems (ADS) and calculations using the PHITS code and JENDL-4.0/HE. The relevant experiments have been conducted mainly in Japan and include (1) neutron spectra in iron shields using 14 MeV neutron sources, (2) leakage neutron spectra from spherical piles of various materials using 14 MeV neutron sources, (3) neutron spectra after penetration through shields using several tens of MeV neutron sources, (4) neutron spectra produced from the target by high-energy heavy-ion bombardment, and (5) induced radioactivity in concrete using heavy-ion nuclear reaction product particles as a source. Throughout, the experimental and calculated values were agreed well. These experimental data are also useful for the validation of all radiation transport calculation codes used in the design of advanced reactor systems.
 Be(p,xn) reaction for new nuclear data library JENDL-5
Be(p,xn) reaction for new nuclear data library JENDL-5Kunieda, Satoshi; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Konno, Chikara; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Ikeda, Yujiro*
Journal of Neutron Research, 24(3-4), p.329 - 335, 2023/01
We have evaluated double-differential cross-sections (DDX) of the  Be(p,xn) reaction based on the function proposed by Wakabayashi et al. up to 12 MeV. Through compilation in the ENDF-6 format file, data processing, and neutronics analysis with MC simulation codes MCNP and PHITS to thick target yield (TTY) measurements, the function was re-confirmed to give more reasonable DDX data than those in our previous library JENDL-4.0/HE and ENDF/B-VIII.0. We finally decided to reduce the absolute cross-sections by 15% for our new nuclear data library JENDL-5 since the prediction ability of neutronics simulation was much better than that based on the original function. Through comprehensive comparisons of the simulation results on TTY at different proton energies and neutron emission angles, we conclude that JENDL-5 gives the best estimation in the world.
Be(p,xn) reaction based on the function proposed by Wakabayashi et al. up to 12 MeV. Through compilation in the ENDF-6 format file, data processing, and neutronics analysis with MC simulation codes MCNP and PHITS to thick target yield (TTY) measurements, the function was re-confirmed to give more reasonable DDX data than those in our previous library JENDL-4.0/HE and ENDF/B-VIII.0. We finally decided to reduce the absolute cross-sections by 15% for our new nuclear data library JENDL-5 since the prediction ability of neutronics simulation was much better than that based on the original function. Through comprehensive comparisons of the simulation results on TTY at different proton energies and neutron emission angles, we conclude that JENDL-5 gives the best estimation in the world.