Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Abe, Takumi; Oizumi, Akito; Nishihara, Kenji; Nakase, Masahiko*; Asano, Hidekazu*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.299 - 304, 2025/05
Currently, much research continues on stable energy sources that do not emit CO in order to achieve a carbon-neutral and sustainable society. Nuclear energy is one of the such sources, and various new reactors and reprocessing technologies are being developed. In order to implement the nuclear fuel cycle with these technologies, a nuclear fuel cycle simulator is required to quantitatively evaluate various quantities, such as the distribution of nuclear fuel materials and the scale of waste loading. For this purpose, NMB4.0 was developed in collaboration with Tokyo Institute of Technology and Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This code calculates the material balance of 179 nuclides including actinides and fission products (FPs) from the front-end to the back-end and simulates the nuclear fuel cycle in an integrated manner. Unlike other nuclear fuel cycle simulators, the code is capable of performing precise back-end analyses such as the number of radioactive wastes and the scale of the geological repository considering heat generation of waste package under diverse nuclear energy scenario, and is an open source code that runs on Microsoft Excel. By these features, it is possible to quantitatively study nuclear energy utilization strategies with various stakeholders. The presentation will detail the numerical model used in NMB4.0.
in order to achieve a carbon-neutral and sustainable society. Nuclear energy is one of the such sources, and various new reactors and reprocessing technologies are being developed. In order to implement the nuclear fuel cycle with these technologies, a nuclear fuel cycle simulator is required to quantitatively evaluate various quantities, such as the distribution of nuclear fuel materials and the scale of waste loading. For this purpose, NMB4.0 was developed in collaboration with Tokyo Institute of Technology and Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This code calculates the material balance of 179 nuclides including actinides and fission products (FPs) from the front-end to the back-end and simulates the nuclear fuel cycle in an integrated manner. Unlike other nuclear fuel cycle simulators, the code is capable of performing precise back-end analyses such as the number of radioactive wastes and the scale of the geological repository considering heat generation of waste package under diverse nuclear energy scenario, and is an open source code that runs on Microsoft Excel. By these features, it is possible to quantitatively study nuclear energy utilization strategies with various stakeholders. The presentation will detail the numerical model used in NMB4.0.
Hirohata, Atsufumi*; Lloyd, D. C.*; Kubota, Takahide*; Seki, Takeshi*; Takanashi, Koki; Sukegawa, Hiroaki*; Wen, Z.*; Mitani, Seiji*; Koizumi, Hiroki*
IEEE Access, 11, p.117443 - 117459, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.16(Computer Science, Information Systems)Okamura, Tomohiro*; Katano, Ryota; Oizumi, Akito; Nishihara, Kenji; Nakase, Masahiko*; Asano, Hidekazu*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.632 - 641, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:42.88(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Okamura explicit method (OEM) for depletion calculation was developed by modifying the matrix exponential method for dynamic nuclear fuel cycle simulation. The OEM suppressed the divergence of the calculation for short half-life nuclides, even for long time steps. The computational cost of the OEM was small, equivalent to the Euler method, and it maintained sufficient accuracy for the fuel cycle simulation.
Okamura, Tomohiro*; Nishihara, Kenji; Katano, Ryota; Oizumi, Akito; Nakase, Masahiko*; Asano, Hidekazu*; Takeshita, Kenji*
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-016, 43 Pages, 2022/03
The quantitative prediction and analysis of the future nuclear energy utilization scenarios are required in order to establish the advanced nuclear fuel cycle. However, the nuclear fuel cycle consists of various processes from front- to back-end, and it is difficult to analyze the scenarios due to the complexity of modeling and the variety of scenarios. Japan Atomic Energy Agency and Tokyo Institute of Technology have jointly developed the NMB code as a tool for integrated analysis of mass balance from natural uranium needs to radionuclide migration of geological disposal. This user manual describes how to create a database and scenario input for the NMB version 4.0.
Okamura, Tomohiro*; Katano, Ryota; Oizumi, Akito; Nishihara, Kenji; Nakase, Masahiko*; Asano, Hidekazu*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Bulletin of the Laboratory for Advanced Nuclear Energy, 6, p.29 - 30, 2022/02
Takeshita Laboratory, Tokyo Institute of Technology, has been developing Nuclear Material Balance code version 4.0 (NMB4.0) in collaboration with Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). This report summarized the outline and functions of NMB4.0.
Okamura, Tomohiro*; Katano, Ryota; Oizumi, Akito; Nishihara, Kenji; Nakase, Masahiko*; Asano, Hidekazu*; Takeshita, Kenji*
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 7, p.19_1 - 19_13, 2021/11
Nuclear Material Balance code version 4.0 (NMB4.0) has been developed through collaborative R&D between Tokyo Institute of Technology and JAEA. Conventional nuclear fuel cycle simulation codes mainly analyze actinides and are specialized for front-end mass balance analysis. However, quantitative back-end simulation has recently become necessary for considering R&D strategies and sustainable nuclear energy utilization. Therefore, NMB4.0 was developed to realize the integrated nuclear fuel cycle simulation from front- to back-end. There are three technical features in NMB4.0: 179 nuclides are tracked, more than any other code, throughout the nuclear fuel cycle; the Okamura explicit method is implemented, which contributes to reducing the numerical cost while maintaining the accuracy of depletion calculations on nuclides with a shorter half-life; and flexibility of back-end simulation is achieved. The main objective of this paper is to show the newly developed functions, made for integrated back-end simulation, and verify NMB4.0 through a benchmark study to show the computational performance.
Okamura, Tomohiro*; Oizumi, Akito; Nishihara, Kenji; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takeshita, Kenji*
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-023, 32 Pages, 2021/03
Nuclear Material Balance code (NMB code) have been developed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The NMB code will be updated with the function of mass balance analysis at the backend process such as reprocessing, vitrification and geological disposal. In order to perform its analysis with high accuracy, it is necessary to expand the number of FP nuclides calculated in the NMB code. In this study, depletion calculation by ORIGEN code was performed under 3 different burn-up conditions such as spent uranium fuel from light water reactor, and nuclides were selected from 5 evaluation indexes such as mass and heat generation. In addition, the FP nuclides required to configure a simple burnup chain with the same calculation accuracy as ORIGEN in the NMB code was selected. As the result, two lists with different number of nuclides, such as "Detailed list" and a "Simplified list", were created.
Okamura, Tomohiro*; Oizumi, Akito; Nishihara, Kenji; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Bulletin of the Laboratory for Advanced Nuclear Energy, 5, P. 31, 2021/02
The Takeshita Laboratory at Tokyo Institute of Technology has started to develop a Nuclear Material Balance code (NMB code) in collaboration with Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This report summarized the results of the joint research conducted in 2019.
Iketani, Shotaro; Yokobori, Tomohiko; Ishikawa, Joji; Yasuhara, Toshiyuki*; Kozawa, Toshiyuki*; Takaizumi, Hirohide*; Momma, Takeshi*; Kurosawa, Shingo*; Iseda, Hirokatsu; Kishimoto, Katsumi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2018-016, 46 Pages, 2018/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) adopts melting process for the waste processing and packaging method of radioactive miscellaneous solid waste in NSRI because melting process is effective in radioactivity evaluation, volume reduction, and stabilization treatment. Metal melting processing facilities, Incinerator, and Nonmetal melting processing facilities (hereinafter referred to as melting process facilities) have taken lots of safety measures, including measures for preventing the recurrence of the fire accidents. To exchange opinions and discuss the validity of these measures and so on with internal personnel and external experts, "Discussions on Melting Process Facilities" was held. As a document collection, this paper summarizes presentation materials of discussion meetings. Presentation materials describe "Outline of AVRF", "Safety measures in the melting facilities in WVRF", "Operation management of the melting facilities in WVRF", "Comparison of the past accident cases between facilities in and outside Japan and WVRF", and "Introduction of past accident cases and safety measures in other facilities from each committee".
Shudo, Yasuyuki*; Izumi, Atsushi*; Hagita, Katsumi*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Shibayama, Mitsuhiro*
Macromolecules, 51(16), p.6334 - 6343, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:43.78(Polymer Science)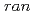 -butadiene) rubbers
-butadiene) rubbersYamaguchi, Daisuke; Yuasa, Takeshi*; Sone, Takuo*; Tominaga, Tetsuo*; Noda, Yohei*; Koizumi, Satoshi*; Hashimoto, Takeji*
Macromolecules, 50(19), p.7739 - 7759, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:53.53(Polymer Science)We elucidated the spatial distribution of filler particles in cross-linked poly(styrene-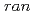 -butadiene) rubbers (SBR) developed under a typical fillers/rubbers compounding process as one of dissipative structures formed under a stress field imposed on the given system. The dispersion state of the fillers in SBR was clarified on the basis of hierarchical structures consisting of five structure levels. More specifically, it has the following characteristics depending on the specific interactions: Small, compact clusters build up compact mass-fractal structures, while large, loose clusters build up open mass-fractal structures.
-butadiene) rubbers (SBR) developed under a typical fillers/rubbers compounding process as one of dissipative structures formed under a stress field imposed on the given system. The dispersion state of the fillers in SBR was clarified on the basis of hierarchical structures consisting of five structure levels. More specifically, it has the following characteristics depending on the specific interactions: Small, compact clusters build up compact mass-fractal structures, while large, loose clusters build up open mass-fractal structures.
Ogoshi, Yurie; Satoyama, Tomonori; Kishimoto, Katsumi; Nanri, Tomohiro; Suzuki, Takeshi; Tomioka, Osamu; Takaizumi, Hirohide*; Kanno, Tomoyuki*; Maruyama, Tatsuya*
JAEA-Technology 2017-017, 152 Pages, 2017/08
At Nuclear Science Research Institute, clearance works for about 4,000 tons of extremely low-level radioactive concrete debris, which were generated from the modification activities of JRR-3 from FY 1985 to FY 1989 and stored in the waste storage facility NL, carried out. First of this clearance works, method for measuring and evaluating radioactivity concentration was approved by Minister of MEXT on July 25, 2008. And then, clearance works were started from FY 2009. Measuring and evaluating radioactivity concentration was achieved by using the approved method, and was confirmed by government. And then, clearance works were completed in FY 2014. The clearance concrete was recycled as a material for restoration works of the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake. This report summarizes the results of measuring and evaluating radioactivity concentration, achievement of confirmation by government, recycling of cleared concrete and cost for clearance works.
Onoda, Shinobu; Haruyama, Moriyoshi; Teraji, Tokuyuki*; Isoya, Junichi*; Kada, Wataru*; Hanaizumi, Osamu*; Oshima, Takeshi
Physica Status Solidi (A), 212(11), p.2641 - 2644, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:45.11(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nakamura, Tetsuya*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Sato, Shinichiro; Sugaya, Takeyoshi*; Mochizuki, Toru*; Okano, Yoshinobu*; Oshima, Takeshi
Proceedings of 11th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-11) (Internet), p.73 - 76, 2015/11
The radiation effect on GaAs p-i-n solar cells with quantum dot (QD) in the i-layer was investigated. In a previous work, we particularly noted the degradation of fill-factor (FF) for the QD cells. In this work, to clarify the reason of the FF degradation in QD cells, generation current due to low-energy proton irradiation, which we call ion beam induced current (IBIC), was observed to characterize behavior of the generated minority carrier by the protons in the depletion region where QDs are located. The energy of protons was adjusted to damage the depletion region, and decrease of generation current was measured during the proton irradiation. The results suggest that the serious degradation of FF is caused by a decrease of the carrier collection efficiency in the depletion region due to proton damage.
Haruyama, Moriyoshi; Onoda, Shinobu; Kada, Wataru*; Teraji, Tokuyuki*; Isoya, Junichi*; Oshima, Takeshi; Hanaizumi, Osamu*
Proceedings of 11th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-11) (Internet), p.184 - 187, 2015/11
Shibata, Yuichi*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Sato, Shinichiro; Oshima, Takeshi; Ooka, Sachiyo*; Takamoto, Tatsuya*
Proceedings of 11th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-11) (Internet), p.65 - 68, 2015/11
Radiation response is one of the important properties for space solar cells. It should be well understood so as to accurately predict their degradation in orbit and also to improve their radiation tolerance. Recently, a phenomenon, recovery from the radiation degradation by light soaking, on inverted metamorphic (IMM) triple-junction (3J) solar cells was found out. In this work, the light soaking annealing effects on electron irradiated IMM 3J solar cells are reported. IMM 3J solar cells irradiated with 1 MeV electrons with the fluence of 3 10
10 e
e /cm
/cm showed the recovery of open-circuit voltage, Voc, up to 43 mV after light (AM0, 1 sun) soaking of 3 hours. The increment of the electroluminescence intensity for InGaP in the IMM 3J cells due to the light soaking suggests that the Voc recovery occurs in InGaP top-cell rather than GaAs middle-cell or InGaAs bottom-cell.
showed the recovery of open-circuit voltage, Voc, up to 43 mV after light (AM0, 1 sun) soaking of 3 hours. The increment of the electroluminescence intensity for InGaP in the IMM 3J cells due to the light soaking suggests that the Voc recovery occurs in InGaP top-cell rather than GaAs middle-cell or InGaAs bottom-cell.
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Takaki, Motonobu*; Miya, Hiroyuki*; Ota, Shinsuke*; Michimasa, Shinichiro*; Shimoura, Susumu*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 6, p.030005_1 - 030005_4, 2015/06
Miyazawa, Yu*; Ikegami, Masashi*; Miyasaka, Tsutomu*; Oshima, Takeshi; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Hirose, Kazuyuki*
Proceedings of 42nd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC-42) (CD-ROM), p.1178 - 1181, 2015/06
Yamaguchi, Hiroshi*; Ijichi, Ryo*; Suzuki, Yoshiyuki*; Ooka, Sachiyo*; Shimada, Keiji*; Takahashi, Naoki*; Washio, Hidetoshi*; Nakamura, Kazuyo*; Takamoto, Tatsuya*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; et al.
Proceedings of 42nd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC-42) (CD-ROM), p.2407 - 2411, 2015/06
Kada, Wataru*; Kambayashi, Yuya*; Iwamoto, Naoya*; Onoda, Shinobu; Makino, Takahiro; Koka, Masashi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Hoshino, Norihiro*; Tsuchida, Hidekazu*; Kojima, Kazutoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 348, p.240 - 245, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:30.44(Instruments & Instrumentation)