Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Park, M.-H.*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 292, p.121061_1 - 121061_13, 2025/06
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:84.88(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dual-phase (DP) steel, composed of soft ferrite and hard martensite, offers excellent strength-ductility balance and low cost. This study found that refining the DP microstructure enhanced both yield strength and strain hardening, improving strength and ductility. Digital image correlation (DIC) revealed strain localization in ferrite, but refinement reduced strain differences between ferrite and martensite, suppressing crack initiation. More ferrite/martensite interfaces promoted plasticity in martensite via enhanced deformation constraint.  neutron diffraction showed martensite bore higher phase stress, which increased with refinement. By combining
neutron diffraction showed martensite bore higher phase stress, which increased with refinement. By combining  -DIC and neutron data, individual stress-strain curves for ferrite and martensite were constructed for the first time, explaining the strength-ductility synergy through interphase constraint. These findings offer guidance for designing heterostructured materials to overcome the strength-ductility trade-off.
-DIC and neutron data, individual stress-strain curves for ferrite and martensite were constructed for the first time, explaining the strength-ductility synergy through interphase constraint. These findings offer guidance for designing heterostructured materials to overcome the strength-ductility trade-off.
Joung, S.*; Ji, Y.-Y.*; Choi, Y.*; Lee, E.*; Ji, W.*; 佐々木 美雪; 越智 康太郎; 眞田 幸尚
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 20(4), p.P04027_1 - P04027_10, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)An airborne survey system named the MARK-A1 was previously developed to be mounted on an unmanned aerial vehicle for the purpose of application in contaminated areas with high dose rate levels. The MARK-A1 system consists of a CZT detector, signal processing unit, and positioning and interface units linked to a PC on the ground. The weight of the system is below 1 kg for loading on a commercial drone. In the current work, for experimental verification, field testing was conducted in a high dose rate environment near the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. With the cooperation of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, the MARK-A1 was installed on an unmanned aerial vehicle to conduct airborne surveys using two flight methods, namely a flat flight and a step flight, at various speeds. The airborne survey data were converted to gamma dose rates at a height of 1 m above the ground using a flat source model to create contamination maps. For a comparative evaluation of the airborne survey results, an in situ survey was also conducted in the survey area, and it was confirmed that the step flight method better matched the surface survey results.
Go, J.*; Park, M.-H.*; Gao, S.*; 松宮 久*; Gong, W.; 辻 伸泰*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1014, p.178749_1 - 178749_10, 2025/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:95.66(Chemistry, Physical)In Mg alloys, basal dislocation slip is the preferential slip system that is activated at room temperature, while non-basal slips are typically difficult to activate owing to their high critical resolved shear stress. Until now, minimal focus has been directed towards the influence of loading direction on slip behavior in pre-twinned AZ31 alloys. This study employed transmission electron microscopy to demonstrate that non-basal slips, specifically prismatic and pyramidal I slips, are activated under deformation conditions where de-twinning is difficult in a pre-twinned AZ31 Mg alloy. When the tensile loading direction is parallel to the precompression direction, de-twinning and basal slip are the primary deformation modes. Conversely, when the tensile loading direction is perpendicular to the precompression direction, where de-twinning is challenging to activate, both basal and non-basal slips, such as prismatic and pyramidal I slips, emerge as the primary deformation modes. These results indicate that the pre-twinned AZ31 Mg alloy cannot deform solely through basal slips, and the activation of either de-twinning or non-basal slips is necessary to satisfy the von Mises criterion. Our findings in this study demonstrate the impact of non-basal slip activity on macroscopic yield stress and overall deformation, hence enhancing the understanding of magnesium alloy deformation mechanisms.
古渡 意彦*; 中上 晃一*; 土方 保和*; 山下 一太*; 平井 悠太*; 松崎 賢*; 盛武 敬*; 辻 智也; Zutz, H.*; Ketelhut, S.*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, p.ncaf061_1 - ncaf061_9, 2025/00
被引用回数:0It is crucial to monitor healthcare workers' radiation exposure, especially given the increasing reliance on X-ray imaging technologies. In response to new evidence that the threshold for lens opacity is lower than previously thought, the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) has revised the annual dose limit for exposure to the lens of the eye. After the revision of the annual eye lens dose limit, the new survey on the dosemeter wearing rate was conducted in Japan. The result showed that despite the presence of monitoring protocols, the dosemeter wearing rate among healthcare workers was still low. Compliance often lacked robust verification measures, especially in smaller medical facilities. Active personal dosemeters (APDs) are commonly used in Japan, although studies suggest that they may underestimate exposure in certain settings, such as pulsed X-ray fields. Passive dosemeters, on the other hand, serve as legal dosemeters, offering a more accurate assessment of radiation exposure. This article addresses issues related to the monitoring of healthcare workers using APDs and clarifies concerns regarding the use of APDs by orthopedic surgeons during procedures involving high-dose X-ray exposure. A series of performance tests suggested that the APDs worn by orthopedic surgeons, who are often exposed to higher dose rates near patients, may underestimate radiation levels during procedures. This underestimation occurs because the surgeons are exposed to pulsed, scattered X-ray fields with energies ranging from 20 and 100 keV. The results also suggest monitoring techniques should be improved to ensure the safety of healthcare workers.
Mao, W.*; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 伊東 達矢; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 278, p.120233_1 - 120233_13, 2024/10
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:96.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using a hybrid method of in situ neutron diffraction and digital image correlation, we found that ultrafine-grained 304 stainless steel exhibits Luders deformation after yielding, in which the deformation behavior changes from a cooperation mechanism involving dislocation slip and martensitic transformation to one primarily governed by martensitic transformation, as the temperature decreases from 295 K to 77 K. Such martensitic transformation-governed Luders deformation delays the activation of plastic deformation in both the austenite parent and martensite product, resulting in delayed strain hardening. This preserves the strain-hardening capability for the later stage of deformation, thereby maintaining a remarkable elongation of 29% while achieving a high tensile strength of 1.87 GPa at 77 K.
曽我部 丞司; 石田 真也; 田上 浩孝; 岡野 靖; 神山 健司; 小野田 雄一; 松場 賢一; 山野 秀将; 久保 重信; 久保田 龍三郎*; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Fuel Cycle (GLOBAL2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
日仏協力の枠組みにおいて、タンク型ナトリウム冷却高速を対象とした過酷事故の評価手法を定義し、解析評価を実施した。
 Sn wires with and without Cu-Nb reinforcement
Sn wires with and without Cu-Nb reinforcement中本 美緒*; 菅野 未知央*; 荻津 透*; 杉本 昌弘*; 谷口 諒*; 廣瀬 清慈*; 川崎 卓郎; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 淡路 智*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 34(5), p.8400806_1 - 8400806_6, 2024/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)For an accelerator magnet, a certain mechanical strength is required to sustain against a transverse compression stress due to Lorentz force. A bronze-route Nb Sn wire with Cu-Nb reinforcement was developed by Tohoku University and Furukawa Electric to enhance the strength against axial tension. The Cu-Nb reinforcement wire also exhibited some indication of strength improvement against transverse compression; however, the details of a reinforcement mechanism for the transverse compression stress have not been clarified. In this study, the internal strains of Nb
Sn wire with Cu-Nb reinforcement was developed by Tohoku University and Furukawa Electric to enhance the strength against axial tension. The Cu-Nb reinforcement wire also exhibited some indication of strength improvement against transverse compression; however, the details of a reinforcement mechanism for the transverse compression stress have not been clarified. In this study, the internal strains of Nb Sn bronze-route wires with and without the Cu-Nb reinforcement under transverse compression stress were evaluated by neutron diffraction at BL19 (TAKUMI) in J-PARC. The samples were attached to jig with solder only at the ends and compression was applied at the center of the samples with 30-mm anvil with 5-mm wide and 8- to 15-mm high beam. Since a critical current, Ic of a superconducting wire depends on the three-dimensional strain, internal strain of Nb
Sn bronze-route wires with and without the Cu-Nb reinforcement under transverse compression stress were evaluated by neutron diffraction at BL19 (TAKUMI) in J-PARC. The samples were attached to jig with solder only at the ends and compression was applied at the center of the samples with 30-mm anvil with 5-mm wide and 8- to 15-mm high beam. Since a critical current, Ic of a superconducting wire depends on the three-dimensional strain, internal strain of Nb Sn along the axial and two orthogonal radial directions were evaluated at room temperature (RT). In the different setup, Ic measurements of the wires under transverse compression stresses were also performed at 4.2 K and 14.5 T. Using 3-mm wide anvil, the transverse compression was applied at 4.2 K or RT. The neutron diffraction results indicated no significant differences in the internal strains of Nb
Sn along the axial and two orthogonal radial directions were evaluated at room temperature (RT). In the different setup, Ic measurements of the wires under transverse compression stresses were also performed at 4.2 K and 14.5 T. Using 3-mm wide anvil, the transverse compression was applied at 4.2 K or RT. The neutron diffraction results indicated no significant differences in the internal strains of Nb Sn under transverse compression between the samples with and without Cu-Nb reinforcement, while the Ic measurements showed potential increase in the irreversible stress (
Sn under transverse compression between the samples with and without Cu-Nb reinforcement, while the Ic measurements showed potential increase in the irreversible stress (
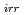 ) for Cu-Nb reinforced wires. The reason for this discrepancy was discussed based on the difference in the experimental setups for each measurement.
) for Cu-Nb reinforced wires. The reason for this discrepancy was discussed based on the difference in the experimental setups for each measurement.
Guo, B.*; Chen, H.*; Chong, Y.*; Mao, W.; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Z.*; Jonas, J. J.*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 268, p.119780_1 - 119780_11, 2024/04
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:94.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)This paper focused on the characterization and mechanism of the dynamic transformation from the alpha to beta phase during the hot deformation of Ti-6Al-4V alloy and pure titanium. The investigation employed in-situ neutron diffraction and atomistic simulations for a comprehensive understanding of the process. Dynamic transformations were observed during deformation of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy and pure titanium below the beta transus temperatures. During isothermal holding after unloading, the in-situ neutron diffraction results for Ti-6Al-4V and pure titanium indicated a sluggish reverse transformation from the beta to alpha phase. The mechanism of dynamic transformation was explored through in-situ neutron diffraction and atomistic simulations, which revealed twofold effects of deformation on dynamic transformation. Firstly, deformation led to a significant rise in the Gibbs energy of the alpha phase relative to the beta phase, expanding the beta phase region and diminishing the alpha phase region. Secondly, deformation lowered the energy barriers associated with dynamic transformation, facilitating the activation of dynamic transformation more readily than in the equilibrium state before deformation.
 complex exhibiting intermolecular proton shifting coupled spin transition
complex exhibiting intermolecular proton shifting coupled spin transitionJi, T.*; Su, S.*; Wu, S.*; 堀 優太*; 重田 育照*; Huang, Y.*; Zheng, W.*; Xu, W.*; Zhang, X.*; 鬼柳 亮嗣; et al.
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 63(25), p.e202404843_1 - e202404843_6, 2024/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)In this study, we investigated reversible intermolecular proton shifting (IPS) coupled with spin transition (ST) in a novel Fe complex. The host Fe
complex. The host Fe complex and the guest carboxylic acid anion were connected by intermolecular hydrogen bonds (IHBs). We extended the intramolecular proton transfer coupled ST phenomenon to the intermolecular system. The dynamic phenomenon was confirmed by variable-temperature single-crystal X-ray diffraction, neutron crystallography, and infrared spectroscopy.
complex and the guest carboxylic acid anion were connected by intermolecular hydrogen bonds (IHBs). We extended the intramolecular proton transfer coupled ST phenomenon to the intermolecular system. The dynamic phenomenon was confirmed by variable-temperature single-crystal X-ray diffraction, neutron crystallography, and infrared spectroscopy.
 neutron diffraction revealing the achievement of excellent combination of strength and ductility in metastable austenitic steel by grain refinement
neutron diffraction revealing the achievement of excellent combination of strength and ductility in metastable austenitic steel by grain refinementMao, W.; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 諸岡 聡; Gao, S.*; 川崎 卓郎; 辻 伸泰*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 176, p.69 - 82, 2024/03
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:59.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fe-24Ni-0.3C(wt.%)準安定オーステナイト鋼の降伏応力は、平均結晶粒径が35 m(粗粒[CG])から0.5
m(粗粒[CG])から0.5 m(超微細粒[UFG])に減少すると3.5倍(158
m(超微細粒[UFG])に減少すると3.5倍(158 551MPa)に増加したが、引張伸びは大きく維持された(0.87
551MPa)に増加したが、引張伸びは大きく維持された(0.87 0.82)。結晶粒径が力学特性と変形機構に及ぼす影響を定量的に明らかにするため、室温での引張変形中にCGとUFG Fe-24Ni-0.3C鋼のその場中性子回折測定を行った。CGとUFG試料における塑性変形の初期段階は転位すべりによって支配され、変形後期には変形誘起マルテンサイト変態(DIMT)も生じた。結晶粒の微細化により、DIMTの開始応力が大きく増加し、ひずみに関するDIMTの速度が抑制されることがわかった。結果として、(i)結晶粒微細化によりオー ステナイトが安定化し、DIMTに対して最も安定な結晶粒である
0.82)。結晶粒径が力学特性と変形機構に及ぼす影響を定量的に明らかにするため、室温での引張変形中にCGとUFG Fe-24Ni-0.3C鋼のその場中性子回折測定を行った。CGとUFG試料における塑性変形の初期段階は転位すべりによって支配され、変形後期には変形誘起マルテンサイト変態(DIMT)も生じた。結晶粒の微細化により、DIMTの開始応力が大きく増加し、ひずみに関するDIMTの速度が抑制されることがわかった。結果として、(i)結晶粒微細化によりオー ステナイトが安定化し、DIMTに対して最も安定な結晶粒である 111
111 //LD(LD:負荷方向)オーステナイト粒でのDIMTの開始が大幅に遅れた。その結果、UFG試験片の
//LD(LD:負荷方向)オーステナイト粒でのDIMTの開始が大幅に遅れた。その結果、UFG試験片の 111
111 //LDオーステナイト粒のほとんどはマルテンサイトに変態しなかった。(ii)結晶粒の微細化は、マルテンサイト変態の自己促進効果も抑制した。それにもかかわらず、UFG試験片の変態速度が低いDIMTは、CG試験片のより応力を増加させるのに効率がよく、変形中に均一な変形を維持するのに適していた。以上の現象は、UFG準安定オーステナイト鋼の優れた強度と延性の両立に相互に寄与している。
//LDオーステナイト粒のほとんどはマルテンサイトに変態しなかった。(ii)結晶粒の微細化は、マルテンサイト変態の自己促進効果も抑制した。それにもかかわらず、UFG試験片の変態速度が低いDIMTは、CG試験片のより応力を増加させるのに効率がよく、変形中に均一な変形を維持するのに適していた。以上の現象は、UFG準安定オーステナイト鋼の優れた強度と延性の両立に相互に寄与している。
上路 林太郎*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 柴田 曉伸*; 木村 勇次*; 井上 忠信*; 土田 紀之*
ISIJ International, 64(2), p.459 - 465, 2024/01
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:36.18(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT) during tensile or compressive deformations of the bainitic steels with various carbon content (0.15%C, 0.25%C, 0.62%C) was studied. In all of the bainitic steels, the tensile deformation exhibited larger work hardening than the compression. This difference indicates the suppression of the DIMT at the compression, and actually the measurements of electron back scattering diffraction (EBSD) confirmed the less reduction of retained austenite at the compression of all the bainitic steels. Additionally, the steel with the highest carbon content was examined by in situ neutron diffraction and clarified the difference similar to that obtained by the EBSD measurement. The regression of the relation between the fraction of austenite and applied strain with the conventional empirical equation revealed that the kinetic of DIMT is strongly dependent with the stress polarity, but not significantly changed by the carbon content.
土田 紀之*; Kuramoto, Shota*; 上路 林太郎*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 廣井 孝介; 河村 幸彦*
ISIJ International, 64(2), p.354 - 360, 2024/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The effects of pre-strain on the mechanical properties of high strength martensitic steels were investigated using either strain tempering (ST) or quenching and tempering (QT) samples. In the tensile tests at deformation temperatures between 296 and 573 K, the ST sample exhibited an increase in both the tensile strength (TS) and uniform elongation (U El) at 473 to 523 K, whereas the QT sample showed an increase in U El with little change in the TS and yield strength (YS). The results of in situ neutron diffraction experiments revealed an increase in the stress partitioning to the bcc phase with an increase in the deformation temperature from 296 to 523 K. The difference in the phase stress between the bcc and cementite phases decreased with an increase in the temperature due to the decrease in the cementite strength. Pre-strain of 0.5% increased the YS at 296 K with a slight work hardening; the initial dislocation density ( ) decreased at 523 K, but increased significantly after yielding, leading to a better combination of TS and U.El. The combination of pre-strain, tempering, and deformation temperatures caused the change in
) decreased at 523 K, but increased significantly after yielding, leading to a better combination of TS and U.El. The combination of pre-strain, tempering, and deformation temperatures caused the change in  before deformation and the increase in
before deformation and the increase in  after yielding of the martensitic steel.
after yielding of the martensitic steel.
Soler, J. M.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Havlov
ha, J.*; Havlov , V.*; Trpko
, V.*; Trpko ov
ov , D.*; et al.
, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 209(11), p.1765 - 1784, 2023/11
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:71.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)The REPRO-TDE test was performed at a depth of about 400 m in the ONKALO underground research facility in Finland. Synthetic groundwater containing radionuclide tracers (HTO, Cl-36, Na-22, Ba-133, Cs-134) was circulated for about four years in a packed-off interval of the injection borehole. Tracer activities were additionally monitored in two observation boreholes. The test was the subject of a modelling exercise by the SKB GWFTS Task Force. Eleven teams participated in the exercise, using different model concepts and approaches. Predictive model calculations were based on laboratory-based information concerning porosities, diffusion coefficients and sorption partition coefficients. After the experimental results were made available, the teams were able to revise their models to reproduce the observations. General conclusions from these back-analysis calculations include the need for reduced effective diffusion coefficients for Cl-36 compared to those applicable to HTO (anion exclusion), the need to implement weaker sorption for Na-22, compared to results from laboratory batch-sorption experiments, and the observation of large differences between the theoretical initial concentrations for the strongly-sorbing Ba-133 and Cs-134 and the first measured values a few hours after tracer injection. Different teams applied different concepts, concerning mainly the implementation of isotropic vs. anisotropic diffusion, or the possible existence of Borehole Disturbed Zones around the different boreholes. The role of microstructure was also addressed in two of the models.
 ders band deformation in an ultrafine grain stainless steel by combining
ders band deformation in an ultrafine grain stainless steel by combining  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation analysis
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation analysisMao, W.; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 辻 伸泰*
Scripta Materialia, 235, p.115642_1 - 115642_6, 2023/10
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:86.78(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)本研究では、巨大なリューダースバンド変形を示す超微細粒(UFG)ステンレス鋼の引張その場中性子回折とデジタル画像相関測定を行い、バンド伝播中の歪硬化に対するオーステナイト母相と変形誘起マルテンサイトの個々の寄与を評価した。定量的解析の結果、UFG構造によって流動応力が大幅に増加した場合、オーステナイト母相のひずみ硬化は均一な変形を維持するには不十分であることがわかった。リューダースバンドの伝播に必要なひずみ硬化は、マルテンサイトの形成とその内部の高い内部応力によってもたらされた。
Mao, W.; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; Bai, Y.*; Harjo, S.; Park, M.-H.*; 柴田 曉伸*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 256, p.119139_1 - 119139_16, 2023/09
被引用回数:36 パーセンタイル:98.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)変形誘起塑性(TRIP)鋼は、変形誘起マルテンサイト変態(DIMT)に伴う加工硬化率の向上により、強度と延性の優れた組み合わせを示す。TRIP鋼や合金の加工硬化挙動におけるDIMTの役割を定量的に評価することは、強度と延性の両立を可能にする先進材料を設計するための指針を与えるが、変形中に相組成が変化し続け、応力と塑性ひずみの両方が構成相間で動的に分配されるため、その評価は困難である。本研究では、Fe-24Ni-0.3C(wt.%)TRIPオーステナイト鋼の引張変形とその場中性子回折測定を行った。中性子回折測定による応力分割と相分割に基づく解析手法を提案し、試験片の引張流動応力と加工硬化率を、オーステナイト母相,変形誘起マルテンサイト、DIMT変態速度に関連する因子に分解し、試料の加工硬化挙動における各因子の役割を考察した。さらに、回折プロファイル解析により測定した転位密度を用いてオーステナイトとマルテンサイト間の塑性ひずみ分配を間接的に推定し、材料中のオーステナイトとマルテンサイト間の応力・ひずみ分配の全体像を構築した。その結果、変形誘起マルテンサイト変態速度とマルテンサイトが負担する相応力の両方が、材料の全体的な引張特性に重要な役割を果たしていることが示唆された。提案した分解解析法は、TRIP現象を示す多相合金の機械的挙動を調べるために広く適用できる可能性がある。
民井 淳*; Pellegri, L.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; 稲倉 恒法*; Khan, E.*; 木戸 英治*; 木村 真明*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; 稲倉 恒法*; Khan, E.*; 木戸 英治*; 木村 真明*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 59(9), p.208_1 - 208_21, 2023/09
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:83.85(Physics, Nuclear)光核反応は原子核構造の観点からも応用の観点からも重要であるにも関わらず、その反応断面積は未だに不定性が大きい。近年、超高エネルギー宇宙線の起源を探るために、鉄よりも軽い原子核の光核反応断面積を正確に知る必要が指摘されている。この状況を打破するため、原子核物理の実験、理論、宇宙物理の共同研究となるPANDORAプロジェクトが始まった。本論文はその計画の概要をまとめたものである。原子核実験ではRCNP、iThembaによる仮想光子実験とELI-NPによる実光子実験などが計画されている。原子核理論では、乱雑位相近似計算、相対論的平均場理論、反対称化分子動力学、大規模殻模型計算などが計画されている。これらで得られた信頼性の高い光核反応データベースと宇宙線伝搬コードを組み合わせ、超高エネルギー宇宙線の起源の解明に挑む。
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionGong, W.; Harjo, S.; 友田 陽*; 諸岡 聡; 川崎 卓郎; 柴田 曉伸*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 250, p.118860_1 - 118860_16, 2023/05
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:90.83(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Martensitic transformation is accompanied by the generation of microscale and macroscale internal stresses during cooling below the martensitic transformation start temperature. These internal stresses have been determined through X-ray or neutron diffraction, but the reported results are not consistent, probably because the measured lattice parameter is influenced not only by the internal stress but also by several factors, including solute elements and crystal defects. Therefore,  neutron diffraction combined with dilatometry measurements during martensitic transformation and subsequent cyclic tempering were performed for an Fe-18Ni alloy. The phase strains calculated by lattice parameter variations show that a hydrostatic compressive strain in austenite and a tensile strain in martensite arose as the martensitic transformation progressed during continuous cooling or isothermal holding. However, the phase stresses of austenite and martensite estimated from these strains failed to hold stress balance law when dense crystal defects involved in the processes. After these crystal defects were removed by appropriate tempering, the stress balance law held well. Meanwhile, the phase stresses of austenite and martensite were changed to opposite, revealing their true identity. Various crystal defects in austenite and martensite, introduced by plastic accommodation, were suggested to affect their lattice parameters and then their phase stresses.
neutron diffraction combined with dilatometry measurements during martensitic transformation and subsequent cyclic tempering were performed for an Fe-18Ni alloy. The phase strains calculated by lattice parameter variations show that a hydrostatic compressive strain in austenite and a tensile strain in martensite arose as the martensitic transformation progressed during continuous cooling or isothermal holding. However, the phase stresses of austenite and martensite estimated from these strains failed to hold stress balance law when dense crystal defects involved in the processes. After these crystal defects were removed by appropriate tempering, the stress balance law held well. Meanwhile, the phase stresses of austenite and martensite were changed to opposite, revealing their true identity. Various crystal defects in austenite and martensite, introduced by plastic accommodation, were suggested to affect their lattice parameters and then their phase stresses.
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction studyGong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Zheng, R.*; 眞山 剛*; Sun, B.*; 相澤 一也; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
Scripta Materialia, 225, p.115161_1 - 115161_5, 2023/03
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:58.32(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Deformation behavior during uniaxial compression at 21 K and 298 K in a commercial AZ31 magnesium alloy was studied by  neutron diffraction. Decreasing the deformation temperature resulted in a slight increase in yield stress (115 MPa
neutron diffraction. Decreasing the deformation temperature resulted in a slight increase in yield stress (115 MPa  139 MPa), but a remarkable enhancement in both the fracture stress (365 MPa
139 MPa), but a remarkable enhancement in both the fracture stress (365 MPa  551 MPa) and fracture strain (12.8%
551 MPa) and fracture strain (12.8%  16.5%). The low temperature sensitivity of the {10
16.5%). The low temperature sensitivity of the {10 2} extension twinning which governed the macroscopic yielding led to the slight increase in yield stress. At 21K, basal slip was suppressed, while the extension twinning was promoted resulted in higher twin volume fraction. In the late stage of deformation, the {10
2} extension twinning which governed the macroscopic yielding led to the slight increase in yield stress. At 21K, basal slip was suppressed, while the extension twinning was promoted resulted in higher twin volume fraction. In the late stage of deformation, the {10 1}-{10
1}-{10 2} double twinning was suppressed, which is considered to be the reason to delay the fracture at 21 K.
2} double twinning was suppressed, which is considered to be the reason to delay the fracture at 21 K.
 phase to
phase to  phase in zirconium alloy revealed by in-situ neutron diffraction during high temperature deformation
phase in zirconium alloy revealed by in-situ neutron diffraction during high temperature deformationGuo, B.*; Mao, W.; Chong, Y.*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Chen, H.*; Jonas, J. J.*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 242, p.118427_1 - 118427_11, 2023/01
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:68.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dynamic transformation from alpha (HCP) to beta (BCC) phase in a zirconium alloy was revealed by the use of in-situ neutron diffraction during hot compression. The dynamic transformation was unexpectedly detected during isothermal compression at temperatures of 900 C and 950
C and 950 C (alpha + beta two-phase region) and strain rates of 0.01 s
C (alpha + beta two-phase region) and strain rates of 0.01 s and 0.001 s
and 0.001 s , even though equilibrium two-phase states were achieved prior to the hot compression. Dynamic transformation was accompanied by diffusion of Sn from beta to alpha phase, which resulted in changes of lattice parameters and a characteristic microstructure of alpha grains. The details of dynamic transformation are discussed using the evolution of lattice constants.
, even though equilibrium two-phase states were achieved prior to the hot compression. Dynamic transformation was accompanied by diffusion of Sn from beta to alpha phase, which resulted in changes of lattice parameters and a characteristic microstructure of alpha grains. The details of dynamic transformation are discussed using the evolution of lattice constants.
土田 紀之*; 上路 林太郎*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.
Scripta Materialia, 222, p.115002_1 - 115002_6, 2023/01
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:53.94(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The present study investigated the tensile deformation behavior of quenched and tempered martensite steels at various austenitization and tempering temperatures using in situ neutron diffraction experiments. Phase lattice strains in the bcc and cementite ( ) phases and dislocation structures in the bcc phase were analyzed. The phase lattice strain in bcc became almost stagnant after yielding as the tempering temperature increased. The phase lattice strain in
) phases and dislocation structures in the bcc phase were analyzed. The phase lattice strain in bcc became almost stagnant after yielding as the tempering temperature increased. The phase lattice strain in  increased linearly with an increase in the flow stress, independent of the austenitization and tempering temperatures. The stress partitioning between bcc and
increased linearly with an increase in the flow stress, independent of the austenitization and tempering temperatures. The stress partitioning between bcc and  was confirmed after the yielding of bcc, which contributed to the work hardening. The phase stresses of bcc and
was confirmed after the yielding of bcc, which contributed to the work hardening. The phase stresses of bcc and  and their stress partitioning improve the mechanical properties of martensite steels, which can be summarized by the systematic changes in phase lattice strain and dislocation properties due to the austenitization and tempering temperatures.
and their stress partitioning improve the mechanical properties of martensite steels, which can be summarized by the systematic changes in phase lattice strain and dislocation properties due to the austenitization and tempering temperatures.