Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Song, Y.*; Xu, S.*; 佐藤 駿介*; Lee, I.*; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 長迫 実*; 川崎 卓郎; 鬼柳 亮嗣; Harjo, S.; et al.
Nature, 638, p.965 - 971, 2025/02
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:94.96(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In advanced applications like aerospace and space exploration, materials must balance lightness, functionality, and extreme thermal fluctuation resistance. Shape-memory alloys show promise with strength, toughness, and substantial strain recovery due to superelasticity, but maintaining low mass and effective operation at cryogenic temperatures is challenging. We hereby introduce a novel shape-memory alloy that adheres to these stringent criteria. Predominantly composed of Ti and Al with a chemical composition of Ti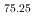 Al
Al Cr
Cr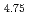 , this alloy 25 is characterized by a low density (4.36
, this alloy 25 is characterized by a low density (4.36 10
10 kg/m
kg/m ) and a high specific strength (185
) and a high specific strength (185 10
10 Pa
Pa m
m /kg) at room temperature, while exhibiting excellent superelasticity. The superelasticity, owing to a reversible stress-induced phase transformation from an ordered body-centered cubic parent phase to an ordered orthorhombic martensite, allows for a recoverable strain exceeding 7%. Remarkably, this functionality persists across a broad range of temperatures, from deep cryogenic 4.2 K to above room temperature, arising from an unconventional temperature dependence of transformation stresses. Below a certain threshold during cooling, the critical transformation stress inversely correlates with temperature. We interpret this behavior from the perspective of a temperature-dependent anomalous lattice instability of the parent phase. This alloy holds potential in everyday appliances requiring flexible strain accommodations, as well as components designed for extreme environmental conditions such as deep space and liquefied gases.
/kg) at room temperature, while exhibiting excellent superelasticity. The superelasticity, owing to a reversible stress-induced phase transformation from an ordered body-centered cubic parent phase to an ordered orthorhombic martensite, allows for a recoverable strain exceeding 7%. Remarkably, this functionality persists across a broad range of temperatures, from deep cryogenic 4.2 K to above room temperature, arising from an unconventional temperature dependence of transformation stresses. Below a certain threshold during cooling, the critical transformation stress inversely correlates with temperature. We interpret this behavior from the perspective of a temperature-dependent anomalous lattice instability of the parent phase. This alloy holds potential in everyday appliances requiring flexible strain accommodations, as well as components designed for extreme environmental conditions such as deep space and liquefied gases.
伊東 達矢; Xu, S.*; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 貝沼 亮介*
Shape Memory and Superelasticity, 9 Pages, 2025/00
The microstructure, crystal structures, cold workability, and martensitic transformation temperatures of several Cu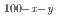 Mn
Mn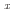 Al
Al (40
(40 
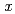
 55; 10
55; 10 
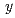
 13; at%) alloys were analyzed. For the first time, martensitic transformation was revealed Mn-rich Cu-Mn-Al alloys. The surface relief of the martensite phase reversibly appeared and disappeared during cooling and heating, along with small thermal hysteresis, implying a thermoelastic transformation. The crystal structures of the parent and martensite phases are B2 and 2M(BCT), respectively, with c
13; at%) alloys were analyzed. For the first time, martensitic transformation was revealed Mn-rich Cu-Mn-Al alloys. The surface relief of the martensite phase reversibly appeared and disappeared during cooling and heating, along with small thermal hysteresis, implying a thermoelastic transformation. The crystal structures of the parent and martensite phases are B2 and 2M(BCT), respectively, with c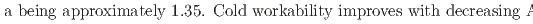 Mn
Mn Al
Al (at%) sample. This alloy demonstrates moderate cold workability and cost-effectiveness, exhibiting potential as an alternative for conventional shape memory alloys in various applications.
(at%) sample. This alloy demonstrates moderate cold workability and cost-effectiveness, exhibiting potential as an alternative for conventional shape memory alloys in various applications.
今富 大介*; 石川 遼典*; 仲田 玲*; 伊東 達矢; Han, K.*; 長迫 実*; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 貝沼 亮介*
Journal of Phase Equilibria and Diffusion, 45(1), p.3 - 17, 2024/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:11.66(Chemistry, Physical)Mn-Zn二元系における相平衡を、組成分析、結晶構造解析、熱分析により実験的に決定した。これまでの報告と比較し、 相、
相、 相、
相、 相の存在領域に違いが見られた。
相の存在領域に違いが見られた。 相の領域から急冷した試料で
相の領域から急冷した試料で Mn相と同じ不規則な体心立方構造が確認されたため、
Mn相と同じ不規則な体心立方構造が確認されたため、 -B2の単相域は確認できなかった。先行研究において、
-B2の単相域は確認できなかった。先行研究において、 相が
相が ,
, ,
,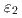 相に分離しているかどうかが論争になっていきたが、拡散対といくつかの合金組成の調査により、
相に分離しているかどうかが論争になっていきたが、拡散対といくつかの合金組成の調査により、 相、
相、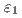 相、
相、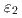 相は分離しておらず、単一の
相は分離しておらず、単一の 相となっていることが示された。さらに、熱分析によって対応する不変系反応が検出されなかったことから、
相となっていることが示された。さらに、熱分析によって対応する不変系反応が検出されなかったことから、 相はZn過剰領域には存在しない。
相はZn過剰領域には存在しない。
 MnGaメタ磁性形状記憶合金の開発
MnGaメタ磁性形状記憶合金の開発伊東 達矢; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 貝沼 亮介*
物性研だより, 63(3), p.8 - 10, 2023/10
メタ磁性形状記憶合金は磁場により駆動することが出来る形状記憶合金であり、センサーやアクチュエーター等での応用が期待されている。しかし、これまでに開発されてきた合金系ではマルテンサイト変態に伴うエネルギーロスが大きいという問題点があった。近年、我々の研究グループではPd MnGa合金において初めて相変態によるエネルギーロスの小さなメタ磁性形状記憶合金を発見した。本稿ではその内容を紹介する。
MnGa合金において初めて相変態によるエネルギーロスの小さなメタ磁性形状記憶合金を発見した。本稿ではその内容を紹介する。
Xu, X.*; 大平 拓実*; Xu, S.*; 平田 研二*; 大森 俊洋*; 植木 洸輔*; 上田 恭介*; 成島 尚之*; 長迫 実*; 貝沼 亮介*; et al.
Advanced Materials & Processes, 180(7), p.35 - 37, 2022/10
Metallic biomaterials are widely used to replace or support failing hard tissues due to excellent mechanical properties and high wear resistance, with demand increasing as the global population continues to age. It is widely accepted that successful metallic biomaterials should have good biocompatibility, high corrosion resistance, and strong wear resistance. In addition, a low Young's modulus similar to human bone is now recognized as another important factor, in order to avoid bone atrophy due to the stress shielding effect. While the Young's modulus of stainless steels and conventional fcc CoCr alloys is as high as 190-240 GPa, for  -type Ti-base alloys it is generally in the range of 50-80 GPa. Young's modulus values are as low as 35 GPa for Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr, close to that of human bone at approximately 10-30 GPa. However, Ti-base alloys come with the compromise of low wear resistance. In fact, alloys that feature a low Young's modulus along with high wear resistance have been difficult to realize. This article explores the recently developed bcc CoCr-base alloy Co-Cr-Al-Si as a potential solution to these issues, i.e., the difficulty in combining a low Young's modulus with high wear resistance, and the challenge of realizing large superelastic strains.
-type Ti-base alloys it is generally in the range of 50-80 GPa. Young's modulus values are as low as 35 GPa for Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr, close to that of human bone at approximately 10-30 GPa. However, Ti-base alloys come with the compromise of low wear resistance. In fact, alloys that feature a low Young's modulus along with high wear resistance have been difficult to realize. This article explores the recently developed bcc CoCr-base alloy Co-Cr-Al-Si as a potential solution to these issues, i.e., the difficulty in combining a low Young's modulus with high wear resistance, and the challenge of realizing large superelastic strains.
Xu, S.*; 大平 拓実*; 佐藤 駿介*; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Seiner, H.*; Zoubkov , K.*; 村上 恭和*; et al.
, K.*; 村上 恭和*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.5307_1 - 5307_8, 2022/09
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:82.31(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Crystalline metals can have large theoretical elastic strain limits. However, a macroscopic block of conventional crystalline metals practically suffers a very limited elastic deformation of  0.5% with a linear stress-strain relationship obeying Hooke's law. Here, we report on the experimental observation of a large tensile elastic deformation with an elastic strain of
0.5% with a linear stress-strain relationship obeying Hooke's law. Here, we report on the experimental observation of a large tensile elastic deformation with an elastic strain of  4.3% in a Cu-based single crystalline alloy at its bulk scale at room temperature. The large macroscopic elastic strain that originates from the reversible lattice strain of a single phase is demonstrated by in situ microstructure and neutron diffraction observations. Furthermore, the elastic reversible deformation, which is nonhysteretic and quasilinear, is associated with a pronounced elastic softening phenomenon. The increase in the stress gives rise to a reduced Young's modulus, unlike the traditional Hooke's law behaviour. The experimental discovery of a non-Hookean large elastic deformation offers the potential for the development of bulk crystalline metals as high-performance mechanical springs or for new applications via "elastic strain engineering."
4.3% in a Cu-based single crystalline alloy at its bulk scale at room temperature. The large macroscopic elastic strain that originates from the reversible lattice strain of a single phase is demonstrated by in situ microstructure and neutron diffraction observations. Furthermore, the elastic reversible deformation, which is nonhysteretic and quasilinear, is associated with a pronounced elastic softening phenomenon. The increase in the stress gives rise to a reduced Young's modulus, unlike the traditional Hooke's law behaviour. The experimental discovery of a non-Hookean large elastic deformation offers the potential for the development of bulk crystalline metals as high-performance mechanical springs or for new applications via "elastic strain engineering."
大平 拓実*; Xu, S.*; 平田 研二*; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 植木 洸輔*; 上田 恭介*; 成島 尚之*; 長迫 実*; Harjo, S.; et al.
Advanced Materials, 34(27), p.2202305_1 - 2202305_11, 2022/07
被引用回数:30 パーセンタイル:91.45(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The demand for biomaterials has been increasing along with the increase in the population of elderly people worldwide. The mechanical properties and high wear resistance of metallic biomaterials makes them well-suited for use as substitutes or as support for damaged hard tissues. However, unless these biomaterials also have a low Young's modulus similar to that of human bones, bone atrophy inevitably occurs. Because a low Young's modulus is typically associated with poor wear resistance, it is difficult to realize a low Young's modulus and high wear resistance simultaneously. Also, the superelastic property of shape memory alloys makes them suitable for biomedical applications, like vascular stents and guide wires. However, due to the low recoverable strain of conventional biocompatible shape memory alloys, the demand for a new alloy system is high. The novel body-center-cubic cobalt-chromium-based alloys in this paper provide a solution to both of these problems. We believe our novel alloys are promising candidates for biomedical applications.
大沼 郁雄*; 貝沼 亮介*; 宇田 実*; 岩立 孝治*; 内田 宗範*; 河村 弘; 石田 清仁*
JAERI-Conf 2004-006, p.172 - 183, 2004/03
先進中性子増倍材料として期待されているベリリウム金属間化合物について、特にBe-Ti, Be-Vの2元系状態図について研究した。中性子増倍材料として実用可能な高Be側(Be-5 23at%Ti,Be-5
23at%Ti,Be-5 25at%V)の試料をアーク溶解法で作成し、1200
25at%V)の試料をアーク溶解法で作成し、1200 1450
1450 Cにて熱処理したものについて、電子プローブマイクロアナライザ(EPMA)を用いて生成する相を詳細に固定した。その結果、今まで不明であった特にBe-rich側での同系の状態図を明らかにした。
Cにて熱処理したものについて、電子プローブマイクロアナライザ(EPMA)を用いて生成する相を詳細に固定した。その結果、今まで不明であった特にBe-rich側での同系の状態図を明らかにした。
今富 大介*; 石川 遼典*; 仲田 玲*; 伊東 達矢; Han, K.*; 長迫 実*; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 貝沼 亮介*
no journal, ,
高Mn鋼への亜鉛めっき処理において界面反応の理解のためにFe-Mn-Zn状態図の決定が必要不可欠である。そこで本研究ではまず基本となるMn-Zn二元系状態図について決定した。
清水 来紀*; Xu, X.*; 伊東 達矢; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 大森 俊洋*; 貝沼 亮介*
no journal, ,
Co-Cr-Al-Si合金は約15%程度の超弾性回復ひずみを有するが、応力誘起マルテンサイト変態開始時の過剰な応力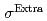 が超弾性疲労特性を劣化させる可能性がある。本研究では中性子回折により
が超弾性疲労特性を劣化させる可能性がある。本研究では中性子回折により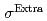 の起源を調査する。
の起源を調査する。