Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 TaS
TaS
Park, P.*; Cho, W.*; Kim, C.*; An, Y.*; Avdeev, M.*; 飯田 一樹*; 梶本 亮一; Park, J.-G.*
Physical Review B, 109(6), p.L060403_1 - L060403_7, 2024/02
Spontaneous Hall conductivity has recently been reported in the triangular lattice antiferromagnet Co TaS
TaS under a zero magnetic field. This phenomenon originates from the distinctive noncoplanar triple-
under a zero magnetic field. This phenomenon originates from the distinctive noncoplanar triple-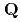 magnetic ground state, possessing uniform real-space Berry curvature characterized by scalar spin chirality. We investigated the physical properties of Co
magnetic ground state, possessing uniform real-space Berry curvature characterized by scalar spin chirality. We investigated the physical properties of Co TaS
TaS by judiciously controlling the composition, revealing a drastic change in its bulk properties, even by slight variations in cobalt composition, despite the same crystal structure. For
by judiciously controlling the composition, revealing a drastic change in its bulk properties, even by slight variations in cobalt composition, despite the same crystal structure. For 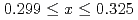 , Co
, Co TaS
TaS keeps all the characteristics of the ground state consistent with the previous studies --- two antiferromagnetic phase transitions at
keeps all the characteristics of the ground state consistent with the previous studies --- two antiferromagnetic phase transitions at 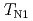 and
and 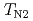 (
(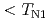 ), a large spontaneous Hall conductivity [
), a large spontaneous Hall conductivity [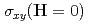 ], and a weak ferromagnetic moment along the
], and a weak ferromagnetic moment along the  axis. However, samples with
axis. However, samples with 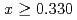 exhibit distinct bulk properties, including the absence of both
exhibit distinct bulk properties, including the absence of both 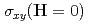 and the weak ferromagnetic moment. Our neutron diffraction data reveal that Co
and the weak ferromagnetic moment. Our neutron diffraction data reveal that Co TaS
TaS with
with 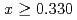 develops coplanar helical magnetic order with
develops coplanar helical magnetic order with 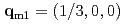 . This is entirely different from what has been seen in
. This is entirely different from what has been seen in 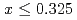 , explaining the observed composition dependence.
, explaining the observed composition dependence.
 Sn
Sn
Huang, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Ye, H.*; Bao, S.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Liao, J.*; Cao, S.*; 梶本 亮一; 池内 和彦*; Deng, G.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 109(1), p.014434_1 - 014434_9, 2024/01
被引用回数:0TbMn Sn
Sn is a correlated topological magnet with a Mn-based kagome lattice, in which a Chern gap opens at the Dirac point at low temperatures. The magnetic moment direction of the ferrimagnetic order changes from in the kagome plane to the out-of-plane upon cooling, which is essential for generating the Chern gap, but the underlying mechanism for the spin reorientation remains elusive. Here, we investigate the spin-reorientation transition in TbMn
is a correlated topological magnet with a Mn-based kagome lattice, in which a Chern gap opens at the Dirac point at low temperatures. The magnetic moment direction of the ferrimagnetic order changes from in the kagome plane to the out-of-plane upon cooling, which is essential for generating the Chern gap, but the underlying mechanism for the spin reorientation remains elusive. Here, we investigate the spin-reorientation transition in TbMn Sn
Sn using neutron scattering. We provide direct evidence for the spin-reorientation transition and unveil the coexistence of two Tb modes at 200 K. To account for these results, we put forward a model based on SU(N) spin-wave theory, in which there is a temperature evolution of the ground state Tb
using neutron scattering. We provide direct evidence for the spin-reorientation transition and unveil the coexistence of two Tb modes at 200 K. To account for these results, we put forward a model based on SU(N) spin-wave theory, in which there is a temperature evolution of the ground state Tb 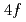 orbitals, driven by the crystalline electric field, single-ion anisotropy, and exchange interactions between Tb and Mn ions. Our findings shed light on the complex magnetism of TbMn
orbitals, driven by the crystalline electric field, single-ion anisotropy, and exchange interactions between Tb and Mn ions. Our findings shed light on the complex magnetism of TbMn Sn
Sn , despite its relatively simple ground state magnetic structure, and provide insights into the mechanisms for tuning magnetic topological materials.
, despite its relatively simple ground state magnetic structure, and provide insights into the mechanisms for tuning magnetic topological materials.
 TaS
TaS
Park, P.*; Cho, W.*; Kim, C.*; An, Y.*; Kang, Y.-G.*; Avdeev, M.*; Sibille, R.*; 飯田 一樹*; 梶本 亮一; Lee, K. H.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.8346_1 - 8346_9, 2023/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The triangular lattice antiferromagnet (TLAF) has been the standard paradigm of frustrated magnetism for several decades. The most common magnetic ordering in insulating TLAFs is the 120 structure. However, a new triple-
structure. However, a new triple-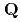 chiral ordering can emerge in metallic TLAFs, representing the short wavelength limit of magnetic skyrmion crystals. We report the metallic TLAF Co
chiral ordering can emerge in metallic TLAFs, representing the short wavelength limit of magnetic skyrmion crystals. We report the metallic TLAF Co TaS
TaS as the first example of tetrahedral triple-
as the first example of tetrahedral triple-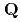 magnetic ordering with the associated topological Hall effect (non-zero
magnetic ordering with the associated topological Hall effect (non-zero 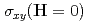 ). We also present a theoretical framework that describes the emergence of this magnetic ground state, which is further supported by the electronic structure measured by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Additionally, our measurements of the inelastic neutron scattering cross section are consistent with the calculated dynamical structure factor of the tetrahedral triple-
). We also present a theoretical framework that describes the emergence of this magnetic ground state, which is further supported by the electronic structure measured by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Additionally, our measurements of the inelastic neutron scattering cross section are consistent with the calculated dynamical structure factor of the tetrahedral triple-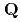 state.
state.
Bao, S.*; Gu, Z.-L.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, B.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Wang, W.*; 梶本 亮一; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.6093_1 - 6093_9, 2023/09
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:61.99(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Magnon polarons are novel elementary excitations possessing hybrid magnonic and phononic signatures, and are responsible for many exotic spintronic and magnonic phenomena. Despite long-term sustained experimental efforts in chasing for magnon polarons, direct spectroscopic evidence of their existence is hardly observed. Here, we report the direct observation of magnon polarons using neutron spectroscopy on a multiferroic Fe Mo
Mo O
O possessing strong magnon-phonon coupling. Specifically, below the magnetic ordering temperature, a gap opens at the nominal intersection of the original magnon and phonon bands, leading to two separated magnon-polaron bands. Each of the bands undergoes mixing, interconverting and reversing between its magnonic and phononic components. We attribute the formation of magnon polarons to the strong magnon-phonon coupling induced by Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction. Intriguingly, we find that the band-inverted magnon polarons are topologically nontrivial. These results uncover exotic elementary excitations arising from the magnon-phonon coupling, and offer a new route to topological states by considering hybridizations between different types of fundamental excitations.
possessing strong magnon-phonon coupling. Specifically, below the magnetic ordering temperature, a gap opens at the nominal intersection of the original magnon and phonon bands, leading to two separated magnon-polaron bands. Each of the bands undergoes mixing, interconverting and reversing between its magnonic and phononic components. We attribute the formation of magnon polarons to the strong magnon-phonon coupling induced by Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction. Intriguingly, we find that the band-inverted magnon polarons are topologically nontrivial. These results uncover exotic elementary excitations arising from the magnon-phonon coupling, and offer a new route to topological states by considering hybridizations between different types of fundamental excitations.
 Ti
Ti O
O single crystals
single crystals高濱 隆成*; 有薗 実駿*; 犬童 代梧*; 吉永 汰正*; 寺倉 千恵子*; 竹下 直*; 白崎 巧*; 野田 正亮*; 桑原 英樹*; 梶本 亮一; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 38, p.011114_1 - 011114_6, 2023/05
We investigated the transport and magnetic properties of single crystals of the pseudobrookite Al Ti
Ti O
O for
for 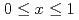 grown using a floating zone. We found a correlation of spin-singlet Ti
grown using a floating zone. We found a correlation of spin-singlet Ti -Ti
-Ti dimers even in the conductive
dimers even in the conductive  and
and  phases which develops with increasing
phases which develops with increasing  . The development of the dimer correlation suppresses the magnetic susceptibility at the low temperature and enhances the electric conductivity perhaps due to the suppression of the magnetic scattering at the isolated Ti
. The development of the dimer correlation suppresses the magnetic susceptibility at the low temperature and enhances the electric conductivity perhaps due to the suppression of the magnetic scattering at the isolated Ti ions. The compound shows the best conductivity in the
ions. The compound shows the best conductivity in the  phase near the phase boundary between the
phase near the phase boundary between the  and
and  phases where the dimer correlation is much developed. Some exotic conductive state may be realized under the background of fluctuation of the spin-singlet dimer in the
phases where the dimer correlation is much developed. Some exotic conductive state may be realized under the background of fluctuation of the spin-singlet dimer in the  phase near the phase boudary.
phase near the phase boudary.
 He position-sensitive detector system
He position-sensitive detector system佐藤 節夫*; 梶本 亮一; 稲村 泰弘
Journal of Neutron Research, 24(3-4), p.427 - 434, 2023/01
In many neutron scattering experiments,  He-gas position-sensitive detectors (PSDs) are employed to obtain high-quality data. However, the exact position where a neutron is detected cannot be determined if two or more neutrons are simultaneously captured at different positions. This results in noise and degrades the quality of the data. In particular, such noise is a serious source of spurious scattering in inelastic neutron scattering instruments equipped with a large number of long PSDs recently developed at pulsed neutron sources. Herein, we introduce a pulse-width-discriminating PSD system that monitors the pulse width and height of the collected data. The system utilizes previously developed neutron-readout boards and removes instances of two or more simultaneous captures from the data to significantly improve the performance of PSDs. We also propose a new program to monitor the pulse width from PSD data using a hardware function implemented for other purposes. We confirm that the noise decreases to a level almost equal to that of the background. Although the developed program is applied to an inelastic scattering experiment, it is applicable to other types of experiments in which mispositioned signals should be eliminated as noise.
He-gas position-sensitive detectors (PSDs) are employed to obtain high-quality data. However, the exact position where a neutron is detected cannot be determined if two or more neutrons are simultaneously captured at different positions. This results in noise and degrades the quality of the data. In particular, such noise is a serious source of spurious scattering in inelastic neutron scattering instruments equipped with a large number of long PSDs recently developed at pulsed neutron sources. Herein, we introduce a pulse-width-discriminating PSD system that monitors the pulse width and height of the collected data. The system utilizes previously developed neutron-readout boards and removes instances of two or more simultaneous captures from the data to significantly improve the performance of PSDs. We also propose a new program to monitor the pulse width from PSD data using a hardware function implemented for other purposes. We confirm that the noise decreases to a level almost equal to that of the background. Although the developed program is applied to an inelastic scattering experiment, it is applicable to other types of experiments in which mispositioned signals should be eliminated as noise.
Wu, P.*; 村井 直樹; Li, T.*; 梶本 亮一; 中村 充孝; 古府 麻衣子; 中島 健次; Xia, K.*; Peng, K.*; Zhang, Y.*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 25(1), p.013032_1 - 013032_11, 2023/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The understanding of the lattice dynamics is essential for engineering the thermal transport properties in quantum materials. Based on the canonical point of view, acoustic phonons are believed to be the principal thermal carriers in heat flow. Here, in this work, optical phonons are elucidated to play a pivotal role in determining the lattice thermal conductivity in thermoelectric material SnS by using the state-of-the-art inelastic neutron scattering technique combined with first-principles calculations. Additionally, in contrast to acoustic phonons, optical phonons are observed to exhibit pronounced softening and broadening with temperature. Our observations not only shed light on the significance of the optical phonons in thermal transport but also provide a vital clue to suppress the propagation of optical phonons to optimize the thermoelectric performance of SnS.
梶本 亮一; 中村 充孝; 蒲沢 和也*; 稲村 泰弘; 飯田 一樹*; 池内 和彦*; 石角 元志*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 272, p.02007_1 - 02007_8, 2022/11
4SEASONS is a direct geometry time-of-flight spectrometer installed in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility, the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex. It is used to study atomic andspin dynamics in the energy range of 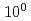 meV to
meV to 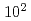 meV. Since more than a decade has crossed after the first inelastic scattering experiment, it is essential to consider upgrading the instrument to improve its flexibility and performance. In this paper, we discuss the possible medium-term upgrades of key components of the instrument like the chopper system, which are achievable with the current technology and at reasonable cost. Herein, we demonstrated that 4SEASONS can improve the energy resolution by a factor of two, remove frame overlap of adjacent incident energies, significantly improve the asymmetry in the pulse shape, and increase the flux by a factor of
meV. Since more than a decade has crossed after the first inelastic scattering experiment, it is essential to consider upgrading the instrument to improve its flexibility and performance. In this paper, we discuss the possible medium-term upgrades of key components of the instrument like the chopper system, which are achievable with the current technology and at reasonable cost. Herein, we demonstrated that 4SEASONS can improve the energy resolution by a factor of two, remove frame overlap of adjacent incident energies, significantly improve the asymmetry in the pulse shape, and increase the flux by a factor of  1.5, without major technical difficulties.
1.5, without major technical difficulties.
 La
La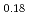 Fe
Fe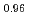 Ni
Ni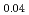 As
As
Xie, T.*; Liu, C.*; 梶本 亮一; 池内 和彦*; Li, S.*; Luo, H.*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 34(47), p.474001_1 - 474001_8, 2022/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Physics, Condensed Matter)We report time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering (INS) investigations on the spin fluctuation spectrum in the 112-type iron-based superconductor (FeSC) Ca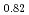 La
La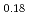 Fe
Fe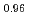 Ni
Ni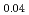 As
As (CaLa-112). In comparison to the 122-type FeSCs with a centrosymmetric tetragonal lattice structure (space group
(CaLa-112). In comparison to the 122-type FeSCs with a centrosymmetric tetragonal lattice structure (space group 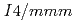 ) at room temperature and an in-plane stripe-type antiferromagnetic (AF) order at low temperature, the 112 system has a noncentrosymmetric structure (space group
) at room temperature and an in-plane stripe-type antiferromagnetic (AF) order at low temperature, the 112 system has a noncentrosymmetric structure (space group 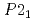 ) with additional zigzag arsenic chains between Ca/La layers and a magnetic ground state with similar wavevector
) with additional zigzag arsenic chains between Ca/La layers and a magnetic ground state with similar wavevector 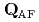 but different orientations of ordered moments in the parent compounds. Our INS study clearly reveals that the in-plane dispersions and the bandwidth of spin excitations in the superconducting CaLa-112 closely resemble to those in 122 systems. While the total fluctuating moments
but different orientations of ordered moments in the parent compounds. Our INS study clearly reveals that the in-plane dispersions and the bandwidth of spin excitations in the superconducting CaLa-112 closely resemble to those in 122 systems. While the total fluctuating moments 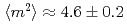
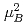 /Fe are larger than 122 system, the dynamic correlation lengths are similar (
/Fe are larger than 122 system, the dynamic correlation lengths are similar (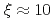
 ). These results suggest that superconductivity in iron arsenides may have a common magnetic origin under similar magnetic exchange couplings with a dual nature from local moments and itinerant electrons, despite their different magnetic patterns and lattice symmetries.
). These results suggest that superconductivity in iron arsenides may have a common magnetic origin under similar magnetic exchange couplings with a dual nature from local moments and itinerant electrons, despite their different magnetic patterns and lattice symmetries.
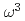 scaling of the vibrational density of states in quasi-2D nanoconfined solids
scaling of the vibrational density of states in quasi-2D nanoconfined solidsYu, Y.*; Yang, C.*; Baggioli, M.*; Phillips, A. E.*; Zaccone, A.*; Zhang, L.*; 梶本 亮一; 中村 充孝; Yu, D.*; Hong, L.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.3649_1 - 3649_10, 2022/06
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:81.66(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The vibrational properties of crystalline bulk materials are well described by Debye theory, which successfully predicts the quadratic 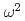 low-frequency scaling of the vibrational density of states. However, the analogous framework for nanoconfined materials with fewer degrees of freedom has been far less well explored. Using inelastic neutron scattering, we characterize the vibrational density of states of amorphous ice confined inside graphene oxide membranes and we observe a crossover from the Debye
low-frequency scaling of the vibrational density of states. However, the analogous framework for nanoconfined materials with fewer degrees of freedom has been far less well explored. Using inelastic neutron scattering, we characterize the vibrational density of states of amorphous ice confined inside graphene oxide membranes and we observe a crossover from the Debye 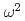 scaling to an anomalous
scaling to an anomalous 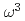 behaviour upon reducing the confinement size L.
behaviour upon reducing the confinement size L.
Do, S.-H.*; 金子 耕士; 梶本 亮一; 蒲沢 和也*; Stone, M. B.*; Lin, J. Y. Y.*; 伊藤 晋一*; 益田 隆嗣*; Samolyuk, G. D.*; Dagotto, E.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 105(18), p.L180403_1 - L180403_6, 2022/05
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:87.73(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report inelastic neutron scattering studies of the prototypical kagome magnetic metal FeSn. The spectra display well defined spin waves extending up to 120 meV. Above this energy, the spin waves become progressively broadened, reflecting interactions with the Stoner continuum. Using linear spin wave theory, we determine an effective spin Hamiltonian that explains the measured dispersion. This analysis indicates that the Dirac magnon at the K point occurs on the brink of a region where well defined spin waves become unobservable. Our results emphasize the influential role of itinerant carriers on the topological spin excitations of metallic kagome magnets.
 kagome-lattice antiferromagnets Cs
kagome-lattice antiferromagnets Cs Cu
Cu SnF
SnF and Rb
and Rb Cu
Cu SnF
SnF
齋藤 睦己*; 高岸 龍之介*; 栗田 伸之*; 渡邊 正理*; 田中 秀数*; 野村 竜司*; 福元 好志*; 池内 和彦*; 梶本 亮一
Physical Review B, 105(6), p.064424_1 - 064424_15, 2022/02
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:73.14(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Cs Cu
Cu SnF
SnF is a spin-
is a spin- antiferromagnet on a nearly uniform kagome lattice. This compound undergoes magnetic ordering with the
antiferromagnet on a nearly uniform kagome lattice. This compound undergoes magnetic ordering with the  = 0 structure and positive chirality, which is mainly caused by the large Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction. Rb
= 0 structure and positive chirality, which is mainly caused by the large Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction. Rb Cu
Cu SnF
SnF is a spin-
is a spin- antiferromagnet on a modified kagome lattice with a
antiferromagnet on a modified kagome lattice with a 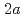

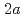 enlarged chemical unit cell at room temperature. Its ground state is a pinwheel valence bond solid (VBS) with an excitation gap. Here, we show the structures of magnetic excitations in Cs
enlarged chemical unit cell at room temperature. Its ground state is a pinwheel valence bond solid (VBS) with an excitation gap. Here, we show the structures of magnetic excitations in Cs Cu
Cu SnF
SnF and Rb
and Rb Cu
Cu SnF
SnF investigated by inelastic neutron scattering in wide energy and momentum ranges. For Cs
investigated by inelastic neutron scattering in wide energy and momentum ranges. For Cs Cu
Cu SnF
SnF , four single-magnon excitation modes were observed. It was confirmed that the energy of single-magnon excitations arising from the
, four single-magnon excitation modes were observed. It was confirmed that the energy of single-magnon excitations arising from the 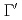 point in the extended Brillouin zones is largely renormalized downwards. It was found that the broad excitation continuum without a marked structure spreads in a wide energy range from
point in the extended Brillouin zones is largely renormalized downwards. It was found that the broad excitation continuum without a marked structure spreads in a wide energy range from 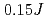 to approximately
to approximately 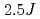 . These findings strongly suggest spinon excitations as elementary excitations in Cs
. These findings strongly suggest spinon excitations as elementary excitations in Cs Cu
Cu SnF
SnF . In Rb
. In Rb Cu
Cu SnF
SnF , singlet-triplet excitations from the pinwheel VBS state and their ghost modes caused by the enlargement of the chemical unit cell were clearly confirmed. It was found that the excitation continuum is structured in the low-energy region approximately below
, singlet-triplet excitations from the pinwheel VBS state and their ghost modes caused by the enlargement of the chemical unit cell were clearly confirmed. It was found that the excitation continuum is structured in the low-energy region approximately below 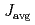 and the almost structureless high-energy excitation continuum extends to approximately
and the almost structureless high-energy excitation continuum extends to approximately 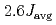 . The characteristics of the high-energy excitation continuum are common to both Cs
. The characteristics of the high-energy excitation continuum are common to both Cs Cu
Cu SnF
SnF and Rb
and Rb Cu
Cu SnF
SnF , irrespective of their ground states. The experimental results strongly suggest that the spin liquid component remains in the ground state as quantum fluctuations in Cs
, irrespective of their ground states. The experimental results strongly suggest that the spin liquid component remains in the ground state as quantum fluctuations in Cs Cu
Cu SnF
SnF and Rb
and Rb Cu
Cu SnF
SnF .
.
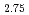 GeTe
GeTe
Bao, S.*; Wang, W.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Cai, Z.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Si, W.*; Ma, Z.*; 梶本 亮一; 池内 和彦*; et al.
Physical Review X, 12(1), p.011022_1 - 011022_15, 2022/02
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:78.27(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In the local or itinerant extreme, magnetic excitations can be described by the Heisenberg model which treats electron spins as localized moments, or by the itinerant-electron model where the exchange interaction between electrons leads to unequal numbers of electrons with up and down spins. However, the nature of the magnetic excitations has been elusive when both local moments and itinerant electrons are present in the intermediate range. Using inelastic neutron scattering, we provide direct spectroscopic evidence on the coexistence of and interplay between local moments and itinerant electrons in a van der Waals metallic ferromagnet Fe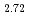 GeTe
GeTe , which can sustain tunable room-temperature ferromagnetism down to the monolayer limit. We find that there exist ferromagnetic spin-wave excitations dispersing from the zone center at low energies resulting from local moments and a columnlike broad continuum at the zone boundary at high energies up to over 100 meV resulting from itinerant electrons. Unlike the two-dimensional crystal structure, the low-energy mode exhibits a three-dimensional nature, and the high-energy mode also has an out-of-plane dependence. Both modes persist well above the Curie temperature of 160 K. Our neutron spectroscopic data reveal that the low-energy spin waves at 100 K are more coherent than those at 4 K, which is evidence of the weakening of the Kondo screening at high temperatures. These results unambiguously demonstrate the coexistence of local moments and itinerant electrons and the Kondo effect between these two components in Fe
, which can sustain tunable room-temperature ferromagnetism down to the monolayer limit. We find that there exist ferromagnetic spin-wave excitations dispersing from the zone center at low energies resulting from local moments and a columnlike broad continuum at the zone boundary at high energies up to over 100 meV resulting from itinerant electrons. Unlike the two-dimensional crystal structure, the low-energy mode exhibits a three-dimensional nature, and the high-energy mode also has an out-of-plane dependence. Both modes persist well above the Curie temperature of 160 K. Our neutron spectroscopic data reveal that the low-energy spin waves at 100 K are more coherent than those at 4 K, which is evidence of the weakening of the Kondo screening at high temperatures. These results unambiguously demonstrate the coexistence of local moments and itinerant electrons and the Kondo effect between these two components in Fe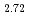 GeTe
GeTe . Such behaviors are generally expected in heavy-fermion systems with heavy
. Such behaviors are generally expected in heavy-fermion systems with heavy  electrons but are rarely clearly observed in materials with light
electrons but are rarely clearly observed in materials with light  electrons. These findings shed light on the understanding of magnetism in transition-metal compounds.
electrons. These findings shed light on the understanding of magnetism in transition-metal compounds.
 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO
池内 和彦*; 脇本 秀一; 藤田 全基*; 福田 竜生; 梶本 亮一; 新井 正敏*
Physical Review B, 105(1), p.014508_1 - 014508_7, 2022/01
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:34.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Spin excitations of layered copper oxide show various characteristic features, depending on the carrier concentration. In this paper, we conducted inelastic neutron-scattering measurements on La Sr
Sr CuO
CuO (LSCO) with
(LSCO) with  = 0, 0.075, 0.18, and 0.30 and La
= 0, 0.075, 0.18, and 0.30 and La Sr
Sr NiO
NiO (LSNO) with 1/3 to clarify the origin of the intensity enhancement in the excitation spectrum of LSCO at the energy (
(LSNO) with 1/3 to clarify the origin of the intensity enhancement in the excitation spectrum of LSCO at the energy ( ) of 16-19 meV [Phys. Rev. B
) of 16-19 meV [Phys. Rev. B 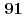 , 224404 (2015),
, 224404 (2015), 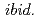
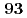 , 094416 (2016)]. We confirmed the presence of a peak structure in the
, 094416 (2016)]. We confirmed the presence of a peak structure in the  dependence of the local spin susceptibility
dependence of the local spin susceptibility 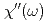 of superconducting (SC) LSCO with a peak energy of 16-19 meV where the spin excitations intersect optical phonon branches. A comparable peak structure is not observed in the insulating La
of superconducting (SC) LSCO with a peak energy of 16-19 meV where the spin excitations intersect optical phonon branches. A comparable peak structure is not observed in the insulating La CuO
CuO , LSNO, and heavily overdoped LSCO with
, LSNO, and heavily overdoped LSCO with  = 0.30. A dome-shaped
= 0.30. A dome-shaped  dependence of the integrated intensity around the peak energies is revealed for the SC phase by summarizing the present and previously reported results. Furthermore, our phonon calculation on LCO shows the existence of two optical branches at
dependence of the integrated intensity around the peak energies is revealed for the SC phase by summarizing the present and previously reported results. Furthermore, our phonon calculation on LCO shows the existence of two optical branches at  19 meV that could stabilize stripe alignment of carriers due to out-of-plane vibrations of Cu or O of the CuO
19 meV that could stabilize stripe alignment of carriers due to out-of-plane vibrations of Cu or O of the CuO planes. These results indicate the interplay among spin, charge, and lattice dynamics and suggest that the intensity enhancement is associated with their composite excitations.
planes. These results indicate the interplay among spin, charge, and lattice dynamics and suggest that the intensity enhancement is associated with their composite excitations.
 Cu
Cu TeO
TeO
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Cai, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Huang, Z.*; Ma, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; 梶本 亮一; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(22), p.224430_1 - 224430_8, 2021/12
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:7.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dimerized magnets forming alternating Heisenberg chains exhibit quantum coherence and entanglement and thus can find potential applications in quantum information and computation. However, magnetic systems typically undergo thermal decoherence at finite temperatures. Here, we show inelastic neutron scattering results on an alternating antiferromagnetic-ferromagnetic chain compound Na Cu
Cu TeO
TeO that the excited quasiparticles can counter thermal decoherence and maintain strong correlations at elevated temperatures. At low temperatures, we observe clear dispersive singlet-triplet excitations arising from the dimers formed along the crystalline
that the excited quasiparticles can counter thermal decoherence and maintain strong correlations at elevated temperatures. At low temperatures, we observe clear dispersive singlet-triplet excitations arising from the dimers formed along the crystalline  -axis. The excitation gap is of
-axis. The excitation gap is of  18 meV and the bandwidth is about half of the gap. The band top energy has a weak modulation along the [100] direction, indicative of a small interchain coupling. The gap increases while the bandwidth decreases with increasing temperature, leading to a strong reduction in the available phase space for the triplons. As a result, the Lorentzian-type energy broadening becomes highly asymmetric as the temperature is raised. These results are associated with a strongly correlated state resulting from hard-core constraint and quasiparticle interactions. We consider these results to be not only evidence for strong correlations at finite temperatures in Na
18 meV and the bandwidth is about half of the gap. The band top energy has a weak modulation along the [100] direction, indicative of a small interchain coupling. The gap increases while the bandwidth decreases with increasing temperature, leading to a strong reduction in the available phase space for the triplons. As a result, the Lorentzian-type energy broadening becomes highly asymmetric as the temperature is raised. These results are associated with a strongly correlated state resulting from hard-core constraint and quasiparticle interactions. We consider these results to be not only evidence for strong correlations at finite temperatures in Na Cu
Cu TeO
TeO , but also for the universality of the strongly correlated state in a broad range of quantum magnetic systems.
, but also for the universality of the strongly correlated state in a broad range of quantum magnetic systems.
 Ir
Ir O
O observed by inelastic neutron scattering technique
observed by inelastic neutron scattering technique藤田 全基*; 池内 和彦*; 梶本 亮一; 中村 充孝
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(2), p.025001_1 - 025001_2, 2021/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:16.57(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In this short note, we report on the first inelastic neutron scattering (INS) study on high-energy magnetic excitations in Sr Ir
Ir O
O . We observed excitations between
. We observed excitations between  80 meV and
80 meV and  180 meV. The peak position of the excitations is consistent with the dispersion of a single magnon determined by resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) measurement. Thus, our results demonstrate the feasibility of INS for iridates, which has a large neutron absorption cross-section.
180 meV. The peak position of the excitations is consistent with the dispersion of a single magnon determined by resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) measurement. Thus, our results demonstrate the feasibility of INS for iridates, which has a large neutron absorption cross-section.
 symmetry in the tetragonal state of uniaxial strained BaCo
symmetry in the tetragonal state of uniaxial strained BaCo Ni
Ni S
S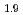
社本 真一; 山内 宏樹; 池内 和彦*; 梶本 亮一; 家田 淳一
Physical Review Research (Internet), 3(1), p.013169_1 - 013169_9, 2021/02
A compound with large anions is known to show large compressibility whereby a novel response may emerge from the degenerated state by a uniaxial pressure. Neutron scattering study of BaCo Ni
Ni S
S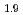 crystal reveals that the tetragonal insulating state has two magnetic domains with in-plane anisotropic antiferromagnetic wave vectors
crystal reveals that the tetragonal insulating state has two magnetic domains with in-plane anisotropic antiferromagnetic wave vectors 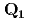 =(
=( , 0) and
, 0) and 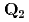 =(0,
=(0,  ). One magnetic domain with
). One magnetic domain with 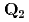 becomes dominant under a weak uniaxial pressure of 1 MPa without a structural phase transition. Correspondingly, the in-plane broken C
becomes dominant under a weak uniaxial pressure of 1 MPa without a structural phase transition. Correspondingly, the in-plane broken C symmetry is observed in the in-plane magnetic excitation. The domain-ratio changes under a uniaxial pressure in the tetragonal state is only slightly smaller than that in the orthorhombic state.
symmetry is observed in the in-plane magnetic excitation. The domain-ratio changes under a uniaxial pressure in the tetragonal state is only slightly smaller than that in the orthorhombic state.
Zhang, D.*; Hu, X.*; Chen, T.*; Abernathy, D. L.*; 梶本 亮一; 中村 充孝; 古府 麻衣子; Foley, B. J.*; Yoon, M.*; Choi, J. J.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(22), p.224310_1 - 224310_10, 2020/12
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:26.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The long carrier lifetime and defect tolerance in metal halide perovskites (MHPs) are major contributors to the superb performance of MHP optoelectronic devices. Large polarons were reported to be responsible for the long carrier lifetime. Yet microscopic mechanisms of the large polaron formation, including the so-called phonon melting, are still under debate. Here, time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering experiments and first-principles density-functional theory calculations were employed to investigate the lattice vibrations (or phonon dynamics) in methylammonium lead iodide, a prototypical example of MHPs. Our findings are that optical phonons lose temporal coherence gradually with increasing temperature which vanishes at the orthorhombic-to-tetragonal structural phase transition. Surprisingly, however, we found that the spatial coherence is still retained throughout the decoherence process. We argue that the temporally decoherent and spatially coherent vibrations contribute to the formation of large polarons in this metal halide perovskite.
 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO (
( = 0.10 and 0.16)
= 0.10 and 0.16)佐藤 研太朗*; 池内 和彦*; 梶本 亮一; 脇本 秀一; 新井 正敏*; 藤田 全基*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(11), p.114703_1 - 114703_7, 2020/11
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:50.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary)To elucidate the spin dynamics of La Sr
Sr CuO
CuO , which couples with the charge degree of freedom, the spin excitations spanning the characteristic energy (
, which couples with the charge degree of freedom, the spin excitations spanning the characteristic energy (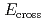
 35-40 meV) are investigated for underdoped
35-40 meV) are investigated for underdoped  = 0.10 and optimally doped (OP)
= 0.10 and optimally doped (OP)  = 0.16 through inelastic neutron scattering measurements. Analysis based on a two-component picture of high-quality data clarified the possible coexistence of upright standing incommensurate (IC) excitations with gapless commensurate (C) excitations in the energy-momentum space. The IC component weakens the intensity toward
= 0.16 through inelastic neutron scattering measurements. Analysis based on a two-component picture of high-quality data clarified the possible coexistence of upright standing incommensurate (IC) excitations with gapless commensurate (C) excitations in the energy-momentum space. The IC component weakens the intensity toward 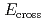 with increasing energy transfer (
with increasing energy transfer (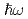 ), whereas the C component strengthens at high-
), whereas the C component strengthens at high-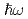 regions. The analysis results imply that the superposition of two components with a particular intensity balance forms an hourglass-shaped excitation in appearance. Furthermore, the temperature dependence of the intensity of each component exhibits different behaviors; the IC component disappears near the pseudo-gap temperature (
regions. The analysis results imply that the superposition of two components with a particular intensity balance forms an hourglass-shaped excitation in appearance. Furthermore, the temperature dependence of the intensity of each component exhibits different behaviors; the IC component disappears near the pseudo-gap temperature (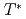 ) upon warming, whereas the C component is robust against temperature. These results suggest the itinerant electron spin nature and the localized magnetism of the parent La
) upon warming, whereas the C component is robust against temperature. These results suggest the itinerant electron spin nature and the localized magnetism of the parent La CuO
CuO in IC and C excitations, respectively, similar to the spin excitations in the OP YBa
in IC and C excitations, respectively, similar to the spin excitations in the OP YBa Cu
Cu O
O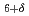 and HgBa
and HgBa CuO
CuO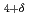 with higher superconducting-transition temperatures.
with higher superconducting-transition temperatures.
梶本 亮一; 中村 充孝; 飯田 一樹*; 蒲沢 和也*; 池内 和彦*; 稲村 泰弘; 石角 元志*
Journal of Neutron Research, 22(2-3), p.99 - 107, 2020/10
The elastic energy resolution, integrated intensity, and peak intensity of the direct-geometry neutron chopper spectrometer 4SEASONS at Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) were re-investigated. This was done with respect to the incident energy and the rotation speed of the Fermi chopper using incoherent scattering of vanadium and simple analytical formulas. The model calculations reproduced the observed values satisfactorily. The present work should be useful for estimating in instrument performance in experiments.