Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Taniguchi, Takumi; Matsumoto, Saori; Hiraki, Yoshihisa; Sato, Junya; Fujita, Hideki*; Kaneda, Yoshihisa*; Kuroki, Ryoichiro; Osugi, Takeshi
JAEA-Review 2024-059, 20 Pages, 2025/03
The basic performance required for solidifying waste into cement, such as fluidity before curing and strength after curing, is expected to be affected by the chemical effects of substances and components contained in the waste. The fluidity before curing and the strength properties after curing are greatly influenced by the curing speed of the cement. We investigated existing knowledge with a focus on chemical substances that affect the curing speed of cement. In this report, chemical substances that affect fluidity are broadly classified into inorganic substances such as (1) anion species, (2) metal elements such as heavy metals, (3) inorganic compounds as cement admixtures, and (4) organic compounds as cement admixtures. Based on the investigation, we actually added chemicals and measured the setting time. As a result, it was found that there are multiple mechanisms contributing to accelerated hardening. We investigated chemical substances that inhibit the curing reaction of cement, and were able to compile information to consider ingredients that are contraindicated in cement curing.
Fukada, Yukimasa; Aoyagi, Yumito*; Yokoyama, Misaki*; Horibe, Yoichi*; Kano, Jun*; Kaneda, Miyu*; Fujii, Tatsuo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Kobata, Masaaki; Fukuda, Tatsuo; et al.
Journal of Electronic Materials, 54, p.686 - 692, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Kaneda, Kazuko*; Shirakami, Yoshifumi*; Kadonaga, Yuichiro*; Watabe, Tadashi*; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Yin, X.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Shirasaki, Kenji*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; et al.
International Journal of Molecular Sciences (Internet), 25(2), p.933_1 - 933_14, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:91.66(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology) At]NaAt and [
At]NaAt and [ I]NaI in an NIS-expressing thyroid cancer mouse model
I]NaI in an NIS-expressing thyroid cancer mouse modelWatabe, Tadashi*; Liu, Y.*; Kaneda, Kazuko*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Shirakami, Yoshifumi*; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Toyoshima, Atsushi*; Shimosegawa, Eku*; Wang, Y.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
International Journal of Molecular Sciences (Internet), 23(16), p.9434_1 - 9434_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:73.73(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)In this study, we compare the therapeutic effect between [ At]NaAt and [
At]NaAt and [ I]NaI. In vitro analysis of double-stranded DNA break (DSB) and colony formation assay were performed using K1-NIS cells. [
I]NaI. In vitro analysis of double-stranded DNA break (DSB) and colony formation assay were performed using K1-NIS cells. [ At]NaAt induced higher numbers of DSBs and had a reduced colony formation than [
At]NaAt induced higher numbers of DSBs and had a reduced colony formation than [ I]NaI. In K1-NIS mice, dose-dependent therapeutic effects were observed in both [
I]NaI. In K1-NIS mice, dose-dependent therapeutic effects were observed in both [ At]NaAt and [
At]NaAt and [ I]NaI. The superior therapeutic effect of [
I]NaI. The superior therapeutic effect of [ At]NaAt suggests the promising clinical applicability of targeted alpha therapy using [
At]NaAt suggests the promising clinical applicability of targeted alpha therapy using [ At]NaAt in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer refractory to standard [
At]NaAt in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer refractory to standard [ I]NaI treatment.
I]NaI treatment.
Komura, Keitaro*; Kaneda, Heitaro*; Tanaka, Tomoki*; Kojima, Satoru*; Inoue, Tsutomu*; Nishio, Tomohiro
Geomorphology, 365, p.107214_1 - 107214_22, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:26.47(Geography, Physical)On the basis of pit excavations and sediment cores at an off-fault deep-seated gravitational slope deformation (DGSD) site and a trench excavation across the active Neodani fault at a nearby site, we examined the records of DGSD and surface-rupturing paleoearthquakes of the Neodani fault. We found the four most recent DGSD events and the four most recent surface-rupturing earthquakes, respectively and conclude that the ages of events are overlapped each other. We infer that static crustal strain from repeated seismogenic faulting plays an important role in the occurrence of DGSD events, at least in the immediate vicinity of active faults, although coseismic severe shaking would have at least some effect on them. Our case study suggests that off-fault DGSDs can be used to reconstruct or refine the paleoseismic history of a nearby active fault.
Fukaya, Masaaki*; Hata, Koji*; Akiyoshi, Kenji*; Sato, Shin*; Takeda, Nobufumi*; Miura, Norihiko*; Uyama, Masao*; Kaneda, Tsutomu*; Ueda, Tadashi*; Hara, Akira*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2016-002, 195 Pages, 2016/03
The researches on examination of the plug applied to the future reflood test was conducted as a part of (5) development of technologies for restoration and/on reduction of the excavation damage relating to the engineering technology in the MIU (2014), specifically focused on (1) plug examination (e.g. functions, structure and material) and the quality control methods and (2) analytical evaluation of rock mass behavior around the plug through the reflood test. As the result, specifications of the plug were determined. These specifications should be able to meet requirements for the safety structure and surrounding rock mass against predicted maximum water pressure, temperature stress and seismic force, and for controlling the groundwater inflow, ensuring the access into the reflood gallery and the penetration performance of measurement cable. Also preliminary knowledge regarding the rock mass behavior around the plug after flooding the reflood gallery by installed plug was obtained.
Fukaya, Masaaki*; Hata, Koji*; Akiyoshi, Kenji*; Sato, Shin*; Takeda, Nobufumi*; Miura, Norihiko*; Uyama, Masao*; Kaneda, Tsutomu*; Ueda, Tadashi*; Toda, Akiko*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2014-040, 199 Pages, 2015/03
The researches on engineering technology in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project consists of (1) development of design and construction planning technologies, (2) development of construction technology, (3) development of countermeasure technology, (4) development of technology for security, and (5) development of technologies for restoration and/or reduction of the excavation damage. The researches on engineering technology such as verification of the initial design were being conducted by using data measured during construction as a part of the second phase of the MIU plan. Examination about the plug for reflood test in the GL-500m Access/Research Gallery-North as part of the development of technologies for restoration and/or reduction of excavation damage were carried out. Specifically, Literature survey was carried out about the plug, based on the result of literature survey, examination of the design condition, design of the plug and rock stability using numerical simulation, selection of materials for major parts, and grouting for water inflow from between rock and plug, were carried out in this study.
Fukaya, Masaaki*; Noda, Masaru*; Hata, Koji*; Takeda, Nobufumi*; Akiyoshi, Kenji*; Ishizeki, Yoshikazu*; Kaneda, Tsutomu*; Sato, Shin*; Shibata, Chihoko*; Ueda, Tadashi*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2014-019, 495 Pages, 2014/08
The researches on engineering technology in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) plan consists of (1) research on engineering technology deep underground, and (2) research on engineering technology as a basis of geological disposal. The former research is mainly aimed in this study, which is categorized in (a) development of design and construction planning technologies, (b) development of construction technologies, (c) development of countermeasure technologies, and (d) development of technologies for security. In this study, the researches on engineering technology are being conducted in these four categories by using data measured during construction as a part of the second phase of the MIU plan.
Zaima, Naoki; Nakashima, Shinichi; Kaneda, Koji; Kado, Kazumi
JAEA-Technology 2010-046, 31 Pages, 2011/02
The uranium mass assay systems for 200-litter wastes drums applied neutron and  measurements by NDA method had been developed. The measurement systems and trial data are described in this preliminary report. The systems are composed of the 16 pieces of helium-3 proportional counters for neutron detection and a large sized NaI(Tl) scintillation detector for
measurements by NDA method had been developed. The measurement systems and trial data are described in this preliminary report. The systems are composed of the 16 pieces of helium-3 proportional counters for neutron detection and a large sized NaI(Tl) scintillation detector for  ray detection. The extensive testing trials using the calibrated uranium sources with different enrichment and some kinds of matrices in drums were performed. Through the one year testing the useful experiences of this system concerning neutron and
ray detection. The extensive testing trials using the calibrated uranium sources with different enrichment and some kinds of matrices in drums were performed. Through the one year testing the useful experiences of this system concerning neutron and  ray measurements for uranium mass were obtained. Almost all instruments and software were so good performance as is designed. As the next step we are scheduled to try measurements for actual wastes that are stored in the Uranium Refining and Conversion Plant at Ningyo-toge, and put practical uses near future. Our research was accomplished with the support of LANL.
ray measurements for uranium mass were obtained. Almost all instruments and software were so good performance as is designed. As the next step we are scheduled to try measurements for actual wastes that are stored in the Uranium Refining and Conversion Plant at Ningyo-toge, and put practical uses near future. Our research was accomplished with the support of LANL.
Tomimoto, Hiroshi; Kato, Yasushi; Owada, Hiroyuki; Sato, Nao; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Kozawa, Takayuki; Shinohara, Masanori; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Tochio, Daisuke; Nojiri, Naoki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-025, 29 Pages, 2009/06
The first driver fuel of the HTTR (High Temperature Engineering test Reactor) was loaded in 1998 and the HTTR reached first criticality state in the same year. The HTTR has been operated using the first driver fuel for a decade. In Fuel elements assembling, 4770 of fuel rods which consist of 12 kinds of enrichment uranium are loaded into 150 fuel graphite blocks for HTTR second driver fuel elements. Measures of prevention of fuel rod miss loading, are employed in fuel design. Additionally, precaution of fuel handling on assembling are considered. Reception of fuel rods, assembling of fuel elements and storage of second driver fuels in the fresh fuel storage rack in the HTTR were started since June, 2008. Assembling, storage and pre-service inspection were divided into three parts. The second driver fuel assembling was completed in September, 2008. This report describes concerns of fuel handling on assembling and storage work for the HTTR fuel elements.
Kaneda, Tsutomu*
Tonneru To Chika, 40(2), p.148 - 149, 2009/02
An overview of the directional control borehole drilling applied to the MIZ-1 borehole drilling at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory is described as an example of the control borehole drilling reamed with outer casing.
Akiyoshi, Kenji*; Mikake, Shinichiro; Kaneda, Tsutomu*; Noda, Masatoshi*
Tonneru Kogaku Hokokushu (CD-ROM), 17, p.105 - 111, 2007/11
The purpose of this study grasps the effect of the solidified shape as the auxiliary method for ground improvement of deep shaft excavation in weathered rock.
Hirouchi, Daisuke*; Yasue, Kenichi; Uchida, Chikara*; Hiramatsu, Takahiro*; Taniguchi, Kaoru*; Sugito, Nobuhiko*; Kaneda, Heitaro*
Katsudanso Kenkyu, (27), p.201 - 209, 2007/06
The Yugamine fault, 10 km in length, is in the north-central part of the Atera fault zone. We studied Holocene activity of the Yugamine fault through a trenching survey. Some humic layers and fluvial gravels are exposed on the trench walls. The Yugamine fault has cut through these layers to form a linear depression on its NE side. From the structural evidence along the fault plane and angular unconformity, we recognize at least four faulting events in this trench.
Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Li, Z.*; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Nakamura, Shu*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Shirai, Toshiyuki*; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 14(4), p.043104_1 - 043104_6, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:64 Percentile:87.43(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Fast protons are observed by a newly-developed 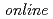 time-of-flight spectrometer, which provides
time-of-flight spectrometer, which provides 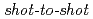 proton-energy distributions immediately after the irradiation of a laser pulse having an intensity of
proton-energy distributions immediately after the irradiation of a laser pulse having an intensity of 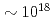 W/cm
W/cm onto a 5-
onto a 5- m-thick copper foil. The maximum proton energy is found to increase when the intensity of a fs-prepulse arriving 9 ns before the main pulse increases from 10
m-thick copper foil. The maximum proton energy is found to increase when the intensity of a fs-prepulse arriving 9 ns before the main pulse increases from 10 to 10
to 10 W/cm
W/cm . Interferometric measurement indicates that the preformed-plasma expansion at the front surface is smaller than 15
. Interferometric measurement indicates that the preformed-plasma expansion at the front surface is smaller than 15  m, which corresponds to the spatial resolution of the diagnostics. This sharp gradient of the plasma makes a beneficial effect on increasing the absorption efficiency of the main-pulse energy, resulting in the increase in the proton energy. This is supported by the result that the X-ray intensity from the laser plasma clearly increases with the prepulse intensity.
m, which corresponds to the spatial resolution of the diagnostics. This sharp gradient of the plasma makes a beneficial effect on increasing the absorption efficiency of the main-pulse energy, resulting in the increase in the proton energy. This is supported by the result that the X-ray intensity from the laser plasma clearly increases with the prepulse intensity.
Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Kaneda, Ayako*; Matsuzaki, Tomoaki*; Kanazawa, Shinichi*; Yagi, Toshiaki; Tran, M. Q.*; Mitomo, Hiroshi*; Yoshii, Fumio; Tamada, Masao; Quynh, T. M.*
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 53, 2007/02
Poly(L-lactic acid), PLA was irradiated using electron beams (EB) in the presence of polyfunctional monomers (PFM) as crosslinking agent. Among the PFMs, triallyl isocyanurate (TAIC) at 3% concentration was found to be the most effective for crosslinking of PLA by irradiation technique. The crosslinked PLA obtained has heat resistance higher than 200 C. From this fact, the crosslinked PLA is applied on heat-shrinkable tube, cup and plate. The shrinkable tube has several advantages such as high heat resistance and transparency. It is therefore proven that crosslinking technology is beneficial to expanding the application of PLA.
C. From this fact, the crosslinked PLA is applied on heat-shrinkable tube, cup and plate. The shrinkable tube has several advantages such as high heat resistance and transparency. It is therefore proven that crosslinking technology is beneficial to expanding the application of PLA.
Hamamoto, Shimpei; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Shimizu, Atsushi; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Kondo, Makoto; Oyama, Sunao; Kawano, Shuichi; Kobayashi, Shoichi; Kawamoto, Taiki; Suzuki, Hisashi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2006-030, 58 Pages, 2006/03
During normal operation of High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), the reactivity is controlled by the Control Rods (CRs) system which consists of 32 CRs (16 pairs) and 16 Control Rod Drive Mechanisms (CRDMs). The CR system is located in stand-pipes accompanied by the Reserved Shutdown System (RSS). In the unlikely event that the CRs fail to be inserted, the RSS is provided to insert B C/C pellets into the core. The RSS shall be designed so that the reactor should be held subcriticality from any operation condition by dropping in the pellets. The RSS consists of B
C/C pellets into the core. The RSS shall be designed so that the reactor should be held subcriticality from any operation condition by dropping in the pellets. The RSS consists of B C/C pellets, hoppers which contain the pellets, electric plug, driving mechanisms, guide tubes and so on. In accidents when the CRs cannot be inserted, an electric plug is pulled out by a motor and the absorber pellets fall into the core by gravity. A trouble, malfunction of one RSS out of sixteen, occurred during a series of the pre-start up checks of HTTR on February 21, 2005. We investigated the cause of the RSS trouble and took countermeasures to prevent the issue. As the result of investigation, the cause of the trouble was attributed to the following reason: In the motor inside, The Oil of grease of the multiplying gear flowed down from a gap of the oil seal which has been deformed and was mixed with abrasion powder of brake disk. Therefore the adhesive mixture prevented a motor from rotating.
C/C pellets, hoppers which contain the pellets, electric plug, driving mechanisms, guide tubes and so on. In accidents when the CRs cannot be inserted, an electric plug is pulled out by a motor and the absorber pellets fall into the core by gravity. A trouble, malfunction of one RSS out of sixteen, occurred during a series of the pre-start up checks of HTTR on February 21, 2005. We investigated the cause of the RSS trouble and took countermeasures to prevent the issue. As the result of investigation, the cause of the trouble was attributed to the following reason: In the motor inside, The Oil of grease of the multiplying gear flowed down from a gap of the oil seal which has been deformed and was mixed with abrasion powder of brake disk. Therefore the adhesive mixture prevented a motor from rotating.
Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Kaneda, Ayako*; Kanazawa, Shinichi*; Yagi, Toshiaki; Mitomo, Hiroshi*; Yoshii, Fumio; Tamada, Masao
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 236(1-4), p.611 - 616, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:81 Percentile:97.71(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 -lactic acid) by radiation-induced crosslinking
-lactic acid) by radiation-induced crosslinkingMitomo, Hiroshi*; Kaneda, Ayako*; Tran, M. Q.*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Yoshii, Fumio
Polymer, 46(13), p.4695 - 4703, 2005/06
Times Cited Count:118 Percentile:93.98(Polymer Science)no abstracts in English
Yasue, Kenichi; Kaneda, Heitaro*; Kondo, Hisao*
Nihon Jishin Gakkai Nyusu Reta, 16(6), p.15 - 17, 2005/00
Focusing on the cover layer materials (as the Radon Barrier Materials), which could have the effect to restrain the radon from scattering into the air and the effect of the radiation shielding, we produced the radon barrier materials with crude bentonite on an experimental basis, using the rotary type comprehensive unit for grinding and mixing, through which we carried out the evaluation of the characteristics thereof.
Yokokawa, Mitsuo; Saito, Minoru*; Ishihara, Takashi*; Kaneda, Yukio*
Hai Pafomansu Komputingu To Keisan Kagaku Shimpojium (HPCS2002) Rombunshu, p.125 - 131, 2002/01
With the advent of supercomputers, large-scale direct numerical simulations(DNS) of the Navier-Stokes equations are possible to carry out. However, larger scale DNS is required to make turbulence clear and to make a parameterization of turbulence. The Earth Simulator is a distributed memory parallel supercomputer whose peak speed is 40 Tflop/s and it is very useful to make a very large-scale DNS. Simulation codes named 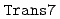 have been developed for the Earth Simulator and their correctness have been validated by compareing the simulation results by
have been developed for the Earth Simulator and their correctness have been validated by compareing the simulation results by 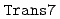 with ones by a conventinal code. The sustatined performance of 3.72Gflop/s is obtained in the execution of the serial version with the problem size of
with ones by a conventinal code. The sustatined performance of 3.72Gflop/s is obtained in the execution of the serial version with the problem size of 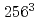 on an arithmetic processor(AP) of the Earth Simulator. Speedup of about 7 is achieved in 8APs by the parallelized code. Sppedup is degraded by the execution of 8 processor nodes, however, efficiency of 25% against the peak performance is obtained for the problem size of
on an arithmetic processor(AP) of the Earth Simulator. Speedup of about 7 is achieved in 8APs by the parallelized code. Sppedup is degraded by the execution of 8 processor nodes, however, efficiency of 25% against the peak performance is obtained for the problem size of 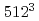 .
.