Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Luce, T. C.*; Challis, C. D.*; 井手 俊介; Joffrin, E.*; 鎌田 裕; Politzer, P. A.*; Schweinzer, J.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Stober, J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 54(1), p.013015_1 - 013015_15, 2013/12
被引用回数:45 パーセンタイル:87.18(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The ITPA IOS group has coordinated experimental and modeling activity on the development of advanced inductive scenarios for applications in the ITER tokamak. This report documents the present status of the physics basis and the prospects for applications in ITER. The key findings are: (1) inductive scenarios capable of higher 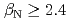 than the ITER baseline scenario (
than the ITER baseline scenario (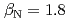 ) with normalized confinement at or above the standard H-mode scaling have been established under stationary conditions on the four largest diverted tokamaks (AUG, DIII-D, JET, JT-60U) in a broad range in
) with normalized confinement at or above the standard H-mode scaling have been established under stationary conditions on the four largest diverted tokamaks (AUG, DIII-D, JET, JT-60U) in a broad range in 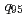 and density; (2) MHD modes can play a key role in reaching stationary high performance, but also define the stability and confinement limits; (3) the experiments have yielded clearer measurements of the normalized gyroradius scalin; and (4) coordinated modeling activity supports the present research by clarifying the most significant uncertainties in the projections to ITER.
and density; (2) MHD modes can play a key role in reaching stationary high performance, but also define the stability and confinement limits; (3) the experiments have yielded clearer measurements of the normalized gyroradius scalin; and (4) coordinated modeling activity supports the present research by clarifying the most significant uncertainties in the projections to ITER.
Tillack, M. S.*; Turnbull, A. D.*; Kessel, C. E.*; 朝倉 伸幸; Garofalo, A. M.*; Holland, C.*; Koch, F.*; Linsmeier, Ch.*; Lisgo, S.*; Maingi, R.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 53(2), p.027003_1 - 027003_23, 2013/02
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:20.23(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)周辺プラズマ物理及びプラズマ対向材相互作用の専門家によるITER後の核融合炉について現状の検討と今後の課題について評価するARIESワークショップが2010年5月に開催された。ダイバータ物理,モデリング,実験結果,それらの比較検討、核融合炉計画プログラムなどのトピックスが議論された。
Imbeaux, F.*; Citrin, J.*; Hobirk, J.*; Hogeweij, G. M. D.*; K chl, F.*; Leonov, V. M.*; 宮本 斉児; 中村 幸治*; Parail, V.*; Pereverzev, G. V.*; et al.
chl, F.*; Leonov, V. M.*; 宮本 斉児; 中村 幸治*; Parail, V.*; Pereverzev, G. V.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(8), p.083026_1 - 083026_11, 2011/08
被引用回数:38 パーセンタイル:80.74(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In order to prepare adequate current ramp-up and ramp-down scenarios for ITER, present experiments from various tokamaks have been analysed by means of integrated modelling in view of determining relevant heat transport models for these operation phases. A set of empirical heat transport models for L-mode has been validated on a multi-machine experimental dataset for predicting the 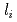 dynamics within
dynamics within  0.15 accuracy during current ramp-up and ramp-down phases. The most accurate heat transport models are then applied to projections to ITER current ramp-up, focusing on the baseline inductive scenario (main heating plateau current of
0.15 accuracy during current ramp-up and ramp-down phases. The most accurate heat transport models are then applied to projections to ITER current ramp-up, focusing on the baseline inductive scenario (main heating plateau current of 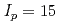 MA). These projections include a sensitivity study to various assumptions of the simulation. While the heat transport model is at the heart of such simulations, more comprehensive simulations are required to test all operational aspects of the current ramp-up and ramp-down phases of ITER scenarios. Recent examples of such simulations, involving coupled core transport codes, free-boundary equilibrium solvers and a poloidal field (PF) systems controller are also described, focusing on ITER current ramp-down.
MA). These projections include a sensitivity study to various assumptions of the simulation. While the heat transport model is at the heart of such simulations, more comprehensive simulations are required to test all operational aspects of the current ramp-up and ramp-down phases of ITER scenarios. Recent examples of such simulations, involving coupled core transport codes, free-boundary equilibrium solvers and a poloidal field (PF) systems controller are also described, focusing on ITER current ramp-down.
Imbeaux, F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Budny, R.*; Casper, T.*; Citrin, J.*; Fereira, J.*; 福山 淳*; Garcia, J.*; Gribov, Y. V.*; 林 伸彦; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
In order to prepare adequate current ramp-up and ramp-down scenarios for ITER, present experiments from various tokamaks have been analysed by means of integrated modelling in view of determining relevant heat transport models for these operation phases. The most accurate heat transport models are then applied to projections to ITER current ramp-up, focusing on the baseline inductive scenario (main heating plateau current of Ip = 15 MA). These projections include a sensitivity studies to various assumptions of the simulation. Recent examples of such simulations, involving coupled core transport codes, free boundary equilibrium solvers and a poloidal field (PF) systems controller are described in the second part of the paper, focusing on ITER current ramp-down.
Imbeaux, F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Budny, R.*; Casper, T.*; Citrin, J.*; Fereira, J.*; 福山 淳*; Garcia, J.*; Gribov, Y. V.*; 林 伸彦; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/10
ITERでの電流立ち上げ・立ち下げシナリオの準備に向けて、これら運転状態においてどの熱輸送モデルが適切であるかを決定するために、代表的なトカマクでの現在の実験結果を統合モデルシミュレーションにより解析した。本研究では、トカマク実験の解析結果をもとに、ITER標準誘導運転(プラズマ電流15MA)の電流立ち上げ・立ち下げシナリオでの予測を行った。統合モデルシミュレーション結果を、ASDEX Upgrade, C-Mod, DIII-D, JET, Tore Supraのオーミック加熱プラズマ及び外部加熱・電流駆動プラズマ実験データと比較することにより、さまざまな輸送モデルの検証を行った。最も実験結果の再現性の良かった幾つかのモデルを用いて、ITERの電流立ち上げ・立ち下げ段階での電子密度・電流密度プロファイルの予測を行った。電子温度プロファイルには輸送モデルによって大きな差が見られたが、最終的な電流密度プロファイルはモデル間でよく一致することがわかった。
Sips, A. C. C.*; Casper, T.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; Gribov, Y.*; Hobirk, J.*; Hogeweij, G. M. D.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hutchinson, I.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(8), p.085015_1 - 085015_11, 2009/08
被引用回数:58 パーセンタイル:87.66(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)ITERにおける放電の時間発展に関して、実験的に検証した。すなわち、着火から電流立ち上げ,電流フラットトップ,電流立ち下げである。着火に関しては、JETのような大型トカマクではECRFによる補助なしで、またECRFによる補助が有る場合にはすべての装置でITERの要求である一周電界 0.35V/mでの着火を確認できた。立ち上げ時には、早期にダイバータ移行し大きなプラズマ断面を早くに形成することによりインダクタンスをよく制御できることがわかった。フラットトップでの種々の特性、特にH-mode遷移後と逆遷移後のインダクタンスの変化についてデータが得られた。
0.35V/mでの着火を確認できた。立ち上げ時には、早期にダイバータ移行し大きなプラズマ断面を早くに形成することによりインダクタンスをよく制御できることがわかった。フラットトップでの種々の特性、特にH-mode遷移後と逆遷移後のインダクタンスの変化についてデータが得られた。
Roach, C. M.*; Walters, M.*; Budny, R. V.*; Imbeaux, F.*; Fredian, T. W.*; Greenwald, M.*; Stillerman, J. A.*; Alexander, D. A.*; Carlsson, J.*; Cary, J. R.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 48(12), p.125001_1 - 125001_19, 2008/12
被引用回数:35 パーセンタイル:25.40(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)本論文では、国際トカマク物理活動において構築し2008年に一般公開した分布データベースについて述べる。分布データベースは、プラズマ輸送特性を記述するモデルの検証に活用される。1998年に一般公開した分布データベースに加えて、世界のトカマク装置(11台)で得られた代表的な分布データ(約100放電)を新たに登録している。例えば、JETとTFTRで実施されたDT放電、各装置で得られた内部輸送障壁を持つ放電やハイブリッド運転シナリオの放電などが含まれており、新規登録されたすべての放電の目的や特徴を装置ごとに記述している。また、分布データベースはftp, http, MDSplusを通して読み出しが可能である。
Giruzzi, G.*; Park, J. M.*; Murakami, M.*; Kessel, C. E.*; Polevoi, A.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Artaud, J. F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Bonoli, P.*; Budny, R. V.*; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
The modeling of the steady-state ITER scenarios is reviewed, as a subject of common work of the ITPA-SSO group. Focus is made not only on the basic physics issues, resulting from theory and experiments, but also on the difficulties and the needs of integrated modeling. Specific issues connected with high bootstrap fraction in the long pulse operation are addressed. Bootstrap current can be enhanced either by large pedestal temperatures, or by Internal Transport Barriers (ITB). Recent simulations for both high-pedestal scenarios and ITB scenarios are compared. Results of code benchmarking for typical parameters of ITER scenarios are also analyzed, and prospects for improvement of the integrated modeling capability will be discussed.
Sips, A. C. C.*; Casper, T. A.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; Gribov, Y.*; Hobirk, J.*; Hogeweij, G. M. D.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hutchinson, I.*; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
ITERにおける放電の時間発展に関して、実験的に検証した。すなわち、着火から電流立ち上げ,電流フラットトップ,電流たち下げである。着火に関しては、JETのような大型トカマクではECRFによる補助なしで、またECRFによる補助が有る場合にはすべての装置でITERの要求である一周電界 0.35V/mでの着火を確認できた。立ち上げ時には、早期にダイバータ移行し大きなプラズマ断面を早くに形成することによりインダクタンスをよく制御できることがわかった。フラットトップでの種々の特性、特にH-mode遷移後と逆遷移後のインダクタンスの変化についてデータが得られた。
0.35V/mでの着火を確認できた。立ち上げ時には、早期にダイバータ移行し大きなプラズマ断面を早くに形成することによりインダクタンスをよく制御できることがわかった。フラットトップでの種々の特性、特にH-mode遷移後と逆遷移後のインダクタンスの変化についてデータが得られた。
Hender, T. C.*; Wesley, J. C.*; Bialek, J.*; Bondeson, A.*; Boozer, A. H.*; Buttery, R. J.*; Garofalo, A.*; Goodman, T. P.*; Granetz, R. S.*; Gribov, Y.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S128 - S202, 2007/06
被引用回数:1017 パーセンタイル:98.25(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)本論文は、1999年の"ITER Physics Basis"の刊行以降に世界各国の装置で得られた重要な成果について記述したものであり、本章ではMHD安定性及びディスラプションに関する成果が記述されている。MHD安定性に関しては、(1)鋸歯状振動,(2)新古典テアリングモード,(3)抵抗性壁モード,(4)誤差磁場,(5)先進シナリオにおけるMHD安定性に関する成果が記述されていて、ディスラプションに関しては、(1)ディスラプションの特徴・原因・頻度,(2)サーマルクエンチによるエネルギーの損失と堆積,(3)電流クエンチのダイナミクス,(4)ディスラプションにより発生する逃走電子,(5)統合モデルとシミュレーション,(6)ディスラプションの回避・予測・緩和に関する成果が記述されている。
Gormezano, C.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Luce, T. C.*; 井手 俊介; Becoulet, A.*; Litaudon, X.*; 諫山 明彦; Hobirk, J.*; Wade, M. R.*; 及川 聡洋; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S285 - S336, 2007/06
被引用回数:349 パーセンタイル:75.44(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)国際熱核融合実験炉(ITER)におけるプラズマ開発に向けた物理的基盤について最近の研究の国際的な進展についてまとめたものである。この章ではITERにおける定常運転に関して、以下の点に重点を置いて記述する。統合運転シナリオ, 運転シナリオの最近の開発状況について、定常運転のための加熱/電流駆動装置、定常運転へ向けた制御の課題について、ITERにおける定常運転とハイブリッド運転のシミュレーション。
及川 聡洋; 嶋田 道也; Polevoi, A. R.*; 内藤 磨; Bonoli, P. T.*; 林 伸彦; Kessel, C. E.*; 小関 隆久
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2007/03
ITER定常運転シナリオにおける低域混成波(LH)による電流駆動性能を相対論的1次元フォッカープランクコードとトロイダル光線追跡コードを用いて評価した。現在のLHランチャー設計では電流駆動効率1.8 10
10 AW
AW m
m を実現し、LH駆動電流分布は周辺分布となり負磁気シア配位の形成に有利である。LHパワースペクトルのさらなる最適化についても検討した。また、中性粒子電流駆動(NBCD)について異なる計算手法を採る理論コードを使って検討した。バウンス平均したフォッカープランク方程式に基づくNBCD理論コードはトロイダル系での粒子の軌道効果を含むので、粒子軌道追跡モンテカルロコードによる結果と良い一致を示した。
を実現し、LH駆動電流分布は周辺分布となり負磁気シア配位の形成に有利である。LHパワースペクトルのさらなる最適化についても検討した。また、中性粒子電流駆動(NBCD)について異なる計算手法を採る理論コードを使って検討した。バウンス平均したフォッカープランク方程式に基づくNBCD理論コードはトロイダル系での粒子の軌道効果を含むので、粒子軌道追跡モンテカルロコードによる結果と良い一致を示した。
Bonoli, P. T.*; Harvey, R. W.*; Kessel, C. E.*; Imbeaux, F.*; 及川 聡洋; Schneider, M.*; Barbato, E.*; Decker, J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; Forest, C. B.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
ITER定常運転プラズマを対象として、複数の低域混成波(LH)電流駆動計算コードを比較した。LH計算コードには2次元速度空間で定義されたFokker-Planck方程式をもとにしたコード及び1次元Fokker-Planck方程式をもとにしたコードがあり、2次元Fokker-Planckコードは最も適切な取り扱いをしていると考えられる。2次元コードは1次元コードに比べて40%程度大きいLH駆動電流を与えた。また、捕捉粒子効果の考慮も重要であることもわかった。さらに、バウンス平均したオペレータの導入が必要であり、バウンス平均していないオペレータを使った場合30%程度計算結果が異なる。また、核融合生成物である3.5MeVのアルファ粒子によるLH波の吸収を評価した。アルファ粒子の異常輸送によりLH波吸収領域でのアルファ粒子密度が増加する場合でも、LH波周波数3.7GHzにおいてアルファ粒子により吸収されるLHパワーは7.7%と小さく、LH機器の設計値である5GHzに対して周波数選択の余地があることを示した。
Kessel, C. E.*; Giruzzi, G.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Budny, R. V.*; Artaud, J. F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Imbeaux, F.*; Joffrin, E.*; Schneider, M.*; Luce, T.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
国際トカマク物理活動の定常運転グループでは統合シミュレーションコードのベンチマークを始めており、CRONOS, ONETWO, TRANSP, TOPICS, ASTRAといった複数の1.5次元輸送コードを用いてITERハイブリッド運転のシミュレーションを行った。平衡配位,加熱電流駆動機器のジオメトリ、熱・粒子輸送モデル等について共通ガイドラインを設けて極力同じ計算条件となるようにしている。世界的に利用されている輸送コードのほとんどが参加したベンチマークは初めてであり、結果の違いについて結論できる段階には至っていないが、各コードにおいて改良すべき点を客観的に評価できることを明らかにした。