Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:96.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Tajima, Yoshihiro; Kuwabara, Jun; Oyokawa, Atsushi; Kabuto, Shoji; Araya, Naoyuki; Kikuchi, Kaoru; Miyamoto, Shingo; Nemoto, Hideyuki; Oe, Osamu
JAEA-Review 2016-003, 56 Pages, 2016/05
Nuclear Facilities Management Section implements the operation, maintenance and decommissioning of the first nuclear ship "MUTSU" and the operation and maintenance of the liquid waste facility and the solid waste facility where a small amount of nuclear fuel is used. This is the report on the operations of the Nuclear Facilities Management Section for FY 2012 and FY 2013.
Urano, Hajime; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Nakano, Tomohide; Fujita, Takaaki; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 53(8), p.083003_1 - 083003_8, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:78.38(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dependence of heat transport, edge pedestal and confinement on isotopic composition was investigated in conventional H-mode plasmas. Identical profiles for the electron density, electron temperature, and ion temperature were obtained for hydrogen and deuterium plasmas, whereas the required power clearly increased for hydrogen, which resulted in reduction of heat diffusivity for deuterium. The inverse of the ion-temperature-gradient (ITG) scale length which is required for a given ion heat diffusivity increased by a factor of approximately 1.2 for deuterium compared with that for hydrogen.
Urano, Hajime; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Nakano, Tomohide; Fujita, Takaaki; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; JT-60 Team
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/01
Dependence of heat transport on isotopic composition is investigated in conventional H-mode plasmas for the application to ITER. The identical profiles of 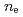 ,
, 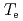 and
and 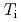 are obtained for hydrogen and deuterium plasmas while the required power becomes clearly larger for hydrogen, resulting in the reduction of the heat diffusivity for deuterium. The result of the identical temperature profiles in spite of different heating power suggests that the characteristics of heat conduction differs essentially between hydrogen and deuterium even at the same scale length of temperature gradient. On the other hand, the edge stability is improved by increased total
are obtained for hydrogen and deuterium plasmas while the required power becomes clearly larger for hydrogen, resulting in the reduction of the heat diffusivity for deuterium. The result of the identical temperature profiles in spite of different heating power suggests that the characteristics of heat conduction differs essentially between hydrogen and deuterium even at the same scale length of temperature gradient. On the other hand, the edge stability is improved by increased total 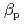 regardless of the difference of the isotropic composition.
regardless of the difference of the isotropic composition.
 -mode plasmas
-mode plasmasUrano, Hajime; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Nakano, Tomohide; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamada, Yutaka
Physical Review Letters, 109(12), p.125001_1 - 125001_5, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:78.55(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The dependence of the ion temperature gradient scale length on the hydrogen isotope mass was examined in conventional  -mode plasmas in JT-60U tokamak. While identical profiles for density and temperature were obtained for hydrogen and deuterium plasmas, the ion conductive heat flux necessary for hydrogen to sustain the same thermal stored energy was two times that required for deuterium, resulting in a clearly higher ion heat diffusivity for hydrogen at the same ion temperature gradient scale length. The ion temperature gradient scale length for deuterium is less than that for hydrogen at a given ion heat diffusivity.
-mode plasmas in JT-60U tokamak. While identical profiles for density and temperature were obtained for hydrogen and deuterium plasmas, the ion conductive heat flux necessary for hydrogen to sustain the same thermal stored energy was two times that required for deuterium, resulting in a clearly higher ion heat diffusivity for hydrogen at the same ion temperature gradient scale length. The ion temperature gradient scale length for deuterium is less than that for hydrogen at a given ion heat diffusivity.
Urano, Hajime; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Nakano, Tomohide; Fujita, Takaaki; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (Internet), 36F, p.P1.016_1 - P1.016_4, 2012/00
Energy confinement properties for hydrogen and deuterium H-mode plasmas were examined in JT-60U. The energy confinement time became larger by a factor of  1.2-1.3 for deuterium than for hydrogen at a given
1.2-1.3 for deuterium than for hydrogen at a given 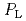 . When the plasma energy was fixed, the profiles of density and temperature became identical for both cases while higher heating power was required for hydrogen. The ion conductive heat flux for hydrogen became approximately two times that for deuterium. Hence, the ion heat diffusivity for hydrogen was higher than for deuterium. It was found that the ion-temperature-gradient scale length became smaller by a factor of
. When the plasma energy was fixed, the profiles of density and temperature became identical for both cases while higher heating power was required for hydrogen. The ion conductive heat flux for hydrogen became approximately two times that for deuterium. Hence, the ion heat diffusivity for hydrogen was higher than for deuterium. It was found that the ion-temperature-gradient scale length became smaller by a factor of  1.2 for deuterium than for hydrogen.
1.2 for deuterium than for hydrogen.
Matsukawa, Makoto; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Hayashi, Takao; Higashijima, Satoru; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Ishida, Shinichi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.795 - 803, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:71.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Fujita, Takaaki; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Bialek, J.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Sakurai, Shinji; Suzuki, Yutaka; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(11), p.1512 - 1523, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:63.18(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Design of modification of JT-60U, JT-60SA, has been optimized in viewpoint of plasma control, and operation regimes have been evaluated. Upper and lower divertors with different geometry are prepared for flexibility of plasma shape control. The beam lines of negative-ion NBI are shifted downward for off-axis current drive, in order to obtain a weak/reversed shear plasma. The feedback control coils along the port hole in the stabilizing plate are found effective to suppress the resistive wall mode (RWM) and sustain high 
 close to the ideal wall limit. The regime of full current drive operation has been extended with upgraded heating and current drive power. Full current drive operation for 100 s with reactor-relevant high values of normalized beta and bootstrap current fraction (
close to the ideal wall limit. The regime of full current drive operation has been extended with upgraded heating and current drive power. Full current drive operation for 100 s with reactor-relevant high values of normalized beta and bootstrap current fraction (
 = 2.4 MA,
= 2.4 MA, 
 = 4.4,
= 4.4, 
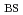 = 0.70,
= 0.70, 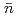
 /
/
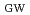 = 0.86, H
= 0.86, H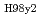 = 1.3) is expected in a highly-shaped low-aspect-ratio configuration (
= 1.3) is expected in a highly-shaped low-aspect-ratio configuration ( = 2.65). High
= 2.65). High 
 , high-density ELMy H-mode is also expected.
, high-density ELMy H-mode is also expected.
Hirose, Akira; Wada, Shigeru; Sasajima, Fumio; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi; Kameyama, Iwao*; Aizawa, Ryoji*; Kikuchi, Naoyuki*
JAEA-Technology 2006-059, 122 Pages, 2007/01
It is expected that the demand for NTD-Si increases rapidly because of recent productive increase of hybrid-cars. In order to meet the demand, we have investigated the expansion technology of the NTD-Si productivity using the JRR3. This report describes the production of equipment for the external cooling device while proposed as one of the result of the investigation for the JRR-3 uniformity irradiation equipment. After an ingot was irradiated once, it is turned over manually and irradiated again in order irradiate the ingot uniformly. With the conventional equipment, it was necessary to wait the radioactivity of ingot decrease less than the permissible level with holding the ingot in the irradiation equipment. It was effective to shorten the waiting period by using an external cooling device for production increase of NTD-Si. It is expected that the productivity of NTD-Si will be increased by using the external cooling device.
Kimura, Haruyuki; Inutake, Masaaki*; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Ogawa, Yuichi*; Kamada, Yutaka; Ozeki, Takahisa; Naito, Osamu; Takase, Yuichi*; Ide, Shunsuke; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 83(1), p.81 - 93, 2007/01
no abstracts in English
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Akiba, Masato; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Inoue, Nobuyuki; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S428 - S432, 2006/12
To contribute DEMO and ITER, the design to modify the present JT-60U into superconducting coil machine, named National Centralized Tokamak (NCT), is being progressed under nationwide collaborations in Japan. Mission, design and strategy of this NCT program is summarized.
Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Fujita, Takaaki; Takase, Yuichi*; Sakurai, Shinji; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kurita, Genichi; Morioka, Atsuhiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(3), p.S29 - S38, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:40.56(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The National Centralized Tokamak (NCT) facility program is a domestic research program for advanced tokamak research to succeed JT-60U incorporating Japanese university accomplishments. The mission of NCT is to establish high beta steady-state operation for DEMO and to contribute to ITER. The machine flexibility and mobility is pursued in aspect ratio and shape controllability, feedback control of resistive wall modes, wide current and pressure profile control capability for the demonstration of the high-b steady state.
Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1599 - 1605, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 plasma operation
plasma operationTamai, Hiroshi; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujita, Takaaki; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ichimura, Makoto*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(12), p.1676 - 1683, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:44.52(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Design studies are shown on the National Centralized Tokamak facility. The machine design is carried out to investigate the capability for the flexibility in aspect ratio and shape controllability for the demonstration of the high-beta steady state operation with nation-wide collaboration, in parallel with ITER towards DEMO. Two designs are proposed and assessed with respect to the physics requirements such as confinement, stability, current drive, divertor, and energetic particle confinement. The operation range in the aspect ratio and the plasma shape is widely enhanced in consistent with the sufficient divertor pumping. Evaluations of the plasma performance towards the determination of machine design are presented.
Sakasai, Akira; Ishida, Shinichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Akino, Noboru; Ando, Toshinari*; Arai, Takashi; Ezato, Koichiro; Hamada, Kazuya; Ichige, Hisashi; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 44(2), p.329 - 334, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:22.40(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Sakasai, Akira; Ishida, Shinichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Akino, Noboru; Ando, Toshinari*; Arai, Takashi; Ezato, Koichiro; Hamada, Kazuya; Ichige, Hisashi; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 44(2), p.329 - 334, 2004/02
no abstracts in English
Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Miura, Yushi; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Kudo, Yusuke; et al.
Plasma Science and Technology, 6(1), p.2141 - 2150, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.31(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The dominant issue for the the modification program of JT-60 (JT-60SC) is to demonstrate the steady state reactor relevant plasma operation. Physics design on plasma parameters, operation scenarios, and the plasma control method are investigated for the achievement of high- . Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
. Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Kimura, Haruyuki; Kawashima, Hisato; Sato, Masayasu; Kamiya, Kensaku; Shinohara, Koji; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Bakhtiari, M.; Kasai, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(10), p.1288 - 1293, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:72.81(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Chujo, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
no abstracts in English
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Cho, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:67.95(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English