Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sugita, Yutaka; Ono, Hirokazu; Beese, S.*; Pan, P.*; Kim, M.*; Lee, C.*; Jove-Colon, C.*; Lopez, C. M.*; Liang, S.-Y.*
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 42, p.100668_1 - 100668_21, 2025/06
The international cooperative project DECOVALEX 2023 focused on the Horonobe EBS experiment in the Task D, which was undertaken to study, using numerical analyses, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (or thermo-hydro) interactions in bentonite based engineered barriers. One full-scale in-situ experiment and four laboratory experiments, largely complementary, were selected for modelling. The Horonobe EBS experiment is a temperature-controlled non-isothermal experiment combined with artificial groundwater injection. The Horonobe EBS experiment consists of the heating and cooling phases. Six research teams performed the THM or TH (depended on research team approach) numerical analyses using a variety of computer codes, formulations and constitutive laws.
Go, G.*; Goli, D. P.*; Esaki, Nanse; Tserkovnyak, Y.*; Kim, S. K.*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 7(2), p.L022066_1 - L022066_7, 2025/06
Kawasaki, Takuro; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Yamanaka, Satoru*; Murayama, Ichiro*; Kato, Takanori*; Baba, Masaaki*; Hashimoto, Hideki*; Harjo, S.; Aizawa, Kazuya; Tanaka, Hirohisa*; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 137(9), p.094101_1 - 094101_7, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Suzuki, Seiya; Katsube, Daiki*; Yano, Masahiro; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Terasawa, Tomoo; Ozawa, Takahiro*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki; Kim, Y.*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Yuhara, Junji*; et al.
Small Methods, 9(3), p.2400863_1 - 2400863_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Osawa, Naoki*; Kim, S.-Y.*; Kubota, Masahiko*; Wu, H.*; Watanabe, So; Ito, Tatsuya; Nagaishi, Ryuji
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 56(3), p.812 - 818, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kim, Y.*; Oka, Makoto; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 107(7), p.074015_1 - 074015_15, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:65.40(Astronomy & Astrophysics)A chiral effective theory of scalar and vector diquarks is formulated, which is based on 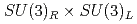 chiral symmetry and includes interactions between scalar and vector diquarks with one or two mesons. We find that the diquark interaction term with two mesons breaks the
chiral symmetry and includes interactions between scalar and vector diquarks with one or two mesons. We find that the diquark interaction term with two mesons breaks the 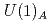 and flavor
and flavor 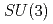 symmetries. To determine the coupling constants of the interaction Lagrangians, we investigate one-pion emission decays of singly heavy baryons
symmetries. To determine the coupling constants of the interaction Lagrangians, we investigate one-pion emission decays of singly heavy baryons 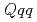 (
(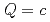 ,
,  and
and 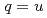 ,
,  ,
,  ), where baryons are regarded as diquark-heavy-quark two-body systems. Using this model, we present predictions of the unobserved decay widths of singly heavy baryons. We also study the change of masses and strong decay widths of singly heavy baryons under partial restoration of chiral symmetry.
), where baryons are regarded as diquark-heavy-quark two-body systems. Using this model, we present predictions of the unobserved decay widths of singly heavy baryons. We also study the change of masses and strong decay widths of singly heavy baryons under partial restoration of chiral symmetry.
Akuzawa, Tadashi*; Kim, S.-Y.*; Kubota, Masahiko*; Wu, H.*; Watanabe, So; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Arai, Tsuyoshi*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 331(12), p.5851 - 5858, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:61.74(Chemistry, Analytical) Fe
Fe O
O spinel and postspinel with elevating pressure
spinel and postspinel with elevating pressureYamanaka, Takamitsu*; Rahman, S.*; Nakamoto, Yuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Jang, B. G.*; Kim, D. Y.*; Mao, H.-K.*
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 167, p.110721_1 - 110721_10, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.72(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)High-pressure neutron diffraction proved that MnFe O
O and Mn
and Mn FeO
FeO spinels transform into CaMn
spinels transform into CaMn O
O -type structure above 18 GPa and 14 GPa, respectively. The transition pressure of Mn
-type structure above 18 GPa and 14 GPa, respectively. The transition pressure of Mn Fe
Fe O
O solutions decreases with increasing Mn content. Synchrotron X-ray M
solutions decreases with increasing Mn content. Synchrotron X-ray M ssbauer experiments revealed that Fe
ssbauer experiments revealed that Fe and Fe
and Fe distribution at the tetrahedral (A) and octahedral (B) sites in the spinel structure changes with pressure. MnFe
distribution at the tetrahedral (A) and octahedral (B) sites in the spinel structure changes with pressure. MnFe O
O and Mn
and Mn FeO
FeO spinels are ferrimagnetic and the CaMn
spinels are ferrimagnetic and the CaMn O
O -type phase is paramagnetic. The temperature dependence of resistivity indicates that both spinels are semiconductors wherein electrons hop between cations at the A and B sites. A pressure-induced shortening of B-B distance promoted conduction via greater electron mobility between adjacent B cations. The Fe
-type phase is paramagnetic. The temperature dependence of resistivity indicates that both spinels are semiconductors wherein electrons hop between cations at the A and B sites. A pressure-induced shortening of B-B distance promoted conduction via greater electron mobility between adjacent B cations. The Fe and Fe
and Fe occupancies at the B sites in MnFe
occupancies at the B sites in MnFe O
O are much larger than those in Mn
are much larger than those in Mn FeO
FeO . The CaMn
. The CaMn O
O -type phase is metallic. Theoretical calculation confirmed the metallic character and Fe d-orbitals strongly renormalized compared to Mn d-orbitals.
-type phase is metallic. Theoretical calculation confirmed the metallic character and Fe d-orbitals strongly renormalized compared to Mn d-orbitals.
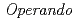 structure observation of pyroelectric ceramics during power generation cycle
structure observation of pyroelectric ceramics during power generation cycleKawasaki, Takuro; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Yamanaka, Satoru*; Sakamoto, Tomokazu*; Murayama, Ichiro*; Kato, Takanori*; Baba, Masaaki*; Hashimoto, Hideki*; Harjo, S.; Aizawa, Kazuya; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 131(13), p.134103_1 - 134103_7, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.30(Physics, Applied)Kim, Y.*; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 105(7), p.074021_1 - 074021_17, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:95.10(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Energy spectrum of doubly heavy tetraquarks, 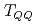 (
(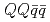 with
with 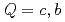 and
and 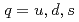 ), is studied in the potential chiral-diquark model. Using the chiral effective theory of diquarks and the quark-diquark-based potential model, the
), is studied in the potential chiral-diquark model. Using the chiral effective theory of diquarks and the quark-diquark-based potential model, the 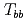 ,
, 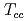 , and
, and 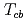 tetraquarks are described as a three-body system composed of two heavy quarks and an antidiquark. We find several
tetraquarks are described as a three-body system composed of two heavy quarks and an antidiquark. We find several 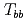 bound states, while no
bound states, while no 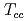 and
and 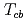 (deep) bound state is seen. We also study the change of the
(deep) bound state is seen. We also study the change of the 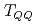 tetraquark masses under restoration of chiral symmetry.
tetraquark masses under restoration of chiral symmetry.
Ito, Tatsuya; Osugi, Haruka*; Osawa, Naoki*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; Kim, S.-Y.*; Nagaishi, Ryuji
Analytical Sciences, 38(1), p.91 - 97, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.50(Chemistry, Analytical)A novel ionic liquid (IL) functionalized with thiodiglycol amic acid containing a soft S donor was synthesized for the effective and efficient extraction of platinum group metals (Ru, Rh, and Pd) from aqueous nitric acid solutions, such as high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW). The IL allowed a rapid extraction of Pd(II) with an extraction ratio of approximately 100%. The extractions of Ru(III) and Rh(III) by the IL were slower than that of Pd(II), but the rates were accelerated by temperature elevation. The extractions of Ru(III) and Rh(III) at 50 C reached equilibrium within 4 and 8 h, respectively, with the extraction ratios of over 90% without assisting agents or other methods for the extraction system. Furthermore, the IL could extract more than 90% of Ru(III), Rh(III), and Pd(II) from the simulated HLLW within 2 h at 50
C reached equilibrium within 4 and 8 h, respectively, with the extraction ratios of over 90% without assisting agents or other methods for the extraction system. Furthermore, the IL could extract more than 90% of Ru(III), Rh(III), and Pd(II) from the simulated HLLW within 2 h at 50 C.
C.
Kim, Y. S.*; Chae, H.*; Woo, W.*; Kim, D.-K.*; Lee, D.-H.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Lee, S. Y.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 828, p.142059_1 - 142059_10, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:88.45(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Kim, Y.*; Liu, Y.-R.*; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 104(5), p.054012_1 - 054012_18, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:72.62(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Chiral effective theory of scalar and vector diquarks is formulated according to the linear sigma model. The main application is to describe the ground and excited states of singly heavy baryons with a charm or bottom quark. Applying the potential quark model between the diquark and the heavy quark (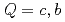 ), we construct a heavy-quark-diquark model. The spectra of the positive- and negative-parity states of
), we construct a heavy-quark-diquark model. The spectra of the positive- and negative-parity states of 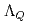 ,
, 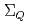 ,
, 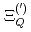 and
and 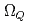 are obtained. The masses and interaction parameters of the effective theory are fixed partly from the lattice QCD data and also from fitting low-lying heavy baryon masses. We find that the negative parity excited states of
are obtained. The masses and interaction parameters of the effective theory are fixed partly from the lattice QCD data and also from fitting low-lying heavy baryon masses. We find that the negative parity excited states of 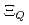 (flavor
(flavor 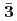 ) are different from those of
) are different from those of 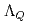 , because of the inverse hierarchy of the pseudoscalar diquark. On the other hand,
, because of the inverse hierarchy of the pseudoscalar diquark. On the other hand, 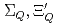 and
and 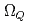 (flavor
(flavor 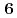 ) baryons have similar spectra. We compare our results of the heavy-quark-diquark model with experimental data as well as the quark model.
) baryons have similar spectra. We compare our results of the heavy-quark-diquark model with experimental data as well as the quark model.
Kwon, H.*; Pietrasiak, E.*; Ohara, Takashi; Nakao, Akiko*; Chae, B.*; Hwang, C.-C.*; Jung, D.*; Hwang, I.-C.*; Ko, Y. H.*; Kim, K.*; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 60(9), p.6403 - 6409, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear) /Y
/Y Fe
Fe O
O layers via longitudinal spin Seebeck effect
layers via longitudinal spin Seebeck effectLee, W.-Y.*; Park, N.-W.*; Kang, M.-S.*; Kim, G.-S.*; Jang, H. W.*; Saito, Eiji; Lee, S.-K.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 11(13), p.5338 - 5344, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:57.30(Chemistry, Physical)Kim, Y.*; Hiyama, Emiko*; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 102(1), p.014004_1 - 014004_9, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:75.26(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Applying the chiral effective theory of diquarks, we analyze the spectrum and structure of singly heavy baryons. We introduce the phenomenological quark-model potentials for the confinement. We predict the charmed and bottom baryon spectrum showing the inverse mass hierarchy.
Yeom, Y. S.*; Han, M. C.*; Choi, C.*; Han, H.*; Shin, B.*; Furuta, Takuya; Kim, C. H.*
Health Physics, 116(5), p.664 - 676, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:80.10(Environmental Sciences)Recently, Task Group 103 of the ICRP developed the mesh-type reference computational phantoms (MCRPs), which are planned for use in future ICRP dose coefficient calculation. Performance of major Monte Carlo particle transport codes (Geant4, MCNP6, and PHITS) were tested with MCRP. External and internal exposure of various particles and energies were calculated and the computational times and required memories were compared. Additionally calculation for voxel-mesh phantom was also conducted so that the influence of different mesh-representation in each code was studied. Memory usage of MRCP was as large as 10 GB with Geant4 and MCNP6 while it is much less with PHITS (1.2 GB). In addition, the computational time required for MRCP tends to increase compared to voxel-mesh phantoms with Geant4 and MCNP6 while it is equal or tends to decrease with PHITS.
Kim, S. K.*; Nakata, Koki; Loss, D.*; Tserkovnyak, Y.*
Physical Review Letters, 122(5), p.057204_1 - 057204_6, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:65 Percentile:93.66(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically study the thermal Hall effect by magnons in skyrmion crystal phases of ferrimagnets in the vicinity of the angular momentum compensation point (CP). For an experimental proposal, we predict that themagnonic thermal Hall conductivity changes its sign when the ferrimagnet is tuned across the CP, providing a way to control heat flux in spin-caloritronic devices on the one hand and a feasible way todetect the CP of ferrimagnets on the other hand.
Nagano, Hirohiko; Kim, Y.*; Lee, B.-Y.*; Shigeta, Haruka*; Inubushi, Kazuyuki*
Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 64(6), p.793 - 802, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.76(Plant Sciences)In this study, we conducted an incubation experiment on a frozen soil core collected from a black spruce forest in Interior Alaska, in order to investigate potential changes in greenhouse gaseous (GHG) and microbial dynamics during thawing of frozen soil. The soil thawing is an important environmental process determining the annual GHG balance in the northern high-latitude ecosystem. A core spanning the ground surface to upper permafrost with a depth of 90 cm was vertically grouped into three layers (top, middle, and bottom layers). Then, 12 soil samples from 3 layers (i.e., 4 soil samples per layer) were incubated for 3 weeks, and net carbon dioxide (Co ) and methane (CH
) and methane (CH ) release/uptake rates were estimated. During the incubation, temperature was changed weekly from 0 to 5, then 10
) release/uptake rates were estimated. During the incubation, temperature was changed weekly from 0 to 5, then 10 C. The net amounts of CO
C. The net amounts of CO released by six of the eight soil samples from the top and middle layers were 1.5 to 19.2-fold greater at 5
released by six of the eight soil samples from the top and middle layers were 1.5 to 19.2-fold greater at 5 C than at 0
C than at 0 C, while the release at 10
C, while the release at 10 C was reduced in the cases of three of these six soil samples. Net CH
C was reduced in the cases of three of these six soil samples. Net CH release was the greatest in bottom-layer soil samples incubated at 0
release was the greatest in bottom-layer soil samples incubated at 0 C. Then, low but apparent CH
C. Then, low but apparent CH release was observed in top and middle-layer soil samples incubated at 0
release was observed in top and middle-layer soil samples incubated at 0 C. At 5 and 10
C. At 5 and 10 C, net CH
C, net CH release from bottom-layer soil samples was decreased. Then, net CH
release from bottom-layer soil samples was decreased. Then, net CH uptake was observed in the top and the middle-layer soil samples. Both net uptake and release of CH
uptake was observed in the top and the middle-layer soil samples. Both net uptake and release of CH were reduced upon the addition of a chemical inhibitor (i.e., 2-bromoethane sulfonate) of anaerobic methanotrophic and methanogenic activity. The bacterial and archaeal community structures based on 16S rRNA amplicon analysis were changed along the depth, while they were less changed during thawing. Thus, it was found that soil GHG dynamics responded sensitively and variously to thawing, while there was less change in 16S rRNA-based microbial community structures during the thawing prog
were reduced upon the addition of a chemical inhibitor (i.e., 2-bromoethane sulfonate) of anaerobic methanotrophic and methanogenic activity. The bacterial and archaeal community structures based on 16S rRNA amplicon analysis were changed along the depth, while they were less changed during thawing. Thus, it was found that soil GHG dynamics responded sensitively and variously to thawing, while there was less change in 16S rRNA-based microbial community structures during the thawing prog
Kobayashi, Hideki*; Suzuki, Rikie*; Yang, W.*; Ikawa, Hiroki*; Inoue, Tomoharu*; Nagano, Hirohiko; Kim, Y.*
Polar Data Journal (Internet), 2, p.14 - 29, 2018/11
The Arctic and boreal regions have been experiencing a rapid warming in the 21st century. It is important to understand the dynamics of boreal forest at the continental scale under the climate and environmental changes. While the role of understory vegetation in boreal forest ecosystems on carbon and nutrient cycling cannot be ignored, they are still one of least understood components in boreal ecosystems. Spectroscopic measurements of vegetation are useful to identify species and their biochemical characteristics. In this data paper, we present spectral reflectances of 44 typical understory formations and five 30-m long transects. The spectral reflectance covers the spectral region of visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared (350-2500 nm). For the transect measurements, we decided the length of transect at 30 m, similar to the scale of one pixel of a Landsat type satellite imagery. The photographs at all positions, where spectral reflectances were obtained, are included to understand the structure and status of each sample. The data set contains six dwarf shrubs (blueberry (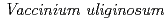 ), cowberry (
), cowberry (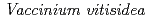 ), feltleaf willow (
), feltleaf willow (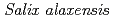 ), young birch (
), young birch (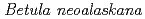 ), young aspen (
), young aspen (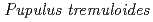 ), and young black spruce (
), and young black spruce (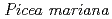 )), two herbaceous (cottongrass (
)), two herbaceous (cottongrass (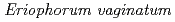 ) and marsh Labrador tea (
) and marsh Labrador tea ( )), three mosses (Sphagnum moss, splendid feather moss (
)), three mosses (Sphagnum moss, splendid feather moss ( ), and polytrichum moss (
), and polytrichum moss ( )), and reindeer lichen (
)), and reindeer lichen ( ). Spectral reflectances from several non-vegetative such as snow, litter, and soil are also included. This spectral and photographic data set can be used for understanding the spectral characteristics of understory formations, designing newly planned spectral observations, and developing and validating the remote sensing methodology of large scale understory monitoring.
). Spectral reflectances from several non-vegetative such as snow, litter, and soil are also included. This spectral and photographic data set can be used for understanding the spectral characteristics of understory formations, designing newly planned spectral observations, and developing and validating the remote sensing methodology of large scale understory monitoring.