Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshida, Masato; Iguchi, Satoshi; Hirano, Hiroshi*; Kitamura, Akihiro
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 431, p.113691_1 - 113691_16, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Plutonium Fuel Fabrication Facility is currently in the decommissioning phase, with glovebox dismantling operations ongoing since 2010. During conventional glovebox dismantling operations, the glovebox to be dismantled is enclosed within plastic tents to contain contamination. The glovebox is then dismantled by workers wearing air-fed suits with thermal or mechanical cutting tools, which typically generate dross or sparks in the form of radioactive aerosols during cutting. Despite the longevity and meticulous organization of this manual method, the workload remains considerable, while the allowable working time is limited. In addition, the potential for inhalation exposure to plutonium is elevated in the event of an accident given the contamination of the work area. To overcome disadvantages associated with conventional glovebox dismantling methods, new methods are currently being developed. The primary objective is to reduce the reliance on operation based on air-fed suits and enhance worker safety by introducing remote equipment and a new floor-reinforcing panel. Another objective is to suppress waste generation by reusing all equipment on multiple occasions which is achieved by developing a containment system that have a large open port with a pallet for the storage and reuse of equipment for successive operations. Furthermore, a glove operation compartment is designed and tested for the manual handling of dismantled materials as an additional strategy to reduce work based on air-fed suits and mitigate secondary waste generation.
Kitamura, Ryo; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Nemoto, Yasuo*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2687(7), p.072006_1 - 072006_6, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)The mitigation of heat loading is one of the important issues for beam instrumentation to measure the high-power proton beam. Recently, the highly-oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) material was used for the target probe of the bunch-shape monitor at the front-end in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). Since the thermal conductivity of the HOPG is high, it is suitable to measure the beam profile under the condition of high heat loading. As an application of the HOPG, for example, the thin HOPG may be used as a substitutive material of the target wire for the transverse profile monitor such as the wire scanner monitor. The possibility of the HOPG target for the beam profile monitor is discussed from some results of the test experiment using the 3-MeV negative hydrogen ion beam at the test stand.
Arai, Sora; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Kitamura, Ryo
JAEA-Technology 2023-009, 18 Pages, 2023/05
The linac located at the head of the J-PARC accelerators and required to provide the stable and high-quality beam. One of the accelerating cavities in the linac is the Separated-type Drift Tube Linac (SDTL). It is important to appropriately apply the RF power into the cavity for the stable operation. However, after the recovery from the Great East Japan Earthquake, the RF power could not be applied into the cavities for several SDTL cavities because the voltage standing wave ratio increased around the designed operating power. The investigation revealed that the inner surface of the cavity was exposed to high humidity and the backflow of oil from the rotary pump for a long period of time after the earthquake. It was suggested that the residue on the inner surface caused the multipactor resulted in the failure when the power was applied. The residue was wiped out with organic solvents and acids, resulted in solving the failure. This report describes the method and results of the cleaning for the cavity in 2021.
Kosaka, Satoshi*; Arai, Sora; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Kitamura, Ryo
JAEA-Technology 2023-003, 34 Pages, 2023/05
The negative hydrogen (H ) ion beam is accelerated with a peak current of 50 mA in the J-PARC linac. The linac consists of the H
) ion beam is accelerated with a peak current of 50 mA in the J-PARC linac. The linac consists of the H ion source and four kinds of accelerating cavities; a radio-frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ), a drift-tube linac (DTL), a separated-DTL (SDTL), and an annular-ring coupled structure linac (ACS). The accelerating electric field exists between the drift-tubes in the tank of the DTL. The quadrupole magnet for the beam focusing (DTQ) is installed in the drift-tube. The DTQ at J-PARC employs electromagnets to generate the magnetic field. It is important to set correctly the polarity of the magnetic field of the DTQ for tuning the beam. In this paper, we report the method of confirming the magnetic field polarity of DTQ, that is, the current wiring polarity by measuring DC current using a clamp meter on the power supply side and visually confirming the cable wiring connection on the electromagnet side.
ion source and four kinds of accelerating cavities; a radio-frequency quadrupole linac (RFQ), a drift-tube linac (DTL), a separated-DTL (SDTL), and an annular-ring coupled structure linac (ACS). The accelerating electric field exists between the drift-tubes in the tank of the DTL. The quadrupole magnet for the beam focusing (DTQ) is installed in the drift-tube. The DTQ at J-PARC employs electromagnets to generate the magnetic field. It is important to set correctly the polarity of the magnetic field of the DTQ for tuning the beam. In this paper, we report the method of confirming the magnetic field polarity of DTQ, that is, the current wiring polarity by measuring DC current using a clamp meter on the power supply side and visually confirming the cable wiring connection on the electromagnet side.
Kitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 26(3), p.032802_1 - 032802_12, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:60.26(Physics, Nuclear)A bunch-shape monitor (BSM) is a useful device for performing longitudinal beam tuning using the pointwise longitudinal phase distribution measured at selected points in the beam transportation. To measure the longitudinal phase distribution of a low-energy negative hydrogen (H ) ion beam, highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was adopted for the secondary-electron-emission target to mitigate the thermal damage due to the high-intensity beam loading. The HOPG target enabled the measurement of the longitudinal phase distribution at the center of a 3-MeV H
) ion beam, highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was adopted for the secondary-electron-emission target to mitigate the thermal damage due to the high-intensity beam loading. The HOPG target enabled the measurement of the longitudinal phase distribution at the center of a 3-MeV H ion beam with a high peak current of about 50 mA. The longitudinal bunch width was measured using HOPG-BSM at the test stand, which was consistent with the beam simulation. The correlation measurement between the beam transverse and longitudinal planes was demonstrated using HOPG-BSM. The longitudinal Twiss and emittance measurement with the longitudinal Q-scan method was conducted using HOPG-BSM.
ion beam with a high peak current of about 50 mA. The longitudinal bunch width was measured using HOPG-BSM at the test stand, which was consistent with the beam simulation. The correlation measurement between the beam transverse and longitudinal planes was demonstrated using HOPG-BSM. The longitudinal Twiss and emittance measurement with the longitudinal Q-scan method was conducted using HOPG-BSM.
 beam
beamKitamura, Ryo; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Morishita, Takatoshi
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.330 - 332, 2023/01
In the J-PARC linac, a new bunch-shape monitor (BSM) is developed to stably measure the high-intensity and low-energy H beam by improving the strength of the target probe for the heat loading. The new target probe is made of the graphite. The first measurement of the longitudinal beam profile has been realized with the BSM at the core region of the high-intensity beam. Since the beam profile can be measured with the new BSM at any transverse position thanks to the new target probe, we propose the advanced application of the beam diagnostics with the BSM. In this presentation, some new approaches of the beam diagnostics with the BSM; the transverse profile measurement using the secondary electrons and the beam current evaluation from the transverse profile measurement, are discussed beyond the original usage of the BSM.
beam by improving the strength of the target probe for the heat loading. The new target probe is made of the graphite. The first measurement of the longitudinal beam profile has been realized with the BSM at the core region of the high-intensity beam. Since the beam profile can be measured with the new BSM at any transverse position thanks to the new target probe, we propose the advanced application of the beam diagnostics with the BSM. In this presentation, some new approaches of the beam diagnostics with the BSM; the transverse profile measurement using the secondary electrons and the beam current evaluation from the transverse profile measurement, are discussed beyond the original usage of the BSM.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Otani, Masashi*; Cicek, E.*; Ego, Hiroyasu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; et al.
Proceedings of 31st International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2022) (Internet), p.636 - 641, 2022/09
The muon linac project for the precise measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic and electric dipole moments, which is currently one of the hottest issues of the elementary particle physics, is in progress at J-PARC. The muons from the J-PARC muon facility are once cooled to room temperature, then accelerated up to 212 MeV with a normalized emittance of 1.5  mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
Nakazawa, Yuga*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Iwata, Yoshiyuki*; Cicek, E.*; Ego, Hiroyasu*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Mizobata, Satoshi*; Otani, Masashi*; et al.
Proceedings of 31st International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2022) (Internet), p.275 - 278, 2022/09
We conducted a high-power test of a prototype cavity of a 324-MHz inter-digital H-mode drift tube linac (IH-DTL) for the muon g-2/EDM experiment at J-PARC. This prototype cavity (short-IH) was developed to verify the fabrication methodology for the full-length IH cavity with a monolithic DT structure. After 40 h of conditioning, the short-IH has been stably operated with an RF power of 88 kW, which corresponds to 10% higher accelerating field than the design field (E0) of 3.0 MV/m. In addition, the thermal characteristics and frequency response were measured, verifying that the experimental data was consistent with the three-dimensional model. In this paper, the high-power tests of this IH-DTL for muon acceleration are described.
 beam with 3 MeV by the bunch-shape monitor
beam with 3 MeV by the bunch-shape monitorKitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011012_1 - 011012_6, 2021/03
The new bunch shape monitor (BSM) is required to measure the bunch size of the high-intensity H beam with 3 MeV at the front-end section in the J-PARC linac. The carbon-nano tube wire and the graphene stick are good candidates for the target wire of the BSM, because these materials have the enough strength to detect the high-intensity beam. However, since the negative high voltage of more than a few kV should be applied to the wire in the BSM, the suppression of the discharge is the challenge to realize the new BSM. After the high-voltage test to investigate the effect of the discharge from the wire, the detection of the signal from the BSM was successful at the beam core with the peak current of 55 mA using the graphene stick. The preliminary result of the bunch-size measurement is reported in this presentation.
beam with 3 MeV at the front-end section in the J-PARC linac. The carbon-nano tube wire and the graphene stick are good candidates for the target wire of the BSM, because these materials have the enough strength to detect the high-intensity beam. However, since the negative high voltage of more than a few kV should be applied to the wire in the BSM, the suppression of the discharge is the challenge to realize the new BSM. After the high-voltage test to investigate the effect of the discharge from the wire, the detection of the signal from the BSM was successful at the beam core with the peak current of 55 mA using the graphene stick. The preliminary result of the bunch-size measurement is reported in this presentation.
Kitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 17th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.251 - 253, 2020/09
A bunch-shape monitor (BSM) in the low-energy region is being developed in the J-PARC linac to accelerate the high-intensity proton beam with the low emittance. A highly-oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was introduced as the target of the BSM to mitigate the thermal loading. The stable measurement of the BSM was realized thanks to the HOPG target, while the tungsten target was broken by the thermal loading from the high-intensity beam. However, since the longitudinal distribution measured with the BSM using the HOPG target was wider than the expected one, the improvement of tuning parameters is necessary for the BSM. The BSM consists of an electron multiplier, a bending magnet, and a radio-frequency deflector, which should be tuned appropriately. Behavior of these components were investigated and tuned. The longitudinal distribution measured with the BSM after the tuning was consistent with the expected one.
Taruta, Yasuyoshi; Yanagihara, Satoshi*; Hashimoto, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Shigeto*; Iguchi, Yukihiro; Kitamura, Koichi; Koda, Yuya; Tomoda, Koichi
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2020/08
Decommissioning is a long-term project during which generations are expected to change. Therefore, it is necessary to appropriately transfer knowledge and technology to the next generation. In recent years, in the world of decommissioning, attempts have been made to apply advanced technologies such as utilization of knowledge management and virtual reality. This study describes adaptation in decommissioning from the viewpoint of utilizing IT technology called digital twin from the viewpoint of knowledge management.
 beam with 3 MeV using the carbon material
beam with 3 MeV using the carbon materialKitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.51 - 54, 2019/07
The longitudinal measurement and tuning at the beam transport after the RFQ are important to reduce the beam loss and the emittance growth in the J-PARC linac, when the high-intensity H beam of more than 60 mA is supplied. The new bunch shape monitor (BSM) using the carbon-nanotube (CNT) wire is necessary to measure the bunch shape of the high-intensity H
beam of more than 60 mA is supplied. The new bunch shape monitor (BSM) using the carbon-nanotube (CNT) wire is necessary to measure the bunch shape of the high-intensity H beam with 3 MeV, because the CNT wire has a high-temperature tolerance and a small energy deposit. However, when the high voltage was applied to the CNT wire to extract the secondary electron derived, the discharge prevents the power supply from applying the voltage. Therefore, the discharge should be suppressed to measure the bunch shape with stability. Considering the characteristics of the CNT as the emitter, when the length of the CNT wire was short, the high voltage of -10 kV was applied to the CNT wire. The current status and future prospects of the BSM using the CNT wire are reported in this presentation.
beam with 3 MeV, because the CNT wire has a high-temperature tolerance and a small energy deposit. However, when the high voltage was applied to the CNT wire to extract the secondary electron derived, the discharge prevents the power supply from applying the voltage. Therefore, the discharge should be suppressed to measure the bunch shape with stability. Considering the characteristics of the CNT as the emitter, when the length of the CNT wire was short, the high voltage of -10 kV was applied to the CNT wire. The current status and future prospects of the BSM using the CNT wire are reported in this presentation.
Kitamura, Ryo; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Otani, Masashi*; Kosaka, Satoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.2543 - 2546, 2019/06
A bunch shape monitor (BSM) is one of the important instruments to measure the longitudinal phase space distribution. For example in the J-PARC linac, three BSMs using the tungsten wire are installed at the ACS section to measure the bunch shapes between the accelerating cavities. However, this conventional BSM is hard to measure the bunch shape of H beam with 3 MeV at the beam transport between the RFQ and DTL sections, because the wire is broken around the center region of the beam. The new BSM using the carbon-nano-tube (CNT) wire is being developed to be able to measure the bunch shape of the H
beam with 3 MeV at the beam transport between the RFQ and DTL sections, because the wire is broken around the center region of the beam. The new BSM using the carbon-nano-tube (CNT) wire is being developed to be able to measure the bunch shape of the H beam with 3 MeV. The careful attention should be paid to apply the high voltage of
beam with 3 MeV. The careful attention should be paid to apply the high voltage of  10 kV to the CNT wire. The several measures are taken to suppress the discharge from the wire and operate the CNT-BSM. This presentation reports the current status of the development and future prospective for the CNT-BSM.
10 kV to the CNT wire. The several measures are taken to suppress the discharge from the wire and operate the CNT-BSM. This presentation reports the current status of the development and future prospective for the CNT-BSM.
Taruta, Yasuyoshi; Yanagihara, Satoshi*; Iguchi, Yukihiro; Kitamura, Koichi; Tezuka, Masashi; Koda, Yuya
Chishiki Kyoso (Internet), 8, p.IV 2_1 - IV 2_12, 2018/08
no abstracts in English
Taruta, Yasuyoshi; Yanagihara, Satoshi*; Iguchi, Yukihiro; Kitamura, Koichi; Tezuka, Masashi; Koda, Yuya
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2018/07
The IAEA are developed the discussion for those situations and pointed out the importance of nuclear knowledge management. The nuclear knowledge management is developing a database as nuclear knowledge management. In recent years, the IAEA has also advanced knowledge taxonomies on nuclear accidents. These studies are attempts to appropriately arrange and utilize huge amounts of information. Even in nuclear facilities in Japan, it is pointed out that veteran staff aging and loss of knowledge and skill caused by retirement. Therefore, we created a prototype database system to utilize past knowledge and information for ATR Fugen. Now, there are few cases of past decommissioning that can be utilized. This study of pilot model concept revealed that it is not sufficient to just prepare a past data and information. This is what information other than the construction report requires the decommissioning and what kind of information should be gathered.
 mutant
mutantKitamura, Satoshi; Ono, Yutaka; Narumi, Issey*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 64, 2016/02
Forward genetics approaches have helped elucidate the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in plants. We used the 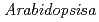 banyuls (ban) mutant, which accumulates anthocyanins, instead of colorless proanthocyanidin precursors, in immature seeds. In contrast to standard screens for mutants lacking anthocyanins in leaves/stems, we mutagenized ban plants and screened for mutants showing differences in pigmentation of immature seeds. The pale banyuls1 (pab1) mutation was found to show reduced levels of anthocyanins in immature seed coat. Here we characterize this mutant at the molecular level.
banyuls (ban) mutant, which accumulates anthocyanins, instead of colorless proanthocyanidin precursors, in immature seeds. In contrast to standard screens for mutants lacking anthocyanins in leaves/stems, we mutagenized ban plants and screened for mutants showing differences in pigmentation of immature seeds. The pale banyuls1 (pab1) mutation was found to show reduced levels of anthocyanins in immature seed coat. Here we characterize this mutant at the molecular level.
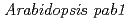 , a mutant with reduced anthocyanins in immature seeds from
, a mutant with reduced anthocyanins in immature seeds from 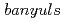 , harbors a mutation in the MATE transporter
, harbors a mutation in the MATE transporter 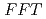
Kitamura, Satoshi; Ono, Yutaka; Narumi, Issey*
Plant Molecular Biology, 90(1-2), p.7 - 18, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:67.71(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Here, we used the Arabidopsis banyuls (ban) mutant, which accumulates anthocyanins, instead of colorless proanthocyanidin precursors, in immature seeds. We mutagenized ban plants and screened for mutants showing differences in pigmentation of immature seeds. The pale banyuls1 (pab1) mutation caused reduced anthocyanin pigmentation in immature seeds compared with ban, but showed normal expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes. Map-based cloning showed that two independent pab1 alleles disrupted the MATE-type transporter gene FFT/DTX35. Complementation of pab1 with FFT confirmed that mutation in FFT causes the pab1 phenotype. During development, FFT promoter activity was detected in the seed-coat layers that accumulate flavonoids. Anthocyanins accumulate in the vacuole and FFT fused to GFP mainly localized in the vacuolar membrane.
Yuyama, Takahiro; Ishibori, Ikuo; Kurashima, Satoshi; Yoshida, Kenichi; Ishizaka, Tomohisa; Chiba, Atsuya; Yamada, Keisuke; Yokoyama, Akihito; Usui, Aya; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; et al.
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.302 - 304, 2015/09
no abstracts in English
 exhibiting different anthocyanin accumulation patterns
exhibiting different anthocyanin accumulation patternsKitamura, Satoshi; Ono, Yutaka; Narumi, Issey*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 72, 2015/03
Ion beams have been used for isolation of novel mutants in a number of plant species in our laboratory. Re-mutagenesis by secondary irradiation of ion beams to already-established ion beam-induced mutants would be effective to modify plant characters step-by-step, because ion beams are likely to induce mutations at the limited regions of the genome. Here, we try to adapt the re-mutagenesis by secondary ion beam irradiation in model plant  , for obtaining flavonoid mutants that have not been found so far by standard mutagenesis and screening methods.
, for obtaining flavonoid mutants that have not been found so far by standard mutagenesis and screening methods.
 -ray sensitivity in
-ray sensitivity in  exhibiting different flavonoid accumulation patterns
exhibiting different flavonoid accumulation patternsKitamura, Satoshi; Narumi, Issey*
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 71, 2014/03
In this study, to understand more deeply the physiological functions of flavonoids in plants, we analyze the responses to  -irradiation in Arabidopsis thaliana exhibiting different flavonoid accumulation patterns. When dry seeds were exposed to
-irradiation in Arabidopsis thaliana exhibiting different flavonoid accumulation patterns. When dry seeds were exposed to  -rays, obvious differences in
-rays, obvious differences in  -ray sensitivities were detected between WT and a complete flavonoid-less mutant, tt4. When dry seeds of tt12, seed-specific flavonoid mutant, were exposed to
-ray sensitivities were detected between WT and a complete flavonoid-less mutant, tt4. When dry seeds of tt12, seed-specific flavonoid mutant, were exposed to  -rays, a survival rate was also reduced compared to WT. In addition, to know the relationship between
-rays, a survival rate was also reduced compared to WT. In addition, to know the relationship between  -ray sensitivity and radical scavenging activity of flavonoids, ROS scavenging ability in dry seeds was determined for each genotype. These results suggest that flavonoids would contribute ROS scavenging within irradiated seeds, even in the case where the flavonoid accumulating tissues are apart from the rudimentary plant body, an embryo.
-ray sensitivity and radical scavenging activity of flavonoids, ROS scavenging ability in dry seeds was determined for each genotype. These results suggest that flavonoids would contribute ROS scavenging within irradiated seeds, even in the case where the flavonoid accumulating tissues are apart from the rudimentary plant body, an embryo.