Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 gamma-ray imager using detector response patterns
gamma-ray imager using detector response patterns北山 佳治; 野上 光博*; 人見 啓太朗*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(7), p.076502_1 - 076502_8, 2024/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)三次元空間に無作為に配置した複数のガンマ線検出器の応答強度パターンから、ガンマ線源の入射方向を推定する新しいガンマ線イメージング技術の開発を行っている。本論文では、8個のGAGG (Ce)シンチレータキューブと18個の鉛キューブで構成されるガンマ線イメージャー、Coded Cube Camera for Gamma-ray (C3G)を製作し、 Cs線源の4
Cs線源の4 イメージング実験を実施した。実験の結果、3m先にある10MBqの
イメージング実験を実施した。実験の結果、3m先にある10MBqの Cs線源を10分間の測定で、angle uncertainty5度の精度でイメージングできることを確認した。一般にガンマ線イメージャーは数百から数千の読み出しチャンネル数が必要となるが、C3Gは僅か8チャンネルの読み出し回路で構成される。そのため回路や再構成アルゴリズムはシンプルにすることができ、安価かつ信頼性の高いイメージャーが実現する。C3Gは大きさ86mm
Cs線源を10分間の測定で、angle uncertainty5度の精度でイメージングできることを確認した。一般にガンマ線イメージャーは数百から数千の読み出しチャンネル数が必要となるが、C3Gは僅か8チャンネルの読み出し回路で構成される。そのため回路や再構成アルゴリズムはシンプルにすることができ、安価かつ信頼性の高いイメージャーが実現する。C3Gは大きさ86mm  86mm
86mm  86mmのハウジングに格納されており、重量は約600gである。小型軽量で4
86mmのハウジングに格納されており、重量は約600gである。小型軽量で4 視野を持ち、高角度分解能を持つ本技術は、天文学や医療、核セキュリティ、原子力発電所の廃止措置など広範な応用が期待される。
視野を持ち、高角度分解能を持つ本技術は、天文学や医療、核セキュリティ、原子力発電所の廃止措置など広範な応用が期待される。
 field-of-view gamma-ray imaging
field-of-view gamma-ray imaging北山 佳治
IEEE NPSS Newsletter (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/06
At the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station decommissioning site, there's a need for gamma-ray imaging technology that is compact and lightweight enough to be mounted on autonomous exploration robots, has a wide FOV and can operate in high-dose-rate environments. Coded masks and Compton cameras, although small and light, suffer from limitations such as a narrow FOV, susceptibility to background noise, or poor angular resolution and unsuitability for high-dose environments, respectively. Therefore, we developed a novel gamma-ray imaging technology that weighs about 600 g, has a cubic form measuring 8.6 cm on each side, offers a 4 FOV, has an angular resolution of approximately 5
FOV, has an angular resolution of approximately 5 , and is expected to operate in environments with radiation levels up to 100 mSv/h with only eight readout channels.
, and is expected to operate in environments with radiation levels up to 100 mSv/h with only eight readout channels.
北山 佳治; 野上 光博*; 人見 啓太朗*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(3), p.032005_1 - 032005_6, 2024/03
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:40.97(Physics, Applied)検出器の応答パターンを利用した新しいガンマ線イメージング技術を紹介する。この方法では、三次元状にランダムに配置された複数の遮蔽体キューブを使用する。これらのキューブで定義された領域内では、ガンマ線の入射方向に基づいて固有のガンマ線フラックスパターンが形成される。このパターンは、複数のシンチレーターキューブの応答パターンとして測定される。ガンマ線の入射方向と対応する検出器応答パターンを事前に測定することで、アンフォールディング法を用いて入射方向を推定することができる。 Cs点線源を用いてシミュレーションを行った。その結果、10MBqの
Cs点線源を用いてシミュレーションを行った。その結果、10MBqの Cs線源をイメージャーから3m離れた位置に設置した場合、約10
Cs線源をイメージャーから3m離れた位置に設置した場合、約10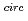 の角度分解能で撮像できることがわかった。これらの結果は、我々の新しい方法が既存のガンマ線イメージング技術と同等以上の性能を有することを示唆している。この撮像法の応用としては、原子力発電所の廃止措置、核医学、セキュリティ、天文学などが考えられる。
の角度分解能で撮像できることがわかった。これらの結果は、我々の新しい方法が既存のガンマ線イメージング技術と同等以上の性能を有することを示唆している。この撮像法の応用としては、原子力発電所の廃止措置、核医学、セキュリティ、天文学などが考えられる。
北山 佳治; 野上 光博*; 人見 啓太朗*
KEK Proceedings 2022-3, p.46 - 53, 2023/01
街灯の光で夜道に映し出された自分の影の向きや形から街灯の位置を予想することができる。この考えをガンマ線イメージャーに応用したものはCoded apertureとして知られている。今回、立体的な遮蔽とシンチレータ結晶配置を持ったCoded Cube Camera - POrtable (C3PO)を発案した。C3POは鉛、シンチレータ、空乏でできたキューブを3 3
3 3のルーリックキューブ状にランダムに配置したもので、各シンチレータの出力は3次元影模様を作り出す。三次元影からアンフォールディングによって線源方向分布にもどる。今回、Geant 4を用いたシミュレーションでその特性や実現可能性を検討した。
3のルーリックキューブ状にランダムに配置したもので、各シンチレータの出力は3次元影模様を作り出す。三次元影からアンフォールディングによって線源方向分布にもどる。今回、Geant 4を用いたシミュレーションでその特性や実現可能性を検討した。
森下 祐樹; 高崎 浩司; 北山 佳治; 田川 明広; 柴田 卓弥; 星 勝也; 金子 純一*; 樋口 幹雄*; 大浦 正利*
Radiation Measurements, 160, p.106896_1 - 106896_10, 2023/01
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:92.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)福島第一原子力発電所のアルファおよびベータ汚染をリアルタイム弁別測定するためのPhoswichアルファ/ベータ検出器を開発した。検出器は、アルファ線とベータ線を検出する2層のシンチレータ(プラスチックシンチレータ及びGPSシンチレータ)で構成した。パルス波形弁別(PSD)法を使用して、高ベータ線および高ガンマ線環境でアルファ線をリアルタイムを弁別測定できた。さらに、この検出器は、最大9.0mSv/hのバックグラウンド線量下でアルファ線を識別することができた。
北山 佳治
Gamma Ray Imaging; Technology and Applications, p.165 - 179, 2023/00
ガンマ線イメージャーは放射線源分布をイメージングするための強力なツールである。近年は福島第一原子力発電所の廃止措置に応用されている。廃止措置現場においては、小型軽量でかつ定量評価が可能であることが求められている。小角コンプトン散乱を用いたガンマ線イメージャー(Gamma-ray Imager using Small-Angle Scattering: GISAS)はそれらすべての要求を満たしたイメージャーである。GISASは遮蔽体を必要としない指向性ガンマ線検出器群によって構成される。シミュレーションと実験によって、本手法の実現可能性の検討を実施した。適切なエネルギーウインドウを散乱体と吸収体に設定することで、超昇格散乱イベントのみを選別し指向性を得ることが可能であることを実証した。
北山 佳治; 寺阪 祐太; 佐藤 優樹; 鳥居 建男
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 7(4), p.042006_1 - 042006_7, 2021/10
Gamma-ray imaging is a technique to visualize the spatial distribution of radioactive materials. Recently, gamma-ray imaging has been applied to research on decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) accident and environmental restoration, and active research has been conducted. This study is the elemental technology study of the new gamma-ray imager GISAS (Gamma-ray Imager using Small-Angle Scattering), which is assumed to be applied to the decommissioning site of FDNPS. GISAS consists of a set of directional gamma-ray detectors that do not require a shield. In this study, we investigated the feasibility of the shield free directional gamma-ray detector by simulation. The simulation result suggests that by measuring several keV of scattered electron energy by scatterer detector, gamma rays with ultra-small angle scattering could be selected. By using Compton scattering kinematics, a shield-free detector with directivity of about 10 could be feasible. By arranging the directional gamma-ray detectors in an array, it is expected to realize the GISAS, which is small, light, and capable of quantitative measurement.
could be feasible. By arranging the directional gamma-ray detectors in an array, it is expected to realize the GISAS, which is small, light, and capable of quantitative measurement.
北山 佳治; 寺阪 祐太; 佐藤 優樹; 鳥居 建男
Proceedings of International Youth Nuclear Congress 2020 (IYNC 2020) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2020/05
At the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), various works are under-way for decommissioning. Depending on work places, there are radioactive hotspot. Therefore measuring the position of the hotspot in advance is important for safety of the worker. The system that can easily measure the dose rate distribution in work place has been demanded. There are two methods for imaging a dose rate distribution: a pinhole camera and a Compton camera. A pinhole camera can determine direction of radiation source in one event, but the weight becomes heavy because a shield is required. On the other hand, since the Compton camera does not require a shield, it can be reduced in the size and weight. However, Compton imaging method generate many ghosts of cone traces, which reduce the signal-to-noise ratio. We propose a new gamma-ray imager that works like a pinhole camera without a shield. This is achieved by arranging directional gamma ray detectors that does not require a shield. In this work, we have performed principle verification of a directional gamma-ray detector that is a basic component of the new gamma-ray imager by using Geant4 Monte Carlo simulation.
北山 佳治
人見 啓太朗*; 野上 光博*
【課題】視野が広く、放射線エネルギーの適用範囲が広く、且つ、小型軽量化を図ることが可能な新しい放射線検出装置を提供することを目的とする。 【解決手段】放射線検出装置1は、放射線を検出する複数の検出素子12が3次元的に配置された検出素子群11を備える放射線検出装置である。検出素子群11の構造は、任意の仮想面S上に検出素子12が敷き詰められた仮想検出素子群から任意の位置の検出素子12を取り除いて形成された空乏13を有する構造である。空乏13は、任意の方向に沿って配置された一の検出素子12A及び他の検出素子12Bの各検出値の差分が、当該方向を入射方向とする放射線が入射する場合と当該方向の逆方向を入射方向とする放射線が入射する場合とにおいて、異なる値を示す位置に設けられる。
北山 佳治
人見 啓太朗*; 野上 光博*
A radiation detection device is provided that is wide in visual field, wide in application range of radiation energy, and which is smaller and lighter in weight as compared to other devices. The device includes a detecting element group has a plurality of detecting elements that detect radiation are three-dimensionally arranged. The detecting element group has a structure with a depletion formed by removing the detecting element at any position from a virtual detecting element group in which the detecting elements are laid out on any virtual surface. The depletion is provided at a position at which a difference of detected values between one detecting element and another detecting element arranged along any direction exhibits different values in a case where the radiation having the direction as an incident direction enters and a case where the radiation having an opposite direction of the direction as an incident direction enters.
北山 佳治
no journal, ,
三次元空間に無作為に配置されたガンマ線検出器群の応答パターンから、ガンマ線の入射方向を推定する技術についてシミュレーション及び実験により特性評価を重ねてきた。これまでは、福島第一原子力発電所廃炉や環境回復を主な目的として研究してきたため、イメージング対象核種として Cs (662keV)を設定してきたが、今回は医療応用を目的として
Cs (662keV)を設定してきたが、今回は医療応用を目的として Co (122keV),
Co (122keV),  F (511keV)の同時イメージングを実施した。
F (511keV)の同時イメージングを実施した。 Coは、SPECTでよく用いられる
Coは、SPECTでよく用いられる Tc (141keV)の代わりに用いた。実験とシミュレーションによって、その特性を評価し、医療応用への検討を行った。
Tc (141keV)の代わりに用いた。実験とシミュレーションによって、その特性を評価し、医療応用への検討を行った。
森下 祐樹; 北山 佳治
no journal, ,
この論文では、パルス形状弁別技術を使用してアルファ線、ベータ線、ガンマ線を区別できるホスウィッチ検出器の開発について説明している。検出器には、アルファ粒子とベータ粒子を検出するためのスチルベン シンチレーターと、ガンマ線を検出するためのGAGGシンチレーターの2層のシンチレーターがある。この研究は、ホスウィッチ検出器からのデータを使用して、機械学習技術を放射線測定に適用することを目的としている。K-最近傍アルゴリズムを使用して、さまざまな種類の放射線を分類した。結果は、近傍数を増やすと精度が向上することを示し、放射線分類には値20が選択された。この研究は、効率的かつ自動的なアルファ線、ベータ線、ガンマ線の識別と放射性核種の同定における機械学習の有効性を実証しており、放射線の経験がほとんどない作業員が現場で作業するのに役立つ。
北山 佳治; 野上 光博*; 人見 啓太朗*
no journal, ,
空間に無作為に配置した複数の遮蔽体によって、測定環境のガンマ線フラックス場を局所的に変調し、その三次元的なフラックス強度パターンからガンマ線源分布を推定する、新しいガンマ線イメージング手法を開発している。これまで、本手法を利用したガンマカメラであるC3Gを製作し、単一線源を用いたイメージング実験を実施してきた。本研究では、線・面状分布を持ったガンマ線源に対してのイメージングについてシミュレーションによる評価を行った。長さ2m, 4m, 6mの線状線源、また一片の長さが2m, 4m, 6mの正方形線源を3m先に置いた状況を仮定した。 Cs (662keV)と
Cs (662keV)と Co (122keV)の二核種をターゲットとした。その結果、分布線源の形状に応じたイメージング結果が得られることを確認した。また、ガンマ線のエネルギーによってイメージング精度に差が出ることも分かった。
Co (122keV)の二核種をターゲットとした。その結果、分布線源の形状に応じたイメージング結果が得られることを確認した。また、ガンマ線のエネルギーによってイメージング精度に差が出ることも分かった。
野上 光博*; 北山 佳治; 人見 啓太朗*; 田村 雄介*; 金子 慎一郎*; 高田 英治*; 鳥居 建男*
no journal, ,
ガンマ線源分布を調査するための指向性検出器の開発に取り組んでいる。ロボットに搭載することを前提に開発を行っているため、重量やサイズに制限がある中で、シンチレータとガンマ線遮蔽体として鉛アンチモンを採用した多面体型指向性検出器を製作し、その評価を実施している。本発表では、それらの詳細についての報告を行う。
 線カメラ
線カメラ北山 佳治
no journal, ,
小型・軽量・低コストで製作可能な新しいガンマ線イメージャーを開発している。この技術は、全方位のガンマ線を一度に可視化できる特長を有しており、従来の装置よりもシンプルな構造で低価格化が実現できる。本来は福島第一原子力発電所の廃止措置を目的とした技術であったが、ガンマ線イメージングを用いる様々な分野に応用できる可能性がある。具体的な応用先として、複数台の連携による広域モニタリング、核医学におけるRI薬剤の可視化、さらには人工衛星への搭載による宇宙線観測などを挙げ、既存技術との優位性について説明する。
北山 佳治; 寺阪 祐太; 佐藤 優樹
no journal, ,
車両搭載型のガンマ線イメージングシステムiRIS-Vを開発した。このシステムは車両周囲のガンマ線イメージングだけでなく、モニタリングカーと同様な走行サーベイも可能である。本発表では、iRIS-Vによる帰還困難区域内35号線の走行サーベイと、試験用 Cs線源を用いた車両全周囲のガンマ線イメージング試験の結果を報告する。
Cs線源を用いた車両全周囲のガンマ線イメージング試験の結果を報告する。
北山 佳治; 野上 光博*; 人見 啓太朗*
no journal, ,
街灯によって夜道に映し出された自分の影の数や形,濃淡をよく観察すると、街灯の数と方向を推測することができる。これをガンマ線イメージングに応用した例として、コーデッドマスクがよく知られている。コーデッドマスク方式のガンマ線イメージャーは、コーデッドマスクと呼ばれる複数の穴の開いた金属板によって、位置敏感型検出器上に映し出されたガンマ線の影模様から、光源、すなわちガンマ線源の方向と数を推定するものである。本研究はこの考えを三次元的に拡張し、符号化立体が作る三次元的な影模様を計測することで、4 方向の視野を持ったガンマ線イメージャーの実現を目指すものである。ガンマ線の作る三次元影という新しい概念を導入することで、既存のガンマ線イメージャーの抱えていた多くの欠点を克服でき、将来的に様々な応用可能性を持ったガンマ線イメージング手法が実現できる可能性が示された。
方向の視野を持ったガンマ線イメージャーの実現を目指すものである。ガンマ線の作る三次元影という新しい概念を導入することで、既存のガンマ線イメージャーの抱えていた多くの欠点を克服でき、将来的に様々な応用可能性を持ったガンマ線イメージング手法が実現できる可能性が示された。
野上 光博*; 北山 佳治; 人見 啓太朗*; 高田 英治*; 鳥居 建男*; 石井 慶造*
no journal, ,
先進放射線計測研究グループでは、福島第一原子力発電所建屋内で使用することを念頭において、斜方立方八面体型鉛遮蔽体とシンチレータを組み合わせた指向性検出器の開発に取り組んでいる。本発表では、今まで実施した基礎的な検討内容について報告を行う。
野上 光博*; 北山 佳治; 人見 啓太朗*; 高田 英治*; 鳥居 建男*; 石井 慶造*
no journal, ,
シンチレータと多面体ガンマ線遮蔽体からなる多面体型指向性検出器の開発に取り組んでいる。現在までに、LYSO(Ce)シンチレータと多面体型鉛アンチモン遮蔽体を組み合わせた多面体型検出器の製作を行い、またその評価を実施している。本発表では、それら詳細について報告を行う。
 field of view gamma-ray imaging method
field of view gamma-ray imaging method北山 佳治; 野上 光博*; 人見 啓太朗*
no journal, ,
In the present study, we devised a new gamma-ray imaging technique (Three-Dimentional Shadow Method: TDSM) that uses three-dimensional shadows of gamma rays. This technique is based on the fact that the three-dimensional shading of gamma-ray flux, which is uniquely determined by the direction of gamma-ray irradiation, is generated by randomly arranging shields in space. In this study, we developed a new prototype gamma-ray imager (Coded Cube Camera for Gamma-ray: C3G) and performed 4 gamma-ray imaging experiments targeting a
gamma-ray imaging experiments targeting a  Cs source. C3G is a gamma-ray imager designed to apply TDSM, consisting of 8 GAGG (Ce) scintillator cubes, 18 lead cubes, and one empty cube randomly arranged in a Rubik's cube configuration. The size of each cube is 10 mm
Cs source. C3G is a gamma-ray imager designed to apply TDSM, consisting of 8 GAGG (Ce) scintillator cubes, 18 lead cubes, and one empty cube randomly arranged in a Rubik's cube configuration. The size of each cube is 10 mm  10 mm
10 mm  10 mm; the entire C3G is 86 mm
10 mm; the entire C3G is 86 mm  86 mm
86 mm  86 mm and weighs about 600 g. The experiments were conducted indoors and outdoors under the condition that the 10 MBq
86 mm and weighs about 600 g. The experiments were conducted indoors and outdoors under the condition that the 10 MBq  Cs source was placed at a 3 m from the C3G. As a result, it was experimentally confirmed that 4
Cs source was placed at a 3 m from the C3G. As a result, it was experimentally confirmed that 4 imaging could be performed by the C3G with an angular resolution of approximately 10 degrees. This result suggests that the performance of our proposed method is equivalent to or better than that of the existing imaging methods. Further development of this technique is expected to significantly contribute to decommissioning, decontamination, nuclear medicine, astronomy, etc.
imaging could be performed by the C3G with an angular resolution of approximately 10 degrees. This result suggests that the performance of our proposed method is equivalent to or better than that of the existing imaging methods. Further development of this technique is expected to significantly contribute to decommissioning, decontamination, nuclear medicine, astronomy, etc.