Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Motooka, Takafumi; Ishikawa, Akiyoshi; Numata, Masami; Endo, Shinya; Itonaga, Fumio; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Kizaki, Minoru
JAEA-Research 2007-031, 20 Pages, 2007/03
An effect of neptunium ions on corrosion of stainless steel in nitric acid solution was investigated by corrosion tests. Type SUS304L stainless steel was used for the tests. The corrosion tests were conducted in 9kmol/m nitric acid solutions containing neptunium ions, where test specimens were immersed or heat-transferred. As a result, we found that neptunium ions promote corrosion of stainless steels in nitric acid solution. This finding would contribute to modifications of the materials for spent fuel reprocessing process.
nitric acid solutions containing neptunium ions, where test specimens were immersed or heat-transferred. As a result, we found that neptunium ions promote corrosion of stainless steels in nitric acid solution. This finding would contribute to modifications of the materials for spent fuel reprocessing process.
Endo, Shinya; Usami, Koji; Nakata, Masahito; Fukuda, Takuji*; Onozawa, Atsushi; Harada, Akio; Kizaki, Minoru; Kikuchi, Hiroyuki
HPR-366, Vol.1 (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Nakayama, Shinichi; Nagao, Seiya*; Kizaki, Minoru
Radiochimica Acta, 95(2), p.115 - 125, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.97(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Diffusive transport of neptunium, plutonium, tritiated water, Cs and I
and I in compacted sand-bentonite mixtures was studied by a through diffusion method. Experiments for Np were performed in the presence of carbonate where Np was stable as Np
in compacted sand-bentonite mixtures was studied by a through diffusion method. Experiments for Np were performed in the presence of carbonate where Np was stable as Np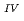 (CO
(CO )
) (OH)
(OH)
 and those for Pu in the presence of fulvic acid where the Pu was stable as fulvic complexes. These experiments were performed under Ar (
and those for Pu in the presence of fulvic acid where the Pu was stable as fulvic complexes. These experiments were performed under Ar (
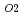
 10
10 atm). Effective diffusivity (De) values of (1.81
atm). Effective diffusivity (De) values of (1.81 0.03)
0.03) 10
10 , (1.8
, (1.8 0.8)
0.8) 10
10 , (5.1
, (5.1 0.8)
0.8) 10
10 and (9.0
and (9.0 4.1)
4.1) 10
10 m
m s
s were obtained for HTO, Cs
were obtained for HTO, Cs , I
, I and Np
and Np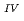 (CO
(CO )
) (OH)
(OH)
 , respectively. The ratio of the De to the diffusivity in bulk of the water was around 0.1 for Np
, respectively. The ratio of the De to the diffusivity in bulk of the water was around 0.1 for Np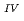 (CO
(CO )
) (OH)
(OH)
 , HTO and Cs
, HTO and Cs , which is consistent with the pore diffusion model. Observed diffusive transport of Pu was much smaller than those of HTO, Cs
, which is consistent with the pore diffusion model. Observed diffusive transport of Pu was much smaller than those of HTO, Cs , I
, I and Np
and Np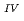 (CO
(CO )
) (OH)
(OH)
 probably because Pu was present as colloidal forms and that confined pore space in the compacted sand-bentonite mixtures does not allow diffusive transport of colloidal plutonium.
probably because Pu was present as colloidal forms and that confined pore space in the compacted sand-bentonite mixtures does not allow diffusive transport of colloidal plutonium.
Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Takano, Masahide; Ito, Akinori; Akabori, Mitsuo; Minato, Kazuo; Kizaki, Minoru
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 355(1-3), p.114 - 118, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:77.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The thermal diffusivity of AmN was measured from 373 to 1473 K by a laser flash method. The AmN sample was prepared from AmO by the carbothermic reduction. The obtained AmN product was grinded and pressed at about 400 MPa to form a disk. The disk was sintered at 1823 K for 10 hours in flowing N
by the carbothermic reduction. The obtained AmN product was grinded and pressed at about 400 MPa to form a disk. The disk was sintered at 1823 K for 10 hours in flowing N +4%H
+4%H gas. The thermal diffusivity slightly decreased from 3.4
gas. The thermal diffusivity slightly decreased from 3.4 10
10 to 2.8
to 2.8 10
10 m
m /s with increasing temperature. As the specific heat capacity of AmN was not available in literature, the thermal conductivity of AmN was tentatively estimated from the measured thermal diffusivity, bulk density and the specific heat capacity of PuN. It was found that the thermal conductivity of AmN slightly increased with temperature. The thermal conductivity of AmN corrected to 100%TD was found to be smaller than those of UN, NpN and PuN, whereas that of AmN was larger than those of UO
/s with increasing temperature. As the specific heat capacity of AmN was not available in literature, the thermal conductivity of AmN was tentatively estimated from the measured thermal diffusivity, bulk density and the specific heat capacity of PuN. It was found that the thermal conductivity of AmN slightly increased with temperature. The thermal conductivity of AmN corrected to 100%TD was found to be smaller than those of UN, NpN and PuN, whereas that of AmN was larger than those of UO and (U
and (U Pu
Pu )O
)O .
.
Ugachi, Hirokazu; Nakano, Junichi; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Kondo, Keietsu; Miwa, Yukio; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Tsukada, Takashi; Kizaki, Minoru; Omi, Masao; Shimizu, Michio
JAEA-Conf 2006-003, p.253 - 265, 2006/05
Irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) is one of the critical concerns when stainless steel components have been in service in the light water reactors (LWRs) for a long period. In general, IASCC can be reproduced on the materials irradiated over a certain threshold fluence level of fast neutron by the post-irradiation examinations (PIEs) at hot laboratories. On the other hand, recently in the Japanese boiling water reactor (BWR) power plants, many incidents of stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of structural material such as the reactor core shrouds and primary loop recirculation (PLR) system piping were reported. In order to investigate the cause of SCC, PIEs at hot laboratories were carried out on the sample material extracted from BWR power plants. SCC studies require various kind of PIE techniques, because the SCC is caused by a complicated synergistic effects of stress and chemical environment on material that suffered degradations by irradiation and/or thermal aging. In this paper, we describe the PIE techniques adopted recently for our SCC studies, especially the crack growth measurement, uniaxial constant load (UCL) tensile test method, in-situ observation during slow strain rate test (SSRT) and several metallurgical test techniques using the FEtype transmission electron microscopy (FE-TEM), focused ion beam (FIB) processing technique, three Dimensional Atom Probe (3DAP) analysis and atomic force microscopy (AFM).
Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Ioka, Ikuo; Tanabe, Makoto*; Nanjo, Yoshiyasu*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Tsukatani, Ichiro; Ochiai, Takamasa; Kizaki, Minoru; Kato, Yoshiaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2006-023, 173 Pages, 2006/03
The research concerning new cladding materials for ultra-high burnup of fuel elements with MOX fuels aiming at 100 GWd/t of BWR was pursued for 5 years from 2001 to 2005. On the Phase 1, the modified stainless steel of Fe-25Cr-35Ni-0.2Ti as fuel claddings and Nb-Mo alloy as a liner for inhibiting the pellet- clad interaction were selected as candidate materials, by evaluating fundamental properties required to BWR cladding materials, that are the nuclear economy, radioactivity, mass-transfer, irradiation properties, mechanical properties so on. On the present study, the making process of cladding tubes, lining by diffusion bonding, end plug by laser welding were developed and optimized, by considering the practical use of fuel elements consists of these candidates. The practical applicability was basically examined by irradiation tests using the accelerator of TIARA and the research reactor of JRR-3, for mainly confirming the resistance to IGSCC as one of the current important issues of BWR core materials of low carbon grade stainless steels. Creep and fatigue testing data were also obtained for evaluating the long performance of candidate materials. The behavior as fuel elements was analyzed with the safety calculation code for BWRs. The obtained results were established as a data base system, by considering the applicability to the fuel design and in-pile loop tests.
Kizaki, Minoru
Genshiryoku Hyakka Jiten ATOMICA (Internet), 4 Pages, 2006/00
no abstracts in English
Endo, Shinya; Usami, Koji; Nakata, Masahito; Fukuda, Takuji*; Numata, Masami; Kizaki, Minoru; Nishino, Yasuharu
Proceedings of 2005 JAEA-KAERI Joint Seminar on Advanced Irradiation and PIE Technologies, p.S2_7_1 - S2_7_11, 2005/11
no abstracts in English
Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Takano, Masahide; Ito, Akinori; Akabori, Mitsuo; Minato, Kazuo; Kizaki, Minoru
JAERI-Tech 2005-051, 13 Pages, 2005/09
An apparatus has been developed to measure the thermal diffusivities of minor actinide (MA) compounds. By installing the laser flash apparatus in a glove box with highly purified inert gas atmosphere, the thermal diffusivities measurement of MA compounds of  -decay nuclides was enabled. A new sample holder has been also developed to measure the thermal diffusivities of very small samples. The performance of this new apparatus was confirmed by measuring the thermal diffusivities of small samples of tantalum, nickel and cerium oxides. The thermal diffusivity values obtained in this work agreed well with the literature values and the values measured by a conventional thermal diffusivities measurement apparatus. Accordingly, this apparatus was found to be useful for thermal diffusivities measurement of MA compounds.
-decay nuclides was enabled. A new sample holder has been also developed to measure the thermal diffusivities of very small samples. The performance of this new apparatus was confirmed by measuring the thermal diffusivities of small samples of tantalum, nickel and cerium oxides. The thermal diffusivity values obtained in this work agreed well with the literature values and the values measured by a conventional thermal diffusivities measurement apparatus. Accordingly, this apparatus was found to be useful for thermal diffusivities measurement of MA compounds.
 Cm-
Cm- Pu oxide and mononitride
Pu oxide and mononitrideTakano, Masahide; Ito, Akinori; Akabori, Mitsuo; Ogawa, Toru; Numata, Masami; Kizaki, Minoru
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.3), p.842 - 845, 2002/11
no abstracts in English
Kizaki, Minoru; Honda, Junichi; Usami, Koji; Ouchi, Asao*; Oeda, Etsuro; Matsumoto, Seiichiro
JAERI-Tech 2000-087, 50 Pages, 2001/02
no abstracts in English
Saito, Junichi; ; Jitsukawa, Shiro; ; Omi, Masao; Kizaki, Minoru
KAERI-NEMAC/TR-32/95, 0, p.210 - 219, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Masahide; Onizawa, Kunio; Kizaki, Minoru
JAERI-Research 94-015, 74 Pages, 1994/09
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Tatsuo; Hishinuma, Akimichi; Noda, Kenji; Eto, Motokuni; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Nakajima, Hajime; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Ono, Hideo; Ogawa, Toru; Omichi, Hideki; et al.
Genshiryoku Kogyo, 39(8), p.1 - 80, 1993/08
no abstracts in English
Jitsukawa, Shiro; Kizaki, Minoru; ; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Hishinuma, Akimichi
Small Specimen Test Techniques; ASTM STP 1204, p.289 - 307, 1993/00
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:98.45(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Tsukada, Takashi; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; G.E.C.Bell*; Nakajima, Hajime; Kizaki, Minoru; Omi, Masao; Sudo, Kenji; Goto, Ichiro
JAERI-M 92-081, 27 Pages, 1992/06
no abstracts in English
Tsukada, Takashi; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Omi, Masao; Kizaki, Minoru; ; Nakajima, Hajime
Proc. of the 3rd Asian Symp. on Research Reactor, 8 Pages, 1991/00
no abstracts in English
Hoshiya, Taiji; ; Kizaki, Minoru; ; Sudo, Kenji; ;
JAERI-M 89-205, 68 Pages, 1989/12
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Motoe; Kizaki, Minoru;
JAERI-M 88-217, 60 Pages, 1988/11
no abstracts in English
 and carbonato complexes of Np(IV) in compacted bentonite
and carbonato complexes of Np(IV) in compacted bentoniteYamaguchi, Tetsuji; Nakayama, Shinichi; Kizaki, Minoru
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English