Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:96.69(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,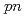 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
Matsui, Hiroya; Watanabe, Kazuhiko*; Mikake, Shinichiro; Niimi, Katsuyuki*; Kobayashi, Shinji*; Toguri, Satohito*
Dai-47-Kai Gamban Rikigaku Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koenshu (Internet), p.293 - 298, 2020/01
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been observed seismic motions induced by earthquakes, at ground surface, galleries at 100m, 300m and 500m depth of Mizunami underground research laboratory for over 10 years. The results suggested that the amplitude of the seismic motion decreases with depth as the previous study on crystalline rock at Kamaishi mine indicated. Detailed analysis on the observed seismic motions shows that the Fourier amplitude and the phase difference of the earthquake occurred near epicenter correspond with the one calculated by one-dimensional multiple reflection theory.
Toguri, Satohito*; Kobayashi, Shinji*; Tsuji, Masakuni*; Yahagi, Ryoji*; Yamada, Toshiko*; Matsui, Hiroya; Sato, Toshinori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Aoyagi, Yoshiaki
JAEA-Technology 2017-005, 43 Pages, 2017/03
The study on engineering technology in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project roughly consists of (1) development of design and construction planning technologies, (2) development of construction technology, (3) development of countermeasure technology, (4) development of technology for security, and (5) development of technologies regarding restoration and mitigating of the excavation effect. In FY2015, as a part of the important issues on the research program, water-tight grouting method has been developed. Grouting methods utilized in the MIU were evaluated and the post-excavation grouting at the -500m Access/Research Gallery-South was planned based on these evaluation results. Also, technology development from the viewpoint of geological disposal was summarized, and information on the alternative method to the grouting method was collected and organized.
Tsuji, Masakuni*; Kobayashi, Shinji*; Mikake, Shinichiro; Sato, Toshinori; Matsui, Hiroya
Procedia Engineering, 191, p.543 - 550, 2017/00
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:92.43(Mining & Mineral Processing)This paper shows the application of two post-grouting works to a gallery at 500 m depth of Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory in Japan. Three new grouting concepts were applied to the post-grouting works; a new grout material, a new injection system, and a new post-grouting zone. As for a grout material, "durable liquid-type colloidal silica grout (CSG)" was applied to seal the narrow fractures. As for an injection system, "complex dynamic grouting method" was applied to improve the penetrability of the grout material. The grouting works were successful in reducing the abundant water inflow from the rock mass with many fractures.
Tsuji, Masakuni*; Kobayashi, Shinji*; Sato, Toshinori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Matsui, Hiroya
Proceedings of 8th Nordic Grouting Symposium, p.171 - 185, 2016/09
This paper presents the application of a durable liquid-type colloidal silica grout (CSG), to the great depth of the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU). The CSG had been invented decades ago in Japan for the purpose of the ground improvement. A post-grouting experiment with the CSG carried out in 300 m depth of MIU confirmed its applicability and good durability at a great depth more than 3 years. Furthermore, a comparison study of applying the CSG between this experiment and a Swedish project indicated good applicability of the Swedish theoretical design to MIU. The CSG with the Swedish design were applied to the post-grouting campaign in a gallery at 500 m depth for further reducing water ingress and for developing the latest grouting methodology. The grouting was successful in reducing the abundant inflow from the rock with many fractures. The conductivity of the grouted rock mass of the latter fans is estimated to be lower than 10 m/s.
m/s.
Kobayashi, Shinji*; Niimi, Katsuyuki*; Tsuji, Masakuni*; Yamada, Toshiko*; Aoyagi, Yoshiaki; Sato, Toshinori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Osawa, Hideaki
JAEA-Technology 2015-039, 170 Pages, 2016/02
The researches on engineering technology in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) plan consists of (1) development of design and construction planning technologies, (2) development of construction technology, (3) development of countermeasure technology, (4) development of technology for security, and (5) development of technologies regarding restoration or reversal and mitigating of the excavation effect. To develop design and construction planning technologies, and countermeasure technology, the analysis of measured data during earthquake and seismic movement characteristics at deep underground, and the examination of grouting method were carried out. For the characteristics of earthquake ground motion, measurement data obtained by seismometers installed in the Mizunami Underground Laboratory were analyzed, and the comprehensive assessment of the relationship between the measurement data and the geological condition at each depth was performed. As for "Study on grouting method at deep underground ", post grouting was carried out and evaluated based on the Construction plan in FY2013. Furthermore, target of the future R&D was proposed.
Tsuji, Masakuni*; Kobayashi, Shinji*; Sato, Toshinori; Mikake, Shinichiro
Dai-44-Kai Gamban Rikigaku Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.359 - 364, 2016/01
Pre-excavation grouting of shafts and galleries has been conducted during the construction of Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory in the aspect of safe works and reducing the discharge treatment of the water inflow. The grouting methodology has been simultaneously studied and developed as there is less experience of grouting in low conductive rock with high water pressure, especially in Japan. After excavating GL.-500m gallery on the ventilation shaft side, a post-excavation grouting campaign was performed on a 16-meter section of the pre-grouted area. Three new options for the grouting design were adopted and found to be effective with sufficiently decreasing the water inflow into the gallery.
Yamaga, Chikanobu; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Kobayashi, Naoki; Naoi, Yosuke; Oda, Tetsuzo; Mochiji, Toshiro
JAEA-Review 2015-023, 108 Pages, 2015/10
The JAEA held "International Forum on Peaceful Use of Nuclear Energy, Nuclear Non-proliferation and Nuclear Security -Future direction toward promoting non-proliferation and the ideal method of developing human resources using COEs following the New Strategic Energy Plan -" on 3 December 2014. In the Forum, officials and experts from Japan, the United States explained their efforts. Discussion was made in two panels, entitled "Effective and efficient measures to ensure nuclear non-proliferation based on domestic and foreign issues and the direction and role of technology development" and "Roles of nuclear security COEs and future expectations". In Panel Discussion 1, how to implement effective and efficient safeguards was discussed. In Panel Discussion 2, panelists discussed current status of NSSCs and COEs, new role for COEs and regional cooperation. This report includes abstracts of keynote speeches, summaries of two panel discussions and materials of the presentations in the forum.
Tsuji, Masakuni*; Kobayashi, Shinji*; Sato, Toshinori; Mikake, Shinichiro
Proceedings of the ISRM Regional Symposium EUROCK 2015 & 64th Geomechanics Colloquium; Future Development of Rock Mechanics, p.35 - 41, 2015/10
Rock grouting has been an essential measure to reduce water ingress into the deep underground during the excavation of Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory project in Japan. This paper shows an overview of grouting works performed at a gallery of 120 m at 500 m depth. After completion of its excavation with the pilot borehole investigation and pre-grouting mainly by Super-fine Portland cement, the inflow from the whole gallery was 200-220 Liter/min within the requirement. Then, at a limited section of 16 m, post-grouting was performed with new designs, applying colloidal silica grout, complex dynamic grouting, and grouting outside of the pregrouted zone. These designs were effective and the inflow at the section reduced from 35 to 11 Liter/min. These experiences must be fruitful for advancing the present technology and there should have been potential for reducing further inflow if any of the new designs are applied from the pre-grouting phase.
Sekine, Yurina; Kobayashi, Riki*; Chi, S.*; Fernandez-Baca, J. A.*; Suzuya, Kentaro; Fujisaki, Fumika*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Fukazawa, Tomoko*; Yamauchi, Hiroki; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.033009_1 - 033009_6, 2015/09
Neutron diffraction profiles of low-D O-content poly-N,N,-dimethylacrylamide (PDMAA) hydrogels were measured from 100 to 300 K to investigate the structure and properties of water in hydrogels. A broad diffraction observed at temperatures lower than 220 K indicates the existence of amorphous ice in the hydrogels at low temperatures. During the heating process, diffraction peaks from ice crystals appear in the profiles. These peaks indicate that cubic ice and hexagonal ice exist at T
O-content poly-N,N,-dimethylacrylamide (PDMAA) hydrogels were measured from 100 to 300 K to investigate the structure and properties of water in hydrogels. A broad diffraction observed at temperatures lower than 220 K indicates the existence of amorphous ice in the hydrogels at low temperatures. During the heating process, diffraction peaks from ice crystals appear in the profiles. These peaks indicate that cubic ice and hexagonal ice exist at T  220 K. We refined the structure parameters of these ices in the hydrogel, which indicate the existence of low-density ice in the hydrogel.
220 K. We refined the structure parameters of these ices in the hydrogel, which indicate the existence of low-density ice in the hydrogel.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sato, Toshinori; Horiuchi, Yasuharu*; Mikake, Shinichiro; Okihara, Mitsunobu*; Yahagi, Ryoji*; Kobayashi, Shinji*
Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 50, p.68 - 78, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.4(Construction & Building Technology)The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is implementing the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project to establish the scientific and technological basis for the geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW) in crystalline rocks. Excavation cycle times were recorded during the Ventilation Shaft sinking and compared with the planned excavation cycle times for evaluation of the baseline design plan. This included review of the cycle times in the design process and comparison with the actual construction results. The recorded results indicate that actual cycle times were twice as long as the design plan. This paper describes discussions on differences in cycle times between the design and actual times.
Kobayashi, Shinji*; Niimi, Katsuyuki*; Okihara, Mitsunobu*; Tsuji, Masakuni*; Yamada, Toshiko*; Sato, Toshinori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Horiuchi, Yasuharu*; Aoyagi, Yoshiaki
JAEA-Technology 2014-035, 172 Pages, 2015/01
The researches on engineering technology in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) plan consists of (1) development of design and construction planning technologies, (2) development of construction technology, (3) development of countermeasure technology, (4) development of technology for security, and (5) development of technologies regarding restoration or reversal and mitigating of the excavation effect. To develop design and construction planning technologies, and countermeasure technology, the analysis of measured data during earthquake and seismic movement characteristics at deep underground, and the examination of grouting method were carried out. The knowledge of the seismic movements at deep underground was obtained by which observation records of seismometers at Mizunami underground research laboratory were analyzed to verify the earthquake-resistant design of the shafts and tunnels. As for" Study on grouting method at deep underground", Existing post-grouting methods for crystalline rock were reviewed, the applicability of pre-grouting technology was evaluated and study on experiment plan in MIU was carried out following the previous year.
Tsuji, Masakuni*; Kobayashi, Shinji*; Sato, Toshinori; Mikake, Shinichiro
Dai-43-Kai Gamban Rikigaku Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.7 - 12, 2015/01
Pre-excavation grouting of shafts and galleries has been conducted during the construction of Mizunami Underground research laboratory in the aspect of safe works and reducing the discharge treatment of the water inflow. The grouting methodology has been simultaneously studied an developed as there is less experience of grouting in low conductive rock with high water pressure, especially in Japan. Ahead of excavating GL.-500m gallery on the ventilation shaft side, grouting design was performed based on the estimation of water inflow by the pilot-boring investigations and the design was properly revised during the campaign. The gallery satisfied the inflow requirement with good sealing effect.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sato, Toshinori; Horiuchi, Yasuharu*; Mikake, Shinichiro; Okihara, Mitsunobu*; Yahagi, Ryoji*; Kobayashi, Shinji*
Proceedings of 8th Asian Rock Mechanics Symposium (ARMS-8) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2014/10
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is implementing the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project to establish the scientific and technological basis for the geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW) in crystalline rocks. Excavation cycle times were recorded during the Ventilation Shaft sinking and compared with the planned excavation cycle times for evaluation of the baseline design plan. This included review of the cycle times in the design process and comparison with the actual construction results. The recorded results indicate that actual cycle times were twice as long as the design plan. This paper describes discussions on differences in cycle times between the design and result.
Sato, Toshinori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Kobayashi, Shinji*; Tsuji, Masakuni*
Proceedings of 8th Asian Rock Mechanics Symposium (ARMS-8) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2014/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is operating Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory project focusing on crystalline rock. Grouting for reducing water inflow is an essential countermeasure technology utilized during construction of underground facilities. Pre-excavation grouting and post-excavation grouting using Ordinary Portland cement, super-fine Portland cement and liquid-type colloidal silica were performed to investigate their performance as countermeasures for reducing groundwater inflow at many locations in the shafts and galleries in the laboratory. The results show that pre-excavation grouting successfully attained the target hydraulic conductivity of 2 Lu for Ordinary Portland cement and 0.2 Lu for super-fine Portland cement using criteria of Lugeon value and changing W/C. Liquid-type colloidal silica was able to drastically lower the hydraulic conductivity of 0.29 Lu and seemed to be stable for water pressures of at least 5 MPa and to be important material used in deep underground.
 sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden and Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory in Japan
Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden and Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory in JapanTsuji, Masakuni*; Funehag, J.*; Kobayashi, Shinji*; Sato, Toshinori; Mikake, Shinichiro
Proceedings of 8th Asian Rock Mechanics Symposium (ARMS-8) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2014/10
Silica sol is a material that seems to fulfill the non-hazardous requirement and capable of penetrating into narrow fractures. The rock grouting strategy with silica sol has been studied and applied for some recent projects in Sweden. The design methodology is based on the determination of the fracture transmissivity distribution and the theoretical penetration length. In 2008, grouting with silica sol was applied in the construction of a short tunnel at 450 m depth in the  sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory, the TASS-tunnel. In 2010, a grouting experiment with silica sol was performed in a gallery at 300 m depth in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU experiment). It can be suggested that Swedish methodology can be applied to design and evaluate the grouting works in Japanese rock with higher intensity of fractures in general. Furthermore, an additional pumping time or the use of Japanese silica sol might improve the grouting quality in Sweden.
Hard Rock Laboratory, the TASS-tunnel. In 2010, a grouting experiment with silica sol was performed in a gallery at 300 m depth in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU experiment). It can be suggested that Swedish methodology can be applied to design and evaluate the grouting works in Japanese rock with higher intensity of fractures in general. Furthermore, an additional pumping time or the use of Japanese silica sol might improve the grouting quality in Sweden.
Fukaya, Masaaki*; Noda, Masaru*; Hata, Koji*; Takeda, Yoshinori*; Akiyoshi, Kenji*; Ishizeki, Yoshikazu*; Kaneda, Tsutomu*; Sato, Shin*; Shibata, Chihoko*; Ueda, Tadashi*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2014-019, 495 Pages, 2014/08
The researches on engineering technology in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) plan consists of (1) research on engineering technology deep underground, and (2) research on engineering technology as a basis of geological disposal. The former research is mainly aimed in this study, which is categorized in (a) development of design and construction planning technologies, (b) development of construction technologies, (c) development of countermeasure technologies, and (d) development of technologies for security. In this study, the researches on engineering technology are being conducted in these four categories by using data measured during construction as a part of the second phase of the MIU plan.
Sato, Toshinori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Noda, Masaru*; Kobayashi, Shinji*
Tonneru To Chika, 45(7), p.501 - 510, 2014/07
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency conducts studies and research associated with the excavation of underground research facility at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory in Mizunami City, Gifu Prefecture. The research laboratory is an underground facility consisting of two shafts and some drifts and excavation has currently extended to a depth of 500 m. This report contains the evaluation results of measures to control the welling of water and measures to prevent ground collapse based on construction records up to now. For measures to control the welling of water, we carried out pre-grouting from umbrella-shaped grouthing holes placed at the bottom of the shaft and observed improvements in given permeability. For measures to prevent ground collapse, we conducted safe shaft sinking along faults by combining reinforecement works using rock bolts and fore-poling works using silica-resin grouting. Both measures were conducted using a shaft sinking drill carriage "Shaft Jumbo" that made it possible to efficiently incorporate short step shaft sinking cycles.
 -wave one-neutron halo configuration on
-wave one-neutron halo configuration on  Mg
MgKobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Barthelemy, R.*; Famiano, M. A.*; Fukuda, Naoki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 112(24), p.242501_1 - 242501_5, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:94.35(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 -wave halos at the drip-line;
-wave halos at the drip-line; 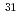 Ne
NeNakamura, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Sato, Yoshiteru*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Gibelin, J.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 112(14), p.142501_1 - 142501_5, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:91.04(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English