Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hirano, Koichiro; Ito, Takashi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Shinto, Katsuhiro; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012077_1 - 012077_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.28(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have upgraded a 3-MeV linac at J-PARC. The ion source is same as the J-PARC linac's, and the old 30-mA RFQ is replaced by a spare 50-mA RFQ, therefore, the beam energy is 3 MeV and the nominal beam current is 50 mA. The main purpose of this system is to test the spare RFQ, but also used for testing of various components required in order to keep the stable operation of the J-PARC accelerator. The accelerator has been already commissioned, and measurement programs have been started. In this paper, present status of this 3-MeV linac is presented.
Katata, Genki; Kajino, Mizuo*; Hiraki, Takatoshi*; Aikawa, Masahide*; Kobayashi, Tomiki*; Nagai, Haruyasu
Journal of Geophysical Research, 116(D20), p.D20102_1 - D20102_14, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:59.27(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)To apply the meteorological model to investigate fog occurrence, acidification, and deposition in mountain forests, the meteorological model WRF was modified to calculate the fog deposition by the simple linear function of fog deposition onto vegetation. The modified version of WRF that includes fog deposition (fog-WRF) was tested in a mountain forest of Mt. Rokko in Japan. The fog-WRF provided a clearly better prediction of liquid water content of fog (LWC) than the original version of WRF. The fog-WRF successfully simulated measured throughfall observations due to fog deposition inside the forest. Using the linear relationship between fog deposition and the altitude given by the fog-WRF calculations and the data from throughfall observations at the certain altitude, vertical distribution of fog deposition can be roughly estimated in mountain forest. The meteorological model that includes the fog deposition is useful for mapping the fog deposition in mountain cloud forests.
Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kobayashi, Tetsuya; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Hori, Yoichiro*; Kubota, Chikashi*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.621 - 623, 2010/05
The J-PARC RFQ accelerates a negative hydrogen beam from 50 keV to 3 MeV. Beam commissioning of the J-PARC linac started in November 2006 and the linac has delivered beams to the 3 GeV synchrotron since September 2007. Trip rates of the RFQ, however, unexpectedly increased in September 2008. We tried to recover by tender conditioning, improvement of vacuum properties, etc. User operations for the Material and Life Experimental Facilities were successfully carried out at 20 kW in June 2009, and the beam power was increased to 120 kW in November. The high power operation at 300 kW for one hour was also demonstrated. Status and improvement of the J-PARC RFQ are presented.
Hasegawa, Kazuo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo; Kobayashi, Tetsuya; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshioka, Masakazu*; Matsumoto, Hiroshi*; Kawamata, Hiroshi*; Hori, Yoichiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 6th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (CD-ROM), p.693 - 695, 2010/03
The J-PARC RFQ (length 3.1m, 4-vane type, 324 MHz) accelerates a beam from the ion source to the DTL. The beam test of the linac was started in November 2006 and 181 MeV beam was successfully accelerated in January 2007. Since then, the linac has been delivered beams for commissioning of the linac itself, downstream accelerators and facilities. Trip rates of the RFQ, however, suddenly increased in Autumn 2008, and we are suffering from this issue for user run operation. We tried to recover by tender conditioning, modification of RF control, improvement of vacuum and so on. We manage to have beam operation. In this report, we describe the status of the RFQ.
Sato, Susumu; Miura, Akihiko; Igarashi, Zenei*; Ikegami, Masanori*; Ueno, Akira; Sako, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Takatoshi; Yoshikawa, Hiroshi; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kobayashi, Tetsuya
Proceedings of 6th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (CD-ROM), p.298 - 300, 2010/03
no abstracts in English
Hirano, Koichiro; Ao, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Takatoshi; Asano, Hiroyuki; Hori, Toshihiko; Yamazaki, Masayoshi; Kobayashi, Tetsuya; Kubota, Chikashi*; Yamazaki, Yoshishige
Proceedings of 5th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 33rd Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan (CD-ROM), p.497 - 499, 2008/00
An ACS (Annular Coupled Structure) module has been developing for the 190-MeV to 400-MeV part of the J-PARC Linac. We have conducted the high power test of the first ACS module which consists of two accelerating tanks with 17 cells and a bridge tank with 9 cells. This paper describes results of the high power RF tests. The module achieved an average axial accelerating gradient of E0 = 4.5 MV/m at 1.8 MW RF input power, 0.6 ms pulse width, and 50 Hz repetition rate.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Akikawa, Hisashi; Anami, Shozo*; Asano, Hiroyuki*; Fukui, Yuji*; Igarashi, Zenei*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Ikegami, Masanori*; Ito, Takashi; Kawamura, Masato*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 29th Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan, p.156 - 158, 2004/08
A commissioning of the J-PARC linac DTL1 is now under way at KEK. A 30mA H beam was accelerated to 19.7-MeV, and 100% transmission was obtained with a 20-msec-pulse-width and 12.5-Hz-repetition beam. In this paper, present status of the DTL1 commissioning and preliminary results of the commissioning, such as emittance measurements, are presented.
beam was accelerated to 19.7-MeV, and 100% transmission was obtained with a 20-msec-pulse-width and 12.5-Hz-repetition beam. In this paper, present status of the DTL1 commissioning and preliminary results of the commissioning, such as emittance measurements, are presented.
 Re-MAG3-A7 anti-colorectal cancer monoclonal antibody; Comparison with
Re-MAG3-A7 anti-colorectal cancer monoclonal antibody; Comparison with  I-counterpart
I-counterpartKinuya, Seigo*; Yokoyama, Kunihiko*; Kobayashi, Katsutoshi; Motoishi, Shoji; Onoma, Katsuyuki; Watanabe, Naoto*; Shuke, Noriyuki*; Bunko, Hisashi*; Nichigishi, Takatoshi*; Tonami, Norihisa*
Annals of Nuclear Medicine, 15(3), p.199 - 202, 2001/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:31.12(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)no abstracts in English
 Re-labeled monoclonal antibody
Re-labeled monoclonal antibodyKinuya, Seigo*; Yokoyama, Kunihiko*; Kudo, Miho*; Kasahara, Yoshihito*; Kobayashi, Katsutoshi; Motoishi, Shoji; Onoma, Katsuyuki; Bunko, Hisashi*; Nichigishi, Takatoshi*; Tonami, Norihisa*
Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 42(4), p.596 - 600, 2001/04
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Takatoshi*; Yokobori, Hitoshi*; Sasaki, Makoto*; Tada, Keiko*
PNC TJ206 73-07, 228 Pages, 1973/04
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Takatoshi*; Sugawara, Akira*; Seki, Yuji*; Ikezawa, Hiroko*
PNC TJ206 71-11T, 30 Pages, 1971/08
As a continuation of the previous research, heterogeneity effects of neutron spectra and axial leakage have been examined. Spectra in a two-region cell were computed by a collision probability method and the heterogeneity effect was found to be small. The analysis of the axial leakage was carried out with the benoist's directional collision probability method and it turned out that the heterogeneity has negative contribution to the sodium void coefficient. Combining the results of the previous research and the current one, the heterogeneous void coefficient in a prototype fast reactor moves towards the positive direction from the homogeneous result.
Kobayashi, Takatoshi*; Sugawara, Akira*; Seki, Yuji*; Ikezawa, Hiroko*
PNC TJ206 70-01T, 40 Pages, 1970/08
As a continuation of the previous research, heterogeneity effects ofneutron spectra and axial leakage have been examined.Spectra in a two-region cell were computed by a collision probabilitymethed and the heterogeneity effect was found to be small.The analysis of the axial leakage was carried out with the Benoist'sdirectional collision probability method and it turned out that theheterogeneity has negative contribution to the sodium void coefficient. Combining the results of the previous research and the current one,the heterogeneous void coefficient in a prototype fast reactor moves towardsthe positive direction from the homegeneous result.
Katata, Genki; Kajino, Mizuo*; Hiraki, Takatoshi*; Aikawa, Masahide*; Kobayashi, Tomiki*
no journal, ,
Water and matter deposition via fog precipitation onto the ceder trees was investigated using the models of three-dimensional mesoscale model (WRF), aerosol transport model (EMTACS), and land surface model including fog deposition on vegetation (SOLVEG). Simulations using WRF, EMTACS, and SOLVEG were independently carried out to produce meteorological variables, chemical compositions, and fog precipitation, respectively. Meteorological variables were overall reproduced by WRF. Fog precipitation estimation by SOLVEG using the output from WRF significantly underestimated throughfall measurements. It was considerable that "edge effect' enhanced fog precipitation in measurements in addition to fog deposition by turbulent vertical mixing of fog water. EMTACS resolved temporal evolutions in chemical compositions in fog water and size distribution of aerosols. WRF-SOLVEG-EMTACS system should be improved in future to assess matter deposition via fog precipitation.
Katata, Genki; Kajino, Mizuo*; Hiraki, Takatoshi*; Aikawa, Masahide*; Kobayashi, Tomiki*; Nagai, Haruyasu
no journal, ,
Water and matter input via fog deposition onto a mountainous forest (Mt. Rokko, Japan) was investigated using detailed land surface model that includes fog deposition onto vegetation (SOLVEG). Simulations using SOLVEG were carried out under meteorological and chemical fields produced by off-line coupled meso-scale meteorological/aerosol chemical transport model (WRF/EMTACS). The SOLVEG clearly underestimated the cumulative fog deposition calculated from throughfall data. This suggests that an enhancement of fog deposition by "edge effect" which is the phenomenon that fog droplets carried by horizontal advection are captured by leaves under canopy clustering and inhomogeneity. The deposition of atmospheric pollutants onto the forest floor due to fog deposition was estimated from the fog deposition by SOLVEG and chemical concentrations in fog water predicted by WRF/EMTACS.
Kajino, Mizuo*; Katata, Genki; Hiraki, Takatoshi*; Aikawa, Masahide*; Kobayashi, Tomiki*
no journal, ,
In order to predict water and matter deposition to forests, accurate estimation of chemical and physical properties of fog and aerosols are indispensable. We have developed a new aerosol chemical transport model (EMTACS) coupled with a meteorological model (WRF) and applied it to investigate uplift fog events occurred over a mountainous forest (Mt. Rokko, Japan). The EMTACS model is unique to dynamically solve temporal evolutions of mixing states of fog and aerosols, in addition to their chemical compositions and size distributions, and thus aerosol-fog interaction processes are considered in one coherent framework. The model performance was evaluated using meteorological and chemical observation data. Formation, evolution and acidification processes of fog and aerosols over the forest region were discussed.
Katata, Genki; Kajino, Mizuo*; Hiraki, Takatoshi*; Aikawa, Masahide*; Kobayashi, Tomiki*; Nagai, Haruyasu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kajino, Mizuo*; Katata, Genki; Hiraki, Takatoshi*; Aikawa, Masahide*; Kobayashi, Tomiki*; Ueda, Hiromasa*
no journal, ,
We numerically evaluated depositional pathways of major air pollutants such as SO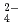 , NH
, NH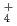 , NO
, NO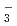 , Cl
, Cl , and Na
, and Na over mountain forest areas in Mt. Rokko in July 1999. A modified WRF model including fog deposition (fog-WRF) and Regional Air Quality Model 2 (RAQM2) was used for simulations. To show the consistency of the model performance, the measured chemical components in fog water were compared with the modeled concentrations. During the simulation period, the persistent southerly wind carried humid air from the Osaka Bay to Mt. Rokko and caused condensation along mountain ridges higher than 400 m in altitude during nights. Simulation results showed that fog deposition was dominant for all depositional components, while dry deposition of nitrate was large due to the high deposition velocity of HNO
over mountain forest areas in Mt. Rokko in July 1999. A modified WRF model including fog deposition (fog-WRF) and Regional Air Quality Model 2 (RAQM2) was used for simulations. To show the consistency of the model performance, the measured chemical components in fog water were compared with the modeled concentrations. During the simulation period, the persistent southerly wind carried humid air from the Osaka Bay to Mt. Rokko and caused condensation along mountain ridges higher than 400 m in altitude during nights. Simulation results showed that fog deposition was dominant for all depositional components, while dry deposition of nitrate was large due to the high deposition velocity of HNO gas.
gas.
Katata, Genki; Yamaguchi, Takashi*; Horie, Yosuke*; Hiraki, Takatoshi*; Kobayashi, Tomiki*; Aikawa, Masahide*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Katata, Genki; Yamaguchi, Takashi*; Horie, Yosuke*; Kobayashi, Tomiki*; Aikawa, Masahide*; Hiraki, Takatoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English