Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 = 32 shell closure below calcium; Low-lying structure of
= 32 shell closure below calcium; Low-lying structure of  Ar
ArCort s, M. L.*; Rodriguez, W.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Holt, J. D.*; Men
s, M. L.*; Rodriguez, W.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Holt, J. D.*; Men ndez, J.*; 緒方 一介*; Schwenk, A.*; 清水 則孝*; Simonis, J.*; et al.
ndez, J.*; 緒方 一介*; Schwenk, A.*; 清水 則孝*; Simonis, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(6), p.064320_1 - 064320_9, 2020/12
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:75.82(Physics, Nuclear)理化学研究所RIBFにおいて、 =32同位体である
=32同位体である Arの低励起構造を陽子・中性子ノックアウト反応,多核子剥離反応,陽子非弾性散乱と
Arの低励起構造を陽子・中性子ノックアウト反応,多核子剥離反応,陽子非弾性散乱と 線分光によって調査した。すでに知られていた2つに加えて、3
線分光によって調査した。すでに知られていた2つに加えて、3 状態の候補を含む5つの状態を新たに確認した。
状態の候補を含む5つの状態を新たに確認した。
 coincidenceによって得られた準位図は
coincidenceによって得られた準位図は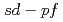 模型空間での殻模型計算やカイラル2体・3体力による第一原理計算と比較した。陽子・中性子ノックアウト反応断面積の理論との比較により、新たに発見された2つの状態は2
模型空間での殻模型計算やカイラル2体・3体力による第一原理計算と比較した。陽子・中性子ノックアウト反応断面積の理論との比較により、新たに発見された2つの状態は2 状態であり、また以前に4
状態であり、また以前に4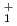 とされていた状態も2
とされていた状態も2 であることが示唆された。
であることが示唆された。
村田 和俊*; 野田 真永*; 尾池 貴洋*; 高橋 昭久*; 吉田 由香里*; 鈴木 義行*; 大野 達也*; 舟山 知夫; 小林 泰彦; 高橋 健夫*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 55(4), p.658 - 664, 2014/07
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:51.16(Biology)ヒト肺がん細胞A549株のRhoシグナル伝達経路を介した遊走能に対し、炭素線照射が及ぼす影響を解析した。照射48時間経過後、炭素線照射したA549細胞の遊走能は大きくなり、遊走突起の形成も増加した。この遊走能の炭素線照射による増加は、X線照射後のそれと類似していた。ウェスタンブロット解析の結果は、照射した細胞がP-MLC2-S19タンパク質発現を増加させている一方で、MLC2タンパク質ファミリー全体の発現量に変化がないことを示した。ROCKタンパク質阻害剤であるY-27632の細胞への投与は、このP-MLC2-S19タンパク質の発現増加を抑制し、遊走能を低下させた。これらの結果より、ヒト肺がん細胞A549細胞への炭素線照射は、細胞遊走能をRhoシグナル伝達経路経由で増加させており、それはROCKタンパク質阻害剤で抑制されることが明らかとなった。
武者 篤*; 吉田 由香里*; 高橋 健夫*; 安藤 興一*; 舟山 知夫; 小林 泰彦; 根岸 明秀*; 横尾 聡*; 中野 隆史*
Journal of Radiation Research, 53(4), p.545 - 550, 2012/07
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:48.03(Biology)The purpose of this study is to clarify the effect of a heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17-AAG), in combination with X-rays or carbon-ion beams on cell killing in human oral squamous cell carcinoma LMF4 cells. Cell survival was measured by colony formation assay. Cell cycle distribution was analyzed by flow cytometry. Expression of DNA repair-related proteins was investigated by western blotting. The results showed 17-AAG having synergistic effects on cell lethality with X-rays, but not with carbon-ion beams. The 17-AAG decreased G /M arrest induced by X-rays, but not by carbon-ion beams. Both X-ray and carbon-ion irradiation up-regulated expression of non-homologous end-joining- associated proteins, Ku70 and Ku80, but 17-AAG inhibited only X-ray-induced up-regulation of Ku70 and Ku80. These results show that 17-AAG with X-rays releases G
/M arrest induced by X-rays, but not by carbon-ion beams. Both X-ray and carbon-ion irradiation up-regulated expression of non-homologous end-joining- associated proteins, Ku70 and Ku80, but 17-AAG inhibited only X-ray-induced up-regulation of Ku70 and Ku80. These results show that 17-AAG with X-rays releases G /M phase arrest and then cells carrying misrepaired DNA damage move to G
/M phase arrest and then cells carrying misrepaired DNA damage move to G phase. We demonstrate, for the first time, that the radiosensitization effect of 17-AAG is not seen for carbon-ion beams because 17-AAG does not affect these changes.
phase. We demonstrate, for the first time, that the radiosensitization effect of 17-AAG is not seen for carbon-ion beams because 17-AAG does not affect these changes.
 1 pathway on human umbilical vein endothelial cells; Comparison between X-ray and carbon-ion beam irradiation
1 pathway on human umbilical vein endothelial cells; Comparison between X-ray and carbon-ion beam irradiation清原 浩樹*; 石崎 泰樹*; 鈴木 義行*; 加藤 弘之*; 浜田 信行*; 大野 達也*; 高橋 健夫*; 小林 泰彦; 中野 隆史*
Journal of Radiation Research, 52(3), p.287 - 292, 2011/03
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:51.68(Biology)Radiation-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expression on endothelial cells was investigated with the use of an inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF- 1) receptor kinase (SB431542) and the effects of X-ray and carbon-ion beam were compared. Expression of ICAM-1 was increased by X-ray and carbon-ion beam irradiation and decreased significantly with SB431542 after both irradiations. The expression of ICAM-1 by 2 Gy of carbon-ion beam irradiation was 6.7 fold higher than that of non-irradiated cells, while 5 Gy of X-ray irradiation increased the expression of ICAM-1 by 2.5 fold. According to ICAM-1 expression, the effect of carbon-ion beam irradiation was about 2.2, 4.4 and 5.0 times greater than that of the same doses of X-ray irradiation (1, 2 and 5 Gy, respectively). The present results suggested that radiation-induced ICAM-1 expression on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVE cells) was, at least partially, regulated by TGF-
1) receptor kinase (SB431542) and the effects of X-ray and carbon-ion beam were compared. Expression of ICAM-1 was increased by X-ray and carbon-ion beam irradiation and decreased significantly with SB431542 after both irradiations. The expression of ICAM-1 by 2 Gy of carbon-ion beam irradiation was 6.7 fold higher than that of non-irradiated cells, while 5 Gy of X-ray irradiation increased the expression of ICAM-1 by 2.5 fold. According to ICAM-1 expression, the effect of carbon-ion beam irradiation was about 2.2, 4.4 and 5.0 times greater than that of the same doses of X-ray irradiation (1, 2 and 5 Gy, respectively). The present results suggested that radiation-induced ICAM-1 expression on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVE cells) was, at least partially, regulated by TGF- 1. Carbon-ion beam induced significantly higher ICAM-1 expression than X-ray.
1. Carbon-ion beam induced significantly higher ICAM-1 expression than X-ray.
神沼 拓也*; 鈴木 義行*; 白井 克幸*; 水井 利幸*; 野田 真永*; 吉田 由香里*; 舟山 知夫; 高橋 健夫*; 小林 泰彦; 白尾 智明*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 51(6), p.627 - 631, 2010/11
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:32.58(Biology)The direct biological effects of radiation, particularly accelerated heavy particle ions, on neurons are not fully known. Hence, the direct effect of carbon-ion beams on immature neurons was investigated by comparing to the effect of X-rays  using primary hippocampal neurons. Primary neurons were prepared from hippocampi of fetal rats at embryonic day 18 from timed pregnant Wistar rats and cultured with Banker's methods. At 7 Days
using primary hippocampal neurons. Primary neurons were prepared from hippocampi of fetal rats at embryonic day 18 from timed pregnant Wistar rats and cultured with Banker's methods. At 7 Days 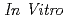 (DIV), the cells were irradiated with 140 kV X-ray and 18.3 MeV/amu carbon-ion beams (LET = 108 keV/
(DIV), the cells were irradiated with 140 kV X-ray and 18.3 MeV/amu carbon-ion beams (LET = 108 keV/ m). The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde at 12 hours after irradiation. Then, the cells were treated with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) and DAPI staining for measuring the percentage of apoptosis (apoptotic index: AI). AI in sham-irradiated hippocampal neurons was 18%. The value of AI (AIs) of the cells irradiated with X-rays at 10 or 30 Gy were 15% or 23%, respectively. AI in cells irradiated with carbon-ion beams at 1 Gy, 3 Gy, 5 Gy and 10 Gy were 22%, 23%, 24% and 33%, respectively. AI was significantly increased by carbon-ion beams at 10 Gy (p
m). The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde at 12 hours after irradiation. Then, the cells were treated with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) and DAPI staining for measuring the percentage of apoptosis (apoptotic index: AI). AI in sham-irradiated hippocampal neurons was 18%. The value of AI (AIs) of the cells irradiated with X-rays at 10 or 30 Gy were 15% or 23%, respectively. AI in cells irradiated with carbon-ion beams at 1 Gy, 3 Gy, 5 Gy and 10 Gy were 22%, 23%, 24% and 33%, respectively. AI was significantly increased by carbon-ion beams at 10 Gy (p  0.001). The apoptosis of hippocampal neurons increased in a dose-dependent manner following both X-ray and carbon-ion beams irradiation. Carbon-ion beams were about 10-fold more effective than X-rays for apoptosis induction in immature hippocampal neurons.
0.001). The apoptosis of hippocampal neurons increased in a dose-dependent manner following both X-ray and carbon-ion beams irradiation. Carbon-ion beams were about 10-fold more effective than X-rays for apoptosis induction in immature hippocampal neurons.
浜田 信行*; 今岡 達彦*; 増永 慎一郎*; 尾方 俊至*; 岡安 隆一*; 高橋 昭久*; 加藤 宝光*; 小林 泰彦; 大西 武雄*; 小野 公二*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 51(4), p.365 - 383, 2010/07
被引用回数:124 パーセンタイル:91.08(Biology)Superb biological effectiveness and dose conformity represent a rationale for heavy-ion therapy, which has thus far achieved good cancer controllability while sparing critical normal organs. Immediately after irradiation, heavy ions produce dense ionization along their trajectories, cause irreparable clustered DNA damage, and alter cellular ultrastructure. These ions, as a consequence, inactivate cells more effectively with less cell-cycle and oxygen dependence than conventional photons. The modes of heavy ion-induced cell death/inactivation include apoptosis, necrosis, autophagy, premature senescence, accelerated differentiation, delayed reproductive death of progeny cells, and bystander cell death. This paper briefly reviews the current knowledge of the biological aspects of heavy-ion therapy, with emphasis on the authors' recent findings. The topics include (1) repair mechanisms of heavy ion-induced DNA damage, (2) superior effects of heavy ions on radioresistant tumor cells (intratumor quiescent cell population, TP53-mutated and BCL2-overexpressing tumors), (3) novel capacity of heavy ions in suppressing cancer metastasis and neoangiogenesis, and (4) potential of heavy ions to induce secondary (especially breast) cancer.
松本 英樹*; 浜田 信行*; 高橋 昭久*; 小林 泰彦; 大西 武雄*
Journal of Radiation Research, 48(2), p.97 - 106, 2007/03
被引用回数:123 パーセンタイル:89.73(Biology)細胞に低線量の放射線をあらかじめ照射しておくと、高線量の放射線に抵抗性を示すことが知られており、この現象は放射線適応応答と呼ばれている。本総説では、放射線適応応答と、バイスタンダー効果(放射線の生物効果が、直接照射された細胞から、その周囲の非照射細胞に伝達される現象)との関連性を概説する。
古牧 睦英; 石川 二郎; 高橋 昭; 横山 淳; 桜井 勉; 大貫 守; 小林 義威; 安達 武雄
日本原子力学会誌, 33(5), p.489 - 497, 1991/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)燃焼度の異なる10種類の使用済軽水炉二酸化ウラン燃料小片(2~3g、5~8年冷却)を4M硝酸に溶解し、発生する揮発性核種(ヨウ素、クリプトン、キセノンおよび気体状トリチウム)の量および同位体組成と燃焼度との関係を求めた。分析法はキセノンを除き、それぞれの放射能測定によった。キセノンはクリプトンと共にガスクロマトグラフにて定量した。分析の結果、燃焼中に放出するヨウ素、クリプトン、キセノン及び気体状トリチウムの量は、燃料の燃焼度の増大に伴い、ほぼ比例して増大した。ヨウ素の大部分は溶解中に揮発し、若干量が溶液中に残存する。 Krの存在比は全燃焼度にわたって、全クリプトン中約5%を占め、キセノンは、重量比で初期ウラン量の約0.4%を占め、気体状トリチウムは生成全トリチウムの約0.5%を占めた。
Krの存在比は全燃焼度にわたって、全クリプトン中約5%を占め、キセノンは、重量比で初期ウラン量の約0.4%を占め、気体状トリチウムは生成全トリチウムの約0.5%を占めた。
安達 武雄; 大貫 守; 吉田 伸彦*; 園部 保; 川村 亘*; 武石 秀世; 郡司 勝文; 木村 貴海; 鈴木 敏夫; 中原 嘉則; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 174, p.60 - 71, 1990/00
被引用回数:44 パーセンタイル:95.19(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)燃焼度7000から39000MWd/tの使用済PWR燃料の硝酸溶解挙動と不溶解性残渣の化学的性質について調べた。燃料棒を3~5mmの長さで切断して得た燃焼度の異なる試料片は3M硝酸により100 Cにおいて2時間以内で溶解した。不溶解性残渣量は7000~30000MWd/tの範囲では燃焼度に比例して増加し、30000MWd/t以上の燃焼度では増加の比率は上昇した。不溶解性残渣の70%以上は核分裂生成物、即ち、Mo、Tc、Ru、Rh、Pdから構成されている。これらの元素の不溶解性残渣中の相対比は、燃料中に生成した元素の相対比とは異なっていること、X線回折により六方晶系のRu合金相が確認されたことから、不溶解性残渣の主成分はRu、Moなどから成る合金と考えられる。
Cにおいて2時間以内で溶解した。不溶解性残渣量は7000~30000MWd/tの範囲では燃焼度に比例して増加し、30000MWd/t以上の燃焼度では増加の比率は上昇した。不溶解性残渣の70%以上は核分裂生成物、即ち、Mo、Tc、Ru、Rh、Pdから構成されている。これらの元素の不溶解性残渣中の相対比は、燃料中に生成した元素の相対比とは異なっていること、X線回折により六方晶系のRu合金相が確認されたことから、不溶解性残渣の主成分はRu、Moなどから成る合金と考えられる。
小林 憲正*; 川本 幸徳*; Sarker, P. K.*; 桑原 秀治*; 大林 由美子*; 金子 竹男*; 三田 肇*; 薮田 ひかる*; 吉田 聡*; 鳴海 一成; et al.
no journal, ,
原始地球上に有機物を届けた媒体としては、彗星などから生じた微小な宇宙塵が隕石や彗星よりも重要であったことが示唆されている。惑星間塵は微小であり、その中の有機物は太陽紫外線や宇宙線に直接曝露されるため、さらに変成を受けると考えられる。しかし、これまで惑星間塵は地球生物圏内で捕集されてはいるが、有機物に関する知見は少ない。本研究では、太陽系星間環境中での有機物の変成と、その有機物の性質解析のため、加速器等を用いた模擬実験を行った。試料として、隕石中に多く含まれるアミノ酸のグリシン及びイソバリン、その前駆体候補のヒダントイン及び5-エチル-5-メチルヒダントイン、複雑態アミノ酸前駆体(一酸化炭素・アンモニア・水への陽子線照射生成物)を用いた。これらの水溶液やそれを乾固したものに対し、290MeV/uの炭素線, 線及び軟X線を照射した。各試料を固相で炭素線照射したものは200kGy照射してもほとんど分解せず、水溶液に照射した場合よりもより高い安定性を示した。溶液の場合、アミノ酸前駆体は遊離アミノ酸よりも安定であった。一方、軟X線照射の場合、イソバリンは40mWhでほぼ分解して0.1%以下になるのに対して、その前駆体は220mWhでも10%以上残存し、高い安定性が示された。また、いずれの試料も不溶性生成物を生じた。
線及び軟X線を照射した。各試料を固相で炭素線照射したものは200kGy照射してもほとんど分解せず、水溶液に照射した場合よりもより高い安定性を示した。溶液の場合、アミノ酸前駆体は遊離アミノ酸よりも安定であった。一方、軟X線照射の場合、イソバリンは40mWhでほぼ分解して0.1%以下になるのに対して、その前駆体は220mWhでも10%以上残存し、高い安定性が示された。また、いずれの試料も不溶性生成物を生じた。
村田 和俊*; 野田 真永*; 尾池 貴洋*; 高橋 昭久*; 吉田 由香里*; 鈴木 義行*; 大野 達也*; 舟山 知夫; 小林 泰彦; 高橋 健夫*; et al.
no journal, ,
本研究では、Rho情報伝達経路を介したヒト肺がん細胞A549株の細胞遊走能に炭素イオン照射が及ぼす影響を明らかにすることを研究の目的とした。細胞遊走能の定量はwound-healingアッセイを、細胞表面突起の形成の評価はFアクチン染色を用いた。細胞生存率はWST-1アッセイを用いて定量し、MLC2タンパク質の発現量および同タンパクセリン19残基のリン酸化量の定量にはウエスタンハイブリダイゼーション法を用いた。炭素イオン照射したA549細胞における照射効果をこれらの方法で解析した結果、炭素イオン照射が、A549細胞の遊走能をRho情報伝達経路を介して増加させる一方で、Rho結合キナーゼ阻害剤によりその照射効果が抑制されることが明らかになった。
芦川 直子*; 朝倉 伸幸; 林 孝夫; 福本 正勝; 倉田 理江*; 小林 真*; 室賀 健夫*; 大矢 恭久*; 奥野 健二*
no journal, ,
LHD及びJT-60Uで採取されたダスト中の水素同位体保持量について発表する。これまで他の装置で測定されたダストのガス保持量の多くはフレーク状の粒子で径が数十 百ミクロンのものが用いられている。しかし、LHDで採取したダストのサイズ分布は1ミクロン以下の粒子も無視できない。そこで、メンブレンフィルタ法により採取したダストを直接昇温脱離法(TDS)により分析するため2つの方法を用いた。JT-60U内側ダイバータ上で採取されたmg程度のダストは、タンタル皿上にダストを載せ分析を行った。LHDでは採取量が0.01-0.05mgと少ないためフィルタ上へSS基板を一緒に載せ、付着したダストを基板ごと分析し、未使用板との比により評価した。ダストの水素同位体保持量の評価はITER等将来装置におけるトリチウム蓄積量の評価や除去方法の最適化に繋がる重要な研究である。
百ミクロンのものが用いられている。しかし、LHDで採取したダストのサイズ分布は1ミクロン以下の粒子も無視できない。そこで、メンブレンフィルタ法により採取したダストを直接昇温脱離法(TDS)により分析するため2つの方法を用いた。JT-60U内側ダイバータ上で採取されたmg程度のダストは、タンタル皿上にダストを載せ分析を行った。LHDでは採取量が0.01-0.05mgと少ないためフィルタ上へSS基板を一緒に載せ、付着したダストを基板ごと分析し、未使用板との比により評価した。ダストの水素同位体保持量の評価はITER等将来装置におけるトリチウム蓄積量の評価や除去方法の最適化に繋がる重要な研究である。
小林 憲正*; 川本 幸徳*; Sarker, P. K.*; 小野 恵介*; 桑原 秀治*; 大林 由美子*; 金子 竹男*; 三田 肇*; 薮田 ひかる*; 吉田 聡*; et al.
no journal, ,
A wide variety of complex organic compounds including precursors of amino acids have been detected in carbonaceous chondrites and comets. It was suggested that organics in them were formed in quite cold environments, such as interstellar space. Irradiation of frozen mixture of possible interstellar molecules with high-energy particles gave complex amino acid precursors with high molecular weights. Such interstellar complex molecules would be altered by cosmic rays and solar light in proto-solar nebula and interplanetary space before the delivery to the Earth by such extraterrestrial bodies as space dusts. We examined possible alteration of amino acids and their precursors by irradiation with photons and heavy ions. Complex amino acid precursors with high molecular weights could be formed in simulated dense cloud environments, and they were much more stable than free amino acids against radiation. They could have been delivered to the Earth by space dusts. We are planning to collect space dusts and expose amino acids and their precursors in the Japan Experimental Module / Exposed Facility (JEM/EF) of the ISS in the Tanpopo Mission.
小林 憲正*; 川本 幸徳*; 岡部 拓人*; Sarker, P. K.*; 大林 由美子*; 金子 竹男*; 三田 肇*; 神田 一浩*; 吉田 聡*; 鳴海 一成
no journal, ,
分子雲環境を模した重粒子線照射実験により、模擬星間物質から高分子態アミノ酸前駆体が生成することが確認されている。このような有機物を原始地球上に有機物を届けた媒体としては、彗星などから生じた微小な宇宙塵(惑星間塵)が隕石や彗星よりも重要であったことが示唆されている。惑星間塵は微小であり、その中の有機物は、太陽紫外線や宇宙線に直接曝露されるため、さらに変成を受けると考えられる。しかし、これまで惑星間塵は地球生物圏内で捕集されてはいるが、有機物に関する知見は少ない。本研究では、太陽系星間環境中での有機物の変成と、その有機物のキャラクタリゼーションのため、加速器等を用いた模擬実験を行った。各試料を固相で炭素線照射したものは200kGy照射してもほとんど分解せず、水溶液に照射した場合よりもより高い安定性を示した。溶液の場合、アミノ酸前駆体は遊離アミノ酸よりも安定であった。一方、軟X線照射の場合、イソバリンは40mWhでほぼ分解して0.1%以下になるのに対し、その前駆体は220mWhでも10%以上残存し、高い安定性が示された。