Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwase, Hiroki*; Akamatsu, Masaaki*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Kasai, Satoshi*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Kobayashi, Kazuki*; Sakai, Hideki*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 56(1), p.110 - 115, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:74.93(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)With the increasing importance of light-responsive materials, it is vital to analyze the relationship between function and structural changes induced by light irradiation. Small-angle scattering (SAS) is effective for such structural analysis. However, quantitatively capturing local molecular structure formation and molecular reactions at a scale of less than 1 nm via SAS is difficult. In this study, to analyze the structure of non-equilibrium phenomena in light-responsive materials, a new sample environment has been developed for a time-of-flight small- and wide-angle neutron scattering instrument (TAIKAN), comprising a UV-Vis irradiation system, UV-Vis absorption measurement equipment and photodetector. Simultaneous measurement of small-angle neutron scattering and UV-Vis absorption was achieved. This system was used to demonstrate the in situ observation of UV-Vis irradiation-induced structural change of micelles formed by a light-responsive surfactant sample in an aqueous solution.
Sakasegawa, Hideo; Nomura, Mitsuo; Sawayama, Kengo; Nakayama, Takuya; Yaita, Yumi*; Yonekawa, Hitoshi*; Kobayashi, Noboru*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Hiyama, Toshiaki*; Murata, Eiichi*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 153, p.104396_1 - 104396_9, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)When dismantling centrifuges in uranium-enrichment facilities, decontamination techniques must be developed to remove uranium-contaminated surfaces of dismantled parts selectively. Dismantled uranium-contaminated parts can be disposed of as nonradioactive wastes or recycled after decontamination appropriate for clearance. previously, we developed a liquid decontamination technique using acidic electrolyzed water to remove uranium-contaminated surfaces. However, further developments are still needed for its actual application. Dismantled parts have various uranium-contaminated surface features due to varied operational conditions, inhomogeneous decontamination using iodine heptafluoride gas, and changes in long-term storage conditions after dismantling. Here, we performed liquid decontamination on specimens with varying uranium-contaminated surfaces cut from a centrifuge made of low-carbon steel. From the results, the liquid decontamination can effectively remove the uranium-contaminated surfaces, and radioactive concentrations fell below the target value within twenty minutes. Although the required time should also depend on dismantled parts' sizes and shapes in their actual application, we demonstrated that it could be an effective decontamination technique for uranium-contaminated steels of dismantled centrifuges.
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*; Hirono, Kazuya*; Homma, Masanobu*; Kobayashi, Hiromi*; Takahashi, Tomoe*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2018-007, 87 Pages, 2018/11
To select the chemical composition of a glass frit which can increase the waste content, the simulated waste glass samples prepared from a borosilicate glass frit including vanadium (V) were investigated by using Laser Ablation (LA) ICP-AES analysis, Raman spectrometry, and synchrotron XAFS measurement in this study on foundation business of the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy.
Nagai, Takayuki; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Shimamura, Keisuke; Oyama, Koichi; Sasage, Kenichi; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yamanaka, Keisuke*; Ota, Toshiaki*
JAEA-Research 2018-005, 72 Pages, 2018/09
Addition of radioactive waste to a borosilicate glass frit affects the local structures of glass-forming elements and waste elements in a waste glass produced in a vitrification process. In this study, simulated waste glass samples were prepared from borosilicate glass frit including phosphorus pentaoxide, and we investigated local structures of sodium (Na), boron (B), and waste elements in these glass samples by using synchrotron XAFS measurements in soft and hard X ray region.
Nagai, Takayuki; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Sasage, Kenichi; Ayame, Yasuo; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yamanaka, Keisuke*; Ota, Toshiaki*
JAEA-Research 2017-005, 54 Pages, 2017/06
Addition of radioactive waste to a borosilicate frit affects the local structures of boron (B) and waste elements in a waste glass. Synchrotron XAFS measurement was applied to investigate the local structural changes by using simulated waste borosilicate glass samples. Following results were obtained by the B K-edge XAFS analysis. It was confirmed that B K-edge XAFS analysis enables us to discriminate sp type boron (BO
type boron (BO ) from sp
) from sp type boron (BO
type boron (BO ). Addition of waste elements to a glass frit increases the percentage of BO
). Addition of waste elements to a glass frit increases the percentage of BO and decreases that of BO
and decreases that of BO . By decreasing the SiO
. By decreasing the SiO /Al
/Al O
O ratio or increasing the (SiO
ratio or increasing the (SiO +B
+B O
O )/Al
)/Al O
O ratio in the glass composition, the BO
ratio in the glass composition, the BO percentage increases and the BO
percentage increases and the BO percentage decreases. Addition of P
percentage decreases. Addition of P O
O decreases the BO
decreases the BO percentage and increases the BO
percentage and increases the BO percentage. Following results were obtained from XAFS measurement of the waste elements. Cerium (Ce) valence is more reduced with the increase of the B
percentage. Following results were obtained from XAFS measurement of the waste elements. Cerium (Ce) valence is more reduced with the increase of the B O
O content. Addition of P
content. Addition of P O
O has a tendency to reduce the Ce valence and to enhance deposition of Zr oxide. Deposition of ruthenium compounds separated from glass phase can not be improved by changing the B
has a tendency to reduce the Ce valence and to enhance deposition of Zr oxide. Deposition of ruthenium compounds separated from glass phase can not be improved by changing the B O
O content. This study was performed as a part of the project, "Improvement of vitrification process of high-level radioactive liquid wastes" on the foundation business of the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy.
content. This study was performed as a part of the project, "Improvement of vitrification process of high-level radioactive liquid wastes" on the foundation business of the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy.
Nagai, Takayuki; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Sasage, Kenichi; Ayame, Yasuo; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Uchiyama, Takafumi*; Okada, Yukiko*; Nezu, Atsushi*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2016-015, 52 Pages, 2016/11
The local structure of waste elements in simulated waste glasses including V was estimated by using synchrotron XAFS measurement in this study. The results are as follows. (1) V has a high possibility which exists in the glass phase in the case of frit, and V can regard both samples as stable 4 coordination structure. (2) Zn, Ce, Nd, Zr, and Mo exist in the glass phase, and the difference is admitted by the percentage of Ce(III) and Ce(IV) by the composition. (3) Ru is separated from the glass phase as RuO crystalline, both of metal and oxide exist in Rh, and Pd is separated out as metal. (4) It was confirmed that the regularity of the local structure of Zr and Mo in the molten glasses retreats as a result of the XAFS measurement at high temperature. (5) The XAFS measurement of molten glasses were performed at 1200
crystalline, both of metal and oxide exist in Rh, and Pd is separated out as metal. (4) It was confirmed that the regularity of the local structure of Zr and Mo in the molten glasses retreats as a result of the XAFS measurement at high temperature. (5) The XAFS measurement of molten glasses were performed at 1200 C, so it would be possible to acquire excellent data by improving the shapes of the sample cell.
C, so it would be possible to acquire excellent data by improving the shapes of the sample cell.
Yamada, Katsunori; Fujii, Katsutoshi; Kanda, Hiroshi; Higashi, Daisuke; Kobayashi, Toshiaki; Nakagawa, Masahiro; Fukami, Tomoyo; Yoshida, Keisuke; Ueno, Yumi; Nakajima, Junya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-033, 51 Pages, 2013/12
After the accident at Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant, various numerical criteria relevant to radiation protection were defined. We surveyed these criteria through internet. As a result of survey, the following 13 items were identified: (1) criteria for taking stable iodine tablets, (2) criteria for the screening of surface contamination, (3) evacuation area, sheltering area, etc., (4) activity concentrations in food, drinking water, etc., (5) dose limit for radiation workers engaged in emergency work, (6) guideline levels of radioactive substances in bathing areas, (7) criteria for use of school buildings and schoolyards, (8) restriction on planting rice, (9) acceptable activity concentrations in feedstuff, (10) acceptable activity concentrations in compost, (11) criteria for export containers and ships, (12) criteria for contaminated waste, (13) standards for radiation workers engaged in decontamination work. In this report, the basis of and issues on these criteria are summarized.
Ata, Seisuke*; Oka, Toshitaka; He, C.-Q.*; Odaira, Toshiyuki*; Suzuki, Ryoichi*; Ito, Kenji*; Kobayashi, Yoshinori*; Ougizawa, Toshiaki*
Journal of Polymer Science, Part B; Polymer Physics, 48(20), p.2148 - 2153, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:22.29(Polymer Science)Surface morphology of bisphenol-A polycarbonate (BAPC) thin films with thickness ranging from 30 to 1000 nm on silicon substrates was studied by atomic force microscopy (AFM). The films were prepared by spincasting from 1,2-dichloroethane solutions of 0.25-5.0 wt % BAPC. Even though longer annealing than 250 h was necessary for complete crystallization for bulk BAPC, high crystallinity was observed for 30 nm thick film after annealing at 200  C for 48 h in vacuum. Positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (PALS) measurements showed that the free volume hole size in 30 nm thick film was larger than that of bulk at 200
C for 48 h in vacuum. Positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (PALS) measurements showed that the free volume hole size in 30 nm thick film was larger than that of bulk at 200  C. Comparison of the BAPC concentration in the precursor solution with the overlap concentration suggests that the high crystallinity of the 30 nm BAPC film is due to less entangled chains caused by rapid removal of the solvent from the dilute solution.
C. Comparison of the BAPC concentration in the precursor solution with the overlap concentration suggests that the high crystallinity of the 30 nm BAPC film is due to less entangled chains caused by rapid removal of the solvent from the dilute solution.
Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Kishi, Toshiaki; Torii, Yoshiya; Sakurai, Yoshinori*; Kobayashi, Toru*
Proceedings of 11th World Congress on Neutron Capture Therapy (ISNCT-11) (CD-ROM), 15 Pages, 2004/10
To carry out the boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) using the epithermal neutron, the epithermal neutron beam intensity was measured by using  Au reaction rate activated on the resonance absorption peak (4.9eV). Two scaling factors, which are the reactor power calibration factor and the calculation/experiment (C/E) scaling factor, are necessary in order to correct with the simulation and actual irradiation experiment. First, an optimum detector position was investigated using MCNP code. The result of MCNP calculation showed that the influence of subject placed at the collimator was below 1% when the detector was placed in the distance of over 20cm from the collimator. Therefore we installed the monitor holders near the bismuth block in order to set three gold wire monitors. The factors were determined in the calibration experiments that measure the thermal neutron flux in the phantom and reaction rate of the gold wire monitors. The monitoring technique to measure epithermal neutron beam intensity was applied to clinical irradiation with the epithermal neutron beam.
Au reaction rate activated on the resonance absorption peak (4.9eV). Two scaling factors, which are the reactor power calibration factor and the calculation/experiment (C/E) scaling factor, are necessary in order to correct with the simulation and actual irradiation experiment. First, an optimum detector position was investigated using MCNP code. The result of MCNP calculation showed that the influence of subject placed at the collimator was below 1% when the detector was placed in the distance of over 20cm from the collimator. Therefore we installed the monitor holders near the bismuth block in order to set three gold wire monitors. The factors were determined in the calibration experiments that measure the thermal neutron flux in the phantom and reaction rate of the gold wire monitors. The monitoring technique to measure epithermal neutron beam intensity was applied to clinical irradiation with the epithermal neutron beam.
; Kobayashi, Toshiaki*
JNC TJ1440 2002-001, 240 Pages, 2003/03
 Ce by the
Ce by the  La(p,n)
La(p,n) Ce reaction
Ce reactionIshioka, Noriko; Izumo, Mishiroku; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Kobayashi, Katsutoshi; Matsuoka, Hiromitsu; Sekine, Toshiaki
JAERI-Tech 2001-095, 23 Pages, 2002/01
no abstracts in English
Ishioka, Noriko; Lambrecht, R. M.*; Matsuoka, Hiromitsu; Osa, Akihiko; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kobayashi, Katsutoshi; Izumo, Mishiroku; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Sekine, Toshiaki
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 47(2), p.171 - 174, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:38.89(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 Re
ReIshioka, Noriko; Matsuoka, Hiromitsu; Osa, Akihiko; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Izumo, Mishiroku; Kobayashi, Katsutoshi; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Sekine, Toshiaki; Lambrecht, R. M.*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 205(1), p.85 - 92, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:95.10(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
 Sr(n,
Sr(n, )
)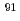 Sr reaction
Sr reactionHarada, Hideo*; Sekine, Toshiaki; ; Ishioka, Noriko; Kobayashi, Katsutoshi; Otsuki, Tsutomu*; Kato, Toshio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 31(3), p.173 - 179, 1994/03
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:86.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 Sr(
Sr( )
)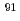 Sr reaction
Sr reactionHarada, Hideo; Sekine, Toshiaki*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Shigeta, Noriko*; Kobayashi, Katsunori*; Otsuki, Tsutomu*; Kato, Toshio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 31(3), p.173 - 179, 1994/03
no abstracts in English
Sekine, Toshiaki; Izumo, Mishiroku; Matsuoka, Hiromitsu; Kobayashi, Katsutoshi; Ishioka, Noriko; Osa, Akihiko; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Motoishi, Shoji; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; ; et al.
Proc. of the 5th Int. Workshop on Targetry and Target Chemistry, 0, p.347 - 352, 1994/00
no abstracts in English
 Cs(n,
Cs(n, )
)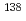 Cs
CsSekine, Toshiaki; ; Kobayashi, Katsutoshi; Harada, Hideo*; Watanabe, Hisashi*; Kato, Toshio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 30(11), p.1099 - 1106, 1993/11
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:91.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 Cs(n,
Cs(n, )
)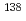 Cs
CsSekine, Toshiaki; ; Kobayashi, Katsutoshi; Harada, Hideo*; Watanabe, Hisashi*; Kato, Toshio*
Proc. of the Nuclear Data for Science and Technology, p.57 - 58, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
 Cs(n,
Cs(n, )
)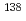 Cs
CsSekine, Toshiaki*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Kobayashi, Katsunori*; Harada, Hideo; Watanabe, Hisashi; Kato, Toshio*
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology, p.57 - 58, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
 Cs(n,
Cs(n, )
)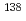 Cs reaction
Cs reactionHarada, Hideo; Watanabe, Hisashi; Sekine, Toshiaki*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Kobayashi, Katsunori*; Kato, Toshio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 27(6), p.577 - 580, 1990/06
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:95.57(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal neutron cross section of the  Cs(n,
Cs(n, )
)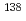 Cs reaction was measured in order to supply a basic data for the nuclear transmutation research of radioactive waste. Irradiated
Cs reaction was measured in order to supply a basic data for the nuclear transmutation research of radioactive waste. Irradiated  Cs samples were chemically purified and their
Cs samples were chemically purified and their  -ray spectra were measured with a HPGe detector. From the intensity ratio between the
-ray spectra were measured with a HPGe detector. From the intensity ratio between the 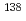 Cs
Cs  -rays and the
-rays and the  Cs
Cs  -ray, the capture cross section was deduced to be 0.250
-ray, the capture cross section was deduced to be 0.250 0.013 barn, which is 2.3 times larger than the one measured by Stupegia.
0.013 barn, which is 2.3 times larger than the one measured by Stupegia.