Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tomioka, Dai; Kochiyama, Mami; Ozone, Kenji; Nakata, Hisakazu; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2024-023, 38 Pages, 2025/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is an implementing organization of near-surface disposal for low-level radioactive wastes generated from research, industrial and medical facilities in Japan. Information on the radioactivity concentration of these radioactive wastes is dispensable for the design and conformity assessment of the waste disposal facilities for the licensing application of the disposal project and its safety review. Radioactive Wastes Disposal Center has been improving the radioactivity evaluation procedure for the dismantling waste generated from the research reactors based on the activation calculation. In order to investigate the applicability of the ORIGEN code (included in SCALE6.2.4), which enables more accurate activation calculations using multigroup neutron spectra, we performed activation calculations with the ORIGEN-code and the ORIGEN-S code (included in SCALE6.0), which has been widely used in the past, for the dismantled wastes from the Rikkyo University Research Reactor, where radioactivity analysis data for the structural materials around the reactor core were compiled. As a result, the calculation time difference between ORIGEN and ORIGEN-S was small and the evaluated radioactivity concentrations of the former were in the range of 0.8-1.0 times those of the latter, which was in good agreement with those of radiochemical analysis in the range of 0.5-3.0 times. The applicability of ORIGEN was confirmed. In addition, activation calculations assuming trace elements in structural materials of nuclear reactor were performed with ORIGEN and ORIGEN-S and the results were compared. The causes of the large differences among 170 nuclides that are important for dose assessment in near-surface disposal were assessed each nuclide.
Nagata, Hiroshi; Kochiyama, Mami; Chinone, Marina; Sugaya, Naoto; Nishimura, Arashi; Ishikawa, Joji; Sakai, Akihiro; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-016, 44 Pages, 2025/03
The elemental composition of the structural materials of nuclear reactor facilities is used as one of the important parameters in activation calculations that are evaluated when formulating decommissioning plans. Regarding the elemental composition of aluminum alloys and other materials used as structural materials for test and research reactors, sufficient data is not available regarding elements other than the major elements. For this reason, samples were collected from aluminum alloy, beryllium, hafnium, and other materials that have been used as the main structural materials of JMTR (Japan Materials Testing Reactor), and their elemental compositions were analyzed. This report summarizes the elemental composition data of 78 elements obtained in FY2023.
Konno, Chikara; Kochiyama, Mami; Hayashi, Hirokazu
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 11(2), p.23-00386_1 - 23-00386_11, 2024/04
Activation cross-section libraries for the ORIGEN and ORIGEN-S codes have been generated from JENDL-5 and JENDL/AD-2017. The ORIGEN activation cross-section libraries of the 200 and 48 group structures were generated with the AMPX-6 code, while the ORIGEN-S activation cross-section libraries with a MAXS format of the 199 group structure were done with the PREPO2018 code. Activation calculations for JPDR were carried out in order to validate the produced ORIGEN and ORIGEN-S activation cross-section libraries. The following comparisons were performed: the ORIGEN calculation results with the produced activation cross-section libraries and bundled ones, the 200 group and 48 group ORIGEN calculations, the ORIGEN and ORIGEN-S calculations with the JENDL-5 activation cross-section libraries, etc. Most of the differences of the calculation results were less than 20%, which demonstrated that the libraries were produced adequately.
Konno, Chikara; Kochiyama, Mami; Hayashi, Hirokazu
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
JENDL-5 released in 2021 includes enough cross section data for neutron activation calculations. Thus we have produced ORIGEN and ORIGEN-S libraries from JENDL 5. We also produced the similar libraries from JENDL/AD-2017 for comparison. Analyses of the JPDR decommissioning data with these libraries demonstrated that the libraries had no problem.
Kochiyama, Mami
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (133), p.76 - 81, 2022/10
The outline of the presentation at the joint session of Research Committee for Nuclear Data and Subcommittee on Nuclear Data in the Atomic Energy Society of Japan 2022 Autumn Meeting was contributed to Nuclear Data News. As part of the study on the near surface disposal of waste from research facilities, we are studying a method for evaluating the radioactivity inventory of waste generated by the dismantling of research reactors. In the radioactivity evaluation of the research reactor, we have investigated the method of calculating the neutron transport in the reactor and using the obtained neutron spectrum to calculate the activation of the internal structure by the ORIGEN-S code. In recent years, we have introduced and evaluated libraries created based on JENDL-4.0 and JENDL/AD-2017, and we will introduce the status of their examination. And we will introduce how to apply the results obtained by the radioactivity evaluation calculation to burial disposal.
Okada, Shota; Murakami, Masashi; Kochiyama, Mami; Izumo, Sari; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Testing 2022-002, 66 Pages, 2022/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is an implementing organization of burial disposal for low-level radioactive waste generated from research, industrial and medical facilities in Japan. Radioactivity concentrations of the waste are essential information for design of the disposal facility and for licensing process. A lot of the waste subjected to the burial disposal is arising from dismantling of nuclear facilities. Radioactive Wastes Disposal enter has therefore discussed a procedure to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations by theoretical calculation for waste arising from the dismantling of the research reactors facilities and summarized the common procedure. The procedure includes evaluation of radioactive inventory by activation calculation, validation of the calculation results, and determination of the disposal classification as well as organization of the data on total radioactivity and maximum radioactivity concentration for each classification. For the evaluation of radioactive inventory, neutron flux and energy spectra are calculated at each region in the reactor facility using two- or three-dimensional neutron transport code. The activation calculation is then conducted for 140 nuclides using the results of neutron transport calculation and an activation calculation code. The recommended codes in this report for neutron transport calculation are two-dimensional discrete ordinate code DORT, three-dimensional discrete ordinate code TORT, or Monte Carlo codes MCNP and PHITS, and for activation calculation is ORIGEN-S. Other recommendation of cross-section libraries and calculation conditions are also indicated in this report. In the course of the establishment of the procedure, Radioactive Wastes Disposal Center has discussed the commonly available procedure at meetings. It has periodically held to exchange information with external operators which have research reactor facilities. The procedure will properly be reviewed and be revised by reflecting future situ
Kochiyama, Mami; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2022-009, 56 Pages, 2022/06
It is necessary to evaluate radioactivity inventory in wastes before disposal of low-level radioactive wastes generated from dismantling research reactors. It is efficient for owners of each research reactor to use a common radioactive evaluation method in order to comply with the license application for disposal facility. In this report, neutron transport and activation calculations were carried out for the Rikkyo University research reactor in order to examine a common radioactivity evaluation method for burial disposal of radioactive wastes generated by dismantling. We adopted the neutron transport codes DORT and MCNP and the activation code ORIGEN-S with cross-section libraries based on JENDL-4.0 and JENDL/AD-2017. The radioactivity concentrations obtained by the radiochemical analysis and both calculation codes were in agreement by 0.4 to 3 times. Therefore, by appropriately considering this difference, the radioactivity evaluation method by DORT, MCNP and ORIGEN-S can be applied to the radioactivity evaluation for buried disposal. In order to classify wastes from dismantling by clearance or buried disposal method according to their radioactivity levels, we also created radioactivity concentration distributions in the concrete area and graphite thermal column area.
Konno, Chikara; Kochiyama, Mami; Hayashi, Hirokazu
JAEA-Conf 2021-001, p.132 - 137, 2022/03
A SCALE6.2 ORIGEN library was produced with the AMPX-6 code from JENDL Activation Cross Section File for Nuclear Decommissioning 2017 (JENDL/AD-2017). For validation of the libraries, JPDR activation calculation was performed with ORIGEN and the libraries, which demonstrated the library had no problem.
Kochiyama, Mami; Okada, Shota; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2021-010, 61 Pages, 2021/07
It is necessary to evaluate the radioactivity inventory in wastes in order to dispose of radioactive wastes generated from dismantling nuclear reactor in the shallow ground. In this report, we examined radioactivity evaluation method for near surface disposal about biological shield concrete near the core generated from the dismantling of JPDR. We calculated radioactive concentration of the target biological concrete using the DORT code and the ORIGEN-S code, and we estimated radioactivity concentration Di (Bq/t). For DORT calculation, the cross-section library created from the MATXSLIB-J40 file from JENDL-4.0 was used, and for ORIGEN-S, the attached library of SCALE6.0 was used. As a result of comparing the calculation results of the radioactivity concentration with the past measured values in the radial direction and the vertical direction, we found that the trends were generally the same. We calculated radioactive concentration of the target biological concrete Di (Bq/t), and we compared with the estimated Ci (Bq/t) equivalent to the dose criteria of trench disposal calculated for 140 nuclides. As a result we inferred that the except for about 2% of target waste could be disposed of in the trench disposal facility. We also preselected important nuclides for trench disposal based on the ratios (Di/Ci) for each nuclide, H-3, C-14, Cl-36, Ca-41, Co-60, Sr-90, Eu-152 and Cs-137 were selected as important nuclides.
Tobita, Minoru*; Haraga, Tomoko; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Seki, Kotaro*; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Kochiyama, Mami; Shimomura, Yusuke; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-016, 72 Pages, 2020/02
In the future, radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried for the near surface disposal. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2, JRR-3 and Hot laboratory facilities. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 25 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Mo,
Mo,  Tc,
Tc, 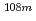 Ag,
Ag,  Sn,
Sn,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Fujii, Hirofumi*; Hara, Kazuhiko*; Hashimoto, Shugo*; Ito, Fumiaki*; Kakuno, Hidekazu*; Kim, S.*; Kochiyama, Mami; Nagamine, Kanetada*; Suzuki, Atsuto*; Takada, Yoshihisa*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2013(7), p.073C01_1 - 073C01_20, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:75.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kochiyama, Mami; Haraga, Tomoko; Kameo, Yutaka; Takahashi, Kuniaki
JAEA-Technology 2011-038, 26 Pages, 2012/02
A nondestructive measurement of gamma-ray emitting nuclides has been studied and Multiple gamma-ray Detection Instrument is newly constructed with 4 detection units consisting of Ge and BGO detectors. Compton scattering was decreased by the combination of Ge and BGO detectors. This instrument was applied to the detection of interested nuclides in radioactive waste sample, which contains significant amount of Co-60, and detection limit of the interested gamma-ray emitting nuclides were improved by a factor of 4 to 12 times than single gamma-ray spectrometer. As for Nb-94, the radioactivity determined from measurements using Multiple gamma-ray Detection Instrument in this sample was agreed with that determined by radiochemical analysis within 15%. It was confirmed that the instrument are useful for radioactivity determination of gamma-ray emitting nuclides in radioactive waste.
Kochiyama, Mami; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Toshimitsu, Masaaki; Katayama, Atsushi; Saito, Naoaki*; Omura, Hideki*; Takahashi, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Konno, Chikara; Kochiyama, Mami
no journal, ,
Multi-group neutron activation cross-section libraries for the ORIGEN code in the SCALE6.2 code system was produced with the AMPX-6 code from JENDL Activation Cross Section File for Nuclear Decommissioning 2017 (JENDL/AD-2017) released in 2018. For V&V of the libraries, JPDR activation calculation was performed with ORIGEN and the libraries.
Konno, Chikara; Kochiyama, Mami
no journal, ,
Activation estimation results in reactor decommissioning depend on neutron fluxes used in the estimation. Thus we studied how neutron fluxes changed in DORT calculations corresponding to neutron group structures; 200, 56, 49, 47 and 44 group structures adopted in the SCALE 6.2 ORIGEN library and a 48 group structure used in JAEA previous JPDR analysis. The calculated DORT neutron flux with JENDL-4.0 were compared with those by using MCNP. The comparison showed that the thermal neutron flux of the 200 group agreed with the MCNP one, while that of the 48 group underestimated by  20%, that of the 47 group underestimated by
20%, that of the 47 group underestimated by  30% and those of the 56, 49 and 44 groups underestimated by
30% and those of the 56, 49 and 44 groups underestimated by  50%.
50%.
Kochiyama, Mami; Sakai, Akihiro
no journal, ,
As part of the study on the burial disposal of waste from research facilities, we are studying a method for evaluating the radioactivity inventory of waste generated by the dismantling of research reactors. In the radioactivity evaluation of the research reactor, we have investigated the method of calculating the neutron transport in the reactor and using the obtained neutron spectrum to calculate the activation of the internal structure by the ORIGEN-S code. In recent years, we have introduced and evaluated libraries created based on JENDL-4.0 and JENDL/AD-2017, and we will introduce the status of their examination. And we will introduce how to apply the results obtained by the radioactivity evaluation calculation to burial disposal.
Konno, Chikara; Kochiyama, Mami; Hayashi, Hirokazu
no journal, ,
We have produced SCALE6.2 ORIGEN decay and fission product yield libraries from JENDL-5. ORIGEN cannot treat m2 metastable nuclei. Thus more important nuclei between m1 and m2 metastable nuclei were redefined as m1 metastable nuclei in the decay and fission product yield libraries the previously produced activation cross section library from JENDL-5 for ORIGEN were also revised. As a result, it is now possible to calculate inventories of all radioactive nuclei that need to be evaluated in reactor decommissioning.
Shimomura, Yusuke; Kochiyama, Mami; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Konno, Chikara; Kochiyama, Mami
no journal, ,
A multi-group neutron activation cross-section library (MAXS/AD-2017) with the MAXS format was produced from JENDL Activation Cross Section File for Nuclear Decommissioning 2017 (JENDL/AD-2017) released in 2018. As one of tests of MAXS/AD-2017, JPDR activation analysis was performed with ORIGEN-S and its library generated from MAXS/AD-2017.
 -ray detector; Detection limits of metallic radioactive wastes
-ray detector; Detection limits of metallic radioactive wastesKochiyama, Mami; Haraga, Tomoko; Kameo, Yutaka; Takahashi, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English