Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Be and
Be and  Al under direct muon-induced spallation in granite quartz and its implications for past high-energy cosmic ray fluxes
Al under direct muon-induced spallation in granite quartz and its implications for past high-energy cosmic ray fluxesSakurai, Hirohisa*; Kurebayashi, Yutaka*; Suzuki, Soichiro*; Horiuchi, Kazuho*; Takahashi, Yui*; Doshita, Norihiro*; Kikuchi, Satoshi*; Tokanai, Fuyuki*; Iwata, Naoyoshi*; Tajima, Yasushi*; et al.
Physical Review D, 109(10), p.102005_1 - 102005_18, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Secular variations of galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) are inseparably associated with the galactic activities and should reflect the environments of the local galactic magnetic field, interstellar clouds, and nearby supernova remnants. The high-energy muons produced in the atmosphere by high-energy GCRs can penetrate deep underground and generate radioisotopes in the rock. As long lived radionuclides such as  Be and
Be and  Al have been accumulating in these rocks, concentrations of
Al have been accumulating in these rocks, concentrations of  Be and
Be and  Al can be used to estimate the long-term variations in high-energy muon yields, corresponding to those in the high-energy GCRs over a few million years. This study measured the production cross sections for muon induced
Al can be used to estimate the long-term variations in high-energy muon yields, corresponding to those in the high-energy GCRs over a few million years. This study measured the production cross sections for muon induced  Be and
Be and  Al by irradiating positive muons with the momentum of 160 GeV/c on the synthetic silica plates and the granite core at the COMPASS experiment line in CERN SPS. In addition, it the contributions of the direct muon spallation reaction and the nuclear reactions by muon-induced particles on the production of long lived radionuclides in the rocks were clarified.
Al by irradiating positive muons with the momentum of 160 GeV/c on the synthetic silica plates and the granite core at the COMPASS experiment line in CERN SPS. In addition, it the contributions of the direct muon spallation reaction and the nuclear reactions by muon-induced particles on the production of long lived radionuclides in the rocks were clarified.
 -methyltransferase involved in flower coloration
-methyltransferase involved in flower colorationAkita, Yusuke; Kitamura, Satoshi; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issei; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*; Kondo, Emiko*; Kameari, Naoko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; et al.
Planta, 234(6), p.1127 - 1136, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:75.76(Plant Sciences) spp., generated by ion-beam irraidation
spp., generated by ion-beam irraidationKondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kameari, Naoko*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 65, 2011/01
no abstracts in English
 spp., generated by ion-beam irradiation
spp., generated by ion-beam irradiationKondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kameari, Naoko*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
Plant Biotechnology, 26(5), p.565 - 569, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:68.56(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)Fragrant cyclamen cultivar (

 ), that bloomed purple flower containing malvidin 3,5-diglucoside as the major anthocyanin, was irradiated with a 320-MeV carbon-ion beam at 0-16 Gy to increase flower color variation by mutation. Some of the M2 plants derived from self-pollination of M1 plants irradiated at 2 Gy were flower-color mutants that retained desirable flower shape, flower size, and leaf color. One of the mutants bloomed novel red-purple flowers, the major anthocyanin of which was delphinidin 3,5-diglucoside. Because the major anthocyanins in flowers of
), that bloomed purple flower containing malvidin 3,5-diglucoside as the major anthocyanin, was irradiated with a 320-MeV carbon-ion beam at 0-16 Gy to increase flower color variation by mutation. Some of the M2 plants derived from self-pollination of M1 plants irradiated at 2 Gy were flower-color mutants that retained desirable flower shape, flower size, and leaf color. One of the mutants bloomed novel red-purple flowers, the major anthocyanin of which was delphinidin 3,5-diglucoside. Because the major anthocyanins in flowers of  spp. were previously restricted to malvidin, peonidin, and cyanidin types, the generation of a cyclamen containing mostly the delphinidin-type anthocyanin is an important breakthrough in cyclamen breeding. We expect this mutant to become not only a commercial cultivar itself, but also a valuable genetic resource for cyclamen breeding.
spp. were previously restricted to malvidin, peonidin, and cyanidin types, the generation of a cyclamen containing mostly the delphinidin-type anthocyanin is an important breakthrough in cyclamen breeding. We expect this mutant to become not only a commercial cultivar itself, but also a valuable genetic resource for cyclamen breeding.

 )
)Kondo, Emiko*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issei; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
JAEA-Review 2008-055, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2007, P. 79, 2008/11
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Emiko*; Kameari, Naoko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kurihara, Yasushi*; Akita, Yusuke; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

 )
)Kameari, Naoko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kondo, Emiko*; Kurihara, Yasushi*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

 )
)Kondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kameari, Naoko*; Kurihara, Yasushi*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

 )
)Kondo, Emiko*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
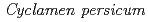 "Golden Boy"
"Golden Boy" 
 ) by ion-beam irradiation
) by ion-beam irradiationKameari, Naoko*; Akita, Yusuke; Kitamura, Satoshi; Hase, Yoshihiro; Kondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kurihara, Yasushi*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Tanaka, Atsushi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Akita, Yusuke*; Kitamura, Satoshi; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issey*; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*; Kondo, Emiko*; Kameari, Naoko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Tanaka, Atsushi
no journal, ,
In this study, using several flower-colored mutants and their parents, we analyzed flavonoid composition in flowers by HPLC, and isolated anthocyanin biosynthetic genes by degenerate PCR. We isolated several anthocyanin biosynthetic genes from C. graecum, C. purpurascens and fragrant cyclamen cultivars. Then, we analyzed their expression patterns between wild-type and flower-colored mutants. Based on their comparison, we selected candidates for anthocyanin biosynthetic genes and confirmed their enzymatic activities in vitro. Furthermore, we also demonstrated the effectiveness of PCR-based screening method in early growth stage of mutagenized cyclamen, using newly developed DNA markers.
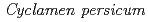 x
x  ) by ion beam re-irradiation
) by ion beam re-irradiationKondo, Emiko*; Kameari, Naoko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
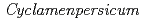

 ) by ion beam irradiation
) by ion beam irradiationKameari, Naoko*; Okubo, Naomi*; Kondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
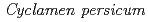

 ) by ion beam re-irradiation
) by ion beam re-irradiationKondo, Emiko*; Kameari, Naoko*; Kitamura, Satoshi; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
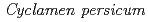

 ) by ion beam irradiation
) by ion beam irradiationKondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kameari, Naoko*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Kitamura, Satoshi; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Akita, Yusuke; Kitamura, Satoshi; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issei; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*; Kondo, Emiko*; Kameari, Naoko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
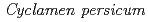

 )
)Kondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kameari, Naoko*; Kurihara, Yasushi*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Emiko*; Kameari, Naoko*; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
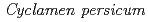

 ) by ion-beam irradiation and analysis of their flower pigments
) by ion-beam irradiation and analysis of their flower pigmentsKondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kameari, Naoko*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Kitamura, Satoshi; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Emiko*; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Emiko*; Nakayama, Masayoshi*; Kameari, Naoko*; Tanikawa, Natsu*; Morita, Yasumasa*; Akita, Yusuke; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi; Ishizaka, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
One of the fragrant cyclamens, Kaori-no-mai, blooms purple flowers containing malvidin 3,5-diglucoside as the major anthocyanin. Here, we irradiated etiolated petioles of Kaori-no-mai with a 320-MeV carbon-ion beam to increase flower color variation by mutation. Some of the M2 plants derived from self-pollination of M1 plants were flower-color mutan. One of the mutants bloomed novel red-purple flowers, the major anthocyanin of which was delphinidin 3,5-diglucoside. The major anthocyanins in flowers of 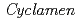 spp. were previously restricted to malvidin, peonidin, and cyanidin types, therefore, the generation of a cyclamen containing mostly the delphinidin-type anthocyanin is an important breakthrough in cyclamen breeding. We expect this mutant to become not only a commercial cultivar itself, but also a valuable genetic resource for cyclamen breeding.
spp. were previously restricted to malvidin, peonidin, and cyanidin types, therefore, the generation of a cyclamen containing mostly the delphinidin-type anthocyanin is an important breakthrough in cyclamen breeding. We expect this mutant to become not only a commercial cultivar itself, but also a valuable genetic resource for cyclamen breeding.