Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 26(3), p.032802_1 - 032802_12, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)A bunch-shape monitor (BSM) is a useful device for performing longitudinal beam tuning using the pointwise longitudinal phase distribution measured at selected points in the beam transportation. To measure the longitudinal phase distribution of a low-energy negative hydrogen (H ) ion beam, highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was adopted for the secondary-electron-emission target to mitigate the thermal damage due to the high-intensity beam loading. The HOPG target enabled the measurement of the longitudinal phase distribution at the center of a 3-MeV H
) ion beam, highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was adopted for the secondary-electron-emission target to mitigate the thermal damage due to the high-intensity beam loading. The HOPG target enabled the measurement of the longitudinal phase distribution at the center of a 3-MeV H ion beam with a high peak current of about 50 mA. The longitudinal bunch width was measured using HOPG-BSM at the test stand, which was consistent with the beam simulation. The correlation measurement between the beam transverse and longitudinal planes was demonstrated using HOPG-BSM. The longitudinal Twiss and emittance measurement with the longitudinal Q-scan method was conducted using HOPG-BSM.
ion beam with a high peak current of about 50 mA. The longitudinal bunch width was measured using HOPG-BSM at the test stand, which was consistent with the beam simulation. The correlation measurement between the beam transverse and longitudinal planes was demonstrated using HOPG-BSM. The longitudinal Twiss and emittance measurement with the longitudinal Q-scan method was conducted using HOPG-BSM.
 beam with 3 MeV by the bunch-shape monitor
beam with 3 MeV by the bunch-shape monitorKitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011012_1 - 011012_6, 2021/03
The new bunch shape monitor (BSM) is required to measure the bunch size of the high-intensity H beam with 3 MeV at the front-end section in the J-PARC linac. The carbon-nano tube wire and the graphene stick are good candidates for the target wire of the BSM, because these materials have the enough strength to detect the high-intensity beam. However, since the negative high voltage of more than a few kV should be applied to the wire in the BSM, the suppression of the discharge is the challenge to realize the new BSM. After the high-voltage test to investigate the effect of the discharge from the wire, the detection of the signal from the BSM was successful at the beam core with the peak current of 55 mA using the graphene stick. The preliminary result of the bunch-size measurement is reported in this presentation.
beam with 3 MeV at the front-end section in the J-PARC linac. The carbon-nano tube wire and the graphene stick are good candidates for the target wire of the BSM, because these materials have the enough strength to detect the high-intensity beam. However, since the negative high voltage of more than a few kV should be applied to the wire in the BSM, the suppression of the discharge is the challenge to realize the new BSM. After the high-voltage test to investigate the effect of the discharge from the wire, the detection of the signal from the BSM was successful at the beam core with the peak current of 55 mA using the graphene stick. The preliminary result of the bunch-size measurement is reported in this presentation.
Takeda, Tetsuaki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Aihara, Jun; Aoki, Takeshi; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ho, H. Q.; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Imai, Yoshiyuki; et al.
High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.5, 464 Pages, 2021/02
As a general overview of the research and development of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) in JAEA, this book describes the achievements by the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) on the designs, key component technologies such as fuel, reactor internals, high temperature components, etc., and operational experience such as rise-to-power tests, high temperature operation at 950 C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Kitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 17th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.251 - 253, 2020/09
A bunch-shape monitor (BSM) in the low-energy region is being developed in the J-PARC linac to accelerate the high-intensity proton beam with the low emittance. A highly-oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) was introduced as the target of the BSM to mitigate the thermal loading. The stable measurement of the BSM was realized thanks to the HOPG target, while the tungsten target was broken by the thermal loading from the high-intensity beam. However, since the longitudinal distribution measured with the BSM using the HOPG target was wider than the expected one, the improvement of tuning parameters is necessary for the BSM. The BSM consists of an electron multiplier, a bending magnet, and a radio-frequency deflector, which should be tuned appropriately. Behavior of these components were investigated and tuned. The longitudinal distribution measured with the BSM after the tuning was consistent with the expected one.
Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Shumpei*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.78_1 - 78_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:55.71(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Searching for effective pathways for the production of proton- and neutron-rich isotopes through an optimal combination of reaction mechanism and energy is one of the main driving forces behind experimental and theoretical nuclear reaction studies as well as for practical applications in nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste. We report on a study on incomplete fusion induced by deuteron, which contains one proton and one neutron with a weak binding energy and is easily broken up. This reaction study was achieved by measuring directly the cross sections for both proton and deuteron for  Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Kitamura, Ryo; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Otani, Masashi*; Kosaka, Satoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.2543 - 2546, 2019/06
A bunch shape monitor (BSM) is one of the important instruments to measure the longitudinal phase space distribution. For example in the J-PARC linac, three BSMs using the tungsten wire are installed at the ACS section to measure the bunch shapes between the accelerating cavities. However, this conventional BSM is hard to measure the bunch shape of H beam with 3 MeV at the beam transport between the RFQ and DTL sections, because the wire is broken around the center region of the beam. The new BSM using the carbon-nano-tube (CNT) wire is being developed to be able to measure the bunch shape of the H
beam with 3 MeV at the beam transport between the RFQ and DTL sections, because the wire is broken around the center region of the beam. The new BSM using the carbon-nano-tube (CNT) wire is being developed to be able to measure the bunch shape of the H beam with 3 MeV. The careful attention should be paid to apply the high voltage of
beam with 3 MeV. The careful attention should be paid to apply the high voltage of  10 kV to the CNT wire. The several measures are taken to suppress the discharge from the wire and operate the CNT-BSM. This presentation reports the current status of the development and future prospective for the CNT-BSM.
10 kV to the CNT wire. The several measures are taken to suppress the discharge from the wire and operate the CNT-BSM. This presentation reports the current status of the development and future prospective for the CNT-BSM.
Nakamura, Shinichi*; Kondo, Hikari*; Suzui, Nobuo; Yin, Y.-G.; Ishii, Satomi; Kawachi, Naoki; Rai, Hiroki*; Hattori, Hiroyuki*; Fujimaki, Shu
Molecular Physiology and Ecophysiology of Sulfur, p.253 - 259, 2015/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:70.56(Plant Sciences) -wave one-neutron halo configuration on
-wave one-neutron halo configuration on  Mg
MgKobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Barthelemy, R.*; Famiano, M. A.*; Fukuda, Naoki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 112(24), p.242501_1 - 242501_5, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:94.35(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 -wave halos at the drip-line;
-wave halos at the drip-line; 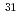 Ne
NeNakamura, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Sato, Yoshiteru*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Gibelin, J.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 112(14), p.142501_1 - 142501_5, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:91.04(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
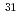 Ne
NeNakamura, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Sato, Yoshiteru*; Aoi, Nori*; Baba, Hidetada*; Deguchi, Shigeki*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Gibelin, J.*; Inabe, Naoto*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 103(26), p.262501_1 - 262501_4, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:198 Percentile:97.52(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kondo, Yoshikazu; Uchida, Naoki; Terunuma, Hirotaka; Tanaka, Kosuke; Oyama, Koichi; Katsurai, Kiyomichi; Washiya, Tadahiro
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycle; Sustainable Options & Industrial Perspectives (Global 2009) (CD-ROM), p.277 - 280, 2009/09
The composition of sludge in the dissolver after dissolution of PWR and ATR fuels at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) was analyzed. As a result the presence of zirconium molybdate was confirmed by the analysis of X-ray diffraction (XRD). To clarify the formation behavior of the precipitates of zirconium molybdate, investigated the dependence of HNO concentration on the precipitation with Mo and Zr solution. To evaluate the adhesion on the metal surface (stainless steel and Ti metal), the deposition amounts of the precipitates of zirconium molybdate on the metal were also examined. In addition, it reports on the comparative result of executing a chemical dissolution of the precipitates by using the solutions of NaOH, C
concentration on the precipitation with Mo and Zr solution. To evaluate the adhesion on the metal surface (stainless steel and Ti metal), the deposition amounts of the precipitates of zirconium molybdate on the metal were also examined. In addition, it reports on the comparative result of executing a chemical dissolution of the precipitates by using the solutions of NaOH, C H
H O
O -HNO
-HNO and H
and H O
O -HNO
-HNO .
.
Tomimoto, Hiroshi; Kato, Yasushi; Owada, Hiroyuki; Sato, Nao; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Kozawa, Takayuki; Shinohara, Masanori; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Tochio, Daisuke; Nojiri, Naoki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-025, 29 Pages, 2009/06
The first driver fuel of the HTTR (High Temperature Engineering test Reactor) was loaded in 1998 and the HTTR reached first criticality state in the same year. The HTTR has been operated using the first driver fuel for a decade. In Fuel elements assembling, 4770 of fuel rods which consist of 12 kinds of enrichment uranium are loaded into 150 fuel graphite blocks for HTTR second driver fuel elements. Measures of prevention of fuel rod miss loading, are employed in fuel design. Additionally, precaution of fuel handling on assembling are considered. Reception of fuel rods, assembling of fuel elements and storage of second driver fuels in the fresh fuel storage rack in the HTTR were started since June, 2008. Assembling, storage and pre-service inspection were divided into three parts. The second driver fuel assembling was completed in September, 2008. This report describes concerns of fuel handling on assembling and storage work for the HTTR fuel elements.
Tochio, Daisuke; Nojiri, Naoki; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Sekita, Kenji; Kondo, Masaaki; Saikusa, Akio; Kameyama, Yasuhiko; Saito, Kenji; Fujimoto, Nozomu
JAEA-Technology 2009-005, 47 Pages, 2009/05
HTTR is now conducted in-service operation through the rise-to power operation with rated operation or high-temperature test operation from achievement of first criticality at 1998. In order to demonstrate to supply stable heat to heat utilization system for long-term, HTTR was conducted rated/parallel-loaded 30-days operation. This paper reports the characteristics of long-term operation for HTTR.
Kondo, Hitoshi; Isozaki, Kazunori; Kawahara, Hirotaka; Tomita, Naoki
JNC TN9410 2003-004, 137 Pages, 2003/06
The MK-III project to improve the irradiation capability of the experimental fast reactor JOYO have been in underway.The MK-III project has three major purposes such as increasing high neutron flux, improvement of plant availability factor and upgrading in irradiation techniques. The increase of fast neutron flux and the enlargement of that field increase the reactor thermal rate from 100MWt to 140MWt. The main components in the cooling system such as intermediate heat exchangers (IHXs) and dump heat exchangers (DHXs) were replaced in MK-III modification in order to increase heat removal capability. These components replacement has been safely carried out from October 30, 2000 to September 21, 2001.The new IHX that has 70MWt rated heat exchange rate was installed to the location where old one was installed, so the mew IHX was designed with almost same geometry as old one. The design was carefully reviewed on structural integrity, shielding performance, thermal hydraulics, pressure loss, flow induced vibration and component design criterion and earthquake-proof class. A newly developed stainless steel named 316FR was adopted as a major structure material of the new IHX. The 316FR was developed for usage of sodium cooled fast reactor and has improved creep rupture and creep fatigue strength. In the design the following problems to be solved were cleared, These problems arise from defect of old IHX, increase of temperature difference between outlet and inlet and increase of sodium flow rate.(1)Reduction of ineffective flow to increase the heat transfer efficiency.(2)Suppression of CP(Corrosion Products) adhesion.(3)To prevent falling down of sodium free surface accompanied by increase of sodium flow.(4)Mitigation of thermal transient.This report describes the specific characteristic in the design and manufacturing, design data and principle of the design for the new IHX. The design was proved on above mentioned problem (3) by measurement of sodium free surface lev
 O
O
Urakawa, Satoru*; Kondo, Tadashi*; Igawa, Naoki; Shimomura, Osamu*; Ono, Hideo
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 21, p.387 - 391, 1994/00
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Naoki; Makino, Hitoshi; Umeki, Hiroyuki; Hirano, Fumio; Ishihara, Yoshinao*
no journal, ,
This presentation shows development and application of systems analysis for holistic management of radioactive waste generated from nuclear fuel cycle.
Kondo, Naoki; Makino, Hitoshi; Umeki, Hiroyuki; Ishihara, Yoshinao*
no journal, ,
This presentation shows development of analysis tools that is able to assess quantitative distinction of waste characteristic from nuclear fuel cycle condition.
Kondo, Naoki; Makino, Hitoshi; Umeki, Hiroyuki; Hioki, Kazumasa; Ishihara, Yoshinao*
no journal, ,
We developed tool that can calculate waste characteristics, and systems analysis that be conducible to waste management.
Nakamura, Shinichi*; Suzui, Nobuo; Kondo, Hikari*; Kawachi, Naoki; Yin, Y.-G.; Ishii, Satomi; Rai, Hiroki*; Hattori, Hiroyuki*; Fujimaki, Shu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Shinichi*; Kondo, Hikari*; Suzui, Nobuo; Yin, Y.-G.; Ishii, Satomi; Kawachi, Naoki; Rai, Hiroki*; Hattori, Hiroyuki*; Fujimaki, Shu
no journal, ,
Kitamura, Ryo; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hayashi, Naoki; Hirano, Koichiro; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kosaka, Satoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Nemoto, Yasuo*; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo
no journal, ,
In the J-PARC linac, the optimization of the longitude beam matching in the medium-energy beam transport1 is on-going using the bunch shape monitor (BSM) to improve the beam quality. In the measurement with the BSM, the phase distribution of the beam bunch is indirectly measured using the secondary electron beam produced from the negative hydrogen ion beam. However, when the bunch shape is measured at the center of the beam, it has not been measured yet, because of the limitation of the thermal loading of the secondary electron target. Therefore, the graphene was adopted as the BSM target, because it could resist the high thermal loading. and the performance evaluation was conducted. When the target was set at the center of the beam, the detection of the signal from the graphene target was successful. Therefore, this graphene target can be used for the BSM to measure the high-intensity beam with the low energy.