Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
古渡 意彦*; 中上 晃一*; 土方 保和*; 山下 一太*; 平井 悠太*; 松崎 賢*; 盛武 敬*; 辻 智也; Zutz, H.*; Ketelhut, S.*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, p.ncaf061_1 - ncaf061_9, 2025/00
被引用回数:0It is crucial to monitor healthcare workers' radiation exposure, especially given the increasing reliance on X-ray imaging technologies. In response to new evidence that the threshold for lens opacity is lower than previously thought, the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) has revised the annual dose limit for exposure to the lens of the eye. After the revision of the annual eye lens dose limit, the new survey on the dosemeter wearing rate was conducted in Japan. The result showed that despite the presence of monitoring protocols, the dosemeter wearing rate among healthcare workers was still low. Compliance often lacked robust verification measures, especially in smaller medical facilities. Active personal dosemeters (APDs) are commonly used in Japan, although studies suggest that they may underestimate exposure in certain settings, such as pulsed X-ray fields. Passive dosemeters, on the other hand, serve as legal dosemeters, offering a more accurate assessment of radiation exposure. This article addresses issues related to the monitoring of healthcare workers using APDs and clarifies concerns regarding the use of APDs by orthopedic surgeons during procedures involving high-dose X-ray exposure. A series of performance tests suggested that the APDs worn by orthopedic surgeons, who are often exposed to higher dose rates near patients, may underestimate radiation levels during procedures. This underestimation occurs because the surgeons are exposed to pulsed, scattered X-ray fields with energies ranging from 20 and 100 keV. The results also suggest monitoring techniques should be improved to ensure the safety of healthcare workers.
古渡 意彦*; 吉富 寛; 谷 幸太郎*; 谷村 嘉彦; 栗原 治*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(16-18), p.1574 - 1579, 2024/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)This study attempted the reconstruction of organ doses of victims who are highly exposed to gamma rays in non-homogeneous exposure accident by a sealed 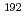 Ir source in Gilan, Iran. According to the accident report by International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), a victim was highly exposed on his right chest and the dose estimation by means of biodosimtry and clinical observation were carried out. However, dose reconstruction by means of physical dosimetry was not completely made. In this study, a series of Monte Carlo (MC) calculations employing the PHITS 3.24 incorporated with the Adult male Mesh-type Reference Computational Phantom was performed to estimate organ doses with reference to an actual radiation accident involved in the
Ir source in Gilan, Iran. According to the accident report by International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), a victim was highly exposed on his right chest and the dose estimation by means of biodosimtry and clinical observation were carried out. However, dose reconstruction by means of physical dosimetry was not completely made. In this study, a series of Monte Carlo (MC) calculations employing the PHITS 3.24 incorporated with the Adult male Mesh-type Reference Computational Phantom was performed to estimate organ doses with reference to an actual radiation accident involved in the 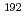 Ir sealed source, and to investigate issues on reconstruction of organ doses of victims who are highly exposed to radiation under non-homogeneous exposure accident. Calculated organ doses for the lungs, the red born marrow, and the small intestine by MC calculation were compared with experimental values taken from the literature and were within 23% in terms of mGy h
Ir sealed source, and to investigate issues on reconstruction of organ doses of victims who are highly exposed to radiation under non-homogeneous exposure accident. Calculated organ doses for the lungs, the red born marrow, and the small intestine by MC calculation were compared with experimental values taken from the literature and were within 23% in terms of mGy h /Ci for the Gilan case. The averaged whole body dose was estimated to be 0.31 Gy, which are less than one-tenth than that estimated by biodosimetry (3.1-4.1 Gy). In the IAEA Gilan report, the average whole body dose was assumed to be 2 Gy for rough estimation of physical dose, having a large discrepancy with those estimated by the MC calculation.
/Ci for the Gilan case. The averaged whole body dose was estimated to be 0.31 Gy, which are less than one-tenth than that estimated by biodosimetry (3.1-4.1 Gy). In the IAEA Gilan report, the average whole body dose was assumed to be 2 Gy for rough estimation of physical dose, having a large discrepancy with those estimated by the MC calculation.
 Am gamma calibration field based on international standards and its conversion coefficients
Am gamma calibration field based on international standards and its conversion coefficients辻 智也; 吉富 寛; 古渡 意彦*; 谷村 嘉彦
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(15), p.1416 - 1424, 2024/09
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)A  Am gamma (
Am gamma ( )-ray calibration field that meets the requirements for a
)-ray calibration field that meets the requirements for a  -ray reference field as specified in the ISO 4037 standard series was established in the Facility of Radiation Standards of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The reference air kerma rates were measured using a reference ionization chamber (IC) calibrated by the N-80 quality X-ray calibration field of the national metrology standard in Japan and with a correction to account for differences in photon energy due to the calibration field. Conversion coefficients for the
-ray reference field as specified in the ISO 4037 standard series was established in the Facility of Radiation Standards of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The reference air kerma rates were measured using a reference ionization chamber (IC) calibrated by the N-80 quality X-ray calibration field of the national metrology standard in Japan and with a correction to account for differences in photon energy due to the calibration field. Conversion coefficients for the  Am
Am  -ray calibration field, including those not listed in the ISO 4037 standard series, were calculated based on the measured
-ray calibration field, including those not listed in the ISO 4037 standard series, were calculated based on the measured  -ray fluence rate spectra.
-ray fluence rate spectra.
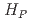 (0.07) for extremity dose monitoring of medical personnel
(0.07) for extremity dose monitoring of medical personnel古渡 意彦*; 吉富 寛; 永元 啓介*; 中上 晃一*; 盛武 敬*; 欅田 尚樹*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(15-16), p.1807 - 1812, 2023/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)An additional individual monitoring using ring badge must be made, when inhomogenous exposure around radiation workers' extremity were critical for radiation workers. The RPLD, the GD-302M and the GD-352M have a dimension of 13.0 mm in length and 2.8 mm in diameter for outer casing and will also be a promising candidate for individual monitoring of the extremities of medical personnel. We investigated the applicability of this commercially available RPLDs to extremity dose monitoring by performing a characterization of the dosemeters by experiments and Monte Carlo (MC) calculations. The results shows that the energy response of GD-352M fully meets the IEC requirement between 20 keV and 200 keV. We also found that no significant angular dependence of responses for each model was observed and orientation of irradiation hardly affected the response. In conclusion, we demonstrated the applicability of a small RPLD to the extremity monitoring in terms of 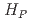 (0.07) for medical personnel.
(0.07) for medical personnel.
古渡 意彦*; 窪田 卓見*; 吉富 寛; 欅田 尚樹*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(11), p.1239 - 1247, 2023/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)We performed an experimental investigation on occupational exposure of the eye lens and the extremity of radiation workers engaged in handling of highly activated materials in a small research accelerator facility. Using a simplified physical phantom to simulate the relevant inhomogeneous radiation exposure situations, the personal dose equivalents obtained at the eye lens and the extremities of radiation workers handling heavily radioactive converters were measured together with the dose measured by personal dosemeters worn on their trunk. Results of a mockup experiments and the Monte Carlo calculations suggest that the quantitative estimation of the eye lens doses can be estimated from the trunk dose, while the extremity doses vary considerably from the dose readings from the trunk, depending on the use of simple point-source or volume source geometry.
古渡 意彦*; 永元 啓介*; 中上 晃一*; 吉富 寛; 盛武 敬*; 欅田 尚樹*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 198(17), p.1303 - 1312, 2022/10
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:28.39(Environmental Sciences)We demonstrate a practical calibration method and its applicability for a commercially available radiophotoluminescence dosemeter (RPLD, GD-352M) to eye lens dose monitoring, by performing the calibration in accord with the ISO recommendations. The calibration was then verified through a series of experiments. For verification of the derived calibration factor (1.21  0.04,
0.04,  = 1) of the RPLD, we performed standard irradiations in the X-ray reference fields and the mockup measurements in the actual radiation fields in a hospital. The commercially available dosemeters, DOSIRIS was also put on the ISO cylinder phantom and the RANDO phantom together with the GD-352M in the verification experiments. The personal dose equivalents
= 1) of the RPLD, we performed standard irradiations in the X-ray reference fields and the mockup measurements in the actual radiation fields in a hospital. The commercially available dosemeters, DOSIRIS was also put on the ISO cylinder phantom and the RANDO phantom together with the GD-352M in the verification experiments. The personal dose equivalents 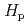 (3) obtained from the GD-352M and those obtained from the DOSIRIS were in good agreement with each other. Our results demonstrate the proper calibration of a commercially available RPLD that is applicable to the additional monitoring of the lens of the eyes for medical personnel.
(3) obtained from the GD-352M and those obtained from the DOSIRIS were in good agreement with each other. Our results demonstrate the proper calibration of a commercially available RPLD that is applicable to the additional monitoring of the lens of the eyes for medical personnel.
古渡 意彦*; 永元 啓介*; 中上 晃一*; 谷村 嘉彦; 盛武 敬*; 欅田 尚樹*
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 47(1), p.39 - 49, 2022/03
For proper monitoring of the eye lens dose, an appropriate calibration factor of a dosimeter and information about the mean energies of X-rays are indispensable. The scattered X-ray energy spectra should be well characterized in medical practices where eye lenses of medical staffs might be high. Scattered X-ray energy spectra were experimentally derived for three different types of X-ray diagnostic and therapeutic equipment. A commercially available CdZnTe (CZT) spectrometer with a lead collimator was employed for the measurement of scattered X-rays. From the obtained energy spectra, the mean energies of the scattered X-rays lied between 40 and 60 keV. This also agreed with that obtained by the conventional half value layer method. The obtained mean energies of the scattered X-rays were found to match the flat region of the dosimeter response.
古渡 意彦; 谷村 嘉彦; Kessler, P.*; Neumaier, S.*; R ttger, A.*
ttger, A.*
Radioisotopes, 70(1), p.1 - 18, 2021/01
For proper environmental radiation monitoring, a method to simultaneously determine ambient dose equivalent rate and radioactivity concentration in the air by using a newly developed scintillation spectrometer, namely a CeBr spectrometer was investigated. The performance of the proposed method, including energy dependence and linearity of the spectrometer, was verified by a series of measurements, conducted according to the procedure of inter-comparison of detectors used for early warning network performed by the European Radiation Dosimetry Group (EURADOS). Measurement results show that the proposed method is suitable for environmental monitoring purposes. After thorough tests, the activity concentration in air was determined in the laboratory by using a point-like sealed
spectrometer was investigated. The performance of the proposed method, including energy dependence and linearity of the spectrometer, was verified by a series of measurements, conducted according to the procedure of inter-comparison of detectors used for early warning network performed by the European Radiation Dosimetry Group (EURADOS). Measurement results show that the proposed method is suitable for environmental monitoring purposes. After thorough tests, the activity concentration in air was determined in the laboratory by using a point-like sealed  Ba source to mimic a radioactive cloud containing
Ba source to mimic a radioactive cloud containing  I and
I and  Xe. The photon fluence rate was obtained from the pulse height distribution by using the unfolding method, and the activity concentration in air for radioisotopes of interest, mainly
Xe. The photon fluence rate was obtained from the pulse height distribution by using the unfolding method, and the activity concentration in air for radioisotopes of interest, mainly  Xe, was estimated from the obtained photon fluence rate by applying the conversion coefficient evaluated via a Monte Carlo calculation. The results additionally show that the method presented in this study is reliable and suitable for the environmental radiation measurement.
Xe, was estimated from the obtained photon fluence rate by applying the conversion coefficient evaluated via a Monte Carlo calculation. The results additionally show that the method presented in this study is reliable and suitable for the environmental radiation measurement.
古渡 意彦; Zutz, H.*; Hupe, O.*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 192(4), p.460 - 472, 2020/12
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:9.64(Environmental Sciences)A commercially available active extremity dosemeter is a promising candidate for medical staff aid individual monitoring of the eye lens. We investigated the applicability of the newly developed active extremity dosemeter, which uses a low-energy photon probe, to eye lens dose monitoring by performing a complete characterization of the dosemeters. Performance tests revealed that the active extremity dosemeter would overestimate personal dose equivalent,  p(3), when the probe is worn close to the lens of the eye of a medial worker without any improvement in the response. Introducing an appropriate filter into the probe for low-energy photon has proven to improve the response. The dosemeter then satisfies the criteria of the personal dosemeter for eye lens dosimetry and can be applicable to individual monitoring of eye lens dose. This article also discusses the applicability of the dosemeter to area monitoring for decision making regarding additional monitoring of the eye lens and the extremities.
p(3), when the probe is worn close to the lens of the eye of a medial worker without any improvement in the response. Introducing an appropriate filter into the probe for low-energy photon has proven to improve the response. The dosemeter then satisfies the criteria of the personal dosemeter for eye lens dosimetry and can be applicable to individual monitoring of eye lens dose. This article also discusses the applicability of the dosemeter to area monitoring for decision making regarding additional monitoring of the eye lens and the extremities.
 scintillation spectrometer due to terrestrial gamma ray components; Application in environmental radiation monitoring
scintillation spectrometer due to terrestrial gamma ray components; Application in environmental radiation monitoring古渡 意彦; 谷村 嘉彦; Kessler, P.*; R ttger, A.*
ttger, A.*
Radiation Measurements, 138, p.106431_1 - 106431_6, 2020/11
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:8.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)In radiological emergency, timely and reliable radiological information such as dose rate or radioactive concentrations due to artificial radionuclides is indispensable to protect general public and the first responder of the situation. The authors have investigated the method for effectively identifying and determining the radioactivity concentration using a scintillation spectrometer. In this study, the authors demonstrate how influence of terrestrial background (BG) component on measured pulse height spectrum can be minimized to obtain the peaks from gamma rays emitted by artificial radioactivity. In some cases of radiological emergency monitoring, subtraction of BG components was probe to be difficult, because the prior measurement of BG component at the place to be monitored is compulsory. By removing the BG component appropriately from measured pulse height spectrum without any prior BG measurement, the effective minimum detection limit of the spectrometer would be declined.
 Cf neutron source with the spherical protection case
Cf neutron source with the spherical protection case古渡 意彦; 西野 翔; Romallosa, K. M. D.*; 吉富 寛; 谷村 嘉彦; 大石 哲也
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 189(4), p.436 - 443, 2020/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)円筒形密封中性子線源に球形ステンレス製保護ケースを取り付け、中性子線源からの中性子の非等方放出について実験的に導出した。事前のモンテカルロシミュレーションで幅広い範囲で中性子放出が一定となることを検証したが、可搬型ロングカウンタによる測定でも確認することができた。予備測定及び線源への衝撃等を考慮し、われわれは更新した線源移動装置で保持できるよう中性子線源保護ケースをデザインした。実験で得られた非等方係数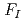 (90)は、1.002
(90)は、1.002 0.002であり、55度から125度の幅広い範囲で、一様な中性子放出が得られることが明らかとなった。
0.002であり、55度から125度の幅広い範囲で、一様な中性子放出が得られることが明らかとなった。
 Am and
Am and  Sr/
Sr/ Y sources in terms of the eye lens monitoring in the nuclear facilities
Y sources in terms of the eye lens monitoring in the nuclear facilities吉富 寛; 古渡 意彦
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 188(2), p.191 - 198, 2020/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:17.49(Environmental Sciences)This paper highlights the issues of exposure inhomogeneity that are relative to eye lens monitoring for low-energy photons from  Am and beta-rays from
Am and beta-rays from  Sr/
Sr/ Y including a personal protective equipment because eye lens exposure has been concerned more than before due to the proposed reduction of relevant dose limit. These nuclides are common sources in the nuclear industry, which are particularly of concern. Our previous study presented a quantitative estimation of exposure inhomogeneity, which was applied to simple but typical exposure situations to the radionuclides. For the present study, exposure inhomogeneity of
Y including a personal protective equipment because eye lens exposure has been concerned more than before due to the proposed reduction of relevant dose limit. These nuclides are common sources in the nuclear industry, which are particularly of concern. Our previous study presented a quantitative estimation of exposure inhomogeneity, which was applied to simple but typical exposure situations to the radionuclides. For the present study, exposure inhomogeneity of  Am was approximately within a factor of 1.6, implying a rather homogeneous situation than expected. Regarding
Am was approximately within a factor of 1.6, implying a rather homogeneous situation than expected. Regarding  Sr/
Sr/ Y exposure, estimation from both
Y exposure, estimation from both 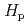 (10) and
(10) and 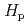 (0.07) on trunk would lead to an over- or underestimation by a factor of more than ten. In contrast,
(0.07) on trunk would lead to an over- or underestimation by a factor of more than ten. In contrast, 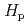 (3) measurement on trunk will improve by up to a factor of two. With respect to the personal protective equipment, lead apron and protective glasses are effective for the 60-keV photons for both anterior-posterior (AP) and rotational (ROT) irradiations, while a full-face respirator can reduce the eye lens dose by approximately 17% for
(3) measurement on trunk will improve by up to a factor of two. With respect to the personal protective equipment, lead apron and protective glasses are effective for the 60-keV photons for both anterior-posterior (AP) and rotational (ROT) irradiations, while a full-face respirator can reduce the eye lens dose by approximately 17% for  Sr/
Sr/ Y betas. As a whole, this study demonstrated that the effect of protective equipment can be effectively incorporated into the homogeneity evaluation.
Y betas. As a whole, this study demonstrated that the effect of protective equipment can be effectively incorporated into the homogeneity evaluation.
古渡 意彦; 吉富 寛; 西野 翔; 谷村 嘉彦; 大石 哲也; Kessler, P.*; Neumaier, S.*; R ttger, A.*
ttger, A.*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 187(1), p.61 - 68, 2019/12
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:25.69(Environmental Sciences)A low dose rate Cs gamma ray calibration field that fully satisfies the requirement of the ISO 4037 series was established in the Facility of Radiation Standards in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Two different methods were employed to determine the reference air kerma rate, namely a conventional ionization chamber and a G(E) function method used a newly developed scintillation spectrometer. To fulfill the requirement of the ISO 4037 and suppress scattering of Cs gamma ray within the room as far as possible, a suitable lead collimator was introduced to limit the irradiation area at test points and placed at the middle height in an irradiation room with a grating floor. From measured results evaluated reference air kerma rates between 1.0 m and 3.0 m from the center of the source, gamma ray scattering from the room structures was found to be negligible. The resulting Cs gamma ray calibration field could provide ambient dose equivalent rates of 0.7-7.2  Sv h
Sv h for use with environmental radiation monitoring devices.
for use with environmental radiation monitoring devices.
古渡 意彦; 吉富 寛; 西野 翔; 谷村 嘉彦; 大石 哲也; Kessler, P.*; Neumaier, S.*; R ttger, A.*
ttger, A.*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 186(4), P. 538, 2019/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)原著論文の表5(B)中の単位について、nSv h とすべきところ
とすべきところ Sv h
Sv h と記載するミスがあったため、訂正する。
と記載するミスがあったため、訂正する。
古渡 意彦; 吉富 寛
Radioisotopes, 68(9), p.595 - 603, 2019/09
The recommended annual limit of equivalent dose to the lens of the eye has decreased to 20 mSv y from the current limit of 150 mSv y
from the current limit of 150 mSv y . In terms of occupational exposure to radiation workers, exposure inhomogeneity plays an important role when estimating the eye lens dose from readings of dosimeters worn by workers on their trunk. The authors focused on homogeneous exposure situations that radiation workers may encounter in nuclear and accelerator facilities. Moreover, the authors investigated how radiation workers are exposed non-homogeneously in homogeneous exposure scenarios, where radiation workers may usually be encountered, regardless of their radiation works. In our previous study, we proposed a methodology to quantitatively evaluate the inhomogeneity of exposure. The homogeneity of exposure was evaluated by performing Monte Carlo calculations with a mathematical phantom under the isotropic and rotational irradiation geometries due to gamma and beta rays.
. In terms of occupational exposure to radiation workers, exposure inhomogeneity plays an important role when estimating the eye lens dose from readings of dosimeters worn by workers on their trunk. The authors focused on homogeneous exposure situations that radiation workers may encounter in nuclear and accelerator facilities. Moreover, the authors investigated how radiation workers are exposed non-homogeneously in homogeneous exposure scenarios, where radiation workers may usually be encountered, regardless of their radiation works. In our previous study, we proposed a methodology to quantitatively evaluate the inhomogeneity of exposure. The homogeneity of exposure was evaluated by performing Monte Carlo calculations with a mathematical phantom under the isotropic and rotational irradiation geometries due to gamma and beta rays. 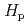 (3)
(3) /
/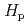 (10)
(10)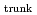 exceeded 1.0 even in the case of homogeneous exposure to gamma rays. Even in the homogeneous exposure scenarios, the
exceeded 1.0 even in the case of homogeneous exposure to gamma rays. Even in the homogeneous exposure scenarios, the 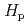 (3)
(3)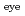 might exceed the revised annual dose limit for radiation workers who are exposed close to annual dose limit.
might exceed the revised annual dose limit for radiation workers who are exposed close to annual dose limit.
吉富 寛; 古渡 意彦; 萩原 雅之*; 長畔 誠司*; 中村 一*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 184(2), p.179 - 188, 2019/08
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:17.25(Environmental Sciences)To manage the equivalent doses for radiation workers, exposure inhomogeneity is an important factor in the decision-making process related to protection measures and additional monitoring. Our previous study proposed the methodology to evaluate the inhomogeneity of exposure quantitatively. In this study, we applied proposed method to five different types of actual exposure situations in the nuclear industry. Two of them were conventionally characterized as homogeneous exposure, but the other three as inhomogeneous exposure. The evaluation of homogeneity exposure was conducted using Monte Carlo calculations with two simplified models, which were then verified with phantom experiments. Consequently, all of the evaluations reproduced the experimental results, implying that our proposed method would be applicable for actual work conditions in the nuclear industry. Furthermore, the two presumed homogeneous exposure situations were found to be rather inhomogeneous because of the contribution of positrons and the limited source region. The investigation also implies that obtaining the information on the most probable posture of the exposed worker, as well as the existence of the weekly penetrating radiation such as 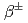 ray as a main source of exposure would be the key for more precise estimation.
ray as a main source of exposure would be the key for more precise estimation.
 scintillation detector coupled with lead shielding
scintillation detector coupled with lead shielding古渡 意彦; 谷村 嘉彦
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 24, p.011037_1 - 011037_7, 2019/01
Authors attempted to apply a CeBr scintillation detector coupled with an appropriate lead shield to in-situ environmental radioactivity measurement for evaluation of surface contamination density on soil in heavily contaminated areas. Contamination by a vast amount of radioactive materials released due to the nuclear accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant still remains. Both decontamination and remediation works have been recognized a challenging practice. Particularly, methodologies for confirmation of decontamination effect in heavily contaminated areas have been being intensively developed. This study preliminary investigates an adaptability of a shielded CeBr
scintillation detector coupled with an appropriate lead shield to in-situ environmental radioactivity measurement for evaluation of surface contamination density on soil in heavily contaminated areas. Contamination by a vast amount of radioactive materials released due to the nuclear accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant still remains. Both decontamination and remediation works have been recognized a challenging practice. Particularly, methodologies for confirmation of decontamination effect in heavily contaminated areas have been being intensively developed. This study preliminary investigates an adaptability of a shielded CeBr scintillation detector for environmental radioactivity measurement. An appropriate shielding to spectrometer would allow to limit the area to be monitored and consequently lead to expand the upper detection limit of surface contamination density on soil. In this study, determination of surface contamination density for
scintillation detector for environmental radioactivity measurement. An appropriate shielding to spectrometer would allow to limit the area to be monitored and consequently lead to expand the upper detection limit of surface contamination density on soil. In this study, determination of surface contamination density for  Cs and
Cs and  Cs was focused. Suitable design of shielded CeBr
Cs was focused. Suitable design of shielded CeBr detector was investigated so that in-situ environmental radioactivity measurement could be performed even in higher dose rate areas.
detector was investigated so that in-situ environmental radioactivity measurement could be performed even in higher dose rate areas.
古渡 意彦; 吉富 寛; 大石 哲也; 吉澤 道夫
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 6, p.86 - 90, 2019/01
This work presents a framework of decision-making for additional monitoring of eye lens dose for radiation workers in reflect to the reduction of the annual dose limit of the eye lens dose. Based on a quantitative scheme to systematically estimate (non-) homogeneity of exposure, the proposed "homogeneity index (HI)" is introduced as a criterion of condition branching for decision making of additional monitoring of eye lens dose.
谷村 嘉彦; 西野 翔; 吉富 寛; 古渡 意彦; 大石 哲也
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 6, p.134 - 138, 2019/01
福島第一原子力発電所事故のような原子力災害時においては、様々な放射性物質が環境中に放出され、線量を増加させることが考えられる。 線スペクトルを測定し、核種を同定することは外部被ばくと内部被ばくの両方に対する放射線防護上重要である。そこで、市販のCdZnTeスペクトロメータを選び、
線スペクトルを測定し、核種を同定することは外部被ばくと内部被ばくの両方に対する放射線防護上重要である。そこで、市販のCdZnTeスペクトロメータを選び、 線入射角度依存性と使用可能な線量率範囲をFRSの校正場で試験した。その結果、全体の85%をカバーできる
線入射角度依存性と使用可能な線量率範囲をFRSの校正場で試験した。その結果、全体の85%をカバーできる 135
135 において感度低下は15%以下であり、200
において感度低下は15%以下であり、200 Gy/h以下の空気カーマ率の場においてスペクトルが測定できることがわかった。
Gy/h以下の空気カーマ率の場においてスペクトルが測定できることがわかった。
 and SrI
and SrI (Eu) scintillation detectors for environmental monitoring
(Eu) scintillation detectors for environmental monitoring古渡 意彦; 谷村 嘉彦; Kessler, P.*; Neumaier, S.*; Roettger, A.*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 6, p.81 - 85, 2019/01
The simultaneous evaluation of dose rate and radioactivity using newly developed scintillation detectors, i.e. CeBr and SrI
and SrI (Eu) was investigated for environmental radiation measurement in emergency situation. Energy dependence and linearity tests of both detectors were conducted in a low background laboratory operated by the German metrological institute and found to be applicable to environmental monitoring purposes. As a result of environmental
(Eu) was investigated for environmental radiation measurement in emergency situation. Energy dependence and linearity tests of both detectors were conducted in a low background laboratory operated by the German metrological institute and found to be applicable to environmental monitoring purposes. As a result of environmental  ray measurements in normal condition, evaluated air kerma rate and radioactivity in/on soil for
ray measurements in normal condition, evaluated air kerma rate and radioactivity in/on soil for  Cs,
Cs,  Cs and
Cs and  K seemed consistent. Results also support that methods developed in the study are reliable and applicable to the environmental radiation measurement.
K seemed consistent. Results also support that methods developed in the study are reliable and applicable to the environmental radiation measurement.