Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
三浦 泰人*; 宮本 慎太郎*; 丸山 一平*; Aili, A.*; 佐藤 拓未; 永江 勇二; 五十嵐 豪*
Case Studies in Construction Materials, 21, p.e03571_1 - e03571_14, 2024/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Construction & Building Technology)In this study, the expansion behavior of cement materials after high-temperature heating and water immersion was observed experimentally. Two experiments were conducted using mortar specimens with different sand-to-cement ratios subjected to different high-temperature histories up to 1000 C. In Case 1, the specimens were immersed in water after high-temperature heating and then cooled naturally; in Case 2, the specimens were immersed in water at high temperatures without the cooling process. Based on the results, it was confirmed that lime expansion due to the rehydration of CaO by heating occurred in Case 1. In contrast, dynamic continuous explosive spalling occurred in Case 2 because of water penetration into the specimen at a high temperature. The explosive spalling in water observed in Case 2 is a phenomenon that has not been reported to date. Possible failure mechanisms for lime expansion and continuous expansive spalling in water are suggested.
C. In Case 1, the specimens were immersed in water after high-temperature heating and then cooled naturally; in Case 2, the specimens were immersed in water at high temperatures without the cooling process. Based on the results, it was confirmed that lime expansion due to the rehydration of CaO by heating occurred in Case 1. In contrast, dynamic continuous explosive spalling occurred in Case 2 because of water penetration into the specimen at a high temperature. The explosive spalling in water observed in Case 2 is a phenomenon that has not been reported to date. Possible failure mechanisms for lime expansion and continuous expansive spalling in water are suggested.
Zheng, X.; 玉置 等史; 柴本 泰照; 丸山 結
日本原子力学会誌ATOMO , 66(11), p.565 - 569, 2024/11
, 66(11), p.565 - 569, 2024/11
原子力安全の継続的な改善のためにはリスク情報と不確かさ情報を活用した合理的な意思決定が重要であり、近年ではこれを効率的に実施するために人工知能/機械学習(AI/ML)を活用することが期待されている。本報では、原子力分野におけるAI/MLの活用例を調査し、日本原子力研究開発機構が行うAI/MLを活用した動的確率論的リスク評価(PRA)と不確かさ評価・感度解析の研究状況を紹介する。具体的には、決定論的解析コードと機械学習による代替評価モデルを柔軟に共用できる多忠実シミュレーション手法を構築することで、ランダムサンプリングを用いた動的PRAとソースターム不確かさ評価・グローバル感度解析の効率的な実施を可能とした。
曽山 和彦; 林田 洋寿*; 丸山 龍治; 山崎 大; 後藤 惟樹*; 小林 勇輝*; 荒川 翔平*; 山本 有悟*; 須場 健太*; 山村 和也*
JAEA-Research 2024-006, 15 Pages, 2024/10
磁性体中の磁場イメージングを目的として、Wolter I型光学系に多層膜スーパーミラーを適用した中性子磁気顕微鏡の光学設計を行った。拡大率12.5倍の拡大結像光学系について、軌跡シミュレーションコードを用いて、偏極中性子の磁性体試料によるdepolarizationの解析、レプリカ法で作製されるWolterミラーの形状精度が顕微鏡の空間分解能へ与える影響の検討を行った。その結果、マイクロメートルオーダーの空間分解能を得るために必要な形状精度に関する知見を得た。
松本 俊慶; 日引 俊*; 丸山 結
International Journal of Energy Research, 2024(1), p.9748588_1 - 9748588_18, 2024/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Energy & Fuels)ウェットキャビティ戦略(格納容器内への事前注水方策)の有効性を評価するために、圧力容器から放出される溶融物条件の不確かさを考慮した確率論的な評価手法を構築した。第1段階では、MELCORコードにより溶融物条件を求めた。炉心溶融進展に関係する5つの不確かさパラメータが選択された。インプットパラメータのセットはラテン超方格サンプリングにより発生された。第2段階ではJASMINEコードにより溶融物挙動が解析された。JASMINE解析のパラメータの確率分布はMELCOR解析の結果から決定された。初期水位は0.5、1.0、2.0mに設定された。デブリの高さが冷却性判定のために基準と比較された。一連の計算の結果としてデブリの冷却確率が取得された。さらにMELCOR-JASMINEを組み合わせた解析手法の成立性と技術的な課題について議論された。
山崎 大; 丸山 龍治; 青木 裕之; 花島 隆泰*; 阿久津 和宏*; 宮田 登*; 曽山 和彦
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 9(2), p.20_1 - 20_12, 2024/06
This study developed a neutron-beam focusing supermirror for grazing-incidence small-angle neutron scattering (GISANS) measurements. It was fabricated by depositing NiC/Ti supermirror film with ion-beam sputtering on a precise elliptic surface of fused quartz figured using the elastic emission machining technique. Neutron measurements at a pulsed neutron reflectometer BL17 of MLF, J-PARC successfully demonstrated that the focusing supermirror enhances a beam intensity twentyfold compared with an optimally collimated beam, achieving the signal-to-background ratio of the focal spot as high as 500. The mirror can be readily installed and used at BL17.
吉田 英一*; 山本 鋼志*; 淺原 良浩*; 丸山 一平*; 刈茅 孝一*; 齊藤 朱音*; 松井 裕哉; 望月 陽人; 城 まゆみ*; 勝田 長貴*; et al.
Communications Engineering (Internet), 3, p.67_1 - 67_10, 2024/05
地下空洞やボーリング孔のような母岩中の水みちの恒久的な閉塞は、例えば、地下を利用する二酸化炭素貯留や放射性廃棄物処分のような多くの地下利用における長期安全性やその効果の維持を確実にするため必要である。通常用いられるセメント系材料による閉塞では、化学的・物理的な性能低下により十分な恒久性を発揮しない可能性がある。天然のカルサイトのコンクリーションの形成に関する研究により、コンクリーション化剤を用いたより恒久的なシーリング技術が開発された。この技術は、地下研究施設の深度350mの坑道近傍に存在する水みちの閉塞のための原位置試験に適用された。その結果、水みちは短期間に急速に閉塞するとともに、地震(M5.4)による攪乱後も再閉塞していた。また、これにより、岩盤は初期の母岩相当まで透水性が低下しており、この方法による閉塞が恒久的でロバストであることが実証された。
藁科 友朗*; 佐藤 朝子*; 比内 浩; Shaikhutdinov, N.*; Shagimardanova, E.*; 森 宙史*; 玉木 聡志*; 斎藤 元文*; 眞田 幸尚; 佐々木 祥人; et al.
Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 90(4), p.e02113-23_1 - e02113-23_23, 2024/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)A major incident occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station following the tsunami triggered by the Tohoku-Pacific Ocean Earthquake in March 2011, whereby seawater entered the torus room in the basement of the reactor building. Here, we identify and analyze the bacterial communities in the torus room water and several environmental samples. Samples of the torus room water (1  10
10 Bq
Bq Cs/L) were collected by the Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings from two sampling points between 30 cm and 1 m from the bottom of the room (TW1) and the bottom layer (TW2). A structural analysis of the bacterial communities based on 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing revealed that the predominant bacterial genera in TW1 and TW2 were similar. TW1 primarily contained the genus Limnobacter, a thiosulfate-oxidizing bacterium.
Cs/L) were collected by the Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings from two sampling points between 30 cm and 1 m from the bottom of the room (TW1) and the bottom layer (TW2). A structural analysis of the bacterial communities based on 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing revealed that the predominant bacterial genera in TW1 and TW2 were similar. TW1 primarily contained the genus Limnobacter, a thiosulfate-oxidizing bacterium.  -Irradiation tests on Limnobacter thiooxidans, the most closely related phylogenetically found in TW1, indicated that its radiation resistance was similar to ordinary bacteria. TW2 predominantly contained the genus Brevirhabdus, a manganese- oxidizing bacterium. Although bacterial diversity in the torus room water was lower than seawater near Fukushima,
-Irradiation tests on Limnobacter thiooxidans, the most closely related phylogenetically found in TW1, indicated that its radiation resistance was similar to ordinary bacteria. TW2 predominantly contained the genus Brevirhabdus, a manganese- oxidizing bacterium. Although bacterial diversity in the torus room water was lower than seawater near Fukushima,  70% of identified genera were associated with metal corrosion. Latent environment allocation - an analytical technique that estimates habitat distributions and co-detection analyses - revealed that the microbial communities in the torus room water originated from a distinct blend of natural marine microbial and artificial bacterial communities typical of biofilms, sludge, and wastewater. Understanding the specific bacteria linked to metal corrosion in damaged plants is important for advancing decommissioning efforts.
70% of identified genera were associated with metal corrosion. Latent environment allocation - an analytical technique that estimates habitat distributions and co-detection analyses - revealed that the microbial communities in the torus room water originated from a distinct blend of natural marine microbial and artificial bacterial communities typical of biofilms, sludge, and wastewater. Understanding the specific bacteria linked to metal corrosion in damaged plants is important for advancing decommissioning efforts.
山田 一夫*; 洞 秀幸*; 丸山 一平*; 粟飯原 はるか; 富田 さゆり*; 東條 安匡*; 渋谷 和俊*; 細川 佳史*; 五十嵐 豪*; 駒 義和
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2024 (WM2024) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2024/03
Estimation of Cs and Sr contamination of concrete below the turbine pits after the Fukushima Daiichi NPP accident was carried out. Considerations were based on the type of cement and aggregate used, drying, carbonation and cracking of the concrete, and the contamination history, i.e. contact with contaminated water after a one-day immersion in seawater from the tsunami. The relationship between crack density and the amount of contaminated concrete was determined from the reproduction of crack density and the acquisition of apparent diffusion coefficients for cracked and uncracked areas from the immersion experiment with contamination history.
中村 孝史*; 山本 幸男*; 荒川 正和*; 丸山 晃生*; 吉越 章隆
産業応用工学会論文誌, 11(2), p.109 - 114, 2023/09
SPring-8のBL23SUに設置された表面化学実験ステーションは、放射光軟X線を使って様々な機能性材料の表面および界面の研究に利用されている。固体表面とガスとの化学反応の理解を進めるためには、ガスの精密流量制御が必須である。本論文では、超高真空(分子流領域)におけるガスと表面の反応の実験精度および再現性を改善するための自動ガス流量コンピュター制御システムを報告する。ガス圧力制御のために、スローリークバルブのフィードバック制御システムを開発した。開発したシステムによって、装置エキスパートの実験者と同等以上の反応実験が可能となった。
Lind, T.*; Kalilainen, J.*; Marchetto, C.*; Beck, S.*; 中村 康一*; 木野 千晶*; 丸山 結; 城戸 健太朗; Kim, S. I.*; Lee, Y.*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.4796 - 4809, 2023/08
The OECD/NEA ARC-F project was established to investigate the accidents at Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power station with the aim of consolidating the observations for deeper understanding of the severe accident progression and the status of reactors and containment vessels. Additionally, the project formed an information sharing framework in reactor safety between Japan and international experts. In order to achieve these objectives, the project focused on three tasks: i) to refine analysis for accident scenarios and associated fission-product transport and dispersion, ii) to compile and manage data on the Fukushima Daiichi NPS accident, and iii) to discuss future long-term projects relevant to the Fukushima Daiichi NPS accident. The work was carried out by 22 partners from 12 countries. In the fission product group, ten organizations worked on five topics which were ranked with a high significance as open issues based on the BSAF project and were thereby selected for further investigations. The five fission product related topics were: i) fission product speciation, ii) iodine chemistry, iii) pool scrubbing, iv) fission product transport and behavior in the buildings, and v) uncertainty analysis and variant calculations. In this paper, the work carried out to investigate these five fission product release and transport topics of special interest in the ARC-F project will be described and summarized.
丸山 結; 杉山 智之*; 島田 亜佐子; Lind, T.*; Bentaib, A.*; Sogalla, M.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Albright, L.*; Clayton, D.*
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.4782 - 4795, 2023/08
The Analysis of Information from Reactor Buildings and Containment Vessels of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) (ARC-F) project was initiated in January 2019 for three years with 22 signatories from 12 countries. Three main tasks were implemented in the ARC-F project, which were relevant to 1) refinement of analysis for accident scenarios and associated fission product (FP) transport and dispersion, 2) compilation and management of data and information, and 3) discussion for the next-phase project. Various activities were performed in Task 1, covering improvement of analysis for accident scenarios, and in-depth analyses for specific phenomena such as in-vessel melt progression, molten core/concrete interaction, FP transport and source term, hydrogen combustion and atmospheric dispersion of FPs. Through these studies, analyses for accident scenarios with severe accident codes were refined and important phenomena with large uncertainties were clarified. In order to share well selected and organized information from the FDNPS with the project partners, two databases, information source database and sample database, were built under Task 2. The analysis techniques including the separation of iodine species were developed also in Task 2 and applied to the analysis of FPs in several samples taken from the FDNPS. The next-phase project was discussed in Task 3, resulting in launching the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Information Collection and Evaluation (FACE) project. The FACE project officially started in July 2022 with the participation of 23 organizations from 12 countries and the European Commission.
南上 光太郎; 塩津 弘之; 丸山 結; 杉山 智之; 岡本 孝司*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(7), p.816 - 823, 2023/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)For proper source term evaluation, we constructed the theoretical model to estimate the mass transfer coefficient of gaseous iodine species under two-phase flow conditions, which complicates the direct experimental measurements. The mass transfer speed is determined by the product of the overall mass transfer coefficient and the interfacial area. By using the ratio of two gas components, the interfacial area, which is an important parameter that is difficult to measure, can be canceled out and the ratio of their overall mass transfer coefficients can be obtained. This ratio is expected to be equal to the ratio of their diffusion coefficients. Therefore, the unknown mass transfer coefficient such as iodine species can be estimated using the diffusion coefficients of two gas components and the reference mass transfer coefficient such as O . We carried out the experiments using the bubble column to confirm this relationship. From the results in this study, we confirmed that the ratio of the overall mass transfer coefficient was in good agreement with the ratio of diffusion coefficient under the bubbly flow conditions. Using this relationship confirmed in this study, we estimated the mass transfer coefficient of I
. We carried out the experiments using the bubble column to confirm this relationship. From the results in this study, we confirmed that the ratio of the overall mass transfer coefficient was in good agreement with the ratio of diffusion coefficient under the bubbly flow conditions. Using this relationship confirmed in this study, we estimated the mass transfer coefficient of I , one of the iodine species.
, one of the iodine species.
深谷 裕司; 丸山 貴大; 後藤 実; 大橋 弘史; 樋口 英明
JAEA-Research 2023-002, 19 Pages, 2023/06
商用高温ガス炉使用済燃料の再処理に由来する廃棄物の処分に関する研究を行った。軽水炉の再処理と高温ガス炉の再処理では燃料の構造の違いによる大きな違いがあるため、軽水炉に対して制定された再処理の廃棄物処理に関する法律の高温ガス炉廃棄物への適用性を確認すべきである。そこで、技術の違いを比較するとともに、全炉心燃焼計算を用いて、黒鉛廃棄物の放射化量及び表面汚染による放射能濃度を評価することにより、再処理廃棄物について比較を行った。その結果、SiC残渣廃棄物は、特定放射性廃棄物の最終処分に関する法律(2000年法律第117号)の第二種特定放射性廃棄物として軽水炉のハル・エンドピースと同様に地層処分されるべきことが分かった。黒鉛廃棄物については、軽水炉のチャンネルボックスと同様に、核原料物質、核燃料物質及び原子炉の規制に関する法律(1957年法律第166号)の第二種廃棄物としてピット処分による浅地中処分されるべきことが分かった。
福井 悠平*; 遠藤 知弘*; 山本 章夫*; 丸山 修平
EPJ Web of Conferences, 281, p.00006_1 - 00006_9, 2023/03
外れ値を含む実験データの新しい核データ調整方法を開発した。本手法は感度係数を用いた従来の核データ調整法にロバスト推定の一種であるM推定を適用することで、外れ値の影響を軽減するものである。本論文では、M推定に基づいて重み付けされた核データ調整式を導出し、重み付けの計算方法を開発した。各実験データの重みは、核特性の測定値と計算値の差から計算される。この重みは特異値分解を用いて核特性間の相関を考慮することにより評価することができる。さらに、提案手法と従来手法を双子実験により比較検証した。双子実験では、核データは意図的に外れ値を含む実験データを使用した。結果、外れ値を含む実験データであっても核データがロバストかつ適切に調整されていることを確認した。
山田 一夫*; 東條 安匡*; 粟飯原 はるか; 富田 さゆり*; 洞 秀幸*; 渋谷 和俊*; 駒 義和; 五十嵐 豪*; 細川 佳史*; 丸山 一平*
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2023/02
Experiments were conducted on mortar made from aggregates used in the Fukushima Daiichi NPP, which were dry carbonated and further cracks were introduced to reproduce the contamination history of the lower part of the turbine pit. The concrete was exposed to contaminated water after being in contact with seawater for one day due to the post-earthquake tsunami; Cs and Sr interacted differently with the constituent materials of the concrete and competitively adsorbed with ions in the seawater. The effects of various factors were quantitatively evaluated by experiment. Dry carbonation conditions enhanced infiltration but had a limited effect on cracking.
 Sc
Sc )
) O
O determined by single-crystal neutron diffraction
determined by single-crystal neutron diffraction田中 誠也*; 鬼柳 亮嗣; 石川 喜久*; 天児 寧*; 飯山 拓*; 二村 竜祐*; 丸山 建一*; 内海 重宣*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(1), p.014403_1 - 014403_11, 2023/01
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:10.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sc-substituted hexagonal ferrite Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O has an incommensurate helimagnetic structure. However, the incommensurate helimagnetic structure has not been sufficiently determined, and the mechanism via which the helimagnetism develops has not been studied. Time-of-flight single-crystal neutron diffraction measurements were performed on single-crystal samples of Ba(Fe
has an incommensurate helimagnetic structure. However, the incommensurate helimagnetic structure has not been sufficiently determined, and the mechanism via which the helimagnetism develops has not been studied. Time-of-flight single-crystal neutron diffraction measurements were performed on single-crystal samples of Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O with Sc concentrations of x = 0, 0.128, 0.153, and 0.193. The magnetic structure analyses revealed that the helimagnetic structure of Ba(Fe
with Sc concentrations of x = 0, 0.128, 0.153, and 0.193. The magnetic structure analyses revealed that the helimagnetic structure of Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O is a cone type whose base is in the ab plane and height is in the c-axis direction. The magnetic moments of Fe2(4
is a cone type whose base is in the ab plane and height is in the c-axis direction. The magnetic moments of Fe2(4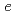 ), Fe4(4
), Fe4(4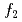 ), and Fe5(12
), and Fe5(12 ) are aligned with distinct angles, leading to the helimagnetic structure of Ba(Fe
) are aligned with distinct angles, leading to the helimagnetic structure of Ba(Fe Sc
Sc )
) O
O , and can be explained by assuming that there is an antiferromagnetic superexchange interaction
, and can be explained by assuming that there is an antiferromagnetic superexchange interaction 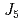 between Fe2(4
between Fe2(4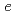 ) and Fe5(12
) and Fe5(12 ) that is negligible in the x = 0 crystal. The shorter bond distance of Fe2-O1 in Sc-rich crystals revealed by the crystal structure analyses enhances the superexchange interaction
) that is negligible in the x = 0 crystal. The shorter bond distance of Fe2-O1 in Sc-rich crystals revealed by the crystal structure analyses enhances the superexchange interaction 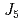 . The relatively strong
. The relatively strong 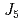 leads to competition among the three superexchange interactions,
leads to competition among the three superexchange interactions, 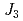 ,
, 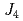 , and
, and 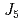 , resulting in the development of the helimagnetic structure. These findings facilitate the understanding of the essentials of the basic magnetic material BaFe
, resulting in the development of the helimagnetic structure. These findings facilitate the understanding of the essentials of the basic magnetic material BaFe O
O .
.
松本 俊慶; 川部 隆平*; 岩澤 譲; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 178, p.109348_1 - 109348_13, 2022/12
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:14.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)シビアアクシデント時の溶融物関連事象を評価するためにFCIコードであるJASMINEの機能拡張を行った。溶融物の冷却性評価ではキャビティ床面上における粒子状・アグロメレーション・ケーキ状デブリ質量割合や最終的な幾何形状の予測が必要である。アグロメレーションモデルでは、熱を保有した粒子同士のくっつきを考慮し、組み込んだ。もう一つのモデル改良は拡がりモデルの改良である。浅水方程式を導入し、拡がり先端部のクラスト成長に基づく拡がり停止条件を組み込んだ。調整係数の最適化のためにスウェーデンKTHにおいて実施されたDEFOR-A及びPULiMS実験を参照した。JASMINEコードによる実験解析では共通のパラメータセットで良い再現性が得られ、主要な現象は適切にモデル化されたことを示した。
Zheng, X.; 玉置 等史; 高原 省五; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Proceedings of Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management (PSAM16) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/09
Uncertainty gives rise to the risk. For nuclear power plants, probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) systematically concludes what people know to estimate the uncertainty in the form of, for example, risk triplet. Capable of developing a definite risk profile for decision-making under uncertainty, dynamic PRA widely applies explicit modeling techniques such as simulation to scenario generation as well as the estimation of likelihood/probability and consequences. When quantifying risk, however, epistemic uncertainties exist in both PRA and dynamic PRA, as a result of the lack of knowledge and model simplification. The paper aims to propose a practical approach for the treatment of uncertainty associated with dynamic PRA. The main idea is to perform the uncertainty analysis by using a two-stage nested Monte Carlo method, and to alleviate the computational burden of the nested Monte Carlo simulation, multi-fidelity models are introduced to the dynamic PRA. Multi-fidelity models include a mechanistic severe accident code MELCOR2.2 and machine learning models. A simplified station blackout (SBO) scenario was chosen as an example to show practicability of the proposed approach. As a result, while successfully calculating the probability of large early release, the analysis is also capable to provide uncertainty information in the form probability distributions. The approach can be expected to clarify questions such as how reliable are results of dynamic PRA.
Zheng, X.; 玉置 等史; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 223, p.108503_1 - 108503_12, 2022/07
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:82.18(Engineering, Industrial)Dynamic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) more explicitly treats timing issues and stochastic elements of risk models. It extensively resorts to iterative simulations of accident progressions for the quantification of risk triplets including accident scenarios, probabilities and consequences. Dynamic PRA leverages the level of detail for risk modeling while intricately increases computational complexities, which result in heavy computational cost. This paper proposes to apply multi-fidelity simulations for a cost- effective dynamic PRA. It applies and improves the multi-fidelity importance sampling (MFIS) algorithm to generate cost-effective samples of nuclear reactor accident sequences. Sampled accident sequences are paralleled simulated by using mechanistic codes, which is treated as a high-fidelity model. Adaptively trained by using the high-fidelity data, low-fidelity model is used to predicting simulation results. Interested predictions with reactor core damages are sorted out to build the density function of the biased distribution for importance sampling. After when collect enough number of high-fidelity data, risk triplets can be estimated. By solving a demonstration problem and a practical PRA problem by using MELCOR 2.2, the approach has been proven to be effective for risk assessment. Comparing with previous studies, the proposed multi-fidelity approach provides comparative estimation of risk triplets, while significantly reduces computational cost.
大島 宏之; 森下 正樹*; 相澤 康介; 安藤 勝訓; 芦田 貴志; 近澤 佳隆; 堂田 哲広; 江沼 康弘; 江連 俊樹; 深野 義隆; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
ナトリウム冷却高速炉(SFR: Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor)の歴史や、利点、課題を踏まえた安全性、設計、運用、メンテナンスなどについて解説する。AIを利用した設計手法など、SFRの実用化に向けた設計や研究開発についても述べる。