Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saito, Hiroshi; Nozawa, Takashi; Takemiya, Hiroshi; Seki, Akiyuki; Matsubara, Takeshi; Saito, Kimiaki; Kitamura, Akihiro
JAEA-Review 2017-040, 34 Pages, 2018/03
The accidents at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station on March 11th 2011, released significant amount of radionuclide to the environment. It has migrated to the human habitation and raised concerns of possible effect on human health, and for that a lot of researches have been performed. JAEA created and opened "Database for Radioactive Substance Monitoring Data" for usage of obtained data. For accurate modelling and future forecast using numerical code and the data, "Supporting Environment for Processing Simulation Codes" has been operated. In addition, research results have been opened as Q&A style "Knowledge Base for Environmental Remediation" in JAEA's website. The "Comprehensive Evaluation System" composed of these components, should act more interrelated and integrated as one system. Besides, information dissemination is not enough to the outside. The report summarizes the current status, remaining issues and expected improvement of each component and the system.
Kimura, Masanori; Hato, Shinji*; Matsubara, Takeshi*; Kanno, Mitsuhiro*; Munakata, Masahiro
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2017 (ASRAM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2017/11
The authors developed a new metabolic model for iodine by combining the respiratory tract model (Publ.66), the gastrointestinal tract model (Publ.30) of the ICRP and the metabolic model for iodine (Johnson's model) in order to evaluate the behavior of radioiodine and stable iodine in the body more realistically. The developed metabolic model indicated that a reduction factor (RF) depends on dosage of stable iodine, timing of the administration of stable iodine, different iodine isotopes ( I -
I -  I), and age groups. Therefore, the RF was calculated by changing these parameters and then a database of the RF was constructed for the application to the OSCAAR code.
I), and age groups. Therefore, the RF was calculated by changing these parameters and then a database of the RF was constructed for the application to the OSCAAR code.
Oshima, Takeshi; Sato, Shinichiro; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Nakamura, Tetsuya*; Sugaya, Takeyoshi*; Matsubara, Koji*; Niki, Shigeru*
Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 108, p.263 - 268, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:51.86(Energy & Fuels)GaAs solar cells which have a PiN structure with 50 self-organized In Ga
Ga As Quantum Dot (QD) layers were irradiated with 1 MeV electrons up to 1
As Quantum Dot (QD) layers were irradiated with 1 MeV electrons up to 1 10
10 /cm
/cm . After irradiation at 1
. After irradiation at 1 10
10 /cm
/cm , the remaining factor of I
, the remaining factor of I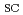 , V
, V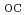 and P
and P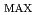 for the InGaAs 50 QD solar cell becomes 80, 90 and 55% of the initial values, respectively. On the other hand, those values for non QD GaAs solar cells decrease to 95, 80 and 63% of the initial values, respectively. Since the i-layer for the 50 QD solar cells (1.1
for the InGaAs 50 QD solar cell becomes 80, 90 and 55% of the initial values, respectively. On the other hand, those values for non QD GaAs solar cells decrease to 95, 80 and 63% of the initial values, respectively. Since the i-layer for the 50 QD solar cells (1.1  m) is thicker than the non QD solar cells (660 nm), the larger degradation of I
m) is thicker than the non QD solar cells (660 nm), the larger degradation of I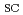 for the 50 QD solar cells than the non QD ones can be interpreted in terms that the carrier recombination in the i-layer for the 50 QD solar cells is larger than that for the non QD solar cells. For V
for the 50 QD solar cells than the non QD ones can be interpreted in terms that the carrier recombination in the i-layer for the 50 QD solar cells is larger than that for the non QD solar cells. For V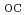 , the 50 QD solar cells showes better radiation resistance than the non QD solar cells. Furthermore, the annealing behavior of the electrical characteristics for the 50 QD and the non QD solar cells was investigated at RT under AM 0 immediately after the irradiation. As a result, the recovery of the electrical characteristics for both solar cells was observed, and the GaAs solar cells shows relatively larger recovery compared to the 50 QD solar cells. Although the mechanism of this recovery has not yet been clarified, the origin of this recovery is thought not to come from the existence of QDs because the GaAs solar cell without QD layers also shows the recovery.
, the 50 QD solar cells showes better radiation resistance than the non QD solar cells. Furthermore, the annealing behavior of the electrical characteristics for the 50 QD and the non QD solar cells was investigated at RT under AM 0 immediately after the irradiation. As a result, the recovery of the electrical characteristics for both solar cells was observed, and the GaAs solar cells shows relatively larger recovery compared to the 50 QD solar cells. Although the mechanism of this recovery has not yet been clarified, the origin of this recovery is thought not to come from the existence of QDs because the GaAs solar cell without QD layers also shows the recovery.
Ishigami, Tsutomu; Mukai, Masayuki; Sukegawa, Takenori; Matsubara, Takeshi*
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-023, 83 Pages, 2012/11
Verification for site release is one of procedures to confirm termination of decommissioning of nuclear installations. The verification procedure would need to confirm that the radioactive concentration at the site is lower than the criterion value by measurement. Then to efficiently perform the measurement and verification it is one of important issues how to efficiently estimate and evaluate overall spatial radioactivity distribution using a sampling method. For the efficient estimation and evaluation we have applied a Kriging technique which in the geostatistics, and have developed a computer program ESRAD (Estimation of Spatial RadioActivity Distribution). The ESRAD program is designed to support sample selection, calculate a variogram, and estimate a radioactivity distribution for the area concerned. This report describes the Kriging technique, structure and functions of ESRAD, input file format, output examples, execution procedure of ERSAR, and sample run with ESRAD.
Matsubara, Takeshi*; Homma, Toshimitsu
Proceedings of International Conference on Environmental Radioactivity (Internet), 5 Pages, 2010/00
no abstracts in English
Takahara, Shogo; Kimura, Masanori; Matsubara, Takeshi*; Homma, Toshimitsu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(Suppl.5), p.714 - 717, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is recognized that good preparedness and arrangement in advance of an emergency can improve the emergency response to a nuclear and radiological emergency. In the preparedness, comprehensive threat assessment is very important to provide technical guidance for developing the protective actions. Probabilistic safety assessment method is useful for assessing accident consequences comprehensively and quantitatively. In this study, an accident consequence assessment code OSCAAR, which was developed at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, is used to provide the information for the guideline of intervention and return criteria for relocation on the long-term emergency situation.
Homma, Toshimitsu; Kimura, Masanori; Matsubara, Takeshi*; Ishikawa, Jun
Proceedings of 9th International Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management Conference (PSAM-9) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/00
Homma, Toshimitsu; Matsubara, Takeshi; Tomita, Kenichi*
Proceedings of International Symposium on Environmental Modeling and Radioecology, p.196 - 203, 2007/03
This paper presents the results obtained from the application of OSCAAR to the Iput dose reconstruction scenario of BIOMASS and also to the Chernobyl  I fallout scenario of EMRAS, both organized by International Atomic Energy Agency. The Iput Scenario deals with
I fallout scenario of EMRAS, both organized by International Atomic Energy Agency. The Iput Scenario deals with  Cs contamination of the catchment basin and agricultural area in the Bryansk Region of Russia, which was heavily contaminated after the Chernobyl accident. This exercise was used to test the chronic exposure pathway models in OSCAAR with actual measurements and to identify the most important sources of uncertainty with respect to each part of the assessment. The OSCAAR chronic exposure pathway models almost successfully reconstructed the whole 10-year time course of
Cs contamination of the catchment basin and agricultural area in the Bryansk Region of Russia, which was heavily contaminated after the Chernobyl accident. This exercise was used to test the chronic exposure pathway models in OSCAAR with actual measurements and to identify the most important sources of uncertainty with respect to each part of the assessment. The OSCAAR chronic exposure pathway models almost successfully reconstructed the whole 10-year time course of  Cs activity concentrations in most requested types of agricultural products and natural foodstuffs. The Plavsk scenario provides an good opportunity to test not only the food chain transfer model of
Cs activity concentrations in most requested types of agricultural products and natural foodstuffs. The Plavsk scenario provides an good opportunity to test not only the food chain transfer model of  I but also the method of assessing
I but also the method of assessing  I thyroid burden. OSCAAR showed in general good capabilities for assessing the important
I thyroid burden. OSCAAR showed in general good capabilities for assessing the important  I exposure pathways, but also limitations using constant isotopic ratio
I exposure pathways, but also limitations using constant isotopic ratio  I /
I / Cs provided by the scenario to estimate
Cs provided by the scenario to estimate  I deposition for whole Plavsk district.
I deposition for whole Plavsk district.
Kimura, Masanori; Matsubara, Takeshi; Ishikawa, Jun; Homma, Toshimitsu
Proceedings of International Symposium on Environmental Modeling and Radioecology, p.348 - 351, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Hashimoto, Takashi; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Ishikawa, Tomoko*; Kawamura, Takashi*; Nakai, Koji*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Miyatake, Hiroari; Tanaka, Masahiko*; Fuchi, Yoshihide*; Yoshikawa, Nobuharu*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 556(1), p.339 - 349, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:88.21(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new type of three dimensional tracking and proportional gas counter has been developed. Adopting a gating-grid system, performance of the detector becomes stable under the injection rate of charged particles less than 4 10
10 pps. It is a useful detection system for astrophysical experiments using radioactive nuclear beams, since the efficiency is so high as 100 %.
pps. It is a useful detection system for astrophysical experiments using radioactive nuclear beams, since the efficiency is so high as 100 %.
Amano, Hikaru; ; Uchida, Shigeo*; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Matsuoka, Shungo*; Ikeda, Hiroshi*; Matsubara, Takeshi*; Kurosawa, Naohiro*
KURRI-KR-80, p.48 - 49, 2001/12
no abstracts in English
Homma, Toshimitsu; Kimura, Masanori; Matsubara, Takeshi; Ishikawa, Jun
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsubara, Takeshi; Homma, Toshimitsu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Komatsubara, Akira*; Teraji, Tokuyuki*; Hori, Masahiro*; Kumagai, Kuninori*; Tamura, Shuto*; Oshima, Takeshi; Onoda, Shinobu; Yamamoto, Takashi; Muller, C.*; Naydenov, B.*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Tetsuya*; Sumita, Taishi*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Sugaya, Takeyoshi*; Matsubara, Koji*; Niki, Shigeru*; Mochizuki, Toru*; Takeda, Akihiro*; Okano, Yoshinobu*; Sato, Shinichiro; et al.
no journal, ,
Radiation effects on GaAs solar cells with InGaAs dot layers were investigated in order to consider the capability of them for space applications. The GaAs solar cells with 50 InGaAs dot layers and also GaAs solar cells with no dot layer were fabricated using a MBE method. They were irradiated with 150 keV-protons at room temperature. As a result, solar cell with dot layers showed higher radiation degradation in short circuit current however, lower degradation in open circuit voltage. Since no significant difference in the degradation of current - voltage characteristics under dark conditions between dot and non-dot solar cells, it is concluded that the degradation of fill fuctor does not come from the degradation of pn diode characteristics but might come from the degradation of minority carrier diffusion length.
Oshima, Takeshi; Nakamura, Tetsuya*; Sugaya, Takeyoshi*; Sumita, Taishi*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Sato, Shinichiro; Matsubara, Koji*; Niki, Shigeru*; Mochizuki, Toru*; Takeda, Akihiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
Oshima, Takeshi; Nakamura, Tetsuya*; Sumita, Taishi*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Sato, Shinichiro; Sugaya, Takeyoshi*; Matsubara, Koji*; Niki, Shigeru*; Mochizuki, Toru*; Okano, Yoshinobu*
no journal, ,
Seki, Akiyuki; Suzuki, Kenta; Takahashi, Yoshitomo; Matsubara, Takeshi; Suto, Shigeo; Saito, Kimiaki; Takemiya, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
Japan Atomic Energy Agency developed a tool which automatically collects the monitoring data published by the related organizations separately. The data was formatted in a common style and published on the same website called "Database for Radioactive Substance Monitoring Data". Since a lot of environmental monitoring results have been accumulated in the past five years since the accident, new contents, which help us understand the change of the distribution of radionuclide by analyzing their time histories, were released on the website.
Miyamura, Hiroko; Matsubara, Takeshi*; Seki, Akiyuki; Takemiya, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
Surveys on the distribution of the air dose rate have been performed continuously after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. The surveyed monitoring datasets are stored in a database that is available for the public. In order to display car monitoring data, we developed a car monitoring survey data visualization application which works on mobile and tablet PCs. In this study, we propose an additional function that helps users observe the measured air dose rate datasets by visualizing them on a captured landscape picture. For realizing the function, we employ an image segmentation method.
Miyamura, Hiroko; Matsubara, Takeshi*; Seki, Akiyuki; Takemiya, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
Surveys on the distribution of the air dose rate have been performed continuously after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. The surveyed monitoring datasets are stored in a database that is available for the public. In this study, we focus on the car monitoring survey datasets, and propose a car monitoring survey data visualization application. It tracks user's position on mobile PCs or tablets. Users can observe air dose rate easily on their current location by utilizing the proposed application.