Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:96.99(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:262 Percentile:99.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
Matsumoto, Yoshitaka*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Aoki, Mizuho*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kakizaki, Takehiko; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Furusawa, Yoshiya*
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 110, 2007/02
Matsumoto, Hideki*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Takahashi, Akihisa*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kakizaki, Takehiko; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 111, 2007/02
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi; Furusawa, Yoshiya*; Aoki, Mizuho*; Shao, C.*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Matsumoto, Yoshitaka*; Kakizaki, Takehiko; et al.
Uchu Seibutsu Kagaku, 18(4), p.235 - 240, 2004/12
no abstracts in English
 S
S
Okane, Tetsuo; Fujimori, Shinichi; Mamiya, Kazutoshi; Okamoto, Jun; Muramatsu, Yasuji; Fujimori, Atsushi; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Matsumoto, Takehiko*; Furubayashi, Takao*; Isobe, Masaaki*; et al.
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 272-276(Suppl.), p.e297 - e298, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:29.70(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The electronic structure of spinel-type chalcogenide CuIr S
S , which exhibits a metal-insulator transition (MIT) as a function of temperature, has been studied by photoemission spectroscopy (PES). Below the transition temperature
, which exhibits a metal-insulator transition (MIT) as a function of temperature, has been studied by photoemission spectroscopy (PES). Below the transition temperature 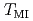 , the valence-band PES spectra indicate a gap formation, while the overall valence-band structure is shifted to the higher binding-energy side. The line shape of the Ir 4
, the valence-band PES spectra indicate a gap formation, while the overall valence-band structure is shifted to the higher binding-energy side. The line shape of the Ir 4 core-level PES spectra shows a dramatic change across
core-level PES spectra shows a dramatic change across 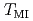 , which may be associated with the variation of the Ir 5
, which may be associated with the variation of the Ir 5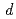 electron states.
electron states.
 O reflector
O reflectorHirota, Jitsuya; Kuroi, Hideo; Goto, Yorio; Furuhashi, Akira; Yasuno, Takehiko; Yamamoto, Ken; Mitani, Hiroshi; Obu, Makoto; Ichimori, Toshihiro; Koyama, Kinji; et al.
JAERI 1034, 50 Pages, 1962/08
no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Hideki*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Takahashi, Akihisa*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kakizaki, Takehiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Wakai, Eiichi; Kikuchi, Takayuki; Hirano, Michiko; Ida, Mizuho; Niitsuma, Shigeto; Kimura, Haruyuki; Nishitani, Takeo; Yamamoto, Michiyoshi; Matsumoto, Hiroshi; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takir, D.*; Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; et al.
no journal, ,
JAXA spacecraft and sample return mission Hayabusa2 has arrived at the near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, which is classified a primitive carbonaceous object. Here we report recent results of near-infrared spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. The observations provide direct measurements of the surface composition of Ryugu and context for the returned samples. NIRS3 has detected a weak and narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micrometer across entire observed surface. This absorption feature is attributed to the presence of OH-bearing minerals. The NIRS3 observations also revealed that Ryugu is the darkest object to be observed up-close by a visiting spacecraft. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are consistent with thermally-and/or shock-metamorphosed, and/or carbon-rich space-weathered primitive and hydrated carbonaceous chondrites.
Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Matsumoto, Yoshihisa*; Oto, Takayo*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Kakizaki, Takehiko; Hosoi, Yoshio*; Suzuki, Norio*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Wada, Seiichi*; Matsumoto, Yoshihisa*; Oto, Takayo*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Fukamoto, Kana; Kakizaki, Takehiko; Suzuki, Michiyo; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Wada, Seiichi; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Yokota, Yuichiro; Matsumoto, Yoshihisa*; Oto, Takayo*; Hosoi, Yoshio*; Suzuki, Norio*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Clustered DNA damages induced by high LET heavy ions are thought non-repairable or difficult to repair. However, much less is known about the reparability of clustered DNA damages. The major DNA repair pathway in mammalian cells is non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). In this study we investigated NHEJ pathway by exposure to high LET heavy ions, by analyzing responses of Ku to DNA damage induced by high LET heavy ions. pGFP and pGFP-Ku80 were transfected into xrs-5 cells (mutated in Ku80). Cells were irradiated with  rays and ion beams (LET=2.7-1610 keV/
rays and ion beams (LET=2.7-1610 keV/ m) at TIARA JAERI-Takasaki. Survival rates were measured by colony formation assay. To examine DNA damage and NHEJ pathway induced by heavy ion beams,
m) at TIARA JAERI-Takasaki. Survival rates were measured by colony formation assay. To examine DNA damage and NHEJ pathway induced by heavy ion beams,  H2AX and GFP signal on the nuclei were observed. Xrs5-GFP-Ku80 cells were radioresistant to
H2AX and GFP signal on the nuclei were observed. Xrs5-GFP-Ku80 cells were radioresistant to  rays and all ion beams, in comparison with xrs5-GFP cells. When the inactivation cross section was calculated to evaluate lethal effects per one particle, the difference of inactivation cross section between xrs5-GFP cells and xrs5-GFP-Ku80 cells became smaller with increasing LET. GFP and
rays and all ion beams, in comparison with xrs5-GFP cells. When the inactivation cross section was calculated to evaluate lethal effects per one particle, the difference of inactivation cross section between xrs5-GFP cells and xrs5-GFP-Ku80 cells became smaller with increasing LET. GFP and  H2AX foci on the nuclei co-localized from 10 to 30 min after C (108 keV/
H2AX foci on the nuclei co-localized from 10 to 30 min after C (108 keV/ m) and Ne ion (321 keV/
m) and Ne ion (321 keV/ m) irradiation. While GFP foci were observed for 10 min after Ar ion (1610 keV/
m) irradiation. While GFP foci were observed for 10 min after Ar ion (1610 keV/ m) irradiation, were not observed for 20 min. The difference of LET of ion beams influenced NHEJ responses.
m) irradiation, were not observed for 20 min. The difference of LET of ion beams influenced NHEJ responses.
Hotokezaka, Hiroyasu*; Ban, Yasutoshi; Ikeda, Hidematsu*; Harada, Masayuki*; Mizuguchi, Koji*; Saso, Michitaka*; Sugai, Hiroshi*; Tokeshi, Manabu*; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*; Morita, Yasuji; et al.
no journal, ,
The following items were studied for developing innovative equipment for analysis that provides high-sensitivity and rapid analysis for ultra small amount of samples utilizing microchip and thermal lens detector: Optimum flow condition for forming two-phase steady laminar flow in micro channel, applicability of thermal lens detector for U(VI) and H concentration analysis, extraction properties of U(VI) from aqueous phase to organic phase in micro channel, and radiation resistance of microchips and capillary tubes. In this presentation the summary of these items are reported.
concentration analysis, extraction properties of U(VI) from aqueous phase to organic phase in micro channel, and radiation resistance of microchips and capillary tubes. In this presentation the summary of these items are reported.
Wada, Seiichi; Funayama, Tomoo; Matsumoto, Yoshihisa*; Oto, Takayo*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Kakizaki, Takehiko; Hosono, Yoshio*; Suzuki, Norio*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Furusawa, Yoshiya*; Matsumoto, Yoshitaka*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kakizaki, Takehiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English