Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Koda, Yuya; Matsuno, Hiroki; Matsushima, Akira; Kubota, Shintaro; Toda, Keisuke; Nakamura, Yasuyuki
JAEA-Review 2024-003, 38 Pages, 2024/06
"Fugen Decommissioning Engineering Center", in planning and carrying out our decommissioning technical development, organizes "Technical special committee on Fugen decommissioning" which consists of the members well-informed, aiming to make good use of Fugen as a place for technological development which is opened domestic and international, as the central place in research and development base of Fukui prefecture, and to utilize the outcome in our decommissioning to the technical development effectively. This report consists of presentation paper are "The current status of Fugen decommissioning", "Regarding dismantling and decontamination of steam drums", "Knowledge of radiation management in dismantling contaminated equipment", "Achievements and considerations for identifying and separating contaminated parts of nonradioactive waste" and "Regarding technology development plans for nuclear reactor dismantling" which is presented in the 41st Technical Special Committee on Fugen Decommissioning.
Yasuda, Satoshi; Matsushima, Hisayoshi*; Harada, Kenji*; Tanii, Risako*; Terasawa, Tomoo; Yano, Masahiro; Asaoka, Hidehito; Gueriba, J. S.*; Di o, W. A.*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki
o, W. A.*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki
ACS Nano, 16(9), p.14362 - 14369, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:83.97(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The fabrication of hydrogen isotope enrichment system is essential for the development of industrial, medical, life science, and nuclear fusion fields, therefore alternative enrichment techniques with high separation factor and economic feasibility have been still explored. Herein, we report the fabrication of heterogeneous electrode with layered structures consisting of palladium and graphene layers for polymer electrolyte membrane electrochemical hydrogen pumping for the hydrogen isotope enrichment. We demonstrated significant bias voltage dependence of hydrogen/deuterium (H/D) separation ability and its high H/D at lower bias voltage. Theoretical analysis also demonstrated that the observed high H/D at low bias voltage stems from hydrogen isotopes tunneling through atomically-thick graphene during the electrochemical reaction, and the bias dependent H/D results in a transition from the quantum tunneling regime to classical over- barrier regime for hydrogen isotopes transfer via the graphene. These findings provide new insight for a novel economical methodology of efficient hydrogen isotope enrichment.
Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Sugitsue, Noritake; Sato, Fuminori; Matsushima, Ryotatsu; Kataoka, Shoji; Okada, Shota; Sasaki, Toshiki; Inoue, Junya
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 62(11), p.658 - 663, 2020/11
, 62(11), p.658 - 663, 2020/11
no abstracts in English
Sato, Fuminori; Matsushima, Ryotatsu; Ito, Yoshiyuki
QST-M-16; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2017, P. 60, 2019/03
Hydrogen gas generation by  -radiation from cement solidified products loading low-level radioactive liquid waste generated at LWTF in Tokai Reprocessing Facility was studied.
-radiation from cement solidified products loading low-level radioactive liquid waste generated at LWTF in Tokai Reprocessing Facility was studied.
Ito, Yoshiyuki; Matsushima, Ryotatsu; Sato, Fuminori
QST-M-8; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2016, P. 69, 2018/03
no abstracts in English
Yamada, Teruaki*; Matsushima, Yuki*; Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Fujita, Ichiro*; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 271, p.323 - 326, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:77.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to investigate the effects of the experimental methodology and the notch angle on the fracture toughness of the fine-grained isotropic nuclear graphites IG-110 and IG-430, the three-point-bending test, which has been recently proposed as the methodology to evaluate the fracture toughness of graphite for high temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs), was performed using two types of the specimens with different notch angles. The results obtained in this study could be summarized as follows: (1) The values of the fracture toughness of IG-110 and IG-430 measured in this study were 0.890 MPa m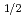 and 1.031 MPa m
and 1.031 MPa m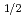 , respectively. It was also found that the value of the fracture toughness of IG-110 was nearly equal to or smaller than the values obtained by the other method reported previously. (2) The values of the fracture toughness of the fine-grained isotropic graphites were not affected between the notch angles introduced by the incisive razor blade. (3) The ratio of the tensile strengths of IG-110 and IG-430 was estimated from Griffith Theory using the experimental data obtained in this study. The estimated strength ratio was in good agreement with the strength ratio obtained from the supplier's data.
, respectively. It was also found that the value of the fracture toughness of IG-110 was nearly equal to or smaller than the values obtained by the other method reported previously. (2) The values of the fracture toughness of the fine-grained isotropic graphites were not affected between the notch angles introduced by the incisive razor blade. (3) The ratio of the tensile strengths of IG-110 and IG-430 was estimated from Griffith Theory using the experimental data obtained in this study. The estimated strength ratio was in good agreement with the strength ratio obtained from the supplier's data.
Yamada, Teruaki*; Matsushima, Yuki*; Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Fujita, Ichiro*; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
In order to investigate the effects of the experimental methodology and the notch angle on the fracture toughness of the fine-grained isotropic nuclear graphites IG-110 and IG-430, the three-point-bending test, which has been recently proposed as the methodology to evaluate the fracture toughness of graphite for high temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs), was performed using two types of the specimens with different notch angles. The results obtained in this study could be summarized as follows: (1) The values of the fracture toughness of IG-110 and IG-430 measured in this study were 0.890 (MPam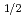 ) and 1.031 (MPam
) and 1.031 (MPam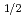 ), respectively. It was also found that the value of the fracture toughness of IG-110 was nearly equal to or smaller than the values obtained by the other method reported previously. (2) The values of the fracture toughness of the fine-grained isotropic graphites were not affected between the notch angles introduced by the incisive razor blade. (3) The ratio of the tensile strengths of IG-110 and IG-430 was estimated from Griffith Theory using the experimental data obtained in this study. The estimated strength ratio was in good agreement with the strength ratio obtained from the supplier's data.
), respectively. It was also found that the value of the fracture toughness of IG-110 was nearly equal to or smaller than the values obtained by the other method reported previously. (2) The values of the fracture toughness of the fine-grained isotropic graphites were not affected between the notch angles introduced by the incisive razor blade. (3) The ratio of the tensile strengths of IG-110 and IG-430 was estimated from Griffith Theory using the experimental data obtained in this study. The estimated strength ratio was in good agreement with the strength ratio obtained from the supplier's data.
Sai, Masataka; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Matsushima, Hiroyuki*; Noda, Masatoshi*; Noda, Masaru*; Ando, Kenichi*; Tanaka, Tatsuya*; Ueda, Tadashi*; Honda, Yuko*; Mizuno, Takashi
JAEA-Data/Code 2010-010, 75 Pages, 2010/09
This report compiles data set of the groundwater chemistry obtained at Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) between the fiscal year 2004 and the fiscal year 2007. These data includes groundwater chemistry of inflow in the shafts and sampled groundwater in the boreholes, which drilled from sub-stages of MIU and from surface (MSB-2, MSB-4, and MIZ-1). Basic information (e.g. sampling location, sampling date, sampling method, analytical method) are also described in terms of quality control and traceability.
Tezuka, Masashi; Mizui, Hiroyuki; Matsushima, Akira; Nakamura, Yasuyuki; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Sano, Kazuya; Nanko, Takashi; Morishita, Yoshitsugu
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycle; Sustainable Options & Industrial Perspectives (Global 2009) (CD-ROM), p.2815 - 2821, 2009/09
FUGEN is a proto-type heavy water moderated, boiling light water cooled, pressure tube type reactor with 165MWe and has been shut downed on Mar. 2003. Following the approval of decommissioning program in 2008, stage of FUGEN was changed to the decommissioning of the facilities. The program consists of following four periods; (1) Spent fuel transportation, (2) Periphery facilities dismantlement, (3) Reactor dismantlement and (4) Building demolition. It is expected that the whole decommissioning will be completed until 2028. As a part of the work in the spent fuel transportation period, the main steam system and the feeder water system etc. are being dismantled in the turbine building. The remaining tritium in the heavy water system is also being removed for facilitating the dismantlement of the heavy water system. Moreover, method on dismantlement of the reactor core is being studied with considering the process under the water for the radiation shielding and the dust suppression.
Tominaga, Shinya*; Busnyuk, A.*; Matsushima, T.*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Ono, Futaba*; Terai, Takayuki*; Yamawaki, Michio*
Fusion Science and Technology, 41(3), p.919 - 923, 2002/05
no abstracts in English
Nemoto, Shinichi; Sakai, Toshiyuki*; Sanyoshi, Hirotaka; Kikuchi, Kenji; Iwasaki, Isao*; Kuribayashi, Masakazu*; Matsushima, Kazumi*
PNC TN8410 93-283, 86 Pages, 1993/11
None
Matsushima, Hidesuke*; Tsutsumi, Kiyoshi*; Kato, Yasuyoshi*; Urushihara, Hiroshi*; Ueda, Yasuyuki*
PNC TJ202 76-01, 151 Pages, 1976/05
no abstracts in English
Ito, Yoshiyuki; Matsushima, Ryotatsu; Sato, Fuminori; Hashimoto, Takanori*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Miyabe, Shinsuke*; Sakuma, Takashi*; Kikuchi, Kaoru*; Izumi, Takeshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsushima, Ryotatsu; Takahashi, Kiyofumi; Saito, Yasuo; Kikuchi, Yukihiro*; Atarashi, Daiki*; Shirozu, Hidetomo
no journal, ,
Low Active Waste Treatment Development Facility (LWTF) is planning to solidify the cement waste liquid generated at the Tokai Reprocessing Facility. In the previous report, it has been shown that the carbonate waste liquid can be solidified by conducting a solidification test on the waste liquid simulating the carbonate waste liquid containing sodium carbonate and sodium nitrate. On the other hand, it is expected that sodium sulfate will coexist as a foreign substances in the carbonate waste liquid, even though it is a trace amount, and it has been confirmed that there is no effect of sodium sulfate coexists in beaker-scale test. In this report, a actual-scale test is carried out, confirm that there is no effect when sodium sulfate coexists, and the results is reported. It was confirmed that the presence or absence of sodium sulfate in the waste liquid had no effect on the fluidity of the sample after kneading, the compressive strength of the sample after curing, etc., and thus had no effect on the solidified body properties.
Matsushima, Kanato*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Fukatsu, Yuta; Eguchi, Ayano; Yotsuji, Kenji*; Tachi, Yukio; Okubo, Takahiro*
no journal, ,
Matsushima, Hiroyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ito, Yoshiyuki; Matsushima, Ryotatsu; Sato, Fuminori; Kojima, Junji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ito, Yoshiyuki; Matsushima, Ryotatsu; Takano, Masato; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Miyabe, Shinsuke*; Sakuma, Takashi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yasuda, Satoshi; Matsushima, Hisayoshi*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Fukutani, Katsuyuki
no journal, ,
We evaluated H/D separation factor of graphene-palladium electrode in hydrogen pumping cell. We revealed that in case of palladium electrode, the separation factor hardly increases while the factor significantly increased for graphene-palladium electrode.
Yasuda, Satoshi; Matsushima, Hisayoshi*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Fukutani, Katsuyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English