Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
都留 智仁; 眞山 剛*
軽金属, 74(9), p.442 - 450, 2024/09
マグネシウム(Mg)合金は、構造材料や生体材料として幅広い応用が拡大している。一方で、力学特性や耐食性には改善の余地があることに加え、顕著な塑性異方性に起因して構造設計や変形挙動の予測に関する課題も多く、現在も材料設計/プロセス設計に基づく材料開発が盛んに行われている。本稿では、Mg合金の力学特性に対する計算材料科学研究として、第一原理計算を用いた合金化による機械的性質への影響を非経験的に評価するための手法、および、結晶塑性有限要素法を用いた多結晶挙動および不均一変形の解析方法について、計算手法に関する基本的な枠組みと具体的な解析例を紹介する。
藤原 比呂*; 戸田 裕之*; 海老原 健一; 小林 正和*; 眞山 剛*; 平山 恭介*; 清水 一行*; 竹内 晃久*; 上椙 真之*
International Journal of Plasticity, 174, p.103897_1 - 103897_22, 2024/03
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:94.71(Engineering, Mechanical)高強度化したアルミ合金において水素脆化は、理解し解決すべき問題である。アルミ合金において、水素が析出物界面に蓄積し脆化の原因となっていると考えられている。しかし、き裂付近の水素分布と応力場の局所的な相互作用について、空間的な複雑さを考慮した定量的な知見は明らかでない。本研究では、結晶塑性有限要素法と水素拡散解析を組み合わせたマルチモーダル3次元画像ベースシミュレーションを用い、実際のき裂近傍の応力分布と、それが水素分布に及ぼす影響およびき裂発生確率に及ぼす影響を捉えることを試みた。その結果、粒界き裂は、その先端近傍の水素蓄積により、MgZn 析出物の半整合界面の凝集エネルギーが低下した領域で擬へき開き裂に遷移することが分かった。この結果は、本シミュレーション手法がナノスケールの剥離とマクロスケールの脆性破壊の橋渡しに成功したことを示すものと考える。
析出物の半整合界面の凝集エネルギーが低下した領域で擬へき開き裂に遷移することが分かった。この結果は、本シミュレーション手法がナノスケールの剥離とマクロスケールの脆性破壊の橋渡しに成功したことを示すものと考える。
萩原 幸司*; 眞山 剛*; 山崎 倫昭*; Harjo, S.; 徳永 透子*; 山本 和輝*; 杉田 三佳*; 青山 海琳*; Gong, W.; 西本 宗矢*
International Journal of Plasticity, 173, p.103865_1 - 103865_21, 2024/02
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:98.10(Engineering, Mechanical)The unique control mechanisms of the plastic deformation of two-phase extruded alloy composed of Mg and long-period stacking ordered (LPSO) phase were clarified by comparison with those of other Mg solid-solution alloys, focusing on the question of why do the Mg/LPSO two-phase alloys exhibit both large elongation and high strength? The stress-strain curves for each grain in the alloys could be imaginary estimated using neutron diffraction analysis during the tensile test. The results demonstrate that the deformation behaviors of the worked and recrystallized grains are significantly different in all the Mg-extruded alloys owing to the strong plastic anisotropy in Mg with hexagonal close-packed (hcp) structure. Therefore, the deformation behavior is controlled by a composite-like deformation mechanism, even in single-phase Mg solid-solution alloys.
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction studyGong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Zheng, R.*; 眞山 剛*; Sun, B.*; 相澤 一也; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
Scripta Materialia, 225, p.115161_1 - 115161_5, 2023/03
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:59.81(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Deformation behavior during uniaxial compression at 21 K and 298 K in a commercial AZ31 magnesium alloy was studied by  neutron diffraction. Decreasing the deformation temperature resulted in a slight increase in yield stress (115 MPa
neutron diffraction. Decreasing the deformation temperature resulted in a slight increase in yield stress (115 MPa  139 MPa), but a remarkable enhancement in both the fracture stress (365 MPa
139 MPa), but a remarkable enhancement in both the fracture stress (365 MPa  551 MPa) and fracture strain (12.8%
551 MPa) and fracture strain (12.8%  16.5%). The low temperature sensitivity of the {10
16.5%). The low temperature sensitivity of the {10 2} extension twinning which governed the macroscopic yielding led to the slight increase in yield stress. At 21K, basal slip was suppressed, while the extension twinning was promoted resulted in higher twin volume fraction. In the late stage of deformation, the {10
2} extension twinning which governed the macroscopic yielding led to the slight increase in yield stress. At 21K, basal slip was suppressed, while the extension twinning was promoted resulted in higher twin volume fraction. In the late stage of deformation, the {10 1}-{10
1}-{10 2} double twinning was suppressed, which is considered to be the reason to delay the fracture at 21 K.
2} double twinning was suppressed, which is considered to be the reason to delay the fracture at 21 K.
 Mg/LPSO dual-phase magnesium alloy monitored by
Mg/LPSO dual-phase magnesium alloy monitored by  neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionHarjo, S.; Gong, W.; 相澤 一也; 川崎 卓郎; 山崎 倫昭*; 眞山 剛*; 河村 能人*
Materials Transactions, 64(4), p.766 - 773, 2023/02
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:72.40(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To elucidate the effect of extrusion ratio in hot-extrusion on the deformation behavior during compression of Mg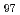 Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy containing about 25-vol% long-period stacking ordered phase (LPSO) in the HCP structured
alloy containing about 25-vol% long-period stacking ordered phase (LPSO) in the HCP structured  matrix (
matrix ( Mg),
Mg),  neutron diffraction measurements were performed under compressive loading using four types of samples: as-cast and after hot extrusion at 623 K with extrusion ratios of 5.0, 7.5 and 12.5. The macroscopic yielding was observed to appear by the occurrence of basal slip of
neutron diffraction measurements were performed under compressive loading using four types of samples: as-cast and after hot extrusion at 623 K with extrusion ratios of 5.0, 7.5 and 12.5. The macroscopic yielding was observed to appear by the occurrence of basal slip of  Mg in the as-cast sample and at the onset of twinning in the hot extruded samples. The applied stress to initiate slip, twinning, and kinking increased by hot extrusion and then decreased with increasing extrusion ratio. LPSO shared higher stress than
Mg in the as-cast sample and at the onset of twinning in the hot extruded samples. The applied stress to initiate slip, twinning, and kinking increased by hot extrusion and then decreased with increasing extrusion ratio. LPSO shared higher stress than  Mg and the ratio to the strength increased as the extrusion ratio increased.
Mg and the ratio to the strength increased as the extrusion ratio increased.
Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 眞山 剛*; 川崎 卓郎; 相澤 一也; Sun, B.*; 辻 伸泰*
no journal, ,
その場中性子回折による極低温圧縮変形中のAZ31マグネシウム合金の変形挙動と変形メカニズムを調べた。21Kでの応力-ひずみ曲線は、室温よりわずかに高い降伏応力を示したが、破断応力と破断ひずみが大幅に高くなったこと分かった。極低温でのc軸引張双晶の促進とc軸圧縮双晶の抑制が、AZ31合金の引張強さ・破断伸びともに向上させる理由であることが明らかにした。
Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 眞山 剛*; 川崎 卓郎; 相澤 一也; Sun, B.*; 辻 伸泰*
no journal, ,
We conducted in-situ neutron diffraction experiments to investigate the temperature dependence of deformation mechanisms at 21 K in an AZ31 Mg alloy. The neutron diffraction results demonstrate that the extension twinning was enhanced at cryogenic temperature, which can provide additional capacity for strain accommodation and work hardening. Moreover, the contraction double twinning, as known to be the crack initiation source in Mg alloys, was suppressed at 21 K. The different sensitivity to temperature of various deformation modes is considered to be the reason for the simultaneous increase in strength and ductility of the commercial AZ31 alloy at 21K.
Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 眞山 剛*; 川崎 卓郎; 相澤 一也; 辻 伸泰*
no journal, ,
Magnesium and its alloys have potential for application in various fields, in which, the applications such as aerospace, storage, and transport of liquid cryogenics, require the materials to withstand high stress at extreme temperature. In present study, we conducted in-situ neutron diffraction experiments to investigate the cryogenic deformation behavior in a commercial extruded AZ31 Mg alloy. The neutron diffraction results demonstrate that the changes in activity of deformation modes are considered to be the reason for the simultaneous increase in strength and ductility of the commercial AZ31 alloy at cryogenic temperature.
Gong, W.; 眞山 剛*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
Mg合金における強度と延性のトレード・オフを克服するため、結晶粒微細化強化の研究が多数行われている。結晶粒微細化によって、強度を増大させると共に引張-圧縮降伏強度非対称性を弱めることができる。しかし、Mg合金における結晶粒径が変形メカニズムに与える影響は、未だ完全に理解されていない。本研究では、その場中性子回折を用いて、AZ31合金の変形挙動に及ぼす結晶粒径の影響を再検討した。
小山 元道*; 北條 智彦*; 宮本 吾郎*; 諸岡 聡; 山下 享介; 澤口 孝宏*; 峯 洋二*; 眞山 剛*; 興津 貴隆*; 榊原 睦海*; et al.
no journal, ,
高強度-高延性鋼を開発するために近年盛んに研究されてきた対象は、高Mn鋼と変態誘起塑性(TRIP)鋼である。高Mn鋼の研究を通して、Mn利用による積層欠陥エネルギーおよび相変態挙動の制御の重要性が再認識された。また、素材コストも睨みながら、従来の延性強度バランスを打破するには、未変態オーステナイトのTRIP効果を利用することが有効であるとの見方も広く受け入れられてきた。これら高Mn鋼とTRIP鋼の研究が合流する形で、TRIP効果を示す中Mn鋼が注目されている。中Mn鋼は優れた延性強度バランスを示す。しかし、複相であること、化学組成や熱処理条件に敏感であること、変形誘起マルテンサイト変態を示すこと、大きなリューダース変形を示すこと、応力ひずみ応答においてセレーションが現れること等に起因して、非常に複雑な塑性変形挙動を呈する。そのため、その優れた力学特性発現の機構は未だ不明瞭である。本講演では、その優れた力学特性の原因を組織発達および塑性変形挙動解析に基づいて明らかとするための研究戦略を示し、その妥当性と応用展開を広く議論する。
Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Zheng, R.*; 眞山 剛*; 相澤 一也; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
no journal, ,
Mg and its alloys possess great potential for a wide range of applications, particularly in cryogenic applications. However, the deformation mechanisms of Mg alloys at cryogenic temperatures are not fully understood due to the absence of appropriate methods. In this study, we investigated the deformation behavior of a commercial AZ31 alloy at cryogenic temperatures using in-situ neutron diffraction. The yield stress of AZ31 alloy significantly increased with decreasing temperature in tensile deformation, but slightly increased in compressive deformation. Interestingly, both the fracture strain and stress at 20 K exhibited a substantial increase compared to 298 K in compressive deformation. In-situ neutron diffraction experiments were conducted using the engineering diffractometer TAKUMI at J-PARC to reveal the deformation mechanisms in the AZ31 alloy at cryogenic temperatures. The stress-strain response of the AZ31 alloy with temperature will be discussed in relation to the temperature-dependent activity of deformation mechanisms.
Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; Zheng, R.*; 眞山 剛*; 相澤 一也; 辻 伸泰*
no journal, ,
Magnesium (Mg) and its alloys have potential for application in various fields. In recent years, the cryogenic temperature applications such as aerospace, storage, and transport of liquid cryogenics, have become increasingly important and widespread in modern materials. To ensure the safety of Mg parts in cryogenic environments, it is necessary to clarify their mechanical properties and intrinsic deformation mechanisms. However, the deformation behavior of Mg alloys at cryogenic temperatures is still far from being understood due to the limited studies and a lack of methods. Here, we conducted in-situ neutron diffraction experiments to reveal the deformation mechanisms at cryogenic temperatures in an AZ31 Mg alloy.