Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
高木 寛貴*; 高木 里奈*; 見波 将*; 野本 拓也*; 大石 一城*; 鈴木 通人*; 柳 有起*; 平山 元昭*; Khanh, N.*; 軽部 皓介*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(7), p.961 - 968, 2023/07
被引用回数:50 パーセンタイル:99.07(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In ferromagnets, electric current generally induces a transverse Hall voltage in proportion to the internal magnetization. This effect is frequently used for electrical readout of the spin up and down states. While these properties are usually not expected in antiferromagnets, recent theoretical studies predicted that non-coplanar antiferromagnetic order with finite scalar spin chirality - meaning a solid angle spanned by neighboring spins - can induce a large spontaneous Hall effect even without net magnetization or external magnetic field. This phenomenon, the spontaneous topological Hall effect, can potentially be used for the efficient electrical readout of the antiferromagnetic states, but it has not been experimentally verified due to a lack of appropriate materials hosting such magnetism. Here, we report the discovery of all-in-all-out type non-coplanar antiferromagnetic order in triangular lattice compounds CoTa S
S and CoNb
and CoNb S
S . These compounds are reported to host unconventionally large spontaneous Hall effect despite their vanishingly small net magnetization, and our analysis reveals that it can be explained in terms of the topological Hall effect that originates from the fictitious magnetic field associated with scalar spin chirality. These results indicate that the scalar spin chirality mechanism offers a promising route to the realisation of giant spontaneous Hall response even in compensated antiferromagnets, and highlight intercalated van der Waals magnets as a promising quasi-two-dimensional material platform to enable various nontrivial ways of electrical reading and possible writing of non-coplanar antiferromagnetic domains.
. These compounds are reported to host unconventionally large spontaneous Hall effect despite their vanishingly small net magnetization, and our analysis reveals that it can be explained in terms of the topological Hall effect that originates from the fictitious magnetic field associated with scalar spin chirality. These results indicate that the scalar spin chirality mechanism offers a promising route to the realisation of giant spontaneous Hall response even in compensated antiferromagnets, and highlight intercalated van der Waals magnets as a promising quasi-two-dimensional material platform to enable various nontrivial ways of electrical reading and possible writing of non-coplanar antiferromagnetic domains.
Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; 浅井 雅人; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; 浅井 雅人; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(6), p.064602_1 - 064602_9, 2020/12
被引用回数:76 パーセンタイル:99.03(Physics, Nuclear)原子番号119及び120を持つ超重元素の合成を目指した探索実験を、それぞれ Ti+
Ti+ Bk及び
Bk及び Ti+
Ti+ Cf核融合-粒子蒸発反応を用いて、ガス充填型反跳分離装置TASCAにて実施した。4ヶ月間におよぶビーム照射実験を行ったが、どちらの元素も検出されず、その生成断面積の上限値は65fb及び200fbであった。119, 120番元素が観測されなかった理由について、安定の島領域の超重元素の核分裂障壁の高さを予測する様々な理論計算値を用いて、核融合-粒子蒸発反応の概念を用いて議論した。
Cf核融合-粒子蒸発反応を用いて、ガス充填型反跳分離装置TASCAにて実施した。4ヶ月間におよぶビーム照射実験を行ったが、どちらの元素も検出されず、その生成断面積の上限値は65fb及び200fbであった。119, 120番元素が観測されなかった理由について、安定の島領域の超重元素の核分裂障壁の高さを予測する様々な理論計算値を用いて、核融合-粒子蒸発反応の概念を用いて議論した。
 Ca+
Ca+ Bk leading to formation of the element Ts (Z=117)
Bk leading to formation of the element Ts (Z=117)Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; 浅井 雅人; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; 浅井 雅人; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(5), p.054306_1 - 054306_16, 2019/05
被引用回数:33 パーセンタイル:92.86(Physics, Nuclear) Ca+
Ca+ B融合反応を用いて117番元素(Ts)合成実験を行い、117番元素に起因すると思われる4つの
B融合反応を用いて117番元素(Ts)合成実験を行い、117番元素に起因すると思われる4つの 崩壊連鎖を観測した。うち2つは長い崩壊連鎖で、
崩壊連鎖を観測した。うち2つは長い崩壊連鎖で、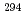 Tsの
Tsの 崩壊に起因するものと同定された。他の2つは短い崩壊連鎖で、
崩壊に起因するものと同定された。他の2つは短い崩壊連鎖で、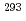 Tsの
Tsの 崩壊に起因すると考えると矛盾しない。今回の結果と過去の文献値を比較したところ、今回の我々の結果は過去の文献値をほぼ再現し、117番元素合成の事実を強く再確認する結果となった。
崩壊に起因すると考えると矛盾しない。今回の結果と過去の文献値を比較したところ、今回の我々の結果は過去の文献値をほぼ再現し、117番元素合成の事実を強く再確認する結果となった。
 C level structure by
C level structure by  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopy細見 健二; Ma, Y.*; 味村 周平*; 青木 香苗*; 大樂 誠司*; Fu, Y.*; 藤岡 宏之*; 二ツ川 健太*; 井元 済*; 垣口 豊*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2015(8), p.081D01_1 - 081D01_8, 2015/08
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:64.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary) 線分光によって
線分光によって Cハイパー核のレベル構造を精密に測定した。ゲルマニウム検出器群Hyperball2を用いて、
Cハイパー核のレベル構造を精密に測定した。ゲルマニウム検出器群Hyperball2を用いて、 C
C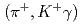 反応からの4本の
反応からの4本の 線遷移を同定することに成功した。基底状態スピン二重項
線遷移を同定することに成功した。基底状態スピン二重項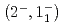 のエネルギー間隔は直接遷移
のエネルギー間隔は直接遷移
 線により、
線により、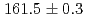 (stat)
(stat)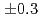 (syst)keVと測定された。また、励起準位である
(syst)keVと測定された。また、励起準位である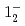 と
と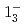 について、それぞれ、
について、それぞれ、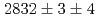 , keVと
, keVと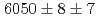 , keVと励起エネルギーを決定した。これらの測定された
, keVと励起エネルギーを決定した。これらの測定された Cの励起エネルギーは反応分光による
Cの励起エネルギーは反応分光による ハイパー核の実験研究において決定的な基準となる。
ハイパー核の実験研究において決定的な基準となる。
 Ca +
Ca +  Bk fusion reaction leading to element Z = 117; Long-lived
Bk fusion reaction leading to element Z = 117; Long-lived  -decaying
-decaying 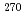 Db and discovery of
Db and discovery of  Lr
LrKhuyagbaatar, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; 浅井 雅人; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; 浅井 雅人; Block, M.*; Boll, R. A.*; Brand, H.*; Cox, D. M.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 112(17), p.172501_1 - 172501_5, 2014/05
被引用回数:228 パーセンタイル:98.37(Physics, Multidisciplinary)ドイツ重イオン研究所のガス充填型反跳核分離装置TASCAを用いて Ca +
Ca +  Bk核融合反応で生成する原子番号117の超重元素の観測に成功した。この結果は、過去にロシアのフレーロフ研究所が報告した117番新元素の結果を再確認するもので、117番元素の合成及び発見を確かなものとする成果である。一方、117番元素からの
Bk核融合反応で生成する原子番号117の超重元素の観測に成功した。この結果は、過去にロシアのフレーロフ研究所が報告した117番新元素の結果を再確認するもので、117番元素の合成及び発見を確かなものとする成果である。一方、117番元素からの 崩壊連鎖の最後の原子核は、過去に報告された
崩壊連鎖の最後の原子核は、過去に報告された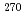 Dbではなく、未知核種
Dbではなく、未知核種 Lrであり、
Lrであり、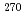 Dbは非常に長い寿命を持つ
Dbは非常に長い寿命を持つ 崩壊核種であることを明らかにした。
崩壊核種であることを明らかにした。
村松 健; 越塚 誠一*; 田南 達也*
no journal, ,
原子力発電施設の安全管理及び安全規制へのリスク情報の活用の進展に伴い、確率論的安全評価(PSA)の品質を確保するための標準の策定が期待されている。日本原子力学会標準委員会発電炉専門部会地震PSA分科会では、原子力発電施設に関するPSAのうち、地震起因事象を対象とするPSAの実施基準を策定した。本発表では、この地震PSA標準のうち、「プラント情報の調査」,詳細な解析に先立って行う「事故シナリオの概括的な分析」、並びに炉心損傷にいたる事故シーケンスの同定と発生頻度の評価を行う「事故シーケンス評価」に関する部分を紹介する。