Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tobita, Minoru*; Goto, Katsunori*; Omori, Takeshi*; Osone, Osamu*; Haraga, Tomoko; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Tsuchida, Daiki; Mitsukai, Akina; Ishimori, Kenichiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-011, 32 Pages, 2023/11
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to the study of radioactivity concentration evaluation methods for radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities, we collected and analyzed concrete samples generated from JRR-3, JRR-4 and JAERI Reprocessing Test Facility. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 23 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Ag,
Ag,  Cs,
Cs,  Ba,
Ba,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2021-2022.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2021-2022.
Aono, Ryuji; Mitsukai, Akina; Tsuchida, Daiki; Konda, Miki; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-002, 81 Pages, 2023/05
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2, JRR-3 and Hot laboratory facilities. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 20 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2020.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2020.
Tobita, Minoru*; Konda, Miki; Omori, Takeshi*; Nabatame, Tsutomu*; Onizawa, Takashi*; Kurosawa, Katsuaki*; Haraga, Tomoko; Aono, Ryuji; Mitsukai, Akina; Tsuchida, Daiki; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2022-007, 40 Pages, 2022/11
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed concrete, ash, ceramic and brick samples generated from JRR-3, JRR4 and JRTF facilities. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 24 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Ba,
Ba,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2020-2021.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2020-2021.
Tsuchida, Daiki; Mitsukai, Akina; Aono, Ryuji; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2022-004, 87 Pages, 2022/07
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until by the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed samples generated from JPDR, JRR-3 and JRR-4. In this report, radioactivity concentrations of 20 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) were determined based on radiochemical analysis and summarized as basic data for the study of evaluation method of radioactive concentration.
Cm) were determined based on radiochemical analysis and summarized as basic data for the study of evaluation method of radioactive concentration.
Tobita, Minoru*; Haraga, Tomoko; Endo, Tsubasa*; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Mitsukai, Akina; Aono, Ryuji; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-013, 30 Pages, 2021/12
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed concrete samples generated from JPDR facility. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 21 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Ag,
Ag,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2018-2019.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2018-2019.
Tsuchida, Daiki; Haraga, Tomoko; Tobita, Minoru*; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Omori, Takeshi*; Murakami, Hideaki*; Mitsukai, Akina; Aono, Ryuji; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-022, 34 Pages, 2021/03
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed concrete samples generated from JRR-3 and JPDR. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 22 radionuclides( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Ag,
Ag,  Ba,
Ba,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples.
Aono, Ryuji; Mitsukai, Akina; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-006, 70 Pages, 2020/08
Radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried at the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JPDR and JRR-4. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 19 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Mitsukai, Akina; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-012, 70 Pages, 2020/02
It is necessary to establish practical evaluation methods to determine radioactivity concentration of radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried for the near surface disposal. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from Post Irradiation Examination Facility. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 19 radionuclides which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Mitsukai, Akina; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Technology 2019-015, 52 Pages, 2019/11
In the future, radioactive waste which generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried for the near surface disposal. It is necessary to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of the radioactive wastes. In this work, we studied the evaluation method of radioactivity concentration based on radiochemical analysis data (H-3, C-14, Cl-36, Co-60, Ni-63, Sr-90, Mo-93, Nb-94, Tc-99, Ag-108m, Sn-126, I-129, Cs-137, Eu-152, Eu-154, U-233+234, U-238, Pu-238, Pu-239+240, Pu-241, Am-241, Am-243, Cm-244) which was generated from research facility Hot Laboratory. As a result of examining the application of the scaling factor method, the correlation with Key-nuclide in some nuclides which are Sr-90, I-129, Eu-154, U-233+234, Pu-238, Pu-239+240, Am-241, Cm-244 confirmed by the correlation coefficient and t-test. In the present radiochemical analysis data, the mean activity concentration method can be applied to all nuclides which could not be applied to the scaling factor method H-3, C-14, Cl-36, Ni-63, Mo-93, Nb-94, Tc-99, Ag-108m, Sn-126, Eu-152, U-238, Pu-241 and Am-243. Ni-63, Tc-99, Eu-152 and U-238 could be applied to the scaling factor method with getting several additional data, this study will be continued to review for the practical evaluation method.
Haraga, Tomoko; Shimomura, Yusuke; Mitsukai, Akina; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-004, 48 Pages, 2019/10
In the future, radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried for the near surface disposal. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2 and JRR-3. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 19 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Beerwerth, R.*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mitsukai, Akina*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Osa, Akihiko; Toyoshima, Atsushi; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 140(44), p.14609 - 14613, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:69.85(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The first ionization potential (IP ) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP
) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP
values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP
of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP
among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP
values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
 SO
SO and HF/HCl solutions into toluene with Aliquat336; Sulfate and fluoride complex formation of Mo and W towards chemical studies of seaborgium (Sg)
and HF/HCl solutions into toluene with Aliquat336; Sulfate and fluoride complex formation of Mo and W towards chemical studies of seaborgium (Sg)Toyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Komori, Yukiko*; Murakami, Masashi; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Sato, Daisuke*; Asai, Masato; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 317(1), p.421 - 430, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.44(Chemistry, Analytical)We have studied extraction behavior of group-6 elements Mo and W to search for suitable conditions for an on-line extraction experiment of their heavier homolog, seaborgium (Sg). Batch-wise extraction of carrier-free radiotracers  Mo and
Mo and 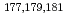 W were carried out from 0.10 - 8.6 M H
W were carried out from 0.10 - 8.6 M H SO
SO and 1.0
and 1.0 10
10 - 5.0 M HF/1.0 M HCl into toluene with a quaternary ammonium compound, Aliquat336. Anionic sulfate complexes of Mo and W with charge - 2 were extracted with Aliquat336 from H
- 5.0 M HF/1.0 M HCl into toluene with a quaternary ammonium compound, Aliquat336. Anionic sulfate complexes of Mo and W with charge - 2 were extracted with Aliquat336 from H SO
SO solutions with concentrations of [H
solutions with concentrations of [H SO
SO ]
]  2 M. In HF/1.0 M HCl, oxyfluoro complexes of Mo and W with charge - 1 were interpreted to be formed and extracted with Aliquat336. From these results, favorable conditions for the extraction of Sg are discussed.
2 M. In HF/1.0 M HCl, oxyfluoro complexes of Mo and W with charge - 1 were interpreted to be formed and extracted with Aliquat336. From these results, favorable conditions for the extraction of Sg are discussed.
 at the single-atom level
at the single-atom levelSteinegger, P.*; Asai, Masato; Dressler, R.*; Eichler, R.*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Mitsukai, Akina*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Piguet, D.*; Sato, Tetsuya; Sch del, M.; et al.
del, M.; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 120(13), p.7122 - 7132, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:64.09(Chemistry, Physical)A new experimental method "vacuum chromatography" has been developed to measure adsorption enthalpy of superheavy elements, and its feasibility has been examined using short-lived thallium isotopes. The short-lived thallium isotopes were produced at the JAEA tandem accelerator. The thallium ion beam prepared with an on-line isotope separator which ionized and mass-separated the thallium isotopes was injected into an isothermal vacuum chromatography apparatus. A temperature-dependent adsorption property of thallium atom on SiO surface were measured. The adsorption enthalpy of thallium was determined to be 158 kJ/mol. The thallium is a homolog of element 113. Thus, the vacuum chromatography developed in this study enables us to perform chemical experiments for short-lived superheavy elements with half-lives of a order of one second.
surface were measured. The adsorption enthalpy of thallium was determined to be 158 kJ/mol. The thallium is a homolog of element 113. Thus, the vacuum chromatography developed in this study enables us to perform chemical experiments for short-lived superheavy elements with half-lives of a order of one second.
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Miyashita, Sunao*; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Kitayama, Yuta*; Lerum, H. V.*; Goto, Naoya*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Komori, Yukiko*; Mitsukai, Akina*; Vascon, A.; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 = 102)
= 102)Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Vascon, A.; Takeda, Shinsaku; Mitsukai, Akina*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Ichikawa, Shinichi; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to determine the IP of the heavy elements, we have developed a novel measurement method based on a surface ionization technique by using a surface ionization ion source coupled to a He/CdI gas-jet transport system for an Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) at the JAEA tandem accelerator facility. In this work, we have determined IP value of No by using the method. In a surface ionization process, an ionization efficiency of an atom depends on its IP. To obtain a relationship between IP and ionization efficiency in present system, we measured ionization efficiencies of various short-lived isotopes. Ionization efficiency of
gas-jet transport system for an Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) at the JAEA tandem accelerator facility. In this work, we have determined IP value of No by using the method. In a surface ionization process, an ionization efficiency of an atom depends on its IP. To obtain a relationship between IP and ionization efficiency in present system, we measured ionization efficiencies of various short-lived isotopes. Ionization efficiency of  No produced in the
No produced in the  Cm(
Cm( C, 4n) reaction was also measured. Measured ionization efficiency of
C, 4n) reaction was also measured. Measured ionization efficiency of  No was 0.8%, which yields IP value of No to be 6.6 eV. This value is in a good agreement with the value which has been evaluated by extrapolation from those of the lighter actinide elements, 6.65 eV.
No was 0.8%, which yields IP value of No to be 6.6 eV. This value is in a good agreement with the value which has been evaluated by extrapolation from those of the lighter actinide elements, 6.65 eV.
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Asai, Masato; Attallah, M. F.*; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Kaneko, Masashi*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
Due to short half-lives less than 10 s and extremely low production rates, transactinide elements heavier than seaborgium (Sg) are produced on an atom per hour scale. Therefore, a continuous rapid chemistry assembly is required to study aqueous-phase chemistry of these heaviest elements. In the present study, we started developments of a continuous chemistry assembly. Our first attempt was made in on-line experiments with Mo and W, lighter homologs of Sg, to optimize a chemistry assembly consisting of a newly developed membrane degasser as an interface between gas-jet and aqueous phase, a flow electrolytic column apparatus utilized to control oxidation states of Mo and W ions, and the continuous liquid-liquid extraction apparatus of SISAK for separation. In the conference, present status of the developments will be presented.
 SO
SO into toluene with Aliquat336 as model experiments for seaborgium (Sg)
into toluene with Aliquat336 as model experiments for seaborgium (Sg)Mitsukai, Akina; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Kaneya, Yusuke; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Sato, Daisuke*; Goto, Naoya*; Tsuto, Shohei*; Komori, Yukiko*; Murakami, Masashi*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
no journal, ,
We report on the extraction behavior of carrier-free radioisotopes  Mo and
Mo and  W, which are lighter homologs of Sg, produced at the RIKEN K70 AVF cyclotron, in the H
W, which are lighter homologs of Sg, produced at the RIKEN K70 AVF cyclotron, in the H SO
SO -Aliquat336 system. Results of the extraction experiments showed that the distribution ratios,
-Aliquat336 system. Results of the extraction experiments showed that the distribution ratios, 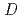 , of Mo and W decrease up to
, of Mo and W decrease up to  3 M as increasing [H
3 M as increasing [H SO
SO ]. This is probably due to protonation reactions of hydrolyzed Mo and W species. In
]. This is probably due to protonation reactions of hydrolyzed Mo and W species. In 
 3 M H
3 M H SO
SO , the
, the 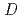 values of W and Mo showed sharp increases. Based on the slope analysis separately carried out, it was suggested that hydrolyzed species of [HMO
values of W and Mo showed sharp increases. Based on the slope analysis separately carried out, it was suggested that hydrolyzed species of [HMO ]
] (M = Mo and W) are extracted in less than
(M = Mo and W) are extracted in less than  3 M [H
3 M [H SO
SO ], while anionic sulphate complexes of [MO
], while anionic sulphate complexes of [MO (SO
(SO )
) ]
] are formed in more than [H
are formed in more than [H SO
SO ]
]
 5 M.
5 M.
Sato, Tetsuya; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina*; Osa, Akihiko; Makii, Hiroyuki; Hirose, Kentaro; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
no journal, ,
Our experimental results on the first ionization potential measurement of lawrencium (Lr, element 103) have strongly suggested that the Lr atom has a [Rn]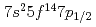 configuration as a result of the influence of strong relativistic effects. The configuration is different from that expected from the lanthanide homologue, lutetium (Lu). According to a semi-empirical consideration, it is expected that the change of the electronic configuration leads higher volatility of Lr than that of Lu. In this work, adsorption behaviors of Lr and various short-lived rare earth isotopes on a tantalum surface were investigated via observation of their surface ionization efficiencies. It was found that Lr would behave like low volatile rare earth elements such as Lu contrary to the semi-empirical expectation.
configuration as a result of the influence of strong relativistic effects. The configuration is different from that expected from the lanthanide homologue, lutetium (Lu). According to a semi-empirical consideration, it is expected that the change of the electronic configuration leads higher volatility of Lr than that of Lu. In this work, adsorption behaviors of Lr and various short-lived rare earth isotopes on a tantalum surface were investigated via observation of their surface ionization efficiencies. It was found that Lr would behave like low volatile rare earth elements such as Lu contrary to the semi-empirical expectation.
Tomitsuka, Tomohiro; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina; Osa, Akihiko; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to investigate the adsorption behavior of Lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) on a Tantalum (Ta) surface, we measured ionization efficiencies of Lr under several temperature conditions of the surface ionization. We observed ionization efficiencies of Lr which were lower than those calculated by the Saha-Langmuir equation in lower temperature region. Based on a temperature dependence of the obtained ionization efficiencies, we discuss the adsorption behavior of Lr on the Ta surface.
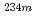 Np isomer
Np isomerKamada, Hiroki*; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Nagame, Yuichiro; Mitsukai, Akina; Tomitsuka, Tomohiro*; Andreyev, A. N.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; et al.
no journal, ,
Existence of the previously unknown isomer 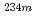 Np was discovered for the first time.
Np was discovered for the first time. 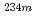 Np was produced by using the JAEA tandem accelerator. Short-lived reaction products were mass-separated by the on-line isotope separator ISOL, and
Np was produced by using the JAEA tandem accelerator. Short-lived reaction products were mass-separated by the on-line isotope separator ISOL, and  and X rays originating from the decay of
and X rays originating from the decay of 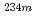 Np were observed. The half-life of
Np were observed. The half-life of 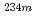 Np was determined to be approximately 9 min, and
Np was determined to be approximately 9 min, and 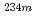 Np was found to decay via the EC decay as well as the isomeric transition. On the basis of the observed
Np was found to decay via the EC decay as well as the isomeric transition. On the basis of the observed  and X rays and the half-life value, we have evaluated level energy, spin-parity, and proton-neutron configuration of
and X rays and the half-life value, we have evaluated level energy, spin-parity, and proton-neutron configuration of 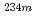 Np.
Np.