Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Johansen, M. P.*; Gwynn, J. P.*; Carpenter, J. G.*; Charmasson, S.*; 森 愛理; Orr, B.*; Simon-Cornu, M.*; Osvath, I.*; McGinnity, P.*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 287, p.107706_1 - 107706_8, 2025/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Radiological ingestion doses from eating seafood are regularly evaluated near coastal nuclear facilities, following accidents/events and frequently in national studies worldwide. However, a recent global review found that published seafood doses varied greatly depending on which radionuclides were selected for evaluation and that there has been a tendency to omit important radionuclides or focus on less significant ones. This indicates a need for clear guidance on which radionuclides to prioritise in such studies. Here, we use worldwide data for 16 key radionuclides contributing to typical background seafood ingestion dose. We account for the loss of radionuclides during cooking and the radioactive decay of the short-lived  Po. Results indicate that for the typical world consumer, naturally-occurring radionuclides account for
Po. Results indicate that for the typical world consumer, naturally-occurring radionuclides account for  99% of the total seafood ingestion dose, of which about 84% comes from
99% of the total seafood ingestion dose, of which about 84% comes from  Po and 8% from
Po and 8% from  Pb. About 5% comes from
Pb. About 5% comes from 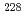 Ra, a far greater proportion than the more frequently-assessed
Ra, a far greater proportion than the more frequently-assessed  Ra (
Ra ( 1%). Other Th- and U-series radionuclides provide far lower contributions (0.07%-0.70%), while
1%). Other Th- and U-series radionuclides provide far lower contributions (0.07%-0.70%), while  C provides about 0.09%. In comparison, the contribution to total seafood ingestion dose from background anthropogenic radionuclides is
C provides about 0.09%. In comparison, the contribution to total seafood ingestion dose from background anthropogenic radionuclides is  1%, with
1%, with  Cs contributing most (0.08%) and
Cs contributing most (0.08%) and  Sr,
Sr,  Tc,
Tc, 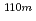 Ag and
Ag and  Pu adding a further 0.05% together. These percentage contributions to dose can vary somewhat depending on consumption patterns (e.g., differing proportions of fish, bivalves, etc.). However,
Pu adding a further 0.05% together. These percentage contributions to dose can vary somewhat depending on consumption patterns (e.g., differing proportions of fish, bivalves, etc.). However,  Po is the dominant contributor irrespective of country-specific diets or restricted diet scenarios (fish-only, seaweed-only, etc.). Study results provide new guidance to improve the design, interpretation and communication of seafood ingestion dose assessments.
Po is the dominant contributor irrespective of country-specific diets or restricted diet scenarios (fish-only, seaweed-only, etc.). Study results provide new guidance to improve the design, interpretation and communication of seafood ingestion dose assessments.
森 愛理; Johansen, M. P.*; McGinnity, P.*; 高原 省五
Communications Earth & Environment (Internet), 6, p.356_1 - 356_11, 2025/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)The presence of radionuclides in seafood following the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in March 2011 have led to widespread and persistent concerns over seafood safety. We assess seafood ingestion doses before and after the accident for adults in the Tohoku Region of Northeast Japan. Using a Monte Carlo approach, we evaluate 23 anthropogenic and natural radionuclides alongside realistic seafood consumption rates. In the first year after the accident, the ingestion dose from accident-derived radionuclides was 19  Sv for consumers exposed to the 95th percentile dose, contributing only 2% of the total seafood ingestion dose, which includes natural radionuclides such as
Sv for consumers exposed to the 95th percentile dose, contributing only 2% of the total seafood ingestion dose, which includes natural radionuclides such as  Po and
Po and  Pb. After the third year, the dose from accident-derived radionuclides was indistinguishable to that from pre-accident background levels. These findings suggest that, with seafood restrictions in place, the impact of accident-related releases on seafood ingestion doses was minor and relatively short-lived compared with that of natural radionuclides.
Pb. After the third year, the dose from accident-derived radionuclides was indistinguishable to that from pre-accident background levels. These findings suggest that, with seafood restrictions in place, the impact of accident-related releases on seafood ingestion doses was minor and relatively short-lived compared with that of natural radionuclides.
Johansen, M. P.*; Gwynn, J. P.*; Carpenter, J. G.*; Charmasson, S.*; McGinnity, P.*; 森 愛理; Orr, B.*; Simon-Cornu, M.*; Osvath, I.*
Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 55(6), p.422 - 445, 2025/00
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:32.78(Environmental Sciences)Seafood is an important source for meeting future global nutrient demands. However, it also contributes disproportionately to the radiological ingestion dose of more than five billion world consumers - up to  70%-80% of the total-foods dose in some countries. Although numerous studies report seafood doses in specific populations, there is still no comprehensive evaluation answering basic questions such as "what is the ingestion dose to the average global seafood consumer?" Analysis of 238 worldwide seafood dose estimates suggests that typical adult consumers receive from 0.13 to 0.21 mSv, with a likely best estimate of 0.15 mSv per annual seafood intake. Those consuming large amounts of seafood, particularly bivalves, may experience ingestion doses exceeding 1 mSv per annual intake, surpassing other routine background dose sources. The published studies suggest that doses of 3 mSv or greater are surpassed in about 150 million adult seafood consumers worldwide. Almost all this dose comes from the natural radionuclides that are prevalent in marine systems - especially
70%-80% of the total-foods dose in some countries. Although numerous studies report seafood doses in specific populations, there is still no comprehensive evaluation answering basic questions such as "what is the ingestion dose to the average global seafood consumer?" Analysis of 238 worldwide seafood dose estimates suggests that typical adult consumers receive from 0.13 to 0.21 mSv, with a likely best estimate of 0.15 mSv per annual seafood intake. Those consuming large amounts of seafood, particularly bivalves, may experience ingestion doses exceeding 1 mSv per annual intake, surpassing other routine background dose sources. The published studies suggest that doses of 3 mSv or greater are surpassed in about 150 million adult seafood consumers worldwide. Almost all this dose comes from the natural radionuclides that are prevalent in marine systems - especially  Po. While trace levels of anthropogenic radionuclides are ubiquitous in seafoods (e.g.,
Po. While trace levels of anthropogenic radionuclides are ubiquitous in seafoods (e.g., Cs and
Cs and  Pu), the added dose from these is typically orders of magnitude lower. Even following the large-scale releases from the Fukushima accident, with food safety controls in place, the additional dose to consumers in Japan was small relative to routine dose from natural background radionuclides. However, the worldwide seafood dose estimates span seven orders of magnitude, indicating a need for an assessment that integrates global seafood radionuclide data as well as incorporating changes in seafood consumption and production patterns.
Pu), the added dose from these is typically orders of magnitude lower. Even following the large-scale releases from the Fukushima accident, with food safety controls in place, the additional dose to consumers in Japan was small relative to routine dose from natural background radionuclides. However, the worldwide seafood dose estimates span seven orders of magnitude, indicating a need for an assessment that integrates global seafood radionuclide data as well as incorporating changes in seafood consumption and production patterns.
 Po retention factors for cooking, decay loss and mariculture
Po retention factors for cooking, decay loss and maricultureJohansen, M. P.*; Carpenter, J. G.*; Charmasson, S.*; Gwynn, J. P.*; McGinnity, P.*; 森 愛理; Orr, B.*; Simon-Cornu, M.*; Osvath, I.*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 268-269, p.107243_1 - 107243_10, 2023/11
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:72.92(Environmental Sciences) Po has been identified as one of the main contributors to ingestion doses to humans, particularly from the consumption of seafood. The amount of
Po has been identified as one of the main contributors to ingestion doses to humans, particularly from the consumption of seafood. The amount of  Po activity concentration data for various types of seafood has increased greatly in recent times. However, to provide realistic seafood dose assessments, most
Po activity concentration data for various types of seafood has increased greatly in recent times. However, to provide realistic seafood dose assessments, most  Po data requires correction to account for losses that can occur before the seafood is actually consumed. We develop generic correction factors for the main processes associated with reduction of
Po data requires correction to account for losses that can occur before the seafood is actually consumed. We develop generic correction factors for the main processes associated with reduction of  Po in seafood - leaching during cooking, radioactive decay between harvest and consumption, and sourcing from mariculture versus wild-caught. When seafood is cooked, the overall mean fraction of
Po in seafood - leaching during cooking, radioactive decay between harvest and consumption, and sourcing from mariculture versus wild-caught. When seafood is cooked, the overall mean fraction of  Po retained is 0.74 for all cooking and seafood types, with the means for various seafoods and cooking categories ranging from 0.56 to 1.03. When considering radioactive decay between harvest and consumption, the overall mean fraction remaining is 0.81 across all seafood preservation/packaging types, with estimates ranging from 0.50 (canned seafood) to 0.98 (fresh seafood). Regarding mariculture influence, the available limited data suggest marine fish and crustaceans raised with processed feed have about one order of magnitude lower
Po retained is 0.74 for all cooking and seafood types, with the means for various seafoods and cooking categories ranging from 0.56 to 1.03. When considering radioactive decay between harvest and consumption, the overall mean fraction remaining is 0.81 across all seafood preservation/packaging types, with estimates ranging from 0.50 (canned seafood) to 0.98 (fresh seafood). Regarding mariculture influence, the available limited data suggest marine fish and crustaceans raised with processed feed have about one order of magnitude lower  Po muscle content than wild-caught seafood of the same or similar species, although this ratio varies. Overall, this study concludes that
Po muscle content than wild-caught seafood of the same or similar species, although this ratio varies. Overall, this study concludes that  Po activity concentrations in seafood at the time of ingestion may be reduced to only about 55% compared to when it was harvested. Therefore, correction factors must be applied to any data derived from environmental monitoring in order to achieve realistic dose estimates. The data also suggest lower
Po activity concentrations in seafood at the time of ingestion may be reduced to only about 55% compared to when it was harvested. Therefore, correction factors must be applied to any data derived from environmental monitoring in order to achieve realistic dose estimates. The data also suggest lower  Po ingestion doses for consumers who routinely favour cooked, long shelf-life and farmed fish/crustaceans. However, more data is needed in some categories, especially for cooking of molluscs and seaweed, and for the
Po ingestion doses for consumers who routinely favour cooked, long shelf-life and farmed fish/crustaceans. However, more data is needed in some categories, especially for cooking of molluscs and seaweed, and for the  Po content in all farmed seafood.
Po content in all farmed seafood.
森 愛理; 瀬口 栄作*; 普天間 章; 岩井 毅行*; 眞田 幸尚
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 17(10), p.P10015_1 - P10015_11, 2022/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Four global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receivers were installed in a helicopter to reduce positioning errors in aerial radiation monitoring. The effect of positioning errors on the conversion of the counting rate of the detector to the ambient dose equivalent rate at the ground level was evaluated. The positioning results obtained by receiving the centimeter-class augmentation signal known as the L-band experiment, which the Quasi-Zenith Satellite System generates on an experimental basis for a limited time, were used as the reference values. A comparison between horizontal and vertical positioning errors among four receivers demonstrated that the vertical errors were larger than the horizontal errors. They did not differ among receivers, whereas the horizontal errors varied according to the characteristics of the receivers, particularly in mountainous areas; the errors tended to be larger when the terrain change at the measurement point was larger. The median effects of the vertical and horizontal errors on the calculated values of the radiation dose rate at the ground level were 3%-6% and 1%-5%, respectively, and the maximum possible effect of the positioning error was 20%-32%. The fact that the receiver with the highest number of available satellites had larger errors than the other receivers indicated that the elevation angles of satellites and the augmentation signals play an important role in improving the positioning accuracy when the number of available satellites reduces in mountainous areas. This study has provided insight into selecting a suitable GNSS receiver for surveying by vehicles such as helicopters, aircraft, and drones, which are required to perform 3D positioning in complex terrains.
森 愛理; 高原 省五; 吉田 浩子*; 眞田 幸尚; 宗像 雅広
Health Physics, 117(6), p.606 - 617, 2019/12
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:8.72(Environmental Sciences)On 1 April 2017, evacuation orders in large areas were lifted. To estimate external radiation doses to children after returning to these areas, a dose estimation model based on a probabilistic approach has been developed. Validation of the model in an area for which individual personal dosimetry measurements were available show that it is valid for infants, kindergarteners, 3rd to 6th grade elementary school students, and junior high school students. As a result of our estimations, 95th percentile doses to all age groups were less than 20 mSv y in period from 2017 to 2020 and in all areas. Doses in some areas were less than 1 mSv y
in period from 2017 to 2020 and in all areas. Doses in some areas were less than 1 mSv y , which is the long-term dosimetric target set by Japanese government. It is noted that our results are preliminary. To estimate doses to the children precisely, further considerations for assumptions and limitations on the environmental contamination conditions and behavioral patterns of children will be needed.
, which is the long-term dosimetric target set by Japanese government. It is noted that our results are preliminary. To estimate doses to the children precisely, further considerations for assumptions and limitations on the environmental contamination conditions and behavioral patterns of children will be needed.
普天間 章; 眞田 幸尚; 古宮 友和; 岩井 毅行*; 瀬口 栄作*; 松永 祐樹*; 河端 智樹*; 萩野谷 仁*; 平賀 祥吾*; 佐藤 一彦*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2019-017, 95 Pages, 2019/11
2011年3月11日に発生した東日本大震災による津波に起因した東京電力福島第一原子力発電所事故によって、大量の放射性物質が周辺環境に飛散した。事故直後より放射性核種の分布を迅速かつ広範囲に測定する手法として、有人ヘリコプター等を用いた航空機モニタリングが活用されている。今後も本モニタリング技術を原子力発電所事故時における緊急時モニタリングに活用し、そのモニタリング結果を迅速に提供することを目指している。そのために、全国の発電所周辺におけるバックグラウンド放射線量や地形的特徴、空域情報等の情報を整備している。2018年度は島根原子力発電所および浜岡原子力発電所周辺について航空機モニタリングを実施した。本報告書は、その結果および実施によって抽出された技術的課題についてまとめたものである。
普天間 章; 眞田 幸尚; 石崎 梓; 古宮 友和; 岩井 毅行*; 瀬口 栄作*; 松永 祐樹*; 河端 智樹*; 萩野谷 仁*; 平賀 祥吾*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2019-016, 116 Pages, 2019/11
2011年3月11日に発生した東日本大震災による津波に起因した東京電力福島第一原子力発電所事故によって、大量の放射性物質が周辺環境に飛散した。事故直後より、放射線の分布を迅速かつ広範囲に測定する手法として、航空機等を用いた空からの測定方法が適用されている。ここでは、2018年度に実施した福島第一原子力発電所周辺におけるモニタリング結果についてまとめた。過去の福島第一原子力発電所周辺におけるモニタリング結果から空間線量率等の変化量を評価し、変化量に寄与する要因について考察した。また、空気中のラドン子孫核種の弁別手法を測定結果に適用して、空気中のラドン子孫核種が航空機モニタリングに与える影響について評価した。さらに、航空機モニタリングによる空間線量率の計算精度向上に資するために、過去の航空機モニタリングデータを用いて地形の起伏を考慮に入れた解析を行なった。地形の起伏を考慮に入れる前後で解析結果を比較し、本手法による精度向上効果を評価した。
森 愛理; 石崎 梓; 普天間 章; 田辺 務; 和田 孝雄; 加藤 貢; 宗像 雅広
保健物理(インターネット), 54(1), p.45 - 54, 2019/04
Large quantities of radionuclides were released as a result of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident. It is known that these radionuclides contaminated inside houses as well as outdoor environment. Considering the radiation protection of residents after a nuclear power station accident, it is important to know the influence of radionuclides inside houses to radiation dose to residents. In this study, we investigated removal factors and fractions of fixed contamination of various materials inside houses in Okuma Town, Futaba Town, and Namie Town to assess the contamination level inside house appropriately. Nine kinds of materials, fibers, woods (smooth), woods rough), glasses, concretes (smooth), concretes (rough), plastics, PVCs and metals, were used in examinations. The lowest and the highest removal factors were 23% - 16% of woods (rough) and 79% - 7.7% of glasses, respectively. Removal factors of all materials were higher than 10% which is recommended by Japanese Industrial Standard. The negative correlation was found between removal factors and fractions of fixed contamination. Using this correlation, the decontamination factor, which means the ratio of the activity removed from the surface by one smear sample to the activity of the total surface activity, was proposed. The air dose rate from the contamination inside house was calculated using obtained decontamination factors and removal factor of 10%. In the case using the removal factor of 10%, the air dose rate derived by indoor contamination was approximately 2 times higher than the case using obtained decontamination factors. We found that the air dose rate derived by indoor contamination was much lower than the air dose rate outside house, and the influence of indoor contamination on the external exposure was small.
普天間 章; 眞田 幸尚; 岩井 毅行*; 瀬口 栄作; 松永 祐樹*; 河端 智樹; 豊田 政幸*; 飛田 晋一朗*; 平賀 祥吾*; 佐藤 一彦*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2018-016, 98 Pages, 2019/02
2011年3月11日に発生した東日本大震災による津波に起因した東京電力福島第一原子力発電所事故によって、大量の放射性物質が周辺に飛散した。事故直後より、放射線の分布を迅速かつ広範囲に測定する手法として、航空機等を用いた空からの測定方法が適用されている。福島で培った航空機モニタリングの技術を原子力発電所事故時の対応技術として適用するために、全国の発電所周辺のバックグラウンドモニタリングを実施した。2017年度は泊発電所, 柏崎刈羽原子力発電所および玄海原子力発電所周辺について実施した。ここでは、その結果および実施によって抽出された技術的課題についてまとめる。
普天間 章; 眞田 幸尚; 石崎 梓; 岩井 毅行*; 瀬口 栄作; 松永 祐樹*; 河端 智樹; 豊田 政幸*; 飛田 晋一朗*; 平賀 祥吾*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2018-015, 120 Pages, 2019/02
2011年3月11日に発生した東日本大震災による津波に起因した東京電力福島第一原子力発電所事故によって、大量の放射性物質が周辺に飛散した。事故直後より、放射線の分布を迅速かつ広範囲に測定する手法として、航空機等を用いた空からの測定方法が適用されている。ここでは、平成29年度に実施した福島第一原子力発電所周辺におけるモニタリング結果についてまとめた。過去の福島第一原子力発電所周辺におけるモニタリング結果から線量率の変化量を評価し、変化量に寄与する要因について考察した。また、これまで課題となっていた空気中のラドン子孫核種の弁別手法の開発およびシステム化を行い、実際の測定結果に本手法を適用して、空気中のラドン子孫核種の測定に与える影響について評価した。さらに、複数のGPS受信機用いて同時にデータ取得することによって、位置測定誤差による解析結果への影響評価を行った。
眞田 幸尚; 森 愛理; 岩井 毅行; 瀬口 栄作; 松永 祐樹*; 河端 智樹; 豊田 政幸*; 飛田 晋一朗*; 平賀 翔吾; 佐藤 義治; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2017-035, 69 Pages, 2018/02
2011年3月11日に発生した東日本大震災による津波に起因した東京電力福島第一原子力発電所事故によって、大量の放射性物質が周辺に飛散した。事故直後より、放射線の分布を迅速かつ広範囲に測定する手法として、航空機等を用いた空からの測定方法が適用されている。福島で培った航空機モニタリングの技術を原子力発電所事故時の対応技術として適用するために、全国の発電所周辺のバックグラウンドモニタリングを実施した。2016年度は、大飯・高浜原子力発電所及び伊方原子力発電所周辺について実施した。ここでは、その結果及び実施によって抽出された技術的課題についてまとめる。
眞田 幸尚; 森 愛理; 岩井 毅行; 瀬口 栄作; 松永 祐樹*; 河端 智樹; 豊田 政幸*; 飛田 晋一朗*; 平賀 翔吾; 佐藤 義治; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2017-034, 117 Pages, 2018/02
2011年3月11日に発生した東日本大震災による津波に起因した東京電力福島第一原子力発電所事故によって、大量の放射性物質が周辺に飛散した。事故直後より、放射線の分布を迅速かつ広範囲に測定する手法として、航空機等を用いた空からの測定方法が適用されている。ここでは、平成28年度に実施した福島第一原子力発電所周辺におけるモニタリング結果についてまとめた。福島第一原子力発電所周辺におけるモニタリング結果は、過去の測定結果からの線量率の変化量を評価し、変化量に寄与する要因について考察した。また、これまで課題となっていた空気中のラドン子孫核種の弁別手法の開発を行い、実際の測定結果に手法を適用して、空気中のラドン子孫核種の測定に与える影響について評価した。さらに、複数の性能の異なったGPSを同時にデータ取得することによって、位置測定誤差による解析結果への影響評価を行った。
森 愛理; 田辺 務; 和田 孝雄; 加藤 貢
JAEA-Technology 2017-006, 38 Pages, 2017/03
福島第一原子力発電所事故により大量の放射性物質が環境に放出され、近隣の市街地や森林等が汚染された。家屋や学校等の周辺の除染は国および地方自治体により進められているが、住環境にある壁や床、窓等については公的な除染が行われていない。本試験では、容易に実施できる作業により効果的に汚染を低減する手法を整備するため、住環境にある様々な部材に対し拭き取り等の試験を行った。試験を実施した部材は繊維類、木材類、ガラス類、コンクリート類、プラスチック類、塩化ビニル類、金属類、その他である。各部材は旧警戒区域(現在の帰還困難区域)内の実家屋から採取しており、事故により放出された放射性物質で汚染されたものである。これらの部材に対して乾式の手法(吸引、拭き取り、吸着、剥離)、湿式の手法(拭き取り、ブラッシング、表面研磨、洗濯)、および物理的な手法(剥離)を適用することで、簡易で効果的な汚染低減手法を検討した。試験の結果、一般的に水の浸透性が低い部材(ガラス、コンクリート、プラスチック、塩化ビニル、および金属)については湿式の手法(拭き取り、表面研磨、またはブラッシング)を用いることで高い汚染低減率が得られることがわかった(90%程度)。一方で水の浸透性がある木材の場合は剥離用塗料が比較的効果的(汚染低減率60%-70%程度)であった。このほか補足的データとして、洗剤の性質による汚染低減率の違い、および剥離用塗料の擦り込みの効果についても検討を行った。最後に、これらの結果を踏まえ最適であると考えられる手法をまとめた。
森 愛理; 高原 省五; 石崎 梓; 飯島 正史; 眞田 幸尚; 宗像 雅広
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 166(Part 1), p.74 - 82, 2017/01
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:23.25(Environmental Sciences)福島第一原子力発電所事故により多量の放射性物質が環境中へ放出され、事故の影響を受けた地域で暮らす住民は日常生活を通して放射線を被ばくしている。住民の被ばく線量を管理するために、年間の追加被ばく線量を1mSv/y以下にするという長期的目標が定められ、この目標を達成するために、測定値における0.23 Sv/hが除染実施の目安値とされた。本研究の目的は、この目安値に基づく除染作業の効果を明らかにし、今後の除染戦略における課題を抽出することである。本研究では確率論的なアプローチを用いて福島県内における屋内作業者、屋外作業者および自宅滞在者の年間の実効線量を評価した。本研究で用いた確率論的なモデルでは、生活パターンおよびCs-137の地表面濃度の変動を考慮した。評価の結果、福島県の全59の自治体のうち53の自治体における屋内作業者および自宅滞在者については、汚染発生から5年後の年間実効線量の95パーセンタイル値が1mSv/yを下回っていた(0.026-0.73mSv/y)。しかし、25の自治体の屋外作業者については1mSv/yを上回っていた(1.0-35mSv/y)。したがって屋内作業者および自宅滞在者に対しては目安値が有効であるが、屋外作業者にさらなる対策をすべきか否かを判断するためには、より現実的な仮定を用いた詳細な評価が必要であることがわかった。
Sv/hが除染実施の目安値とされた。本研究の目的は、この目安値に基づく除染作業の効果を明らかにし、今後の除染戦略における課題を抽出することである。本研究では確率論的なアプローチを用いて福島県内における屋内作業者、屋外作業者および自宅滞在者の年間の実効線量を評価した。本研究で用いた確率論的なモデルでは、生活パターンおよびCs-137の地表面濃度の変動を考慮した。評価の結果、福島県の全59の自治体のうち53の自治体における屋内作業者および自宅滞在者については、汚染発生から5年後の年間実効線量の95パーセンタイル値が1mSv/yを下回っていた(0.026-0.73mSv/y)。しかし、25の自治体の屋外作業者については1mSv/yを上回っていた(1.0-35mSv/y)。したがって屋内作業者および自宅滞在者に対しては目安値が有効であるが、屋外作業者にさらなる対策をすべきか否かを判断するためには、より現実的な仮定を用いた詳細な評価が必要であることがわかった。
 ray in aerial radiation monitoring
ray in aerial radiation monitoring石崎 梓; 眞田 幸尚; 森 愛理; 伊村 光生; 石田 睦司; 宗像 雅広
Remote Sensing, 8(11), p.892_1 - 892_12, 2016/11
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:25.09(Environmental Sciences)積雪がある場合に航空機モニタリングを実施する場合、積雪層による 線の減弱により、空間線量率が適切に換算できない。この問題を解決するため、積雪深情報を用いた補正方法を検討し、実際の測定結果に適用した。本研究では3種類の補正方法を検討し、補正効果を比較した。補正精度のさらなる向上にためには、積雪水量をより正確に推定する必要がある。
線の減弱により、空間線量率が適切に換算できない。この問題を解決するため、積雪深情報を用いた補正方法を検討し、実際の測定結果に適用した。本研究では3種類の補正方法を検討し、補正効果を比較した。補正精度のさらなる向上にためには、積雪水量をより正確に推定する必要がある。
眞田 幸尚; 宗像 雅広; 森 愛理; 石崎 梓; 嶋田 和真; 廣内 淳; 西澤 幸康; 卜部 嘉; 中西 千佳*; 山田 勉*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2016-016, 131 Pages, 2016/10
2011年3月11日に発生した東日本大震災による津波に起因した東京電力福島第一原子力発電所事故によって、大量の放射性物質が周辺に飛散した。事故直後より、放射線の分布を迅速かつ広範囲に測定する手法として、航空機等を用いた空からの測定方法が適用されている。ここでは、平成27年度に実施した福島第一原子力発電所周辺におけるモニタリング結果と川内原子力発電所周辺で行ったバックグラウンド線量率のモニタリング結果についてまとめた。
眞田 幸尚; 森 愛理; 石崎 梓; 宗像 雅広; 中山 真一; 西澤 幸康; 卜部 嘉; 中西 千佳; 山田 勉; 石田 睦司; et al.
JAEA-Research 2015-006, 81 Pages, 2015/07
2011年3月11日に発生した東日本大震災による津波に起因した東京電力福島第一原子力発電所事故によって、大量の放射性物質が周辺に飛散した。事故直後より、放射線の分布を迅速かつ広範囲に測定する手法として、航空機等を用いた空からの測定方法が適用されている。本報告書には、平成26年度に実施した航空機モニタリングの結果についてまとめた。
 SR study of impurity effects on the Cu-spin fluctuations in the overdoped regime of La
SR study of impurity effects on the Cu-spin fluctuations in the overdoped regime of La Sr
Sr Cu
Cu Zn
Zn O
O
Risdiana*; 足立 匡*; 沖 直樹*; 矢入 聡*; 田邊 洋一*; 大森 圭祐*; 鈴木 栄男*; 渡邊 功雄*; 幸田 章宏*; 髭本 亘; et al.
Physica C, 460-462(2), p.874 - 875, 2007/09
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:17.09(Physics, Applied)零磁場ミュオンスピン緩和測定によりLa Sr
Sr Cu
Cu Zn
Zn O
O (LSCO)の
(LSCO)の =0-0.10,
=0-0.10,  =0.30までのオーバードープ領域において動的ストライプ構造が安定化されるかを調べた。その結果、Znドープによる銅スピン揺らぎの低下は
=0.30までのオーバードープ領域において動的ストライプ構造が安定化されるかを調べた。その結果、Znドープによる銅スピン揺らぎの低下は の増加に伴い減少し、
の増加に伴い減少し、 =0.30で消滅することがわかった。ここからストライプピニングモデルは全超伝導領域で成り立ち、また、
=0.30で消滅することがわかった。ここからストライプピニングモデルは全超伝導領域で成り立ち、また、
 0.19近傍には量子臨界点は存在しないことが示唆される。
0.19近傍には量子臨界点は存在しないことが示唆される。
石崎 梓; 森 愛理; 川瀬 啓一; 加藤 貢; 渡邊 雅範; 青木 勲; 宗像 雅広
no journal, ,
After the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) accident in 2011, large amount of radionuclides were released to the environment. An exposed dose is one of the index for decision making of evacuations. To obtain the individual dose equivalent, the air dose rate and time to spend in an arbitrary place are necessary in each area where inhabitants stay. The place where inhabitants stay is categorized roughly according to indoor and outdoor in simple estimation of the exposed dose. It is known that the indoor air dose rate, Di, can be obtained by multiplying the outdoor air dose rate, Do, by reduction factor, RF. In case of wooden house, RF is reported as 0.4 which has the range from 0.2 to 0.5 (IAEA, 2000) and changes with floor area (Furuta and Takahashi, 2015) and indoor position; at the center of the house or by the window. However, the outdoor air-dose-rate distribution changes by the decontamination and the definition of RF become complicated because decontamination efficiency and the outdoor air-dose-rate differ from each location and materials. To evaluate the validity of RF represented as 0.4, in this study, we investigated indoor and outdoor air dose rate before and after decontamination for 17 Japanese wooden houses in four municipalities of Fukushima prefecture.