Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:93.49(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:79.22(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Yogo, Akifumi*; Lan, Z.*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; Mori, Takato*; Golovin, D.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Iwata, Natsumi*; et al.
Physical Review X, 13(1), p.011011_1 - 011011_12, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:93.39(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:96.99(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Yamada, Kunimi; Kusano, Tomohiro; Makuuchi, Ayumu; Takatori, Ryoichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Matsubara, Akihiro; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; et al.
JAEA-Research 2012-024, 132 Pages, 2012/09
This annual report documents the progress of R&D in the 2nd fiscal year during the JAEA 2nd Midterm Plan (FY 2010 - 2014) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planed framework is structured into the following categories: (1) development and systematization of investigation techniques for selecting suitable sites in geosphere stability, (2) development, application and verification of prediction models for evaluating the changes of geological environment in thermal, hydraulic, mechanical and geochemical conditions for a long period of time, and (3) development of new dating techniques for providing information about geologic history and the timing of geologic events. In this paper, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Yamada, Kunimi; Kusano, Tomohiro; Makuuchi, Ayumu; Takatori, Ryoichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Umeda, Koji
JAEA-Review 2012-024, 44 Pages, 2012/07
The concept of geological disposal of HLW in Japan is based on a multi-barrier system which combines a stable geological environment with a robust barrier system. Potential geological host formations and their surroundings are chosen, in particular, for their long-term stability, taking into account the fact that Japan is located in a tectonically active zone. This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of HLW in JAEA, in fiscal year 2012. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2012 are described in detail based on the outline of 5 years plan (fiscal years 2010-2014). In addition, the planed framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Nakamura, Kinya*; Ogata, Takanari*; Kikuchi, Hironobu; Iwai, Takashi; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Kato, Tetsuya*; Arai, Yasuo; Uozumi, Koichi*; Hijikata, Takatoshi*; Koyama, Tadafumi*; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 10(4), p.245 - 256, 2011/12
Sodium-bonded metallic fuel elements were fabricated for the first time in Japan for the irradiation test in the experimental fast test reactor JOYO. U-20Pu-10Zr fuel slugs of 200 mm in length and approximately 5 mm in diameter were fabricated in a small-scale injection casting furnace. Each fuel slug was loaded into the ferritic martenstic stainless steel (PNC-FMS) cladding tube with the sodium thermal bond, thermal insulator and reflector in a helium gas atmosphere glove box. After top-end plug welding to the cladding tube and heat treatment of the welding area, each fuel element was subjected to the sodium bonding process. After the inspection such as element length, gas plenum length and helium-leak tightness, six metallic fuel elements are transported to the JOYO site for the coming irradiation test.
 Bh and
Bh and  Db produced in the
Db produced in the  Cm +
Cm +  Na reaction
Na reactionMorita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sato, Nozomi*; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 78(6), p.064201_1 - 064201_6, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:78.22(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Decay properties of an isotope  Bh and its daughter nucleus
Bh and its daughter nucleus  Db produced by the
Db produced by the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5
Na,5 ) reaction were studied by using a gas-filled recoil separator coupled with a position-sensitive semiconductor detector.
) reaction were studied by using a gas-filled recoil separator coupled with a position-sensitive semiconductor detector.  Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the known nuclide,
Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the known nuclide,  Db. The obtained decay properties of
Db. The obtained decay properties of  Bh and
Bh and  Db are consistent with those observed in the
Db are consistent with those observed in the  113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of
113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of  113.
113.
Yogo, Akifumi*; Lan, Z.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Mori, Takato*; Wei, T.*; Fujioka, Shinsuke*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Lan, Z.*; Yogo, Akifumi*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*; Golovin, D.*; Mori, Takato*; Wei, T.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Lan, Z.*; Yogo, Akifumi*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Wei, T.*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Mirfayzi, R.*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Abe, Yuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Lan, Z.*; Wei, T.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Abe, Yuki*; Morace, A.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Lan, Z.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Wei, T.*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Abe, Yuki*; Mori, Takato*; et al.
no journal, ,
 Bh and its daughter nuclei
Bh and its daughter nucleiMorimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sato, Nozomi; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
A nuclide,  Bh, is the great-grand-daughter of
Bh, is the great-grand-daughter of  113 that is produced in the
113 that is produced in the  Bi +
Bi +  Zn reaction. The identification was based on a genetic link to the known daughter nucleus
Zn reaction. The identification was based on a genetic link to the known daughter nucleus  Db by alpha-decays. The main purpose of this work is to provide further confirmation of the production and identification of the isotope
Db by alpha-decays. The main purpose of this work is to provide further confirmation of the production and identification of the isotope  113. As a present result, a state in
113. As a present result, a state in  Bh, which decays by an alpha emission with the energies ranging from 9.05 to 9.23 MeV, feeds a state in
Bh, which decays by an alpha emission with the energies ranging from 9.05 to 9.23 MeV, feeds a state in  Db, which decays by alpha emission and by SF with a previously known half-life. The result provided a further confirmation of the production and identification of the isotope of the 113th element,
Db, which decays by alpha emission and by SF with a previously known half-life. The result provided a further confirmation of the production and identification of the isotope of the 113th element,  113, studied by a research group at RIKEN.
113, studied by a research group at RIKEN.
 113 produced by the
113 produced by the  Bi(
Bi( Zn,n)
Zn,n) 113 reaction
113 reactionMorimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sato, Nozomi; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We performed the experiment to synthesize an isotope of the element 113 produced by a  Bi(
Bi( Zn,n)
Zn,n) 113 reaction using a gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS) at RIKEN. Two decay chains were observed, and assigned to those originating from an isotope
113 reaction using a gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS) at RIKEN. Two decay chains were observed, and assigned to those originating from an isotope  113. Both chains were connected into the previously known decays of
113. Both chains were connected into the previously known decays of  Bh and
Bh and  Db via previously unknown decays of
Db via previously unknown decays of  113,
113, 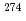 Rg, and
Rg, and 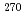 Mt. Although the
Mt. Although the  Bh was known nuclide, a number of atoms reported so far was limited. In order to study more precise decay property of the
Bh was known nuclide, a number of atoms reported so far was limited. In order to study more precise decay property of the  Bh, we performed the direct production of
Bh, we performed the direct production of  Bh by the
Bh by the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5n)
Na,5n) Bh reaction. In this experiment, the
Bh reaction. In this experiment, the  Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the nuclide,
Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the nuclide,  Db. The obtained decay properties of
Db. The obtained decay properties of  Bh and
Bh and  Db are consistent with those observed in the
Db are consistent with those observed in the  113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of
113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of  113.
113.
 Bh and its daughter nuclei
Bh and its daughter nucleiMorimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sato, Nozomi; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shimada, Katsuhiro; Terakado, Tsunehisa; Omori, Yoshikazu; Okano, Jun; Furukawa, Hiroshi; Shibata, Kazuyuki; Terakado, Hiroyuki; Shibata, Takatoshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurihara, Kenichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Lan, Z.*; Yogo, Akifumi*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Wei, T.*; Shi, B.*; Ishimoto, Takashi*; Golovin, D.*; Mori, Takato*; et al.
no journal, ,
Kusano, Tomohiro; Takatori, Ryoichi; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yogo, Akifumi*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*; Iwamoto, Akihumi*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Golovin, D.*; Mori, Takato*; Lan, Z.*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English