Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takeda, Tetsuaki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Aihara, Jun; Aoki, Takeshi; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ho, H. Q.; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Imai, Yoshiyuki; et al.
High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.5, 464 Pages, 2021/02
As a general overview of the research and development of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) in JAEA, this book describes the achievements by the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) on the designs, key component technologies such as fuel, reactor internals, high temperature components, etc., and operational experience such as rise-to-power tests, high temperature operation at 950 C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Fukaya, Yuji; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Goto, Minoru; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Kawakami, Satoru; Uesaka, Takahiro; Morita, Keisuke; Sano, Tadafumi*
KURNS Progress Report 2018, P. 148, 2019/08
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) started the Research and Development (R&D) to improve nuclear prediction techniques for High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGRs). The objectives are to introduce generalized bias factor method to avoid full mock-up experiment for the first commercial HTGR and to introduce reactor noise analysis to High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) experiment. To achieve the objectives, the reactor core of graphite moderation system named B7/4"G2/8"p8EUNU+3/8"p38EU(1) was newly composed in the B-rack of Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). The core plays a role of the reference core of the bias factor method, and the reactor noise was measured to develop the noise analysis scheme. In addition, training of operator of HTTR was also performed during the experiments.
Uosaki, Kohei*; Morita, Jun*; Katsuzaki, Tomoko*; Takakusagi, Satoru*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Mizuki, Junichiro; Kondo, Toshihiro*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 115(25), p.12471 - 12482, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:40.03(Chemistry, Physical)Ag/AgCl reaction at the Ag bilayer, which was underpotentially prepared on a Au(111) surface, was investigated using electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM), scanning tunneling microscopy (STM), surface X-ray scattering (SXS), and electrochemical techniques. When the potential was scanned positively from -200 mV, the Cl ion was adsorbed on the Au(111) electrode surface around 0 mV, and then the phase transition of the adsorbed Cl
ion was adsorbed on the Au(111) electrode surface around 0 mV, and then the phase transition of the adsorbed Cl ion layer from random orientation to (
ion layer from random orientation to (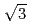

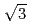 ) structure took place at around +130 mV. The Ag bilayer and Cl
) structure took place at around +130 mV. The Ag bilayer and Cl ions were oxidatively reacted to form the AgCl monolayer with (
ions were oxidatively reacted to form the AgCl monolayer with (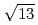

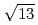 )
)  13.9
13.9 structure around +200 mV, accompanied with the formation of AgCl monocrystalline clusters on the AgCl monolayer surface. The structure of the AgCl monolayer on the Au(111) surface was changed from (
structure around +200 mV, accompanied with the formation of AgCl monocrystalline clusters on the AgCl monolayer surface. The structure of the AgCl monolayer on the Au(111) surface was changed from (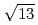

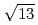 )R13.9
)R13.9 structure to (4
structure to (4 4) structure around +500 mV.
4) structure around +500 mV.
Motojima, Osamu*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Komori, Akio*; Oyabu, Nobuyoshi*; Muto, Takashi*; Kaneko, Osamu*; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Mito, Toshiyuki*; Ida, Katsumi*; Imagawa, Shinsaku*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(10), p.S668 - S676, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:73.64(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The performance of net-current free heliotron plasmas has been developed by findings of innovative operational scenarios in conjunction with an upgrade of the heating power and the pumping/fuelling capability in the Large Helical Device (LHD). Consequently, the operational regime has been extended, in particular, with regard to high density, long pulse length and high beta. Diversified studies in LHD have elucidated the advantages of net-current free heliotron plasmas. In particular, an internal diffusion barrier (IDB) by a combination of efficient pumping of the local island divertor function and core fuelling by pellet injection has realized a super dense core as high as 5 10
10 m
m , which stimulates an attractive super dense core reactor. Achievements of a volume averaged beta of 4.5% and a discharge duration of 54 min with a total input energy of 1.6 GJ (490 kW on average) are also highlighted. The progress of LHD experiments in these two years is overviewed by highlighting IDB, high-beta and long pulse.
, which stimulates an attractive super dense core reactor. Achievements of a volume averaged beta of 4.5% and a discharge duration of 54 min with a total input energy of 1.6 GJ (490 kW on average) are also highlighted. The progress of LHD experiments in these two years is overviewed by highlighting IDB, high-beta and long pulse.
Kondo, Toshihiro*; Morita, Jun*; Hanaoka, Kazuya*; Takakusagi, Satoru*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Mizuki, Junichiro; Uosaki, Kohei*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 111(35), p.13197 - 13204, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:84 Percentile:89.3(Chemistry, Physical)Potential-dependent surface structures of Au(111) and Au(100) single-crystal electrodes in a 50 mM H SO
SO solution were investigated at an atomic level using in situ surface X-ray scattering (SXS) techniques. It was confirmed that both the Au(111) and Au(100) surfaces were reconstructed with an attached submonolayer of an oxygen species, most probably water, at 0 V (vs Ag/AgCl). Results at +0.95 V supported a previously suggested model for both the Au(111) and the Au(100) electrodes that, based on infrared and scanning tunneling microscopy measurements, the surfaces were a (1
solution were investigated at an atomic level using in situ surface X-ray scattering (SXS) techniques. It was confirmed that both the Au(111) and Au(100) surfaces were reconstructed with an attached submonolayer of an oxygen species, most probably water, at 0 V (vs Ag/AgCl). Results at +0.95 V supported a previously suggested model for both the Au(111) and the Au(100) electrodes that, based on infrared and scanning tunneling microscopy measurements, the surfaces were a (1 1) structure with the coadsorbed sulfate anion and hydronium cation (H
1) structure with the coadsorbed sulfate anion and hydronium cation (H O
O ). At +1.05 V, where a small amount of an anodic current flowed, adsorption of a monolayer of oxygen species was observed on both surfaces.
). At +1.05 V, where a small amount of an anodic current flowed, adsorption of a monolayer of oxygen species was observed on both surfaces.
Motojima, Osamu*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Komori, Akio*; Oyabu, Nobuyoshi*; Kaneko, Osamu*; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Mito, Toshiyuki*; Muto, Takashi*; Ida, Katsumi*; Imagawa, Shinsaku*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2007/03
The performance of net-current free Heliotron plasmas has been developed by findings of innovative operational scenarios in conjunction with an upgrade of the heating power and the pumping/fueling capability in the Large Helical Device (LHD). Consequently, the operational regime has been extended, in particular, with regard to high density, long pulse length and high beta. Diversified studies in LHD have elucidated the advantages of net-current free heliotron plasmas. In particular, an Internal Diffusion Barrier (IDB) by combination of efficient pumping of the local island divertor function and core fueling by pellet injection has realized a super dense core as high as 5 10
10 m
m , which stimulates an attractive super dense core reactor. Achievements of a volume averaged beta of 4.5 % and a discharge duration of 54-min. with a total input energy of 1.6 GJ (490 kW in average) are also highlighted. The progress of LHD experiments in these two years is overviewed with highlighting IDB, high
, which stimulates an attractive super dense core reactor. Achievements of a volume averaged beta of 4.5 % and a discharge duration of 54-min. with a total input energy of 1.6 GJ (490 kW in average) are also highlighted. The progress of LHD experiments in these two years is overviewed with highlighting IDB, high  and long pulse.
and long pulse.
Tobita, Yoshiharu; Kondo, Satoru; Yamano, Hidemasa; Morita, Koji*; Maschek, W.*; Coste, P.*; Cadiou, T.*
Nuclear Technology, 153(3), p.245 - 255, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:76 Percentile:97.57(Nuclear Science & Technology)SIMMER-III is a general two-dimensional, three-velocity-field, multiphase, multicomponent, Eulerian, fluid-dynamics code coupled with a space-time and energy-dependent neutron transport kinetics model. The philosophy behind the SIMMER development was to generate a versatile and flexible tool, applicable for the safety analysis of various reactor types with different neutron spectra and coolants, up the new accelerator driven systems (ADS) for waste transmutation. SIMMER-III has proven especially well suited for fast spectrum systems as the LMFR, where it is one of the key codes for safety analysis, including its application within licensing procedures. To serve especially the last purpose, the code must be made sufficiently robust and reliable, and be tested and validated extensively. A comprehensive and systematic assessment program of the code has been conducted. This paper gives the major achievement of this assessment program. The code assessment program is an ongoing effort. Two major milestones have been achieved in the past by completing two assessment campaigns, Phase 1 and Phase 2. Phase 1 for fundamental code assessment of individual models; and Phase 2 for integral code assessment for key phenomena relevant to LMFR safety. Through this systematic code assessment program, comprehensive validation of the physical models has been conducted step-by-step. The assessment program has demonstrated that SIMMER-III is a state-of-the-art code with advanced models sufficiently flexible for simulating transient multiphase phenomena occurring during CDAs. In this paper we will concentrate on the specifics of the code, mainly reflected at its application to sodium experiments related to the safety of LMFR.
Kitabata, Takuya; Yamato, Yoshiaki; Hochin, Koji; Morita, Satoru
JNC TN4410 2003-011, 39 Pages, 2003/09
None
Yamano, Hidemasa; Fujita, Satoshi; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Kamiyama, Kenji; Kondo, Satoru; Morita, Koji*; Fischer, E. A.; Brear, D. J.; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Cao, X.; et al.
JNC TN9400 2003-071, 340 Pages, 2003/08
An advanced safety analysis computer code, SIMMER-III, has been developed to investigate postulated core disruptive accidents in liquid-metal fast reactors (LMFRs). SIMMER-III is a two-dimensional, three-velocity-field, multiphase, multicomponent, Eulerian, fluid-dynamics code coupled with a space-dependent neutron kinetics model. By completing and integrating all the physical models originally intended at the beginning of this code development project, SIMMER-III is now applicable to integral reactor calculations and other complex multiphase flow problems. A systematic code assessment program, conducted in collaboration with European research organizations, has shown that the advanced features of the code have resolved many of the limitations and problem areas in the previous SIMMER-II code. In this report, the models, numerical algorithms and code features of SIMMER-III Version 3.A are described along with detailed program description. Areas which require future model refinement are also discussed. SIMMER-III Version 3.A, a coupled fluid-dynamics and neutronics code system, is expected to significantly improve the flexibility and reliability of LMFR safety analyses.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Fujita, Satoshi; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Kondo, Satoru; Morita, Koji*; Sugaya, Masaaki*; Mizuno, Masahiro*; Hosono, Seigo*; Kondo, Teppei*
JNC TN9400 2003-070, 333 Pages, 2003/08
An advanced safety analysis computer code, SIMMER-III, has been developed at Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) to more realistically investigate postulated core disruptive accidents in liquid-metal fast reactors. The two-dimensional framework of SIMMER-III fluid dynamics has been extended to three dimensions to a new code, SIMMER-IV, which is currently (in Version 2) coupled with the three-dimensional neutronics model. With the completion of the SIMMER-IV version, the applicability of the code is further enhanced and the many of the known limitations in SIMMER-III are eliminated. The sample calculations demonstrated the general validity of SIMMER-IV. This report describes SIMMER-IV Version 2.A, by documenting the models, numerical algorithms and code features, along with the program description and input and output information to aid the users.
Morita, Koji*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Kondo, Satoru
JNC TN9400 2003-047, 116 Pages, 2003/07
The present report gives the SIMMER-III/IV heat- and mass-transfer model describing melting/freezing (M/F) and vaporization/condensation (V/C) processes in multiphase, multicomponent systems. The heat- and mass-transfer processes are modeled in consideration of their importance in and effects on the behavior of reactor-core materials in the fast reactor safety analysis. Applying equilibrium and non-equilibrium transfers generalizes the phase-transition processes except for the structure breakup transfer. The non-equilibrium phase-transition processes occurring at interfaces are described by the heat-transfer limited model, while the mass-diffusion limited model is employed to represent effects of noncondensable gases and multicomponent mixture on the V/C processes. The implicit solution algorithm of V/C calculation is tightly coupled with the analytic equation-of-state (EOS) model. The use of this approach successfully solves numerical problems, which were mainly introduced by thermody
Morita, Koji*; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Fukuda, Kenji*; Suzuki, Toru; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; kondo, Satoru
JNC TY9400 2002-014, 57 Pages, 2002/05
None
Morita, Koji*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; kondo, Satoru
JNC TN9400 2001-074, 108 Pages, 2001/08
The present report gives the SIMMER-IIl heat- and mass-transfer model describing melting/freezing and vaporization/condensation processes in multiphase, multicomponent systems, The heat- and mass-transfer processes are modeled in consideration of their importance in and effects on the behavior of reactor-core materials in the fast reactor safety analysis. Applying equilibrium and non-equilibrium transfers generalizes the phase-transition processes except for the structure breakup transfer. The non-equilibrium transfers occurring at interfases were formulated on the basis of the heat-transfer-limited model. The implicit solution algorithm for basic vaporization/condensation equations is tightly coupled with the analytic equation-of-state (EOS) model. The use of this approach successfully solves numerical problems encountered in the previous codes, which were mainly introduced by thermodynamic inconsistencies in EOS.
kondo, Satoru; Yamano, Hidemasa; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Fujita, Satoshi; Morita, Koji*; Mizuno, Masahiro*; *
JNC TN9400 2001-003, 307 Pages, 2000/11
An advanced safety analysis computer code, SIMMER-III, has been developed at Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) to more realistically investigate postulated core disruptive accidents in liquid-metal fast reactors. The two-dimensional framework of SIMMER-III fluid dynamics has been extended to three dimensions to a new code, SIMMER-IV, which is currently (in Version 1) coupled with the existing two-dimensional neutronics model. With the completion of the first SIMMER-IV version, the applicability of the code is further enhanced and the many of the known limitations in SIMMER-III are eliminated. The sample calculations demonstrated the general validity of SIMMER-IV. This report describes SIMMER-IV version 1.B, by documenting the models, numerical algorithms and code features, along with the program description and input and output information to aid the users. Further extension of the code is planned to couple the three-dimensional neutronics in the future.
Morita, Koji*; *; Fukuda, Kenji*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Suzuki, Toru; kondo, Satoru
JNC TY9400 2000-013, 60 Pages, 2000/04
no abstracts in English
Morita, Koji; Tobita, Yoshiharu; kondo, Satoru; E.A.Fischer*
JNC TN9400 2000-005, 57 Pages, 1999/05
An improved analytic equation-of-state (EOS) model using flexible thermodynamic functions is developed for a reactor safety analysis code, SIMMER-III. The present EOS model is designed to have adequate accuracy in describing thermodynamic properties of reactor-core materials over wide temperature and pressure ranges and to consistently satisfy basic thermodynamic relationships without deterioration of the computing efficiency. The fluid-dynamic algorithm for pressure iteration consistently coupled with the EOS model is also described in the present report. The EOS data of the basic core materials, uranium dioxide, mixed-oxide fuel, stainless steel, and sodium, are developed up to the critical point by compiling the most up-to-date and reliable sources using basic thermodynamic relationships. The thermodynamic consistency and accuracy of the evaluated EOS data are also discussed by comparison with the available sources.
Morita, Koji; Tobita, Yoshiharu; kondo, Satoru; E.A.Fischer*
JNC TN9400 2000-004, 38 Pages, 1999/05
An analytic thermophysical property model using general function forms is developed for a reactor safety analysis code, SIMMER-III. The function forms arc designed to represent correct behavior of properties of reactor-core materials over wide temperature ranges, especially for the thermal conductivity and the viscosity near the critical point. The most up-to-date and reliable sources for uranium dioxide, mixed-oxide fuel, stainless stee1, and sodium available at present are used to determine parameters in the proposed functions. This model is also designed to be consistent with a SIMMER-III model on thermodynamic properties and equations of state for reactor-corc materials.
Niwa, Hajime; Kawata, Norio; Ieda, Yoshiaki; Sato, Ikken; Ohno, Shuji; Uto, Nariaki; Miyahara, Shinya; Kondo, Satoru; Kamide, Hideki; Yamaguchi, Akira; et al.
PNC TN9410 94-154, 317 Pages, 1995/03
None
Simanullang, I. L.*; Fukuhara, Katsuki*; Morita, Keisuke; Fukaya, Yuji; Ho, H. Q.; Nagasumi, Satoru; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Fujimoto, Nozomu*
no journal, ,