Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwasawa, Yuzuru; Matsumoto, Toshinori; Moriyama, Kiyofumi*
JAEA-Data/Code 2025-001, 199 Pages, 2025/06
A steam explosion is defined as a phenomenon that occurs when a hot liquid comes into contact with a low-temperature cold liquid with volatile properties. The rapid transfer of heat from the hot liquid to the cold liquid results in a chain reaction of the explosive vaporization of the cold liquid and fine fragmentation of the hot liquid. The explosive vaporization of the cold liquid initiates the propagation of shock waves in the cold liquid. The expansion of the hot and cold liquid mixture exerts mechanical forces on the surrounding structures. In severe accidents of light water reactors, the molten core (melt) is displaced into the coolant water, resulting in fuel-coolant interactions (FCIs). The explosive FCI, referred to as a steam explosion, has been identified as a significant safety assessment issue as it can compromise the integrity of the primary containment vessel. The JASMINE code is an analytical tool developed to evaluate the mechanical forces imposed by steam explosions in nuclear reactors. It performs numerical simulations of steam explosions in a mechanistic manner. The present report describes modeling concepts, basic equations, numerical solutions, and example simulations, as well as instructions for input preparation, code execution, and the use of supporting tools for practical purpose. The present report is the updated version of the "Steam Explosion Simulation Code JASMINE v.3 User's Guide, JAEA-Data/ Code 2008-014". The present report was compiled and updated based on the latest version of the code, JASMINE 3.3c, with corrections for minor errors of the distributed code JASMINE 3.3b, and conformance to recently widely used compilers on UNIX-like environments such as the GNU compiler. The numerical simulations described in the present report were obtained using the latest version JASMINE 3.3c. The latest parameter adjustment method for a model parameter proposed by the previous study is employed to conduct the numerical simulations.
Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Moriyama, Kiyofumi*; Maruyama, Yu; Yonomoto, Taisuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 49(8), p.768 - 781, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.88(Nuclear Science & Technology)A simple evaluation method for the analysis of thermal-hydraulic transients in reactor pressure vessel (RPV) and primary containment vessel (PCV) is proposed to support understanding the accident behaviors of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (NPP). Since most of the measurements of the plants were unavailable especially in the early stage of the accident, and the accessibility to the plants has been limited by radiation, analytical investigation for the plant is urgently required to understand the plant conditions such as the magnitude of the damages. In order to provide easy-to-use technical tools to support the analytical investigation, we developed a simplified analysis code, named "HOTCB", based on total mass and heat balances in a lamped parameter system. The HOTCB code has capabilities to treat two-phase fluid including water, steam, and non-condensable gas in a wide range of temperature up to highly superheated conditions, and to consider heat structures, i.e. heat capacities and heat transfer to the fluid. The code was provided to Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO) and was practically used for the analysis on the accident. This paper provides the details of the code and simulations of Unit 1 and Unit 2 reactors of Fukushima Dai-ichi NPP as examples to show the usefulness of the code.
Hirano, Masashi; Yonomoto, Taisuke; Ishigaki, Masahiro; Watanabe, Norio; Maruyama, Yu; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Watanabe, Tadashi; Moriyama, Kiyofumi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 49(1), p.1 - 17, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:117 Percentile:93.06(Nuclear Science & Technology)An unprecedented earthquake and tsunami struck the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plants on 11 March 2011. Although extensive efforts have been continuing on investigations into the causes and consequences of the accident, and the Japanese Government has presented a comprehensive report on the accident in the IAEA Ministerial Conference held in June 2011, there is still much to be clarified on what happened during the accident and why. This article aims at identifying what should be clarified further about the progression of the accident at Units 1-3 through the review and analysis of information released from Tokyo Electric Power Company and government authorities. It also discusses the safety issues raised by the accident based on the insights gained, in order to contribute to establishing a new framework that pursues continuous improvement toward the highest standards of safety that can reasonably be achieved.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Chiba, Noriaki; Maruyama, Yu; Nakamura, Hideo; Watanabe, Atsushi*
JAEA-Research 2011-016, 125 Pages, 2011/06
The volatile iodine production due to radiation chemical effects in the containment vessel of light water reactors (LWRs) during severe accidents was investigated by experiments in small scale and with well controlled conditions. Cesium iodide solutions, 10 M, labeled with
M, labeled with  I, at controlled pH by boric acid-sodium hydroxide buffer, were
I, at controlled pH by boric acid-sodium hydroxide buffer, were  -irradiated and swept with a constant gas flow rate. The gaseous iodine released from the solution was collected by species selective filters and quantified separately for I
-irradiated and swept with a constant gas flow rate. The gaseous iodine released from the solution was collected by species selective filters and quantified separately for I and organic iodines. The influences of pH, temperature, inorganic and organic impurities, oxygen and hydrogen concentrations in the cover gas on the iodine release behavior were examined. Data including time dependent gaseous iodine release fractions, comparison of the final iodine release fractions in terms of the parameter effects, as well as the initial, boundary and interface conditions necessary for simulating the experiments by computer codes are provided.
and organic iodines. The influences of pH, temperature, inorganic and organic impurities, oxygen and hydrogen concentrations in the cover gas on the iodine release behavior were examined. Data including time dependent gaseous iodine release fractions, comparison of the final iodine release fractions in terms of the parameter effects, as well as the initial, boundary and interface conditions necessary for simulating the experiments by computer codes are provided.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Chiba, Noriaki; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Maruyama, Yu; Nakamura, Hideo; Watanabe, Atsushi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(6), p.885 - 891, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The leach of remaining solvent in an epoxy paint coating when it is submerged in water was experimentally studied. A leach kinetics model considering the equilibrium of the solvent concentration in the paint matrix and in water was developed. Three model parameters, equilibrium constant  , leaching rate
, leaching rate 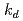 , and initial concentration of the solvent in the paint
, and initial concentration of the solvent in the paint 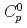 were evaluated based on the experimental results, and empirical correlation equations for them were obtained. The model showed good qualitative and quantitative agreement with the observed evolution of the leached solvent mass in the present experiment. Also the model showed consistency with experimental data by Ball et al. (2003).
were evaluated based on the experimental results, and empirical correlation equations for them were obtained. The model showed good qualitative and quantitative agreement with the observed evolution of the leached solvent mass in the present experiment. Also the model showed consistency with experimental data by Ball et al. (2003).
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Maruyama, Yu; Nakamura, Hideo
JAEA-Data/Code 2010-034, 62 Pages, 2011/03
An iodine chemistry simulation tool, Kiche, was developed for analyses of chemical kinetics relevant to iodine volatilization in the containment vessel of light water reactors (LWRs) during a severe accident. It consists of a Fortran code to solve chemical kinetics models, reaction databases written in plain text format, and peripheral tools to convert the reaction databases into Fortran codes. Potential advantages of Kiche are the text format reaction database separated from the code that provides flexibility of the chemistry model, and being a Fortran code relatively easily coupled with other codes such as severe accident analysis codes. This document describes the model, solution method, code structure, and examples of application for simulation of experiments. The appendixes give practical information for the usage of Kiche system.
Ishikawa, Jun; Moriyama, Kiyofumi
JAEA-Research 2010-051, 42 Pages, 2011/02
At the late phase of severe accident (SA), there is a possibility that gaseous iodine species which dissolved in the pool water at the early phase of accident are released to the containment (CV) atmosphere due to radiation chemical reactions. In order to evaluate the influence on the CV source terms considering iodine chemistry, a coupling analysis method of SA analysis code THALES2 and iodine chemistry analysis code Kiche was developed. The evaluation of thermal-hydraulics conditions and source term in the CV at the late phase of severe accident were conducted for 4 accident scenarios of BWR4/Mark-I by using this coupling method. As for the re-vaporization of iodine to the CV atmosphere, the influence of pH is larger than that of difference of accident sequences. Total release fractions of I to the CV atmosphere at 50 h for pH = 5, 7 and 9 were 10
to the CV atmosphere at 50 h for pH = 5, 7 and 9 were 10 -10
-10 , 10
, 10 and 10
and 10 for the initial core inventory. The lower the pH was, the larger the release fraction of I
for the initial core inventory. The lower the pH was, the larger the release fraction of I was.
was.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Nakamura, Hideo; Nakamura, Koichi*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 103(1), p.463 - 464, 2010/11
A computer code, Kiche, was developed at JAEA for the evaluation of the influence of radiolytic volatilization of iodine in the containment of light water reactors during an accident. It solves a chemical kinetics model including water radiolysis, reactions among iodine species, water radiolysis products, and organic compounds. The reactions and rate constants were collected from the literature. The organic iodine production model of Kiche, which was initially based on LIRIC model, was not applicable to low oxygen concentration conditions like inserted containments of BWRs. We modified the model by considering different reaction paths according to the availability of oxygen. The modified model showed improved agreement with our experimental data with various concentrations of organic impurity and oxygen.
 -irradiated aqueous CsI solution and influence of oxygen and Methyl Isobutyl Ketone (MIBK)
-irradiated aqueous CsI solution and influence of oxygen and Methyl Isobutyl Ketone (MIBK)Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Chiba, Noriaki; Hirayama, Fumio*; Maruyama, Yu; Nakamura, Hideo; Watanabe, Atsushi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 47(3), p.229 - 237, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:75.48(Nuclear Science & Technology)The volatile iodine production due to radiation chemistry is an important uncertainty source in the source term evaluation for LWRs. The gaseous release of molecular iodine and organic iodine from  -irradiated (
-irradiated (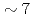 kGy/h, 2h) cesium iodide aqueous solution (1E-4M) containing methyl-isobuthyl-ketone (MIBK) was measured. The solution was buffered at pH
kGy/h, 2h) cesium iodide aqueous solution (1E-4M) containing methyl-isobuthyl-ketone (MIBK) was measured. The solution was buffered at pH 7. The concentration of MIBK (up to 1E-3M) and oxygen were changed as parameters. The total iodine release fraction and the fraction released as organic iodine were 2-47% and 0.02-1.5%, respectively, at the end of the irradiation. With the same cover gas condition, the total iodine release decreased and the organic iodine release increased when the MIBK concentration increased. This behavior can be explained by branching of the reaction path of organic degradation depending on availability of dissolved oxygen and competition between iodine and organic compounds on the consumption of radicals.
7. The concentration of MIBK (up to 1E-3M) and oxygen were changed as parameters. The total iodine release fraction and the fraction released as organic iodine were 2-47% and 0.02-1.5%, respectively, at the end of the irradiation. With the same cover gas condition, the total iodine release decreased and the organic iodine release increased when the MIBK concentration increased. This behavior can be explained by branching of the reaction path of organic degradation depending on availability of dissolved oxygen and competition between iodine and organic compounds on the consumption of radicals.
Sagawa, Jun; Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Nishikizawa, Tomotoshi; Nakamura, Hideo
JAEA-Technology 2008-059, 43 Pages, 2008/09
Electro-chemical electrodes including pH probes, ion-selective electrodes (ISEs) etc. generally have very high output impedances. In order to measure their outputs with generic measurement devices like data recorders, we need impedance conversion amplifiers that convert the ultra-high impedance signals of the probes into low-impedance input signals for ordinary measurement devices. Although specially designed measurement devices for the electro-chemical probes are commercially available, there are very few products that can be applied for multi-channel time series data acquisition. Thus, we designed and fabricated an ultra-high impedance low-offset amplifier fit for this purpose. The primary specification of the amplifier is, input impedance  10G
10G , input range
, input range  1V, gain 1
1V, gain 1 20, response time about 1s, output range
20, response time about 1s, output range  10V, output impedance 50
10V, output impedance 50 , and it has 5 independent channels. This report describes the originally developed design, selection of the element devices, test on the circuit characteristics, and instruction for fabrication.
, and it has 5 independent channels. This report describes the originally developed design, selection of the element devices, test on the circuit characteristics, and instruction for fabrication.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Maruyama, Yu; Nakamura, Hideo
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-014, 118 Pages, 2008/07
A steam explosion occurs when hot liquid contacts with cold volatile liquid. In this phenomenon, fine fragmentation of the hot liquid causes extremely rapid heat transfer from the hot liquid to the cold volatile liquid, and explosive vaporization, bringing shock waves and destructive forces. The steam explosion due to the contact of the molten core material and coolant water during severe accidents of light water reactors has been regarded as a potential threat to the integrity of the containment vessel. We developed a mechanistic steam explosion simulation code, JASMINE, that is applicable to plant scale assessment of the steam explosion loads. This document, as a manual for users of JASMINE code, describes the models, numerical solution methods, and also some verification and example calculations, as well as practical instructions for input preparation and usage of the code.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Takagi, Seiji*; Muramatsu, Ken; Nakamura, Hideo; Maruyama, Yu
JAEA-Research 2007-072, 54 Pages, 2007/11
The containment failure probability due to ex-vessel steam explosions was evaluated for BWR and PWR model plants. A stratified Monte Carlo technique (Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS)) was applied for the evaluation of steam explosion loads, in which a steam explosion simulation code JASMINE was used as a physics model. The evaluation was made for three scenarios: a steam explosion in the pedestal area or in the suppression pool of a BWR model plant with Mark-II containment, and in the reactor cavity of a PWR model plant. The scenario connecting the generation of steam explosion loads and the containment failure was assumed to be displacement of the reactor vessel and pipings, and failure at the penetration in the containment boundary. We evaluated the conditional containment failure probability (CCFP) based on the preconditions of failure of molten core retention within the reactor vessel, relocation of the core melt into the water pool without significant interference, and a strong triggering at the time of maximum premixed mass. The obtained mean and median values of the CCPF were 6.4E-2 (mean) and 3.9E-2 (median) for the BWR suppression pool case, 2.2E-3 (mean) and 2.8E-10 (median) for the BWR pedestal case, and 6.8E-2 (mean) and 1.4E-2 (median) for the PWR cavity case. The evaluation of CCFPs on the basis of core damage needs consideration of probabilities for the above-mentioned preconditions. Thus, the CCFPs per core damage should be lower than the values given above. The specific values of the probability were most dependent on the assumed range of melt flow rate and fragility curve that involved conservatism and uncertainty due to simplified scenarios and limited information. Additionally, the source term significance of the fine particles generated by steam explosions was discussed.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Nakamura, Hideo; Maruyama, Yu*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 236(19-21), p.2010 - 2025, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:82.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)A computer code JASMINE-pre was developed for the prediction of premixing conditions of fuel-coolant interactions and the debris bed formation behavior relevant to severe accidents of light water reactors. JASMINE-pre consists of three melt component models: melt jet, melt particles and melt pool, coupled with a two-phase flow model derived from the ACE-3D code developed at JAERI. Simulations of the FARO corium quenching experiments with a saturated water pool and with a subcooled water pool were performed with JASMINE-pre and 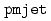 . JASMINE-pre reproduced the pressurization and fragmentation behaviors observed in the experiments with a reasonable accuracy. The results by pmjet showed qualitatively the same trend with JASMINE-pre in the fragmentation behavior.
. JASMINE-pre reproduced the pressurization and fragmentation behaviors observed in the experiments with a reasonable accuracy. The results by pmjet showed qualitatively the same trend with JASMINE-pre in the fragmentation behavior.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Takagi, Seiji*; Muramatsu, Ken; Nakamura, Hideo; Maruyama, Yu*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 43(7), p.774 - 784, 2006/07
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:74.77(Nuclear Science & Technology)The containment failure probability due to ex-vessel steam explosions was evaluated for Japanese BWR and PWR model plants. A stratified Monte Carlo technique (Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS)) was applied for the evaluation of steam explosion loads, in which a steam explosion simulation code JASMINE was used as a physics model. The evaluation was made for three scenarios: a steam explosion in the pedestal area or in the suppression pool of a BWR model plant with a Mark-II containment, and in the reactor cavity of a PWR model plant. The scenario connecting the generation of steam explosion loads and the containment failure was assumed to be displacement of the reactor vessel and pipings, and failure at the penetration in the containment boundary. The mean conditional containment failure probabilities (CCFPs) were 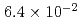 (mean) and
(mean) and 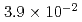 (median) for the BWR suppression pool case,
(median) for the BWR suppression pool case, 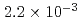 (mean) and
(mean) and 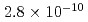 (median) for the BWR pedestal case, and
(median) for the BWR pedestal case, and 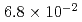 (mean) and
(mean) and 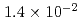 (median) for the PWR cavity case. Note that the specific values of the probability are most dependent on assumed range of melt flow rates and on fragility curves that involve conservatism and uncertainty due to simplified scenarios and limited information. Also, note that these CCFPs were based on the preconditions of failure of accident termination within the reactor vessel, relocation of the core melt into the water pool at the place in question without significant interference, and a strong triggering ofa steam explosion with maximized premixed mass for the given premixing condition. The evaluation of CCFPs on the basis of core damage needs consideration of probabilities for these preconditions. Thus, the CCFPs per core damage should be lower than the values given above.
(median) for the PWR cavity case. Note that the specific values of the probability are most dependent on assumed range of melt flow rates and on fragility curves that involve conservatism and uncertainty due to simplified scenarios and limited information. Also, note that these CCFPs were based on the preconditions of failure of accident termination within the reactor vessel, relocation of the core melt into the water pool at the place in question without significant interference, and a strong triggering ofa steam explosion with maximized premixed mass for the given premixing condition. The evaluation of CCFPs on the basis of core damage needs consideration of probabilities for these preconditions. Thus, the CCFPs per core damage should be lower than the values given above.
 -mode containment failure probability assessment for BWR by ROAAM application
-mode containment failure probability assessment for BWR by ROAAM applicationMayumi, Masami; Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Muramatsu, Ken
JAEA-Research 2006-022, 94 Pages, 2006/03
In-vessel steam explosion-induced containment failure (alpha-mode containment failure) following core melt in nuclear power plants has a potential of large early release of radioactive materials. Therefore, it is an important issue to estimate the outcome frequency with the involved uncertainty in phenomena in PSA. There has been a methodology, called as ROAAM, proposed for resolving this type of issue. In this paper, application method based on ROAAM is studied and the estimation is carried out by this method for alpha-mode containment failure in BWR, which has less studied until now. This analysis verifies the practicability and capability of supplying the process parameter distributions. Analysis results show 95, 97.5 percentile, and expected (average) values to be 3.2 10
10 , 0.03, and 0.012 respectively for containment failure probability (conditional on explosion triggering). In addition, CCDF curves of various process parameters give a good representation for a grasp of whole event.
, 0.03, and 0.012 respectively for containment failure probability (conditional on explosion triggering). In addition, CCDF curves of various process parameters give a good representation for a grasp of whole event.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of Technical Meeting on Severe Accident and Accident Management (CD-ROM), 18 Pages, 2006/03
The steam explosion is one of the phenomena that may threat theintegrity of containment vessel during severe accidents of light waterreactors (LWRs), and has been drawing attention in the field of nuclear safety as well as in many other industrial fields for decades. We developed a code, JASMINE, for the assessment of steam explosion impacts on the LWR safety, and applied the code for simulation of steam explosion experiments and also reactor scale parametric studies. Based on the analytical experiences with JASMINE code and aconsideration on the inter-relation among various fundamental aspects in the steam explosion process, we developed a technical view on aproper application of mechanistic steam explosion analysis codes for plant analysis.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Maruyama, Yu; Usami, Tsutomu*; Nakamura, Hideo
JAERI-Research 2005-017, 173 Pages, 2005/08
A series of experiments on the break-up of high temperature oxide and steel melt jets in a water pool was conducted. The objective was to obtain data for the jet break-up length and size distribution of the droplets produced by the jet break-up, and information on the influence of material properties. Also, we tried to obtain additional information giving a clue to the mechanism governing the melt jet break-up, such as flow intensity of the steam column surrounding the melt jet, and its relation with the droplet size. In the experiments, zirconia-alumina mixture and stainless steel melt jets with diameter  17mm and velocity
17mm and velocity  7.8m/s at the water surface were dropped into a deep (2.1m) or shallow (0.6m) water pool with various subcool. From the results of the present experiments and also by referring other experimental data from literature, we obtained empirical correlation equations for the jet break-up length, the fraction of jet broken-up in a shallow pool where the jet was not completely broken-up, and the droplet size.
7.8m/s at the water surface were dropped into a deep (2.1m) or shallow (0.6m) water pool with various subcool. From the results of the present experiments and also by referring other experimental data from literature, we obtained empirical correlation equations for the jet break-up length, the fraction of jet broken-up in a shallow pool where the jet was not completely broken-up, and the droplet size.
Usami, Tsutomu; Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Nishikizawa, Tomotoshi; Nakamura, Hideo
JAERI-Tech 2005-028, 37 Pages, 2005/05
The steam explosion during a severe accident in a light water reactor, which may occur by the contact of molten core and coolant, has been known as a potential threat on the integrity of the containment vessel, and has been studied in the nuclear safety research field. Prediction of the intensity of steam explosions needs an understanding of the initial premixture. However, visual observation of the premixture in experiments is usually difficult due to the vapor generation. Thus, we investigated the possibility of a high-speed X-ray visualization with a 4500 f/s high speed video camera with an image-intensifier and three kinds of scintillator materials: CdWO , ZnS(Ag) and CsI(Tl). A modeled premixture consisted of metal objects and bubbles in a water vessel was used. The test result showed that the CsI(Tl) scintillator gave the best image quality among the three and the high-speed visualization at 4500 f/s was possible, though in the still picture which carried out one of the recorded picture, the picture became indistinct.
, ZnS(Ag) and CsI(Tl). A modeled premixture consisted of metal objects and bubbles in a water vessel was used. The test result showed that the CsI(Tl) scintillator gave the best image quality among the three and the high-speed visualization at 4500 f/s was possible, though in the still picture which carried out one of the recorded picture, the picture became indistinct.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Takagi, Seiji; Muramatsu, Ken; Nakamura, Hideo; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 2005 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '05) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2005/05
The containment failure probability due to ex-vessel steam explosions were evaluated for a BWR Mk-II model plant. The evaluation was made for two scenarios: a steam explosion in the pedestal area, or in the suppression pool. A probabilistic approach, Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS), was applied for the evaluation of steam explosion loads, in which a steam explosion simulation code JASMINE was used as a physics model. The fragility curves connecting the steam explosion loads and containment failure were developed based on simplified assumptions on the containment failure scenarios. The mean conditional probabilities of containment failure per occurrence of a steam explosion were 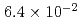 for suppression pool and
for suppression pool and 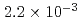 for pedestal area. Note that the results depend on the assumed range of input parameters and fragility curves that involve conservatism and simplification.
for pedestal area. Note that the results depend on the assumed range of input parameters and fragility curves that involve conservatism and simplification.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Nakamura, Hideo; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics, Operations and Safety (NUTHOS-6) (CD-ROM), 18 Pages, 2004/10
A steam explosion simulation code JASMINE is under development at JAERI for the assessment of steam explosion impacts on the integrity of containment vessel during severe accidents in light water reactors. Selected alumina and corium steam explosion experiments, KROTOS-44, 42, 37 and FARO-L33 were simulated with JASMINE code. The experimentally observed difference of the steam explosion intensity with the two materials, alumina and corium, was reproduced in the simulations without changing the model parameters related to the fine fragmentation process, but based on the difference in the premixing behavior predicted by the simulations. The simulation of corium experiments showed more fraction of the melt droplets frozen during premixing, as well as more void fraction, and those two points were likely to be the primary reasons of weak interactions in corium experiments.