Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Kurihara, Yuichi*; Nagata, Kojiro*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Higaki, Shogo*; Kobayashi, Toru; Tanida, Hajime; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; et al.
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 661, p.317 - 332, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:79.28(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 molecular dynamics simulations reveal the hydration structure of the radium(II) ion
molecular dynamics simulations reveal the hydration structure of the radium(II) ionYamaguchi, Akiko; Nagata, Kojiro*; Kobayashi, Keita; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kobayashi, Toru; Tanida, Hajime; Shimojo, Kojiro; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Kaneta, Yui; Matsuda, Shohei; et al.
iScience (Internet), 25(8), p.104763_1 - 104763_12, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:68.88(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Nagata, Kojiro*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kobayashi, Keita; Kobayashi, Toru; Shimojo, Kojiro; Tanida, Hajime; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Kaneta, Yui; Matsuda, Shohei; et al.
Hosha Kagaku, (45), p.28 - 30, 2022/03
no abstracts in English
Asakura, Kazuki; Shimomura, Yusuke; Donomae, Yasushi; Abe, Kazuyuki; Kitamura, Ryoichi; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki; Takamatsu, Misao; Sakamoto, Naoki; Isozaki, Ryosuke; Onishi, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-020, 42 Pages, 2021/10
The disposal of radioactive waste from the research facility need to calculate from the radioactivity concentration that based on variously nuclear fuels and materials. In Japan Atomic Energy Agency Oarai Research and Development Institute, the study on considering disposal is being advanced among the facilities which generate radioactive waste as well as the facilities which process radioactive waste. This report summarizes a study result in FY2020 about the evaluation method to determine the radioactivity concentration in radioactive waste on Oarai Research and Development Institute.
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Shibata, Akira; Nagata, Hiroshi; Kimura, Nobuaki; Otsuka, Noriaki; Saito, Takashi; Nakamura, Jinichi; Matsui, Yoshinori; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Proceedings of 3rd Asian Symposium on Material Testing Reactors (ASMTR 2013), p.52 - 58, 2013/11
In-pile instrumentation systems in present LWR's are indispensable to monitor all situations during reactor operation and reactor shut down. However, those systems did not work sufficiently under the conditions like as the severe accident at the Fukushima Dai-Ichi Nuclear Power Station. Therefore, based on the irradiation measurement technique of experiences accumulated in JMTR, the developments of reactor instrumentation systems to prevent severe core damage accident in advance have been started. The development objects are four instrumentation systems, which are a solid electrolysis type hydrogen concentration sensor, a water gauge of thermocouple type equipped with the heater, a  -ray detector of self-powered type SPGD, and an image analysis system of Cherenkov light for quantification of in-reactor information by CCD cameras. After the developments, the in-pile verification tests of four instrumentation systems are planned at the JMTR.
-ray detector of self-powered type SPGD, and an image analysis system of Cherenkov light for quantification of in-reactor information by CCD cameras. After the developments, the in-pile verification tests of four instrumentation systems are planned at the JMTR.
 Fe
Fe O
O (R=Yb and Lu)
(R=Yb and Lu)Yoshii, Kenji; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Fukuyama, Ryota*; Nagata, Tomoko*; Kambe, Takashi*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Mori, Shigeo*
Solid State Communications, 173, p.34 - 37, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.06(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have investigated the magnetic properties of R Fe
Fe O
O (R=Yb and Lu), which belongs to the homologous family of electronic ferroelectric RFe
(R=Yb and Lu), which belongs to the homologous family of electronic ferroelectric RFe O
O . Magnetization measurements show ferrimagnetic ordering at the Neel temperature (T
. Magnetization measurements show ferrimagnetic ordering at the Neel temperature (T ) of about 270 K, which is slightly higher than that of RFe
) of about 270 K, which is slightly higher than that of RFe O
O (T
(T about 230-250 K). Observation of spin glass and exchange bias shows a coexistence of ferromagnetic and antiferromagneticinteractions, similarly to RFe
about 230-250 K). Observation of spin glass and exchange bias shows a coexistence of ferromagnetic and antiferromagneticinteractions, similarly to RFe O
O . This situation gives rise to a complex magnetic change and a broad peak of magnetic entropy change. Some characteristics, such as refrigeration temperatures higher than in RFe
. This situation gives rise to a complex magnetic change and a broad peak of magnetic entropy change. Some characteristics, such as refrigeration temperatures higher than in RFe O
O , seem to offer a possibility of this system to applications.
, seem to offer a possibility of this system to applications.
 O
O
Kambe, Takashi*; Fukada, Yukimasa*; Kano, Jun*; Nagata, Tomoko*; Okazaki, Hiroyuki*; Yokoya, Takayoshi*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Ikeda, Naoshi*
Physical Review Letters, 110(11), p.117602_1 - 117602_5, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:75.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Shibata, Akira; Nagata, Hiroshi; Miura, Kuniaki*; Sano, Tadafumi*; Kimura, Nobuaki; Otsuka, Noriaki; Saito, Takashi; Nakamura, Jinichi; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Proceedings of 5th International Symposium on Material Testing Reactors (ISMTR-5) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2012/10
In-pile instrumentation systems in present LWR's are indispensable to monitor all situations during reactor operation and reactor shut down. However, those systems did not work sufficiently under the conditions of the severe accident at the Fukushima Dai-ichi (F1) Nuclear Power Plant. Based on instrumentation and irradiation experiences accumulated in JMTR, the developments of reactor instrumentation systems to prevent severe core damage accident in advance have been started. The development objects are water level gauge utilizing  heating, self-powered
heating, self-powered  -ray detector, hydrogen concentration gauge, and analysis system for imaging and quantification of in-reactor information using Cherenkov light.
-ray detector, hydrogen concentration gauge, and analysis system for imaging and quantification of in-reactor information using Cherenkov light.
 Fe
Fe O
O (
( =Y, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu and In)
=Y, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu and In)Yoshii, Kenji; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Nishihata, Yasuo; Maeda, Daisuke*; Fukuyama, Ryota*; Nagata, Tomoko*; Kano, Jun*; Kambe, Takashi*; Horibe, Yoichi*; Mori, Shigeo*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(3), p.033704_1 - 033704_4, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:58.38(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Exchange bias (EB) behavior has been observed for multiferroic  Fe
Fe O
O (
( =Y, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu and In). The materials with the small
=Y, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu and In). The materials with the small 
 ions (
ions ( =Tm, Yb, Lu and In) exhibit large EB fields (
=Tm, Yb, Lu and In) exhibit large EB fields (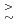 1 kOe) below
1 kOe) below  100-150 K. This property is rooted in a magnetically glassy state, arising from the competition between ferro- and antiferromagnetic domain interactions. In addition, the exchange bias field tends to be more enhanced for smaller
100-150 K. This property is rooted in a magnetically glassy state, arising from the competition between ferro- and antiferromagnetic domain interactions. In addition, the exchange bias field tends to be more enhanced for smaller 
 ions. Hence, the EB is controlled by the substitution at the
ions. Hence, the EB is controlled by the substitution at the  -site in this series.
-site in this series.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:193 Percentile:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
Mishima, Kaichiro*; Saito, Masaki*; Nagata, Takashi*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 52(9), p.536 - 552, 2010/09
, 52(9), p.536 - 552, 2010/09
The 1st of this series that was entitled, "Accelerating Fast Reactor Development: Start of Operation of Commercial Reactors in 2020" introduced mainly the activated development plan and in the major countries. This article introduces the development of the sodium-cooled fast reactor and related fuel cycle that each country is devoting one's energies to development, maily following the presentation in International Conference (FR09) held by organized by IAEA in December 2009, including the situation before and behind the conference. Especially, the development in Russia, India, China, USA, Republic of Korea, France and Japan.
Mizuno, Takashi; Nagata, Hiroshi; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Honda, Teruyuki*
Tokyo Toshi Daigaku Genshiryoku Kenkyusho Kenkyushoho, (36), p.14 - 24, 2010/07
This paper aims to understanding the behavior of the elements related to the change of the chemical properties of sedimentary rocks and granitic rocks distributed in the Tono area, Gifu prefecture, using natural analogue approach. As a result, in the sedimentary rocks, it is indicated that REE and U are migrated in response to the change of pH and/or redox condition. These elements will be dissolved from the rocks and introduced into clayminerals, carbonate minerals and phosphate minerals. On the other hand, ingranitic rocks, these elements do not show the systematical variation. It is needed to more detail analysis (ex. chemical analysis of each separated minerals) for understanding their behavior in the granitic rocks.
Maehata, Keisuke*; Nakamura, Keisuke*; Yasumune, Takashi*; Ishibashi, Kenji*; Takasaki, Koji; Tanaka, Keiichi*; Odawara, Akikazu*; Nagata, Atsushi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 47(3), p.308 - 313, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:34.40(Nuclear Science & Technology)A phase transition edge sensor (TES) microcalorimeter was developed for the energy dispersive measurement of LX-ray photons emitted from transuranium elements. The phase transition temperature of the TES was designed to be 200 mK by using bilayer structure of Au of 120 nm thick and Ti of 50 nm thick. The Au layer of 5.0  m thick was deposited on the Au/Ti bilayer for absorption efficiency of 50% and counting rate of 100 counts per second in the detection of LX-ray photons with the energy from 10 to 20 keV. The TES microcalorimeter was operated for the detection of LX-ray photons emitted from
m thick was deposited on the Au/Ti bilayer for absorption efficiency of 50% and counting rate of 100 counts per second in the detection of LX-ray photons with the energy from 10 to 20 keV. The TES microcalorimeter was operated for the detection of LX-ray photons emitted from  Am,
Am,  Pu and
Pu and  Pu sources. The decay time constant of 180
Pu sources. The decay time constant of 180  s of detection signal pulses allowed the TES microcalorimeter operating with the counting rate higher than 100 counts per second. The energy resolution was obtained to be 50 eV of FWHM value for a peak corresponding to
s of detection signal pulses allowed the TES microcalorimeter operating with the counting rate higher than 100 counts per second. The energy resolution was obtained to be 50 eV of FWHM value for a peak corresponding to  Np L
Np L
 X-ray of 17.75 keV.
X-ray of 17.75 keV.
Nagata, Takashi; Mizuta, Shunji; Nagura, Fuminori
Enerugi Rebyu, 29(5), p.11 - 14, 2009/05
no abstracts in English
Nagata, Takashi; Ichimiya, Masakazu; Funasaka, Hideyuki; Mizuta, Shunji; Nagura, Fuminori
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 51(4), p.234 - 238, 2009/04
, 51(4), p.234 - 238, 2009/04
no abstracts in English
Ishikawa, Makoto; Nagata, Takashi; Kondo, Satoru
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/09
In Japan, the significance of the development of fast reactor (FR) cycle technology has been seriously recognized in the national fundamental nuclear energy policy. Further, nuclear energy as a whole is indispensable worldwide to meet the expansion of energy demand and the solution of environmental problem such as global climate change. Under such circumstances, Japan launched the FR Cycle Technology Development (FaCT) Project in 2006. In FaCT, the design study and the R&D on innovative technologies regarding the main concept are conducted in order to present the conceptual designs of demonstration and commercial FR cycle facilities by around 2015. The main purpose of the near-term R&Ds by 2010 is to judge whether adoption of innovative technologies is feasible. The R&D program on the innovative technologies will be further extended toward 2015, with the demonstration FR expected to be operated in 2025. The concept of the FR cycle system has various aspects from the viewpoints of safety and reliability, economy, sustainability (consisting of reduction of environmental burden, waste management and efficient utilization of uranium resource), and proliferation resistance. The homogeneous recycling of an entire amount of actinides has a significant advantage from these development targets. In the present paper, we will discuss about our scenario of the homogeneous actinide recycling in the FR cycle system, based on our recent studies in the FaCT Project. The studies on the scenario of nuclear energy policy, the management and development of minor actinide (MA)-bearing fuel, reactor physics related to MA-loaded FR cores, and typical nuclear design of MA-loaded FR cores have shown the feasibility to recycle all MA in the future FR-equilibrium society. Also presented are the R&D programs to demonstrate the homogeneous actinide recycling, which are extensively conducted as one of the key national projects in Japan, as well as utilizing international cooperation.
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Ugachi, Hirokazu; Tsukada, Takashi; Nakano, Junichi; Matsui, Yoshinori; Kawamata, Kazuo; Shibata, Akira; Omi, Masao; Nagata, Nobuaki*; Dozaki, Koji*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(8), p.725 - 734, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:43.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)Irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) is one of the critical concerns when stainless steel components have been in service in light water reactors for a long period. In-core IASCC growth tests have been carried out using the compact tension type specimens of type 304 stainless steel that had been pre-irradiated up to a neutron fluence level around 1 10
10 n/m
n/m in pure water simulated boiling water reactor (BWR) coolant condition at the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). In order to investigate the effect of synergy of neutron/
in pure water simulated boiling water reactor (BWR) coolant condition at the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). In order to investigate the effect of synergy of neutron/ radiation and stress/water environment on IASCC growth rate, we performed ex-core IASCC tests on irradiated specimens at several dissolved oxygen contents environments under the same electrochemical potential condition. In this paper, results of the in-core SCC growth tests will be discussed and compared with the result obtained by ex-core tests from a viewpoint of the synergistic effects on IASCC.
radiation and stress/water environment on IASCC growth rate, we performed ex-core IASCC tests on irradiated specimens at several dissolved oxygen contents environments under the same electrochemical potential condition. In this paper, results of the in-core SCC growth tests will be discussed and compared with the result obtained by ex-core tests from a viewpoint of the synergistic effects on IASCC.
Yamasaki, Chisato*; Murakami, Katsuhiko*; Fujii, Yasuyuki*; Sato, Yoshiharu*; Harada, Erimi*; Takeda, Junichi*; Taniya, Takayuki*; Sakate, Ryuichi*; Kikugawa, Shingo*; Shimada, Makoto*; et al.
Nucleic Acids Research, 36(Database), p.D793 - D799, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:70.47(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Here we report the new features and improvements in our latest release of the H-Invitational Database, a comprehensive annotation resource for human genes and transcripts. H-InvDB, originally developed as an integrated database of the human transcriptome based on extensive annotation of large sets of fulllength cDNA (FLcDNA) clones, now provides annotation for 120 558 human mRNAs extracted from the International Nucleotide Sequence Databases (INSD), in addition to 54 978 human FLcDNAs, in the latest release H-InvDB. We mapped those human transcripts onto the human genome sequences (NCBI build 36.1) and determined 34 699 human gene clusters, which could define 34 057 protein-coding and 642 non-protein-coding loci; 858 transcribed loci overlapped with predicted pseudogenes.
Ugachi, Hirokazu; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Matsui, Yoshinori; Endo, Shinya; Kawamata, Kazuo; Tsukada, Takashi; Nagata, Nobuaki*; Dozaki, Koji*; Takiguchi, Hideki*
Proceedings of 15th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-15) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2007/04
Irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) is one of the critical concerns when stainless steel components have been in service in light water reactors (LWRs). It is considered that the reproduced IASCC by PIEs must be carefully distinguished from the actual IASCC in nuclear power plants, because the actual IASCC occurs in the core under simultaneous effects of radiation, stress and high temperature water environment. Hence, we have embarked on a development of the test technique for the in-pile IASCC testing. We adopted the uniaxial constant load (UCL) tensile test method with small tensile specimens for in-pile SCC initiation test, and tried to evaluate the crack initiation behavior as the detection of specimen rupture or detailed observation of surface of loaded specimens. As a result of this study, it was inferred that an acceleration effect of in-pile environment for SCC initiation behavior was not observed under the test condition of this study.
Takase, Yuichi*; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Maekawa, Takashi*; Matsukawa, Makoto; Nagata, Masayoshi*; Nishio, Satoshi; Ono, Yasushi*; Sato, Konosuke*; Tobita, Kenji
Fusion Science and Technology, 51(2T), p.46 - 51, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Japanese tokamak and spherical tokamak (ST) research programs are described. Tokamak research will focus on steady state high(
 = 3.5-5.5) research on JT-60SA (formerly NCT) in support of ITER and DEMO. JT-60SA will also serve as the Satellite Tokamak under the JA-EU Broader Approach framework. ST research has been reorganized as the All-Japan ST Research Program, aiming for creative and innovative research focused on ultra-high and ultra-long pulse regimes. Results of plasma start-up, RF heating, and plasma merging reconnection experiments are summarized. Prospects of contribution of low aspect ratio tokamaks to fusion energy development, are presented.
= 3.5-5.5) research on JT-60SA (formerly NCT) in support of ITER and DEMO. JT-60SA will also serve as the Satellite Tokamak under the JA-EU Broader Approach framework. ST research has been reorganized as the All-Japan ST Research Program, aiming for creative and innovative research focused on ultra-high and ultra-long pulse regimes. Results of plasma start-up, RF heating, and plasma merging reconnection experiments are summarized. Prospects of contribution of low aspect ratio tokamaks to fusion energy development, are presented.