Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kokubun, Yuji; Nakada, Akira; Seya, Natsumi; Nagaoka, Mika; Koike, Yuko; Kubota, Tomohiro; Hirao, Moe; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2023-052, 118 Pages, 2024/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2022. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Kokubun, Yuji; Nakada, Akira; Seya, Natsumi; Koike, Yuko; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Yamada, Ryohei*; Uchiyama, Rei; Yamashita, Daichi; Nagai, Shinji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2023-046, 164 Pages, 2024/03
The Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories conducts environmental radiation monitoring around the reprocessing plant in accordance with the "Safety Regulations for Reprocessing Plant of JAEA, Part IV: Environmental Monitoring". This report summarizes the results of environmental radiation monitoring conducted during the period from April 2022 to March 2023 and the results of dose calculations for the surrounding public due to the release of radioactive materials into the atmosphere and ocean. In the results of the above environmental radiation monitoring, many items were affected by radioactive materials emitted from the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant of Tokyo Electric Power Company, Incorporated (changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016), which occurred in March 2011. Also included as appendices are an overview of the environmental monitoring plan, an overview of measurement methods, measurement results and their changes over time, meteorological statistics results, radioactive waste release status, and an evaluation of the data which deviated of the normal range.
Nakada, Akira; Kanai, Katsuta; Kokubun, Yuji; Nagaoka, Mika; Koike, Yuko; Yamada, Ryohei*; Kubota, Tomohiro; Hirao, Moe; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2022-079, 116 Pages, 2023/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2021. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Nakada, Akira; Kanai, Katsuta; Seya, Natsumi; Nishimura, Shusaku; Futagawa, Kazuo; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Yamada, Ryohei*; Uchiyama, Rei; Yamashita, Daichi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2022-078, 164 Pages, 2023/03
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2021 to March 2022. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. (the trade name was changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016) in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
 and CrUO
and CrUO
Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kusaka, Ryoji; Kumagai, Yuta; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 568, p.153847_1 - 153847_10, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:53.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)FeUO , CrUO
, CrUO , and Fe
, and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO
are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO , their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm
, their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe
in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M
was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO
ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO and Fe
and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe
were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO lost its symmetry around Fe
lost its symmetry around Fe with increasing electron densities around Fe
with increasing electron densities around Fe , as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO
, as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO . Thermogravimetric measurements for UO
. Thermogravimetric measurements for UO , FeUO
, FeUO , and CrUO
, and CrUO showed that the temperature at which FeUO
showed that the temperature at which FeUO decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800
decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800  C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO
C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO started (approximately 1250
started (approximately 1250  C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO
C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
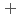 U
U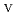
 Fe
Fe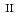
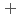 U
U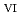 , which would not occur in the CrUO
, which would not occur in the CrUO lattice because Cr
lattice because Cr could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr
could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr in FexCr
in FexCr UO
UO effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe
effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
 , Zr, and stainless-steel
, Zr, and stainless-steelKirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Sato, Nobuaki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 567, p.153842_1 - 153842_15, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:79.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To understand the chemical structure and stability of nuclear fuel debris consisting of UO , Zr, and Stainless Steel (SUS) generated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in Japan in 2011, simulated debris of the UO
, Zr, and Stainless Steel (SUS) generated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in Japan in 2011, simulated debris of the UO -SUS-Zr system and other fundamental component systems were synthesized and characterized. The simulated debris were synthesized by heat treatment for 1 to 12 h at 1600
-SUS-Zr system and other fundamental component systems were synthesized and characterized. The simulated debris were synthesized by heat treatment for 1 to 12 h at 1600 C, in inert (Ar) or oxidative (Ar + 2% O
C, in inert (Ar) or oxidative (Ar + 2% O ) atmospheres.
) atmospheres.  Np and
Np and  Am tracers were doped for the leaching tests of these elements and U from the simulated debris. The characterization of the simulated debris was conducted by XRD, SEM-EDX, Raman spectroscopy, and M
Am tracers were doped for the leaching tests of these elements and U from the simulated debris. The characterization of the simulated debris was conducted by XRD, SEM-EDX, Raman spectroscopy, and M ssbauer spectroscopy, which provided the major uranium phase of the UO
ssbauer spectroscopy, which provided the major uranium phase of the UO  -SUS-Zr debris was the solid solution of U
-SUS-Zr debris was the solid solution of U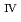 O
O (s.s.) with Zr(IV) and Fe(II) regardless of the treatment atmosphere. The long-term immersion test of the simulated debris in pure water and that in seawater revealed the macro scale crystal structure of the simulated debris was chemically very stable in the wet condition for a year or more. Furthermore, the leaching test results showed that the actinide leaching ratios of U, Np, Am from the UO
(s.s.) with Zr(IV) and Fe(II) regardless of the treatment atmosphere. The long-term immersion test of the simulated debris in pure water and that in seawater revealed the macro scale crystal structure of the simulated debris was chemically very stable in the wet condition for a year or more. Furthermore, the leaching test results showed that the actinide leaching ratios of U, Np, Am from the UO -SUS-Zr debris were very limited and less than 0.08 % for all the experiments in this study.
-SUS-Zr debris were very limited and less than 0.08 % for all the experiments in this study.
 O
O solution
solutionKumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Sasaki, Takayuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(8), p.961 - 971, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:42.88(Nuclear Science & Technology)We investigated potential degradation of fuel debris caused by H O
O , which is the oxidant of major impact from water radiolysis. We performed leaching experiments on different kinds of simulated debris comprising U, Fe, Cr, Ni, and Zr in an aqueous H
, which is the oxidant of major impact from water radiolysis. We performed leaching experiments on different kinds of simulated debris comprising U, Fe, Cr, Ni, and Zr in an aqueous H O
O solution. Chemical analysis of the leaching solution showed that U dissolution was induced by H
solution. Chemical analysis of the leaching solution showed that U dissolution was induced by H O
O . Raman analysis after the leaching revealed that uranyl peroxides were formed on the surface of the simulated debris. These results demonstrate that uranyl peroxides are possible alteration products of fuel debris from H
. Raman analysis after the leaching revealed that uranyl peroxides were formed on the surface of the simulated debris. These results demonstrate that uranyl peroxides are possible alteration products of fuel debris from H O
O reaction. However, the sample in which the main uranium-containing phase was a U-Zr oxide solid solution showed much less uranium dissolution and no Raman signal of uranyl peroxides. Comparison of these results indicates that formation of an oxide solid solution of Zr with UO
reaction. However, the sample in which the main uranium-containing phase was a U-Zr oxide solid solution showed much less uranium dissolution and no Raman signal of uranyl peroxides. Comparison of these results indicates that formation of an oxide solid solution of Zr with UO improves the stability of fuel debris against H
improves the stability of fuel debris against H O
O reaction.
reaction.
 O
O -induced oxidative degradation of simulated fuel debris
-induced oxidative degradation of simulated fuel debrisKumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Sasaki, Takayuki*
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (113), p.61 - 64, 2022/04
The severe accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station resulted in generation of fuel debris. The fuel debris is in contact with water and the radiolysis of water can accelerate degradation of the debris. The analysis of particles sampled from inside or near the damaged reactors indicates the complicated compositions of the fuel debris. It is challenging to estimate the effect of water radiolysis on such a complicated material. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the potential degradation process by leaching experiments of simulated fuel debris in aqueous H O
O solution. The results show that the reaction of H
solution. The results show that the reaction of H O
O induced uranium dissolution from most of the samples and then formation of uranyl peroxides. In contrast, a sample that had U-Zr oxide solid solution as the major phase exhibited remarkable resistance to H
induced uranium dissolution from most of the samples and then formation of uranyl peroxides. In contrast, a sample that had U-Zr oxide solid solution as the major phase exhibited remarkable resistance to H O
O . These findings revealed that the degradation of the simulated debris reflects the reactivity and stability of the uranium phase in the matrices.
. These findings revealed that the degradation of the simulated debris reflects the reactivity and stability of the uranium phase in the matrices.
Nakada, Akira; Nakano, Masanao; Kanai, Katsuta; Seya, Natsumi; Nishimura, Shusaku; Nemoto, Masashi; Tobita, Keiji; Futagawa, Kazuo; Yamada, Ryohei; Uchiyama, Rei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-062, 163 Pages, 2022/02
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2020 to March 2021. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. (the trade name was changed to Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. on April 1, 2016) in March 2011. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring programs, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data which were influenced by the accidental release and exceeded the normal range of fluctuation in the monitoring, were evaluated.
Nakano, Masanao; Nakada, Akira; Kanai, Katsuta; Nagaoka, Mika; Koike, Yuko; Yamada, Ryohei; Kubota, Tomohiro; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-040, 118 Pages, 2021/12
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2020. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Miyagawa, Naoto; Nakano, Masanao; Nakada, Akira; Fujita, Hiroki; Takeyasu, Masanori; Isozaki, Tokuju; Morisawa, Masato; Mizutani, Tomoko; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-056, 181 Pages, 2014/03
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2012 to March 2013. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant of Tokyo Electric Power Co. in March 2011.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Takeyasu, Masanori; Nakada, Akira; Fujita, Hiroki; Isozaki, Tokuju; Morisawa, Masato; Mizutani, Tomoko; Nagaoka, Mika; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-009, 195 Pages, 2013/06
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2011 to March 2012. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant on Tokyo Electric Power Co. in March 2011.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Takeyasu, Masanori; Nakada, Akira; Fujita, Hiroki; Isozaki, Tokuju; Morisawa, Masato; Mizutani, Tomoko; Kokubun, Yuji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-015, 166 Pages, 2012/05
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2010 to March 2011. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant on Tokyo Electric Power Co. in 2011 March. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring program, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data exceeded the normal range of fluctuation by the accidental release was evaluated in the appendices.
Takeyasu, Masanori; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Nakada, Akira; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Sumiya, Shuichi; Furuta, Sadaaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 49(3), p.281 - 286, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:84.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)As a response to the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, emergency environmental radiation monitoring was performed at the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). This paper provisionally describes the results of the monitoring including ambient radiation dose rate and radioactivity concentrations in airborne and fallout. The ambient radiation dose rate began to increase since about 1:00 on March 15 2011, and varied with three peak dose rate of several thousand  Gy/h at 8:00 on March 15, at 5:00 on March 16, and at 4:00 on March 21. The variation over time in radioactivity concentrations in airborne and fallout almost showed the same tendency as that of the dose rate. The fallout of
Gy/h at 8:00 on March 15, at 5:00 on March 16, and at 4:00 on March 21. The variation over time in radioactivity concentrations in airborne and fallout almost showed the same tendency as that of the dose rate. The fallout of  Cs for 1 month from March 15 to April 15 was about 120 times higher than that in May 1986 after the Chernobyl accident. The internal dose by inhalation was estimated from the airborne concentration observed.
Cs for 1 month from March 15 to April 15 was about 120 times higher than that in May 1986 after the Chernobyl accident. The internal dose by inhalation was estimated from the airborne concentration observed.
Furuta, Sadaaki; Sumiya, Shuichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Imaizumi, Kenji; Takeyasu, Masanori; Nakada, Akira; Fujita, Hiroki; Mizutani, Tomoko; Morisawa, Masato; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-035, 89 Pages, 2011/08
As a correspondence to the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, the environmental radiation monitoring was performed at the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, JAEA. This report presented the measurement results of ambient radiation dose rate, radioactivity concentration in the air and radioactivity concentration in fallout and meteorological observation result until May 31, 2011. The ambient radiation dose rate increased, with the peak dose rate of several thousand nGy/h at 7 o'clock in March 15, at 5 o'clock in March 16, and at 4 o'clock in March 21. The variation on the radioactivity concentration in the air and in fallout showed the almost same tendency as that of the dose rate. The concentration ratio of I-131/Cs-137 in the air increased to about 100. The dose was estimated resulting from internal exposure due to inhalation.
Koarashi, Jun; Mikami, Satoshi; Miyauchi, Toru; Kozawa, Tomoyasu*; Yokota, Tomokazu*; Nakada, Akira; Akiyama, Kiyomitsu; Momose, Takumaro
JAEA-Technology 2010-039, 34 Pages, 2010/12
The current methodology for monitoring airborne radioiodine at the Tokai reprocessing plant (TRP) was reviewed, and some investigations were made to re-evaluate collection and measurement techniques in the methodology. The investigations focused particularly on: (1) in situ collection efficiency of an iodine sampler for  I and its dependence on sampling flow rate; (2) evaluation of
I and its dependence on sampling flow rate; (2) evaluation of  I and
I and  I activities collected in an activated charcoal cartridge; (3)
I activities collected in an activated charcoal cartridge; (3)  I collection capacity of an activated charcoal cartridge under reprocessing off-gas conditions; and (4) real-time monitoring system for
I collection capacity of an activated charcoal cartridge under reprocessing off-gas conditions; and (4) real-time monitoring system for  I in airborne effluent. The results obtained gave not only the validity of the TRP's monitoring method, but also technical aspects required for establishing a more reliable and effective monitoring method for radioiodine isotopes.
I in airborne effluent. The results obtained gave not only the validity of the TRP's monitoring method, but also technical aspects required for establishing a more reliable and effective monitoring method for radioiodine isotopes.
Nakada, Akira
Hoken Butsuri, 45(4), p.323 - 327, 2010/12
no abstracts in English
Nakada, Akira; Miyauchi, Toru; Akiyama, Kiyomitsu; Momose, Takumaro; Kozawa, Tomoyasu*; Yokota, Tomokazu*; Otomo, Hiroyuki*
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-018, 134 Pages, 2008/10
This report provides the data set of atmospheric discharges from Tokai reprocessing plant in Tokai-mura, Japan over the period from 1998 to 2007. Daily and weekly data are shown for  Kr that is continuously monitored and for the other nuclide (Alpha emitters, Beta emitters,
Kr that is continuously monitored and for the other nuclide (Alpha emitters, Beta emitters,  H,
H,  C,
C,  I,
I,  I) whose activities are evaluated based on weekly batch-samplings, respectively. The data contained in this report are expected to apply for studying the behavior of the radioactive airborne effluent in the environment.
I) whose activities are evaluated based on weekly batch-samplings, respectively. The data contained in this report are expected to apply for studying the behavior of the radioactive airborne effluent in the environment.
Koarashi, Jun; Mikami, Satoshi; Nakada, Akira; Akiyama, Kiyomitsu; Kobayashi, Hirohide; Fujita, Hiroki; Takeishi, Minoru
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(Suppl.5), p.462 - 465, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:43.42(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tokai reprocessing plant (TRP) has released radionuclides such as  H,
H,  C,
C,  Kr and
Kr and  I into the atmosphere since the start of operation in 1977. We have established the monitoring methodologies for these nuclides, to realize an appropriate and continuous radioactive discharge control. The methodologies having various special technical considerations for matching the monitoring of reprocessing off-gas, were summarized in this paper. Briefly,
I into the atmosphere since the start of operation in 1977. We have established the monitoring methodologies for these nuclides, to realize an appropriate and continuous radioactive discharge control. The methodologies having various special technical considerations for matching the monitoring of reprocessing off-gas, were summarized in this paper. Briefly,  H was collected by a cold-trap technique and the concentration was evaluated being independent of the water collection efficiency;
H was collected by a cold-trap technique and the concentration was evaluated being independent of the water collection efficiency;  C was collected by a monoethanolamine bubbler and then measured by liquid scintillation counting without any interferences from
C was collected by a monoethanolamine bubbler and then measured by liquid scintillation counting without any interferences from  H and
H and  Kr;
Kr;  Kr was continuously measured by combination of two kinds of detectors to cover very wide range of the concentration; and
Kr was continuously measured by combination of two kinds of detectors to cover very wide range of the concentration; and  I was collected by a charcoal filter and a charcoal cartridge in series with a relatively high collecting performance.
I was collected by a charcoal filter and a charcoal cartridge in series with a relatively high collecting performance.
 Po-gross alpha counts
Po-gross alpha countsYamada, Ryohei; Hashimoto, Hiroki*; Tamakuma, Yuki*; Omori, Yasutaka*; Hosoda, Masahiro*; Akata, Naofumi*; Uchiyama, Rei; Nakada, Akira; Endo, Michitaka*; Imajo, Yusuke*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English