Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Koyama, Shinichi; Nakagiri, Toshio; Osaka, Masahiko; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kurata, Masaki; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Takano, Masahide; et al.
Hairo, Osensui Taisaku jigyo jimukyoku Homu Peji (Internet), 144 Pages, 2021/08
JAEA performed the subsidy program for the "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management (Development of Analysis and Estimation Technology for Characterization of Fuel Debris (Development of Technologies for Enhanced Analysis Accuracy and Thermal Behavior Estimation of Fuel Debris))" in 2020JFY. This presentation summarized briefly the results of the project, which will be available shortly on the website of Management Office for the Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management.
Suzuki, Chikashi; Osaka, Masahiko; Nakagiri, Toshio
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.131 - 136, 2020/10
In order to evaluate uranium migration behavior in Ningyo-toge area, we are examining the stability of uranium minerals using DFT calculation. As the first step, we investigated the crystal structure and unit cell composition of ningyoite with its structural details unclear, which is a major uranium mineral there. We analyzed the reported XRD pattern of ningyoite to evaluate a crystal structure of ningyoite using XRD analysis code. This XRD analysis indicates that the distance between U atoms is 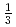
 along
along  axis. We constructed the structure of [CaU(PO
axis. We constructed the structure of [CaU(PO )
) ]
] with three U or Ca atoms aligned along
with three U or Ca atoms aligned along  axis on the basis of this examination, and conducted structural optimization with this structure as initial one using DFT calculation. The theoretical XRD pattern has the maximum peak near 30
axis on the basis of this examination, and conducted structural optimization with this structure as initial one using DFT calculation. The theoretical XRD pattern has the maximum peak near 30 , which the reported XRD pattern of ningyoite has. This result suggests that the structure of ningyoite is based on that of [CaU(PO
, which the reported XRD pattern of ningyoite has. This result suggests that the structure of ningyoite is based on that of [CaU(PO )
) ]
] .
.
Abe, Yuta; Yamashita, Takuya; Sato, Ikken; Nakagiri, Toshio; Ishimi, Akihiro
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 6(2), p.021113_1 - 021113_9, 2020/04
Abe, Yuta; Otaka, Masahiko; Okazaki, Kodai*; Kawakami, Tomohiko*; Nakagiri, Toshio
Proceedings of 2019 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2019) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2019/05
Since the hardness of fuel debris containing boride from B C pellet in control rod is estimated to be two times higher as that of oxide, such as UO
C pellet in control rod is estimated to be two times higher as that of oxide, such as UO and ZrO
and ZrO , it is necessary to select the efficient and appropriate operation for removal of fuel debris formed in the severe accident of nuclear power plants. We focused on the characteristics of LIBS, an innovative rapid chemical in-situ analysis technology that enables simultaneous detection of B, O, and other metal elements in fuel debris. Simulated solidified melt specimens were obtained in the plasma heating tests (CMMR-0/-2, performed by JAEA) of simulated fuel assembly (ZrO
, it is necessary to select the efficient and appropriate operation for removal of fuel debris formed in the severe accident of nuclear power plants. We focused on the characteristics of LIBS, an innovative rapid chemical in-situ analysis technology that enables simultaneous detection of B, O, and other metal elements in fuel debris. Simulated solidified melt specimens were obtained in the plasma heating tests (CMMR-0/-2, performed by JAEA) of simulated fuel assembly (ZrO is used to simulated UO
is used to simulated UO pellet, other materials such as stainless steel, B
pellet, other materials such as stainless steel, B C are same as fuel assembly). The LIBS signals of (B/O)/Zr ratio showed good linear relationship with Vickers hardness. This technique can be also applied as in-situ assessment tool for elemental composition and Vickers hardness of metal-oxide-boride materials.
C are same as fuel assembly). The LIBS signals of (B/O)/Zr ratio showed good linear relationship with Vickers hardness. This technique can be also applied as in-situ assessment tool for elemental composition and Vickers hardness of metal-oxide-boride materials.
Sato, Kazuhiko; Yagi, Naoto; Nakagiri, Toshio
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2019/05
no abstracts in English
Umezawa, Katsuhiro; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Nakayama, Takuya; Nakagiri, Toshio
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2019/05
In December 2016, the Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA Ningyo-toge) announced new concept of "Uranium and Environmental Research Platform". As part of the concept, uranium waste engineering research are now undergoing. The objective of the research is to establish the processing technology for safely and reasonable disposal of uranium waste. In particular, estimation of the amount of uranium and harmful substances and development of technologies to reduce their concentration in the waste to the permissive level for the disposal in shallow ground disposal are needed. We are now developing the technologies to reduce the concentration of uranium and harmful substances shown below. (1) Survey on uranium inventory. Uranium waste is now stored in 10-odd thousands of 200 L drums. We are surveying amount and chemical form of uranium in the drums. (2) Development of decontamination technology of metal and concrete waste. We are investigating decontamination methods for metals and concrete contaminated with uranium. (3) Development of technologies to remove, detoxify and fix the harmful substances. We are surveying the types and amounts of harmful substances in waste. In addition, we are investigating the method to remove, detoxify, and fix harmful substances. (4) Measurement technology of uranium radioactivity. We are investigating and examining ways to improve the quantitative accuracy of measurement and shorten the measurement time. (5) Development of uranium removal technology from sludge. We are investigating new processing method to remove uranium from sludge which is applicable for several kind of sludge. The results of these technological developments and environmental research will be reflected to "small-scale field test" and "disposal demonstration test" which are planned for demonstration of the uranium waste disposal technology.
Yamashita, Takuya; Sato, Ikken; Abe, Yuta; Nakagiri, Toshio; Ishimi, Akihiro; Nagae, Yuji
Proceedings of International Conference on Dismantling Challenges; Industrial Reality, Prospects and Feedback Experience (DEM 2018) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2018/10
no abstracts in English
Abe, Yuta; Yamashita, Takuya; Sato, Ikken; Nakagiri, Toshio; Ishimi, Akihiro; Nagae, Yuji
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/07
Yamashita, Takuya; Sato, Ikken; Abe, Yuta; Nakagiri, Toshio; Ishimi, Akihiro; Nagae, Yuji
Proceedings of 12th International Conference of the Croatian Nuclear Society; Nuclear Option for CO Free Energy Generation (USB Flash Drive), p.109_1 - 109_15, 2018/06
Free Energy Generation (USB Flash Drive), p.109_1 - 109_15, 2018/06
no abstracts in English
Abe, Yuta; Sato, Ikken; Nakagiri, Toshio; Ishimi, Akihiro; Nagae, Yuji
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 4(2), p.020901_1 - 020901_8, 2018/04
A new experimental program using non-transfer type plasma heating is under consideration in JAEA to clarify the uncertainty on core-material relocation (CMR) behavior of BWR. In order to confirm the applicability of this new technology, authors performed preparatory plasma heating tests using small-scale test pieces (107 mm  107 mm
107 mm  222 mm (height)). An excellent perspective in terms of applicability of the non-transfer plasma heating to melting high melting-temperature materials such as ZrO
222 mm (height)). An excellent perspective in terms of applicability of the non-transfer plasma heating to melting high melting-temperature materials such as ZrO has been obtained. In addition, molten pool was formed at the middle height of the test piece indicating its capability to simulate the initial phase of core degradation behavior consistent with the real UO
has been obtained. In addition, molten pool was formed at the middle height of the test piece indicating its capability to simulate the initial phase of core degradation behavior consistent with the real UO fuel Phebus-FPT tests. Furthermore, application of EPMA, SEM/EDX and X-ray CT led to a conclusion that the pool formed consisted mainly of Zr with some concentration of oxygen which tended to be enhanced at the upper surface region of the pool. Based on these results, an excellent perspective in terms of applicability of the non-transfer plasma heating technology to the Severe Accident (SA) experimental study was obtained.
fuel Phebus-FPT tests. Furthermore, application of EPMA, SEM/EDX and X-ray CT led to a conclusion that the pool formed consisted mainly of Zr with some concentration of oxygen which tended to be enhanced at the upper surface region of the pool. Based on these results, an excellent perspective in terms of applicability of the non-transfer plasma heating technology to the Severe Accident (SA) experimental study was obtained.
Nakayama, Takuya; Yagi, Naoto; Sato, Kazuhiko; Hinoda, Shingo; Nakagiri, Toshio; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Umezawa, Katsuhiro; Sugitsue, Noritake
JAEA-Review 2018-005, 163 Pages, 2018/03
The Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center of JAEA has been working together with local communities for more than 60 years. Through our R&D projects on from uranium exploration to uranium enrichment as a part of the nuclear fuel cycle (i.e., front-end), we have accumulated experiences in the fields of management of uranium related technology. Taking advantage of such our potential, we will start new R&D program on "Research on Uranium and the Environment". In December 2016 we announced our new concept of the "Uranium and Environmental Research Platform" as a framework aimed at contributing to regional and international society through R&D programs (environmental research and uranium waste engineering research) that are needed to steadily carry out decommissioning of uranium handling facilities.
Abe, Yuta; Nakagiri, Toshio; Watatani, Satoshi*; Maruyama, Shinichiro*
JAEA-Technology 2017-023, 46 Pages, 2017/10
This is a report on Abrasive Water Jet (AWJ) cutting work carried out on specimen, which was used for Simulated Fuel Assembly Heating Examination by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS) molten core behavior analysis group in February 2016. The simulated fuel assembly is composed of Zirconia for the outer crucible/simulated fuel, stainless steel for the control blade and Zircaloy (Zr) for the cladding tube/channel box. Therefore, it is necessary to cut at once substances having a wide range of fracture toughness and hardness. Moreover, it is a large specimen with an approximate size of 300 mm. In addition, epoxy resin has high stickiness, making it more difficult to cut. Considering these effects, AWJ cutting was selected. The following two points were devised, and this specimen could be cut with AWJ. If it was not possible to cut at one time like a molten portion of boride, it was repeatedly cut. By using Abrasive Suspension Jet (ASJ) system with higher cutting ability than Abrasive Injection Jet (AIJ, conventional method) system, cutting time was shortened. As a result of this work, the cutting method in Simulated Fuel Assembly Heating Examination was established. Incidentally, in the cutting operation, when the cutting ability was lost at the tip of the AWJ, a curved cut surface, which occurs when the jet flowed away from the feeding direction, could be confirmed at the center of the test body. From the next work, to improve the cutting efficiency, we propose adding a mechanism such as turning the cutting member itself for re-cutting from the exit side of the jet and appropriate traverse speed to protect cut surface.
Abe, Yuta; Sato, Ikken; Nakagiri, Toshio; Ishimi, Akihiro; Nagae, Yuji
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2017/04
Abe, Yuta; Sato, Ikken; Ishimi, Akihiro; Nakagiri, Toshio; Nagae, Yuji
Proceedings of 24th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-24) (DVD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2016/06
A new experimental program using non-transfer type plasma heating is under consideration in JAEA to clarify the uncertainty on core-material relocation (CMR) behavior of BWR. In order to confirm the applicability of this new technology, authors performed preparatory plasma heating tests using small-scale test pieces (107 mm  107 mm
107 mm  222 mmh). Based on these preliminary results, an excellent perspective in terms of applicability of the non-transfer plasma heating technology to the SA (Severe Accident) experimental study was obtained. Furthermore, JAEA is preparing for the next step intermediate-scale preparatory tests in 2016 using ca. 50 rods and a control blade that would not only confirm its technical applicability, but also some insights relevant to the issue on CMR itself.
222 mmh). Based on these preliminary results, an excellent perspective in terms of applicability of the non-transfer plasma heating technology to the SA (Severe Accident) experimental study was obtained. Furthermore, JAEA is preparing for the next step intermediate-scale preparatory tests in 2016 using ca. 50 rods and a control blade that would not only confirm its technical applicability, but also some insights relevant to the issue on CMR itself.
Doi, Daisuke; Nakagiri, Toshio
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(3), p.343 - 349, 2014/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Daido, Hiroyuki; Suzuki, Yoji; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Nakagiri, Toshio; Kaku, Masanori*; Kubodera, Masakazu*
Optics Express (Internet), 21(23), p.28182 - 28188, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.49(Optics)We describe the direct measurement of actual transmittance of sodium samples with thickness of a 2 mm and 3 mm in a spectral range  115 nm, resulting in
115 nm, resulting in  50% transmittance of 3 mm thick solid and liquid sodium samples including transmission of a pair of the windows at the wavelength of 120 nm, giving an extinction coefficient of
50% transmittance of 3 mm thick solid and liquid sodium samples including transmission of a pair of the windows at the wavelength of 120 nm, giving an extinction coefficient of  10
10 to
to  10
10 which represents the sodium with a few cm thickness to be partially transparent for this wavelength. To confirm the measurement, we perform simple imaging experiments by the ultra-violet light passing through a 8 mm-thick sodium sample to illuminate a mesh as an object, resulting in obtaining a clear image.
which represents the sodium with a few cm thickness to be partially transparent for this wavelength. To confirm the measurement, we perform simple imaging experiments by the ultra-violet light passing through a 8 mm-thick sodium sample to illuminate a mesh as an object, resulting in obtaining a clear image.
Daido, Hiroyuki; Suzuki, Yoji; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Nakagiri, Toshio; Kaku, Masanori*; Kubodera, Masakazu*; Pirozhkov, A. S.
Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.8849, p.884908_1 - 884908_11, 2013/09
no abstracts in English
Doi, Daisuke; Nakagiri, Toshio
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering and the ASME 2012 Power Conference (ICONE-20 & POWER 2012) (DVD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2012/07
no abstracts in English
Miyahara, Shinya; Nishimura, Masahiro; Nakagiri, Toshio
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 241(12), p.4731 - 4736, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)We measured equilibrium partition coefficients of cesium and iodine between liquid sodium pool and the inert cover gas. The obtained empirical equations were consistent with Castleman's theoretical equations. The effect of cesium concentration upon the partition coefficients was consistent with the theoretical values. That of iodine concentration was incompatible with the theoretical consideration due to the formation of dimmer of NaI (Na I
I ) in the cover gas.
) in the cover gas.
 C
CTakai, Toshihide; Kubo, Shinji; Nakagiri, Toshio; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 36(8), p.4689 - 4701, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:32.75(Chemistry, Physical)A thermo-chemical water-splitting hydrogen production process for sodium cooled FBR is under development based on Westinghouse sulfur process. A unique sulfur trioxide electrolysis is introduced in this process intended for the lowering the reaction temperature around the operation temperature of FBR (500 550
550 C). Key engineering issues for eliminating barriers to industrialization of this process were examined using a laboratory-stage apparatus. Adequacy of the components structure and control method was confirmed from the test results. Further it was found that a continuous hydrogen production system based on this process is achievable.
C). Key engineering issues for eliminating barriers to industrialization of this process were examined using a laboratory-stage apparatus. Adequacy of the components structure and control method was confirmed from the test results. Further it was found that a continuous hydrogen production system based on this process is achievable.