Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Sashida, Sho*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; Honda, Takashi*; Hawai, Takafumi*; Saito, Hiraku*; Ito, Shinichi*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Sakaki, Koji*; et al.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 51(Part A), p.79 - 87, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:48.53(Chemistry, Physical)Sakaki, Koji*; Kim, H.*; Majzoub, E. H.*; Machida, Akihiko*; Watanuki, Tetsu*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Mizuno, Masataka*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakamura, Yumiko*
Acta Materialia, 234, p.118055_1 - 118055_10, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:84.24(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) as the origin of volume collapse
as the origin of volume collapseYu, R.*; Hojo, Hajime*; Watanuki, Tetsu; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Mizokawa, Takashi*; Oka, Kengo*; Kim, H.*; Machida, Akihiko; Sakaki, Koji*; Nakamura, Yumiko*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 137(39), p.12719 - 12728, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:72.31(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Endo, Naruki*; Saita, Itoko*; Nakamura, Yumiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 40(8), p.3283 - 3287, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:36.94(Chemistry, Physical)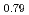 Ti
Ti Zr
Zr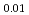
Kim, H.*; Sakaki, Koji*; Asano, Kota*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Machida, Akihiko; Watanuki, Tetsu; Nakamura, Yumiko*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 79(3), p.131 - 136, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)no abstracts in English
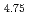 Sn
Sn by time resolved X-ray diffraction
by time resolved X-ray diffractionMachida, Akihiko; Higuchi, Kensuke*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Sakaki, Koji*; Kim, H.*; Nakamura, Yumiko*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 79(3), p.124 - 130, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.95(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Structural changes on hydrogen absorption process of hydrogen absorbing alloy LaNi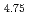 Sn
Sn have been investigated by time-resolved X-ray diffraction measurements using synchrotron radiation source. We have found the transient intermediate phase between the solid solution and hydride phases of LaNi
have been investigated by time-resolved X-ray diffraction measurements using synchrotron radiation source. We have found the transient intermediate phase between the solid solution and hydride phases of LaNi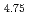 Sn
Sn under non-equilibrium hydrogen pressure condition at room temperature. LaNi
under non-equilibrium hydrogen pressure condition at room temperature. LaNi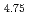 Sn
Sn has transformed into the hydride through three phase co-existing state. The hydrogen content of the intermediate phase estimated from the unit cell volume is independent of the induced hydrogen gas pressure. The variation of lattice constants indicate that the hydrogen atoms are located at the La
has transformed into the hydride through three phase co-existing state. The hydrogen content of the intermediate phase estimated from the unit cell volume is independent of the induced hydrogen gas pressure. The variation of lattice constants indicate that the hydrogen atoms are located at the La Ni
Ni (Ni,Sn)
(Ni,Sn) octahedron and La
octahedron and La (Ni,Sn)
(Ni,Sn) tetrahedron in the intermediate phase.
tetrahedron in the intermediate phase.
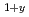 (Fe
(Fe Mn
Mn )
) (
(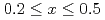 ,
, 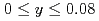 )
)Sakaki, Koji*; Kim, H.*; Machida, Akihiko; Watanuki, Tetsu; Nakamura, Yumiko*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 79(3), p.112 - 117, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.36(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)no abstracts in English
 Pr
Pr Ni
Ni by Changing Mg/Pr ratio
by Changing Mg/Pr ratioSakaki, Koji*; Terashita, Naoyoshi*; Kim, H.*; Majzoub, E. H.*; Proffen, T.*; Machida, Akihiko; Watanuki, Tetsu; Tsunokake, Shigeru*; Nakamura, Yumiko*; Akiba, Etsuo*
Sumato Purosesu Gakkai-Shi, 3(6), p.359 - 366, 2014/11
no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Riyo; Hama, Katsuhiro; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Morikawa, Keita*; Hosoya, Shinichi*; Nakamura, Toshiaki*; Tanaka, Yumiko*
JAEA-Technology 2014-029, 118 Pages, 2014/09
This study is to gain a better understanding of mass transfer phenomena in the geological environment as well as to develop technologies for: measurement of the solute transport parameters, model construction, numerical analysis and validation of all those technologies based on the existing information. As part of solute transport study, laboratory experiments were planned to understand the influence of the geological characteristics of fracture on the solute transport parameters, also understand the differences in test results by the different sizes of the samples used for an experiment, and moreover to validate the parameters obtained by numerical analysis.
 Ti
Ti during hydrogen cycling
during hydrogen cyclingKim, H.*; Sakaki, Koji*; Saita, Itoko*; Enoki, Hirotoshi*; Noguchi, Kazuo*; Machida, Akihiko; Watanuki, Tetsu; Nakamura, Yumiko*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 39(20), p.10546 - 10551, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:32.47(Chemistry, Physical)The effect of the vanadium content on the cyclic stability of V-Ti binary alloys was investigated. V Ti
Ti ,
, 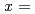 0.2 and 0.5 samples were hydrogenated and dehydrogenated at 410 K and 553 K respectively, for more than 100 times. During hydrogen cycling, reduction in the reversible hydrogen storage capacity was clearly observed from both samples. In addition, the shape of the pressure-composition-isotherm curves was significantly altered over the testing cycle period; the absorption and desorption plateaus got markedly inclined and the hysteresis became evidently smaller. We found that even after the hydrogen storage capacity of V
0.2 and 0.5 samples were hydrogenated and dehydrogenated at 410 K and 553 K respectively, for more than 100 times. During hydrogen cycling, reduction in the reversible hydrogen storage capacity was clearly observed from both samples. In addition, the shape of the pressure-composition-isotherm curves was significantly altered over the testing cycle period; the absorption and desorption plateaus got markedly inclined and the hysteresis became evidently smaller. We found that even after the hydrogen storage capacity of V Ti
Ti was significantly reduced, at low enough temperature V
was significantly reduced, at low enough temperature V Ti
Ti was able to absorb hydrogen as much as it did at the first cycle.
was able to absorb hydrogen as much as it did at the first cycle.
 Pr
Pr Ni
Ni (
( = 0.6 and 1.0)
= 0.6 and 1.0)Sakaki, Koji*; Terashita, Naoyoshi*; Kim, H.*; Majzoub, E. H.*; Machida, Akihiko; Watanuki, Tetsu; Tsunokake, Shigeru*; Nakamura, Yumiko*; Akiba, Etsuo*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 118(13), p.6697 - 6705, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:52.89(Chemistry, Physical)We present an investigation of the degradation mechanism against hydrogenation cycles in Mg Pr
Pr Ni
Ni (
( = 0.6 and 1.0). Mg
= 0.6 and 1.0). Mg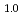 Pr
Pr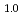 Ni
Ni shows significant degradation and loss of capacity after only a few cycles, while Mg
shows significant degradation and loss of capacity after only a few cycles, while Mg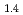 Pr
Pr Ni
Ni did not show any reduction of hydrogen storage capacity until 100 cycles. The peak broadening of X-ray diffraction patterns and accumulation of lattice strain were observed concomitantly with an increase of hydrogenation cycles only in Mg
did not show any reduction of hydrogen storage capacity until 100 cycles. The peak broadening of X-ray diffraction patterns and accumulation of lattice strain were observed concomitantly with an increase of hydrogenation cycles only in Mg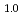 Pr
Pr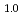 Ni
Ni . These changes were not observed in Mg
. These changes were not observed in Mg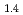 Pr
Pr Ni
Ni . In pair distribution function patterns,
. In pair distribution function patterns,  -dependent peak broadening was observed and it became significant with an increasing number of cycles in Mg
-dependent peak broadening was observed and it became significant with an increasing number of cycles in Mg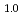 Pr
Pr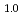 Ni
Ni , suggesting an increase of the dislocation density. Mg
, suggesting an increase of the dislocation density. Mg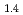 Pr
Pr Ni
Ni showed higher hardness and more pulverization upon hydrogenation than Mg
showed higher hardness and more pulverization upon hydrogenation than Mg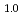 Pr
Pr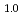 Ni
Ni .
.
 Fe M
Fe M ssbauer spectroscopy of RFe
ssbauer spectroscopy of RFe (R = Y, Gd) hydrides synthesized under ultra-high-pressure hydrogen
(R = Y, Gd) hydrides synthesized under ultra-high-pressure hydrogenMitsui, Takaya; Masuda, Ryo*; Seto, Makoto; Hirao, Naohisa*; Matsuoka, Takehiro*; Nakamura, Yumiko*; Sakaki, Koji*; Enoki, Hirotoshi*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 580(Suppl.1), p.S264 - S267, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:43.41(Chemistry, Physical) Ti
Ti alloys from the atomic pair distribution function analysis
alloys from the atomic pair distribution function analysisKim, H.*; Sakaki, Koji*; Ogawa, Hiroshi*; Nakamura, Yumiko*; Nakamura, Jin*; Akiba, Etsuo*; Machida, Akihiko; Watanuki, Tetsu; Proffen, T.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 117(50), p.26543 - 26550, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:77.33(Chemistry, Physical)Reduction in reversible hydrogen storage capacity with increasing hydrogenation and dehydrogenation cycle number is observed in numerous hydrogen storage materials, but the mechanism behind this unfavorable change has not been elucidated yet. In this study, we have investigated the development of structural defects or disorders in V Ti
Ti H
H ,
,  = 0, 0.2, and 0.5, during the first 15 hydrogen absorption and desorption cycles using the atomic pair distribution function (PDF) analysis of synchrotron X-ray total scattering data to find out the possible structural origin of the poor cyclic stability of V
= 0, 0.2, and 0.5, during the first 15 hydrogen absorption and desorption cycles using the atomic pair distribution function (PDF) analysis of synchrotron X-ray total scattering data to find out the possible structural origin of the poor cyclic stability of V Ti
Ti alloys.
alloys.
 ssbauer study using synchrotron radiation
ssbauer study using synchrotron radiationMasuda, Ryo; Mitsui, Takaya; Ito, Keiji*; Sakaki, Koji*; Enoki, Hirotoshi*; Nakamura, Yumiko*; Seto, Makoto
Hyperfine Interactions, 204(1-3), p.139 - 142, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:75.57(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)We have been developing a system for in situ M ssbauer studies using synchrotron radiation (SR) to elucidate the mechanism of hydrogenation processes. In the system, samples reacts in an atmosphere chamber and SR-based M
ssbauer studies using synchrotron radiation (SR) to elucidate the mechanism of hydrogenation processes. In the system, samples reacts in an atmosphere chamber and SR-based M ssbauer spectra using variable-frequency nuclear monochromator and energy spectra of inelastic nuclear resonant scattering (NRS) of SR are measured. As a feasibility study, the temperature dependence of the M
ssbauer spectra using variable-frequency nuclear monochromator and energy spectra of inelastic nuclear resonant scattering (NRS) of SR are measured. As a feasibility study, the temperature dependence of the M ssbauer and inelastic NRS spectra of
ssbauer and inelastic NRS spectra of  Fe in
Fe in  -GdFe
-GdFe H
H under vacuum were measured. In both spectra, clear differences were observed between 373 K and 573 K. These differences can be interpreted by the change of microscopic environment around Fe at the dehydrogenation. Thus, it is confirmed that this system works well enough to perform the in-situ M
under vacuum were measured. In both spectra, clear differences were observed between 373 K and 573 K. These differences can be interpreted by the change of microscopic environment around Fe at the dehydrogenation. Thus, it is confirmed that this system works well enough to perform the in-situ M ssbauer study on the dehydrogenation of
ssbauer study on the dehydrogenation of  -GdFe
-GdFe H
H .
.
Higuchi, Kensuke; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori; Sakaki, Koji*; Nakamura, Yumiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
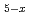 M
M on hydrogen absorption process
on hydrogen absorption processMachida, Akihiko; Higuchi, Kensuke*; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Sakaki, Koji*; Kim, H.*; Nakamura, Yumiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Endo, Naruki; Matsumoto, Itoko*; Nakamura, Yumiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori
no journal, ,
Machida, Akihiko; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Kim, H.*; Sakaki, Koji*; Nakamura, Yumiko*
no journal, ,
Hydrogen absorbing alloys are widely investigated as potential hydrogen storage materials for several applications including fuel cell vehicles as well as stationary energy storage system. In order to investigate the structural changes during the hydrogen absorption/desorption processes, we have developed an in-situ X-ray diffraction measurement setup at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency Beamline BL22XU in SPring-8. The in-situ X-ray diffraction measurement has been performed for the several hydrigen absorbing alloys under equilibrium and non-equilibrium pressure of hydrogen gas. In addition, by using a large area detector and high energy X-ray about 70 keV, we are capable of performing X-ray total scattering experiments to obtain the atomic pair distribution function. In this presentation, we will intorduce our measurement setup and show some preliminary results.
Machida, Akihiko; Higuchi, Kensuke*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Sakaki, Koji*; Kim, H.*; Nakamura, Yumiko*
no journal, ,
To improve performance of hydrogen storage materials, it is essential to understand detailed mechanism of hydrogenation and dehydrogenation reactions. In-situ powder diffraction measurements provide direct information about structural changes accompanying the reactions. We therefore installed a time-resolved X-ray diffraction (XRD) system at a beamline BL22XU at the SPrign-8, a synchrotron radiation facility in Japan. The system equipped area detectors. A sample cell was connected to a hydrogen supply system. The pressure of hydrogen gas was limited to 1 MPa. To demonstrate the performance of the system, we have performed time-resolved XRD experiments for LaNi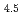 Al
Al . LaNi
. LaNi exhibits the significant broadening of the diffraction peaks by hydrogen absorption; however, LaNi
exhibits the significant broadening of the diffraction peaks by hydrogen absorption; however, LaNi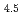 Al
Al shows the no significant broadening. We have succeeded in the measurements of the structural change from the solid solution phase to the hydride phase and have found the formation of the transient intermediate phase on this reaction process. The system is currently used to study several materials.
shows the no significant broadening. We have succeeded in the measurements of the structural change from the solid solution phase to the hydride phase and have found the formation of the transient intermediate phase on this reaction process. The system is currently used to study several materials.
Watanuki, Tetsu; Machida, Akihiko; Kim, H.*; Sakaki, Koji*; Nakamura, Yumiko*; Yu, R.*; Azuma, Masaki*; Oka, Kengo*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English