Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wada, Yuki*; Morimoto, Takeshi*; Wu, T.*; Wang, D.*; Kikuchi, Hiroshi*; Nakamura, Yoshitaka*; Yoshikawa, Eiichi*; Ushio, Tomoo*; Tsuchiya, Harufumi
Science Advances (Internet), 11(21), p.eads6906_1 - eads6906_10, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Pant, A. D.*; Sunagawa, Hikaru*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Fujihara, Masayoshi; Tampo, Motonobu*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.31_1 - 31_6, 2024/12
Yoshida, Go*; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Nakamura, Hajime*; Miura, Taichi*; Toyoda, Akihiro*; Masumoto, Kazuyoshi*; Nakabayashi, Takayuki*; Matsuda, Makoto
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(10), p.1298 - 1307, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Matsumoto, Taku; Hanari, Toshihide; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Nakamura, Keita*; Yashiro, Hiroshi*
Artificial Life and Robotics, 29(2), p.358 - 371, 2024/05
Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Takahashi, Ryuta*; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Masatoshi*; Ishimaru, Sora*; Yamauchi, Sara*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Watanabe, Masao; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 41, p.011010_1 - 011010_7, 2024/05
Baccou, J.*; Glantz, T.*; Ghione, A.*; Sargentini, L.*; Fillion, P.*; Damblin, G.*; Sueur, R.*; Iooss, B.*; Fang, J.*; Liu, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 421, p.113035_1 - 113035_16, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:96.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakamura, Keita; Hanari, Toshihide; Matsumoto, Taku; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Yashiro, Hiroshi*
Journal of Robotics and Mechatronics, 36(1), p.115 - 124, 2024/02
Matsumoto, Taku; Hanari, Toshihide; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Yashiro, Hiroshi*; Nakamura, Keita*
Proceedings of 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (IEEE ROBIO 2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/12
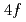 states in the electronic structure of the intermediate-valence superconductor CeIr
states in the electronic structure of the intermediate-valence superconductor CeIr
Fujimori, Shinichi; Kawasaki, Ikuto; Takeda, Yukiharu; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Sasabe, Norimasa*; Sato, Yoshiki*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Nakamura, Ai*; Maruya, A.*; Homma, Yoshiya*; et al.
Electronic Structure (Internet), 5(4), p.045009_1 - 045009_7, 2023/11
Kutsukake, Kenichi; Matsuda, Makoto; Nakamura, Masahiko; Ishizaki, Nobuhiro; Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Otokawa, Yoshinori; Asozu, Takuhiro; Matsui, Yutaka; Nakagawa, Sohei; Abe, Shinichi
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1080 - 1084, 2023/11
no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Taku; Hanari, Toshihide; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Yashiro, Hiroshi*; Nakamura, Keita*
Proceedings of 22nd World Congress of the International Federation of Automatic Control (IFAC 2023) (Internet) , p.12107 - 12112, 2023/07
Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Tada, Kenichi; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.14001_1 - 14001_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:84.55(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ishizaki, Nobuhiro; Matsuda, Makoto; Nakamura, Masahiko; Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Kutsukake, Kenichi; Otokawa, Yoshinori; Asozu, Takuhiro; Matsui, Yutaka; Abe, Shinichi
JAEA-Conf 2022-002, p.5 - 10, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Pant, A. D.*; Natori, Hiroaki*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Tampo, Motonobu*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Teshima, Natsuki*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2462, p.012033_1 - 012033_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Matsuda, Makoto; Nakamura, Masahiko; Ishizaki, Nobuhiro; Kutsukake, Kenichi; Otokawa, Yoshinori; Asozu, Takuhiro; Matsui, Yutaka; Nakagawa, Sohei; Abe, Shinichi
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1109 - 1113, 2023/01
no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Taku; Hanari, Toshihide; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Yashiro, Hiroshi*; Nakamura, Keita*
Proceedings of 28th International Symposium on Artificial Life and Robotics (AROB 28th 2023) (Internet), p.768 - 773, 2023/01
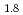 and TiH
and TiH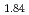 up to 21 GPa by incoherent inelastic neutron scattering
up to 21 GPa by incoherent inelastic neutron scatteringHattori, Takanori; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Iida, Kazuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; Honda, Takashi*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(13), p.134309_1 - 134309_9, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hydrogen vibration excitations of fluorite-type ZrH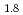 and TiH
and TiH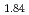 were investigated up to 21 GPa and 4 GPa, respectively, by incoherent inelastic neutron scattering experiments. The first excitation energies increased with pressure, as described by the equations
were investigated up to 21 GPa and 4 GPa, respectively, by incoherent inelastic neutron scattering experiments. The first excitation energies increased with pressure, as described by the equations 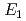 (meV) = 141.4(2) + 1.02(2)
(meV) = 141.4(2) + 1.02(2) (GPa) and
(GPa) and 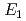 (meV) = 149.4(1) + 1.21(8)
(meV) = 149.4(1) + 1.21(8) (GPa) for ZrH
(GPa) for ZrH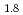 and TiH
and TiH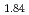 , respectively. Coupling with pressure dependence of lattice parameters, the relations between metal-hydrogen distance (
, respectively. Coupling with pressure dependence of lattice parameters, the relations between metal-hydrogen distance (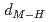 ) and
) and 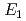 are found to be well described by the equations
are found to be well described by the equations 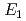 (meV) = 1.62(9)
(meV) = 1.62(9) 10
10
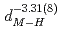 (
(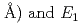 (meV) = 1.47(21)
(meV) = 1.47(21) 10
10
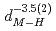 (AA), respectively. The slopes of these curves are much steep compared to the previously reported trend in various fluorite-type metal hydrides at ambient pressure. The hydrogen wave function spreading showed that the local potential field for a hydrogen atom shrinks more intensively than the tetrahedral site. These behavior is likely caused by the rigid metal ion core and the resulting confinement of the hydrogen atom in the narrower potential field at high pressures.
(AA), respectively. The slopes of these curves are much steep compared to the previously reported trend in various fluorite-type metal hydrides at ambient pressure. The hydrogen wave function spreading showed that the local potential field for a hydrogen atom shrinks more intensively than the tetrahedral site. These behavior is likely caused by the rigid metal ion core and the resulting confinement of the hydrogen atom in the narrower potential field at high pressures.
Nakano, Hiroko; Fuyushima, Takumi; Tsuguchi, Akira*; Nakamura, Mutsumi*; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Takemoto, Noriyuki; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2022-007, 34 Pages, 2022/06
In order to investigate the phenomenon of stress corrosion cracking (SCC) for structural materials at the light water reactor (LWR), it is important to manage a water quality for simulating high-temperature and high-pressure water. Generally, dissolved hydrogen (DH) concentration in water loop has been controlled by the bubbling method of pure hydrogen gas or standard gas with high hydrogen concentration. However, it is necessary to equip the preventing hydrogen explosion in the area installed experimental apparatus. In general, in order to prevent accident by hydrogen, it is required to take measures such as limiting the amount of leakage, eliminating hydrogen, shutting off the power supply, and suppressing combustion before an explosion occurs. Thus, the dissolved hydrogen concentration control apparatus by electrolysis method has been developed which has two electrolysis cells to control DH concentration by electrolyzing water loop. In this study, small basic experimental devices were set up. The preliminary data were acquired regarding the simple performance of two electrolysis cells and the change of DH concentration in circulation. Based on the preliminary data, the dissolved hydrogen concentration control apparatus was designed to be connected to the high-temperature and high-pressure water loop test equipment. This report describes the test results with the small basic experimental devices for the design of the dissolved hydrogen concentration control apparatus.
Shibata, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Seki, Misaki; Shibata, Akira; Nakamura, Jinichi; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-018, 42 Pages, 2022/03
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) in Oarai Research and Development Institute of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been developing various reactor materials, irradiation techniques and instruments for more than 30 years. Among them, the development of self-powered neutron detectors (SPNDs) and gamma detectors (SPGDs) has been carried out, and several research results have been reported. However, most of the results are based on the design study of the detector development and the results of in-core irradiation tests and gamma irradiation tests using Cobalt-60. In this report, a numerical code is developed based on the paper "Neutron and Gamma-Ray Effects on Self-Powered In-Core Radiation Detectors" written by H.D. Warren and N.H. Shah in 1974, in order to theoretically evaluate the self-powered radiation detectors.
Ichihara, Yoshitaka*; Nakamura, Naohiro*; Moritani, Hiroshi*; Horiguchi, Tomohiro*; Choi, B.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 21(1), p.1 - 14, 2022/03
In this study, we aim to approximately evaluate the effect of nonlinearity of reinforced concrete structures through seismic response analysis using the equivalent linear analysis method. A simulation analysis was performed for the ultimate response test of the shear wall of the reactor building used in an international competition by OECD/NEA in 1996. The equivalent stiffness and damping of the shear wall were obtained from the trilinear skeleton curves proposed by the Japan Electric Association and the hysteresis curves proposed by Cheng et al. The dominant frequency, maximum acceleration response, maximum displacement response, inertia force-displacement relationship, and acceleration response spectra of the top slab could be simulated well up to a shear strain of approximately  =2.0
=2.0 10
10 . The equivalent linear analysis used herein underestimates the maximum displacement response at the time of ultimate fracture of approximately
. The equivalent linear analysis used herein underestimates the maximum displacement response at the time of ultimate fracture of approximately  =4.0
=4.0 10
10 . Moreover, the maximum shear strain of the shear wall could not capture the locally occurring shear strain compared with that of the nonlinear analysis. Therefore, when employing this method to evaluate the maximum shear strain and test results, including those during the sudden increase in displacement immediately before the fracture, sufficient attention must be paid to its applicability.
. Moreover, the maximum shear strain of the shear wall could not capture the locally occurring shear strain compared with that of the nonlinear analysis. Therefore, when employing this method to evaluate the maximum shear strain and test results, including those during the sudden increase in displacement immediately before the fracture, sufficient attention must be paid to its applicability.