Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kobayashi, Keita; Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Urata, Shingo*; Suzuya, Kentaro
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.18721_1 - 18721_12, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The first sharp peak diffraction peak (FSDP) in the structure factor of amorphous materials is thought to reflect the medium-range order structure in amorphous materials, and the structural origin of the FSDP has been a subject of ongoing debate. In this study, we employed machine learning molecular dynamics (MLMD) with nearly first-principles calculation accuracy to investigate the structural origin of the FSDP in high-density silica glass. First, we successfully reproduced various experimental data of high-density silica glass using MLMD. Furthermore, we revealed that the development (or reduction) of the FSDP in high-density silica glass is characterized by the deformation behavior of ring structures in Si-O covalent bond networks under compression.
Kobayashi, Keita; Nakamura, Hiroki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Okumura, Masahiko
Materia, 62(3), p.175 - 181, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Keita; Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Cooper, M. W. D.*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12(1), p.9808_1 - 9808_11, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:71.37(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Keita; Nakamura, Hiroki; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Okumura, Masahiko
Computational Materials Science, 188, p.110173_1 - 110173_14, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:73.11(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 U
U O
O
Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Nakamura, Hiroki; Kitagaki, Toru; Hoshino, Takanori; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(9-10), p.915 - 921, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)To elucidate the mechanical properties of fuel debris inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, we use first-principles calculations to evaluate mechanical properties of cubic Zr U
U O
O , which is a main component of the fuel debris. We focus on the dependence of mechanical properties on the fraction x of zirconium, compare our results with recent experiment of simulated debris, in which dependences of elastic moduli and fracture toughness on the ZrO
, which is a main component of the fuel debris. We focus on the dependence of mechanical properties on the fraction x of zirconium, compare our results with recent experiment of simulated debris, in which dependences of elastic moduli and fracture toughness on the ZrO content showed deviation from a simple linear relation. We show that elastic moduli drop at around x=0.25 and increase again for larger values of x, as has been observed in experiments. The reason of the drop is a softening owing to disordered atomistic structures induced by the solute zirconium atoms. We also find that stress-strain curves for the x=0.125 case show marked hysteresis owing to the existence of many meta-stable states. We show that this hysteresis leads to slightly increased fracture toughness, but it is not enough to account for the significant increase of fracture toughness observed in experiments.
content showed deviation from a simple linear relation. We show that elastic moduli drop at around x=0.25 and increase again for larger values of x, as has been observed in experiments. The reason of the drop is a softening owing to disordered atomistic structures induced by the solute zirconium atoms. We also find that stress-strain curves for the x=0.125 case show marked hysteresis owing to the existence of many meta-stable states. We show that this hysteresis leads to slightly increased fracture toughness, but it is not enough to account for the significant increase of fracture toughness observed in experiments.
Shamoto, Shinichi; Ito, Takashi; Onishi, Hiroaki; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Matsuura, Masato*; Akatsu, Mitsuhiro*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Nakao, Akiko*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; et al.
Physical Review B, 97(5), p.054429_1 - 054429_9, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:65.6(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nuclear and magnetic structure and full magnon dispersions of yttrium iron garnet Y Fe
Fe O
O have been studied by neutron scattering. The lowest-energy dispersion below 14 meV exhibits a quadratic dispersion as expected from ferromagnetic magnons. The imaginary part of
have been studied by neutron scattering. The lowest-energy dispersion below 14 meV exhibits a quadratic dispersion as expected from ferromagnetic magnons. The imaginary part of  -integrated dynamical spin susceptibility
-integrated dynamical spin susceptibility  "(
"( ) exhibits a square-root energy-dependence in the low energies. The magnon density of state is estimated from the
) exhibits a square-root energy-dependence in the low energies. The magnon density of state is estimated from the  "(
"( ) obtained on an absolute scale. The value is consistent with a single chirality mode for the magnon branch expected theoretically.
) obtained on an absolute scale. The value is consistent with a single chirality mode for the magnon branch expected theoretically.
 -ray fields with novel nuclear emulsion technique
-ray fields with novel nuclear emulsion techniqueIshihara, Kohei*; Takagi, Keisuke*; Minato, Haruna*; Kawarabayashi, Jun*; Tomita, Hideki*; Maeda, Shigetaka; Naka, Tatsuhiro*; Morishima, Kunihiro*; Nakano, Toshiyuki*; Nakamura, Mitsuhiro*; et al.
Radiation Measurements, 55, p.79 - 82, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to measure the neutron under a condition of high intensity of  -ray background, we made new nuclear emulsion based on non-sensitized OPERA emulsion which had small AgBr grain size (AgBr grain size of 60, 90 and 160 nm). The sensitivity of this new emulsion, which was a correlation between stopping power and grain density, was estimated experimentally by irradiating neutrons with several energies. We also simulated the response to
-ray background, we made new nuclear emulsion based on non-sensitized OPERA emulsion which had small AgBr grain size (AgBr grain size of 60, 90 and 160 nm). The sensitivity of this new emulsion, which was a correlation between stopping power and grain density, was estimated experimentally by irradiating neutrons with several energies. We also simulated the response to  -ray induced electrons and compared with some experimental results by using
-ray induced electrons and compared with some experimental results by using  Co
Co  source. The results showed that there might be a threshold energy deposited in one AgBr grain under which it was impossible to develop. We estimated efficiency to the
source. The results showed that there might be a threshold energy deposited in one AgBr grain under which it was impossible to develop. We estimated efficiency to the  -ray and the neutron with this obtained response of the new emulsion.
-ray and the neutron with this obtained response of the new emulsion.
Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*; Kurashima, Satoshi; Okumura, Susumu; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Nara, Takayuki; Ishibori, Ikuo; Yoshida, Kenichi; Yokota, Wataru; Nakamura, Yoshiteru*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 636(1), p.41 - 47, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.65(Instruments & Instrumentation)A phase bunching effect has been achieved for the first time using a rising slope of the dee voltage waveform produced at the first acceleration gap between the RF shielding cover of the inflector and the puller in the new central region of the JAEA AVF cyclotron. The feasibility of the phase bunching effect in the central region for a two-dee system with a span angle of 86  in three acceleration harmonic modes was assessed by a simple geometrical analysis of particle trajectories and a three-dimensional beam orbit simulation. The simulation indicated that the initial beam phase width of 40 RF degrees is compressed to 11 RF degrees in the second harmonic mode. A phase width of 1.5 RF degrees FWHM for a 260 MeV
in three acceleration harmonic modes was assessed by a simple geometrical analysis of particle trajectories and a three-dimensional beam orbit simulation. The simulation indicated that the initial beam phase width of 40 RF degrees is compressed to 11 RF degrees in the second harmonic mode. A phase width of 1.5 RF degrees FWHM for a 260 MeV  Ne
Ne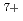 beam accelerated in the second harmonic mode was reduced by the bunching effect, compared with the beam phase width of 7.3 RF degrees FWHM in the same harmonic mode for a 10 MeV H
beam accelerated in the second harmonic mode was reduced by the bunching effect, compared with the beam phase width of 7.3 RF degrees FWHM in the same harmonic mode for a 10 MeV H beam accelerated in the original central region.
beam accelerated in the original central region.
Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Nakamura, Hideo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 47(12), p.1193 - 1205, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)Presented in the paper are experimental results on general performance of core exit thermocouple (CET) to detect core overheat for accident management (AM) action. Thirteen tests simulating small break loss-of-coolant accident (SBLOCA) and abnormal transient are studied by using the Large Scale Test Facility (LSTF) which is a full-height, full-pressure and 1/48 volumetric-scaled PWR model. Clarified are as follows, (1) general CET performance with certain delay in time and temperature rise from core overheating in most cases, (2) one common reason of the delay due to cooling effects of metal structures in core and core exit, (3) an indication of superheat instead of its temperature necessary for significantly high or low pressure transients, (4) no CET heat-up in case of large water fall-back from hot legs and in addition, discussion on applicability to PWR is presented.
Sakanaka, Shogo*; Akemoto, Mitsuo*; Aoto, Tomohiro*; Arakawa, Dai*; Asaoka, Seiji*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.2338 - 2340, 2010/05
Future synchrotron light source using a 5-GeV energy recovery linac (ERL) is under proposal by our Japanese collaboration team, and we are conducting R&D efforts for that. We are developing high-brightness DC photocathode guns, two types of cryomodules for both injector and main superconducting (SC) linacs, and 1.3 GHz high CW-power RF sources. We are also constructing the Compact ERL (cERL) for demonstrating the recirculation of low-emittance, high-current beams using above-mentioned critical technologies.
Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Takeda, Takeshi; Nakamura, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2009-057, 188 Pages, 2010/02
A series of break size parameter tests (SB-PV-07 and SB-PV-08) were conducted at the Large Scale Test Facility of ROSA-V Program to have an insight into effects of accident management action on core cooling during a simulated vessel top break loss-of-coolant accident with a total failure assumption on the high pressure injection (HPI) system at a pressurized water reactor (PWR). Typical phenomena of vessel top break with break sizes between 1.0 and 0.1% cold leg break equivalent were clarified including upper head water level transients related to steam discharge, coolant mass inventory related to core heat-up, performance of core exit thermocouple (CET)and three-dimensional steam flows in core and core exit. Both operator actions of HPI recovery in the 1.0% top break and steam generator depressurization in the 0.1% top break resulted in immediate recovery of core cooling when these were initiated by CET heat-up at 623 K.
Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 17 Pages, 2009/09
Presented are experiment results on performance of core exit thermocouple (CET) and applicability to PWR accident management (AM) during 12 tests of small-break loss-of-coolant accident (SBLOCA) and abnormal transient conducted at the Large Scale Test Facility (LSTF) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, which is the largest PWR simulator with full-height and 1/48 volume scaling. General CET performances are derived including (1) CETs are capable in most cases to detect core overheating with delay of time and temperature increase from core heat-up, (2) one of the reasons of this delay is attributed to cooling effects of structural materials at the core exit and peripheral region, (3) CETs were incapable to detect core overheating in a very small break under steam generator depressurization action as well as a 10% cold leg break due to significant water fall-back from hot legs, and (4) an alternative indication by CET superheat is necessary in extremely high and low pressure conditions.
Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Nakamura, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2009-011, 155 Pages, 2009/07
This report summarizes performances of core exit thermocouples (CETs) observed in 12 ROSA/LSTF tests which include ten small-break loss-of-coolant accident (SBLOCA) tests and two abnormal transient tests as an additional report to the OECD/NEA ROSA Project Test 6-1 report. The contents of this report are prepared to a task group which was set up to review and consolidate background knowledge of CET application to PWR accident management (AM) measures in April 2008 in the Working Group of Analysis and Management of Accident (WGAMA) at OECD/NEA. These tests cover wide ranges of test conditions such as size and location of break, primary pressure, core power, reflux water fall-back and operator actions. CET performances relative to the core temperature history are studied in each test, and general performances of CET are summarized focusing on the time delay and slow and low temperature excursion.
Kurashima, Satoshi; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Okumura, Susumu; Ishibori, Ikuo; Nara, Takayuki; Agematsu, Takashi; Yoshida, Kenichi; Yokota, Wataru; Nakamura, Yoshiteru*; Arakawa, Kazuo; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 80(3), p.033302_1 - 033302_9, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.69(Instruments & Instrumentation)Single-turn extraction from the JAEA AVF cyclotron with a K number of 110 using a flat-top (FT) acceleration system has been achieved to reduce the energy spread of an ion beam for microbeam formation with energy up to hundreds of MeV and to increase extraction efficiency from the cyclotron. In order to generate an FT waveform voltage using the fifth-harmonic frequency on a dee electrode, an FT resonator was designed using MAFIA code to achieve downsizing and low power consumption. The FT resonator, coupled to the main resonator through a coupling capacitor, covered the full range of the fifth harmonic frequency from 55 to 110 MHz. Various ion beams, accelerated using different acceleration harmonic mode of h = 1 and 2, such as 220 MeV  C
C (h = 2), 260 MeV
(h = 2), 260 MeV  Ne
Ne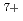 (h = 2), and 45 MeV H
(h = 2), and 45 MeV H (h = 1) were developed by FT acceleration. A clear turn separation of the beam bunches was successfully observed at the extraction region of the large-scale AVF cyclotron with number of revolutions greater than 200. As a result, high extraction efficiency (over 95%) from the cyclotron was achieved. Single-turn extraction was confirmed by counting the number of beam bunches out of the cyclotron for an injected beam pulsed by a beam chopping system in the injection line. The energy spread of the 260 MeV
(h = 1) were developed by FT acceleration. A clear turn separation of the beam bunches was successfully observed at the extraction region of the large-scale AVF cyclotron with number of revolutions greater than 200. As a result, high extraction efficiency (over 95%) from the cyclotron was achieved. Single-turn extraction was confirmed by counting the number of beam bunches out of the cyclotron for an injected beam pulsed by a beam chopping system in the injection line. The energy spread of the 260 MeV  Ne
Ne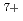 beam was measured using an analyzing magnet and we verified a reduction of the energy spread from
beam was measured using an analyzing magnet and we verified a reduction of the energy spread from  E/E = 0.1% to 0.05% by single-turn extraction.
E/E = 0.1% to 0.05% by single-turn extraction.
Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Takeda, Takeshi; Nakamura, Hideo
Journal of Power and Energy Systems (Internet), 3(1), p.146 - 157, 2009/00
Presented are experiment results of the LSTF with a focus on core exit thermocouple (CET) performance to detect core overheat during a vessel top break LOCA simulation experiment. The break size is equivalent to 1.9% cold leg break. The accident management (AM) action to rapidly open the SG relief valves was initiated when CET temperature rose up to 623 K. The core overheat, however, was detected with a time delay of about 230 s and a large temperature discrepancy was observed between the CETs and the hottest core region. This paper clarified the reasons of time delay and temperature discrepancy between the CETs and heated core including three-dimensional steam flows in the core and core exit. The paper discusses applicability of the LSTF CET performance to PWR conditions and a possibility of alternative indicators for earlier AM action is studied by using symptom-based plant parameters such as a reactor vessel water level detection.
Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Nakamura, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2008-087, 148 Pages, 2008/10
This report presents major results observed in LOCA test (SB-CL-09) conducted at the ROSA/LSTF test facility simulating 10% cold leg break in a 4-loop Westinghouse-type PWR. Following are found in this test with an assumption of high pressure injection system. (1) The relatively large break size resulted in pressure inverse within 2 minutes between the primary and steam generator secondary sides. (2) During a loop-seal clearing (LSC) process started at about 1 minutes after the break, the core water level was suppressed to almost lower end and then it recovered to the middle core height. The water level remained at the middle height was due to remained water levels in the SG U-tube inlet sides which were higher than their outlet sides. (3) Significant core heat-up was observed above the water level at the middle height and core power was tripped off at 111s. (4) The effects of fall-back water from the intact loop hot leg was observed by the local core cooling.
Arakawa, Kazuo; Yokota, Wataru; Agematsu, Takashi; Nakamura, Yoshiteru; Ishibori, Ikuo; Kurashima, Satoshi; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Okumura, Susumu; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Nara, Takayuki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2008-024, 141 Pages, 2008/03
The TIARA facilities (Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application: TIARA) have been constructed at Takasaki Radiation Chemistry Research Establishment (Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute) under 6-year program from 1988. The first phase of the construction including those of a K110 AVF cyclotron and a 3 MV tandem accelerator was complete in October 1991. Large AVF cyclotrons have been used mostly for fundamental nuclear physics and medical applications to radiation therapy and radioisotope production so far. The JAEA K110 AVF cyclotron is the first one dedicated to R&D in materials science and other irradiation purpose. This cyclotron facility consists of three external ion sources, an injection line, a K110 AVF cyclotron, eight main beam transport lines, and a control system. The first beam, 50 MeV  He
He , was extracted from the cyclotron in March 1991. This Report describes an outline of the K110 AVF cyclotron system and results of performance tests.
, was extracted from the cyclotron in March 1991. This Report describes an outline of the K110 AVF cyclotron system and results of performance tests.
Takeda, Takeshi; Asaka, Hideaki; Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of 12th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-12) (CD-ROM), 3 Pages, 2007/09
RELAP5 code analysis was performed to validate the code predictability by using ROSA/LSTF experiment data that simulated a PWR vessel upper head small break loss-of-coolant accident (SBLOCA) with a break equivalent to 1% cold leg break. The JAEA-modified RELAP5/MOD3.2.1.2 code was used by incorporating a break model that employs maximum bounding flow theory with a discharge coefficient (Cd) of 0.61 for two-phase break flow. In the experiment, liquid level in the upper head was found to control break flow rate as coolant in the upper plenum entered the upper head through control rod guide tubes (CRGTs) until the penetration holes at the CRGT bottom were exposed to steam in the upper plenum. The upper head noding and flow paths between the upper plenum and the CRGT were thus modeled to simulate well the liquid level and coolant flow around the upper portion of pressure vessel. The code, however, overpredicted the break flow rate due to the underprediction of break-upstream void fraction especially during two-phase flow discharge period. Cd for two-phase break flow was thus adjusted to be 0.58. Effects of break area on the core cooling were investigated further. The parameter analyses showed that peak cladding temperature (PCT) is the maximum at 1% break case, while the PCT would be lower than 1200 K in the larger break size cases because vapor condensation on injected accumulator coolant induces loop seal clearing and effectively enhances core cooling thereafter.
Kurashima, Satoshi; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Okumura, Susumu; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Yoshida, Kenichi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*; Sato, Takahiro; Nara, Takayuki; Agematsu, Takashi; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 260(1), p.65 - 70, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:59.1(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Takeda, Takeshi; Asaka, Hideaki; Nakamura, Hideo
JAEA-Research 2007-037, 150 Pages, 2007/03
A small break LOCA experiment (SB-PV-06) was conducted at the LSTF of ROSA-V program to study effects of rapid secondary depressuriza-tion action on core cooling as one of accident management (AM) measures for a PWR in case of high pressure injection system failure and non-condensable gas inflow from the accumulator injection system. The break simulated 10 instrument tubes rupture equivalent to 0.2% cold leg break. It was clarified through comparison with former experiments that (1) the depressurization initiated by detecting the vessel level below the primary loop (4545s) was degraded by the gas inflow resulting in whole core uncovery prior to the start of low pressure injection and (2) an alternative start of the depressurization by detecting level decrease at the SG outlet plenum (2330s), would limit the core uncovery suggesting more effective parameter for the AM measures. The report presents the experiment results with the effects of rapid depressurization initiation timing.