Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Nb by activation method and half-life of
Nb by activation method and half-life of  Nb by mass analysis
Nb by mass analysisNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1361 - 1371, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross section (
 ) and resonance integral (I
) and resonance integral (I ) for
) for  Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of
Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of  Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25-
Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25- m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of
m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of 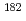 Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by
Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by  -ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the
-ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the 
 and I
and I values were derived as 1.11
values were derived as 1.11 0.04 barn and 10.5
0.04 barn and 10.5 0.6 barn, respectively. After the
0.6 barn, respectively. After the  -ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both
-ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both  -ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of
-ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of  Nb was derived as (2.00
Nb was derived as (2.00 0.15)
0.15) 10
10 years.
years.
Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Kimura, Atsushi; Endo, Shunsuke; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(9), p.1133 - 1142, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In recent years, research has been advanced on lead-cooled fast reactors and accelerator drive systems, and it is required to improve the accuracy of the neutron capture cross section of Pb isotopes. Although  Pb has a small natural abundance, it is of importance because it produces the long-lived radionuclide
Pb has a small natural abundance, it is of importance because it produces the long-lived radionuclide  Pb (17.3 million years) by neutron capture reaction. However, it is difficult to measure its cross section by a conventional activation method using a nuclear reactor because the induced radioactivity of
Pb (17.3 million years) by neutron capture reaction. However, it is difficult to measure its cross section by a conventional activation method using a nuclear reactor because the induced radioactivity of  Pb is weak. Hence, the cross-section measurement was performed by applying mass spectrometry. This presentation gives the details of the experiment and the results obtained in the neutron capture cross-section measurement of
Pb is weak. Hence, the cross-section measurement was performed by applying mass spectrometry. This presentation gives the details of the experiment and the results obtained in the neutron capture cross-section measurement of  Pb using mass spectroscopy.
Pb using mass spectroscopy.
Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2022, P. 73, 2023/07
The present study is concerned with the neutron capture cross-sections that contribute to the evaluation of the amount of radionuclides possessing problems in decommissioning. In this study,  Sc,
Sc,  Cu,
Cu,  Zn,
Zn,  Ag,
Ag,  In and
In and  W were selected among the objective nuclides, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured using TC-Pn equipment of the KUR of the Institute for Integrated Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. High purity metal samples were prepared. A gold-aluminum ally wire, cobalt and molybdenum foils were used to monitor the neutron flux at the irradiation position of TC-Pn. The flux monitors and metal samples were irradiated for 1 hour at 1-MW operation of the KUR. After irradiation, the irradiation capsule was opened, samples and flux monitors were enclosed in a vinyl bag one by one, and then
W were selected among the objective nuclides, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured using TC-Pn equipment of the KUR of the Institute for Integrated Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. High purity metal samples were prepared. A gold-aluminum ally wire, cobalt and molybdenum foils were used to monitor the neutron flux at the irradiation position of TC-Pn. The flux monitors and metal samples were irradiated for 1 hour at 1-MW operation of the KUR. After irradiation, the irradiation capsule was opened, samples and flux monitors were enclosed in a vinyl bag one by one, and then  rays emitted from the samples and monitors were measured with a high-purity Ge detector. The thermal-neutron flux component was derived with the reaction rates of flux monitors (
rays emitted from the samples and monitors were measured with a high-purity Ge detector. The thermal-neutron flux component was derived with the reaction rates of flux monitors ( Au,
Au,  Co and
Co and  Mo) on the basis of Westcott's convention, and found to be (5.92
Mo) on the basis of Westcott's convention, and found to be (5.92 0.10)
0.10) 10
10 n/cm
n/cm /sec at the irradiation position. The measured reaction rate for each metal sample divided by the evaluated thermal-neutron capture cross-section should give the same value of the thermal-neutron flux component if the cross section is suitable. This time, we found that the cross sections of
/sec at the irradiation position. The measured reaction rate for each metal sample divided by the evaluated thermal-neutron capture cross-section should give the same value of the thermal-neutron flux component if the cross section is suitable. This time, we found that the cross sections of  Sc and
Sc and  Zn were consistent with the evaluated one, but those of other nuclides were inconsistent with their evaluated ones; that is, it turned out that their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections should be modified.
Zn were consistent with the evaluated one, but those of other nuclides were inconsistent with their evaluated ones; that is, it turned out that their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections should be modified.
Nishino, Saki; Okada, Jumpei; Watanabe, Kazuki; Furuuchi, Yuta; Yokota, Satoru; Yada, Yuji; Kusaka, Shota; Morokado, Shiori; Nakamura, Yoshinobu
JAEA-Technology 2023-011, 39 Pages, 2023/06
Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) which shifted to decommissioning phase in 2014 had nuclear fuel materials such as the spent fuel sheared powder, the diluted plutonium solution and the uranium solution in a part of the reprocessing main equipment because TRP intended to resume reprocessing operations when it suspended the operations in 2007. Therefore, we have planned to remove these nuclear materials in sequence as Flush-out before beginning the decommissioning, and conducted removal of the spent fuel sheared powder as the first stage. The spent fuel sheared powder that had accumulated in the cell of the Main Plant (MP) as a result of the spent fuel shearing process was recovered from the cell floor, the shearing machine and the distributor between April 2016 and April 2017 as part of maintenance. Removing the recovered spent fuel sheared powder was conducted between June 2022 and September 2022. In this work, the recovered powder was dissolved in nitric acid at the dissolver in a small amount in order to remove it safely and early, and the dissolved solution was sent to the highly radioactive waste storage tanks without separating uranium and plutonium. Then, the dissolved solution transfer route was rinsed with nitric acid and water. Although about 15 years had passed since previous process operations, the removing work was successfully completed without any equipment failure because of the organization of a system that combines veterans experienced the operation with young workers, careful equipment inspections, and worker education and training. Removing this powder was conducted after revising the decommissioning project and obtaining approval from the Nuclear Regulation Authority owing to operating a part of process equipment.
 Gd and
Gd and  Gd in the thermal energy region with the Li-glass detectors and NaI(Tl) spectrometer installed in J-PARC
Gd in the thermal energy region with the Li-glass detectors and NaI(Tl) spectrometer installed in J-PARC MLF
MLF ANNRI
ANNRIKimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Harada, Hideo; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Terada, Kazushi*; Hori, Junichi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.678 - 696, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Hori, Junichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Nakamura, Shoji; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Endo, Shunsuke; Shibahara, Yuji*; Terada, Kazushi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 281, p.00014_1 - 00014_4, 2023/03
Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1388 - 1398, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The present study selected  Np among radioactive nuclides and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section for
Np among radioactive nuclides and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section for  Np in a well-thermalized neutron field by an activation method. A
Np in a well-thermalized neutron field by an activation method. A  Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. A thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with neutron flux monitors:
Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. A thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with neutron flux monitors:  Sc,
Sc,  Co,
Co,  Mo,
Mo,  Ta and
Ta and  Au. The
Au. The  Np sample and flux monitors were irradiated together for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped with the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was carried out twice. After the irradiations, the
Np sample and flux monitors were irradiated together for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped with the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was carried out twice. After the irradiations, the  Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma ray emitted from
Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma ray emitted from  Pa in a radiation equilibrium with
Pa in a radiation equilibrium with  Np. The reaction rates of
Np. The reaction rates of  Np were obtained from gamma-ray peak net counts given by
Np were obtained from gamma-ray peak net counts given by  Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of
Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of  Np was found to be 173.8
Np was found to be 173.8 4.4 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within the limit of uncertainty.
4.4 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within the limit of uncertainty.
 Np(n,
Np(n,  ) reaction with TC-Pn in KUR
) reaction with TC-Pn in KURNakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2021, P. 93, 2022/07
In terms of nuclear transmutation studies of minor actinides in nuclear wastes, the present work selected  Np among them and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of
Np among them and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of  Np using a well-thermalized neutron field by a neutron activation method because there have been discrepancies among reported cross-section data. A
Np using a well-thermalized neutron field by a neutron activation method because there have been discrepancies among reported cross-section data. A  Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. The thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with flux monitors:
Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. The thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with flux monitors:  Sc,
Sc,  Co,
Co,  Mo,
Mo,  Ta and
Ta and  Au. The
Au. The  Np sample was irradiated together with the flux monitors for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped in the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was repeated once more to confirm the reproducibility of the results. After irradiation, the
Np sample was irradiated together with the flux monitors for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped in the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was repeated once more to confirm the reproducibility of the results. After irradiation, the  Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma-ray emitted from
Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma-ray emitted from  Pa in radiation equilibrium with
Pa in radiation equilibrium with  Np. The reaction rates of
Np. The reaction rates of  Np were obtained from the peak net counts of gamma-rays emitted from generated
Np were obtained from the peak net counts of gamma-rays emitted from generated  Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of
Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of  Np was found to be 173.8
Np was found to be 173.8 4.7 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within a limit of uncertainty.
4.7 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within a limit of uncertainty.
 Au with a Cr-filtered neutron beam at the ANNRI beamline of MLF/J-PARC
Au with a Cr-filtered neutron beam at the ANNRI beamline of MLF/J-PARCRovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Kodama, Yu*; Nakano, Hideto*; Sato, Yaoki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(5), p.647 - 655, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)Rovira Leveroni, G.; Iwamoto, Osamu; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Endo, Shunsuke; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Terada, Kazushi*; Kodama, Yu*; Nakano, Hideto*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2021-001, p.156 - 161, 2022/03
 Sm M
Sm M ssbauer and Sm L
ssbauer and Sm L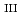 -edge X-ray absorption spectroscopies
-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopiesTsutsui, Satoshi; Higashinaka, Ryuji*; Nakamura, Raito*; Fujiwara, Kosuke*; Nakamura, Jin*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Ito, Takashi; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Kato, Kazuo*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 242(1), p.32_1 - 32_10, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:84.42(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical) Am around 23.5 keV
Am around 23.5 keVKodama, Yu*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Hori, Junichi*; Shibahara, Yuji*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(11), p.1159 - 1164, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:56.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(10), p.1061 - 1070, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:56.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)In a well-thermalized neutron field, it is principally possible to drive a thermal-neutron capture cross-section without considering an epithermal neutron component. This was demonstrated by a neutron activation method using the graphite thermal column (TC-Pn) of the Kyoto University Research Reactor. First, in order to confirm that the graphite thermal column was a well-thermalized neutron field, neutron irradiation was performed with neutron flux monitors:  Au,
Au,  Co,
Co,  Sc,
Sc,  Cu, and
Cu, and  Mo. The TC-Pn was confirmed to be extremely thermalized on the basis of Westcott's convention, because the thermal-neutron flux component took a constant value regardless of the sensitivity of each flux monitor to epithermal neutrons. Next, as a demonstration, the thermal-neutron capture cross section of
Mo. The TC-Pn was confirmed to be extremely thermalized on the basis of Westcott's convention, because the thermal-neutron flux component took a constant value regardless of the sensitivity of each flux monitor to epithermal neutrons. Next, as a demonstration, the thermal-neutron capture cross section of  Ta(n,
Ta(n, )
)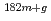 Ta reaction was measured using the graphite thermal column, and then derived to be 20.5
Ta reaction was measured using the graphite thermal column, and then derived to be 20.5 0.4 barn, which supported the evaluated value of 20.4
0.4 barn, which supported the evaluated value of 20.4 0.3 barn. The
0.3 barn. The  Ta nuclide could be useful as a flux monitor that complements the sensitivity between
Ta nuclide could be useful as a flux monitor that complements the sensitivity between  Au and
Au and  Mo monitors.
Mo monitors.
 Np using graphite thermal column
Np using graphite thermal columnNakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2020, P. 94, 2021/08
The present study selected  Np among radioactive nuclides and aimed to converge a contradiction between reported thermal-neutron capture cross sections. Neutron irradiation was carried out using the graphite thermal column equipped with the Kyoto University Research Reactor. A solution equivalent to 950 Bq order of radioactivity was pipetted out of a
Np among radioactive nuclides and aimed to converge a contradiction between reported thermal-neutron capture cross sections. Neutron irradiation was carried out using the graphite thermal column equipped with the Kyoto University Research Reactor. A solution equivalent to 950 Bq order of radioactivity was pipetted out of a  Np standard solution and dropped onto a fiber filter, which was then dried with an infrared lamp to prepare a
Np standard solution and dropped onto a fiber filter, which was then dried with an infrared lamp to prepare a  Np sample. The
Np sample. The  Np sample was quantified using 312-keV gamma ray emitted from
Np sample was quantified using 312-keV gamma ray emitted from  Pa in a radiation equilibrium with
Pa in a radiation equilibrium with  Np. To monitor a thermal-neutron flux component at an irradiation position, the
Np. To monitor a thermal-neutron flux component at an irradiation position, the  Np sample was irradiated together with several stable nuclides as neutron flux monitors:
Np sample was irradiated together with several stable nuclides as neutron flux monitors:  Sc,
Sc,  Co,
Co,  Mo,
Mo,  Ta and
Ta and  Au. The reaction rate of
Au. The reaction rate of  Np was obtained from gamma-ray yields given by
Np was obtained from gamma-ray yields given by  Np and
Np and  Pa, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross section of
Pa, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross section of  Np was derived.
Np was derived.
Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Terada, Kazushi*; Kodama, Yu*; Nakano, Hideto*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1003, p.165318_1 - 165318_10, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:57.13(Instruments & Instrumentation)Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Abe, Yuta; Oishi, Yuji*; Kai, Tetsuya; Toh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Harada, Masahide; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011074_1 - 011074_6, 2021/03
In the decommissioning of the Fukushima-Daiichi (1F) Nuclear Power Plant, it is essential to understand characteristics of the melted core materials. The estimation of boride in the real debris is of great importance to develop safe debris removal plans. Hence, it is required to investigate the amount of boron in the melted core materials with nondestructive methods. Prompt gamma-ray activation analysis (PGAA) is one of the useful techniques to determine the amount of borides by means of the 478 keV prompt gamma-ray from neutron absorption reaction of boron. Moreover, it is well known that the width of the 478 keV gamma-ray peak is typically broadened due to the Doppler effect. The degree of the broadening is affected by coexisting materials, and can be recognized by the width of the prompt gamma-ray peak. As a feasibility study, the prompt gamma-ray from boride samples were measured using the ANNRI, NOBORU, and RADEN beamlines at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) of Japan Proton Accelerator Complex (J-PARC).
 Am(n,
Am(n, )
)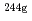 Am and
Am and  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)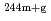 Am reactions
Am reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(3), p.259 - 277, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:53.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Research and development were made for accuracy improvement of neutron capture cross section data on  Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay
Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay  rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of
rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of  Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of
Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of  Am was examined by
Am was examined by  -ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examined by
-ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examined by  -ray measurement. Thermal-neutron capture cross sections and resonance integrals were derived both for the
-ray measurement. Thermal-neutron capture cross sections and resonance integrals were derived both for the  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)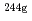 Am and for
Am and for  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)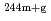 Am reactions.
Am reactions.
Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Hori, Junichi*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Terada, Kazushi*; Tosaka, Kenichi*; Endo, Shunsuke; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2020-001, p.5 - 9, 2020/12
Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Hori, Junichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Terada, Kazushi*; Rovira, G.*; Matsuura, Shota*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.01044_1 - 01044_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:86.93(Nuclear Science & Technology) Am(n,
Am(n, )
)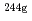 Am,
Am, 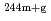 Am reactions
Am reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2019, P. 132, 2020/08
Research and development were made for accuracy improvement of neutron capture cross section data on  Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay
Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay  rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of
rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of  Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of
Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of  Am was examinded by
Am was examinded by  -ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examoned by
-ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examoned by  -ray measurement.
-ray measurement.